Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T65200
(Former ID: TTDC00070)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase 1 (HSD11B1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
HSD11B1; 11beta-HSD1A; 11HSD1; 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1; 11-beta-HSD1; 11-DH; 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HSD11B1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Influenza [ICD-11: 1E30-1E32] | |||||
| 2 | Lupus erythematosus [ICD-11: 4A40] | |||||
| 3 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes reversibly the conversion of cortisol to the inactive metabolite cortisone. Catalyzes reversibly the conversion of 7-ketocholesterol to 7-beta-hydroxycholesterol. In intact cells, the reaction runs only in one direction, from 7- ketocholesterol to 7-beta-hydroxycholesterol.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Short-chain dehydrogenases reductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.1.1.146
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAFMKKYLLPILGLFMAYYYYSANEEFRPEMLQGKKVIVTGASKGIGREMAYHLAKMGAH
VVVTARSKETLQKVVSHCLELGAASAHYIAGTMEDMTFAEQFVAQAGKLMGGLDMLILNH ITNTSLNLFHDDIHHVRKSMEVNFLSYVVLTVAALPMLKQSNGSIVVVSSLAGKVAYPMV AAYSASKFALDGFFSSIRKEYSVSRVNVSITLCVLGLIDTETAMKAVSGIVHMQAAPKEE CALEIIKGGALRQEEVYYDSSLWTTLLIRNPCRKILEFLYSTSYNMDRFINK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T40DIM | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 13 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BVT.2733 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Lupus | [2] | |
| 2 | GLYCYRRHIZIN | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Influenza virus infection | [3], [4] | |
| 3 | INCB13739 | Drug Info | Phase 2a | Type-2 diabetes | [5] | |
| 4 | AZD-4017 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Ocular hypertension | [6], [7] | |
| 5 | BMS-770767 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hypercholesterolaemia | [8] | |
| 6 | JTT-654 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [9] | |
| 7 | RG-4929 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Metabolic disorder | [10] | |
| 8 | UE-2343 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Alzheimer disease | [11], [12] | |
| 9 | URSOLIC ACID | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Metabolic syndrome x | [13] | |
| 10 | Xanamem | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Alzheimer disease | [14] | |
| 11 | AZD8329 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Obesity | [15], [16] | |
| 12 | BI-135585 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [17] | |
| 13 | BMS-816336 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lipid metabolism disorder | [18] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 4 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LY-2523199 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [19] | |
| 2 | AMG-221 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Metabolic disorder | [20] | |
| 3 | PF-915275 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Non-insulin dependent diabetes | [21] | |
| 4 | BVT-3498 | Drug Info | Terminated | Metabolic disorder | [23] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | HPP-851 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Metabolic disorder | [22] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 82 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BVT.2733 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | GLYCYRRHIZIN | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 3 | INCB13739 | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 4 | AZD-4017 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 5 | JTT-654 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 6 | RG-4929 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 7 | UE-2343 | Drug Info | [11], [12] | |||
| 8 | URSOLIC ACID | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 9 | Xanamem | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 10 | AZD8329 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 11 | BMS-816336 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 12 | LY-2523199 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 13 | AMG-221 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 14 | PF-915275 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 15 | HPP-851 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 16 | BVT-3498 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 17 | (11-BETA)-11,21-DIHYDROXY-PREGN-4-ENE-3,20-DIONE | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 18 | (4-methoxyphenyl)(4-phenylazepan-1-yl)methanone | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 19 | 1,1-diphenyl-3-(phenylsulfonyl)propan-2-one | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 20 | 1-(1-phenyl-1H-tetrazol-5-ylthio)propan-2-one | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 21 | 1-(2-adamantyl)-3-benzylpyrrolidin-2-one | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 22 | 1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 23 | 1-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 24 | 1-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)-4-tosylpiperazine | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 25 | 1-(3-methoxyphenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 26 | 1-(3-methylpyridin-2-yl)-4-tosylpiperazine | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 27 | 1-(3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-4-tosylpiperazine | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 28 | 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 29 | 1-(4-chlorophenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylazepan-4-ol | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 30 | 1-(4-ethylphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylazepan-4-ol | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 31 | 1-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-phenylethanone | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 32 | 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 33 | 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(phenylsulfonyl)propan-1-one | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 34 | 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 35 | 1-(4-methoxyphenylsulfonyl)-4-phenylazepan-4-ol | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 36 | 1-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-(phenylsulfonyl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 37 | 1-(4-tert-butylphenylsulfonyl)-4-methoxyazepane | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 38 | 1-(4-tert-butylphenylsulfonyl)azepan-4-ol | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 39 | 1-(phenylsulfonyl)butan-2-one | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 40 | 1-phenyl-2-(1-phenyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yloxy)ethanone | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 41 | 1-phenyl-3-(phenylsulfonyl)propan-1-one | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 42 | 1-phenyl-4-(1-phenyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butan-2-one | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 43 | 11-keto-beta-boswellicacid | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 44 | 11-keto-ursolic acid | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 45 | 2'-Monophosphoadenosine 5'-Diphosphoribose | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 46 | 2-(2-chlorophenylamino)-5-methylthiazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 47 | 2-(4-tosylpiperazin-1-yl)nicotinonitrile | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 48 | 2-(adamantan-1-ylamino)-5,5-diethyl-oxazol-4-one | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 49 | 2-(benzylamino)-5,5-diethyloxazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 50 | 2-(cyclooctylamino)-5,5-diethyloxazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 51 | 2-(N-Morpholino)-Ethanesulfonic Acid | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 52 | 2-(o-toluidino)-5-ethylthiazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 53 | 2-(o-toluidino)-5-isopropylthiazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 54 | 2-(phenylsulfonyl)-1-(thiophen-3-yl)ethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 55 | 2-(phenylsulfonyl)-1-p-tolylethanone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 56 | 3-acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 57 | 3-acetyl-11-keto-ursolic acid | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 58 | 3-benzyl-1-cyclohexylpyrrolidin-2-one | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 59 | 3-epicorosolic acid methyl ester | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 60 | 5,5-diethyl-2-(phenethylamino)oxazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 61 | 5-isopropyl-2-(phenylamino)thiazol-4(5H)-one | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 62 | A-849531 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 63 | Abietic acid | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 64 | Adamantan-1-yl-(4-ethyl-piperazin-1-yl)-methanone | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 65 | Adamantan-1-yl-piperazin-1-yl-methanone | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 66 | Adamantan-1-yl-piperidin-1-yl-methanone | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 67 | Adamantan-1-yl-pyrrolidin-1-yl-methanone | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 68 | Adamantan-2-yl-piperidin-1-yl-methanone | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 69 | Carbenoxolone | Drug Info | [47], [48], [49] | |||
| 70 | CNX-010 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 71 | Corosolic acid | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 72 | EQ-1280 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 73 | FIG 1 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 74 | Flavanone | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 75 | MERCK-544 | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 76 | N-benzyl-N-(phenylsulfonyl)benzamide | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 77 | PF-877423 | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 78 | Piperidine-1-carboxylic acid adamantan-2-yl ester | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 79 | Piperidine-1-carboxylic acid adamantan-2-ylamide | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 80 | SKI-2852 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 81 | Tormentic acid methyl ester | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 82 | [(125)I] RB129 | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 2 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BMS-770767 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 2 | BI-135585 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: BMS-823778 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF 11BETA-HSD1 DOUBLE MUTANT (L262R, F278E) COMPLEXED WITH 2-(3-(1-(4-CHLOROPHENYL)CYCLOPROPYL) -[1,2,4]TRIAZOLO[4,3-A]PYRIDIN-8-YL)PROPAN-2-OL | PDB:5QII | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.45 Å | Mutation | Yes | [54] |
| PDB Sequence |
EFRPEMLQGK
35 KVIVTGASKG45 IGREMAYHLA55 KMGAHVVVTA65 RSKETLQKVV75 SHCLELGAAS 85 AHYIAGTMED95 MTFAEQFVAQ105 AGKLMGGLDM115 LILNHITNTS125 LNLFHDDIHH 135 VRKSMEVNFL145 SYVVLTVAAL155 PMLKQSNGSI165 VVVSSLAGKV175 AYPMVAAYSA 185 SKFALDGFFS195 SIRKEYSVSR205 VNVSITLCVL215 GLIDTETAMK225 AVSGIVHMQA 235 APKEECALEI245 IKGGALRQEE255 VYYDSSRWTT265 LLIRNPCRKI275 LEELYSTSYN 285 MD
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: AZD-4017 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 in complex with an orally bioavailable acidic inhibitor AZD4017. | PDB:4HFR | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.73 Å | Mutation | Yes | [55] |
| PDB Sequence |
EFRPEMLQGK
35 KVIVTGASKG45 IGREMAYHLA55 KMGAHVVVTA65 RSKETLQKVV75 SHCLELGAAS 85 AHYIAGTMED95 MTFAEQFVAQ105 AGKLMGGLDM115 LILNHITNTS125 LNLFHDDIHH 135 VRKSMEVNFL145 SYVVLTVAAL155 PMLKQSNGSI165 VVVSSLAGKV175 AYPLVAAYSA 185 SKFALDGFFS195 SIRKEYSVSR205 VNVSITLCVL215 GLIDTETAMK225 AVMQAAPKEE 240 CALEIIKGGA250 LRQEEVYYDS260 SRWTTLLIRN270 PSRKILEELY280 STSYN |
|||||
|
|
ILE121
3.995
THR124
3.555
LEU126
3.605
SER170
2.677
LEU171
3.736
ALA172
4.293
TYR177
3.424
PRO178
3.658
VAL180
3.665
TYR183
3.077
LEU215
4.161
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
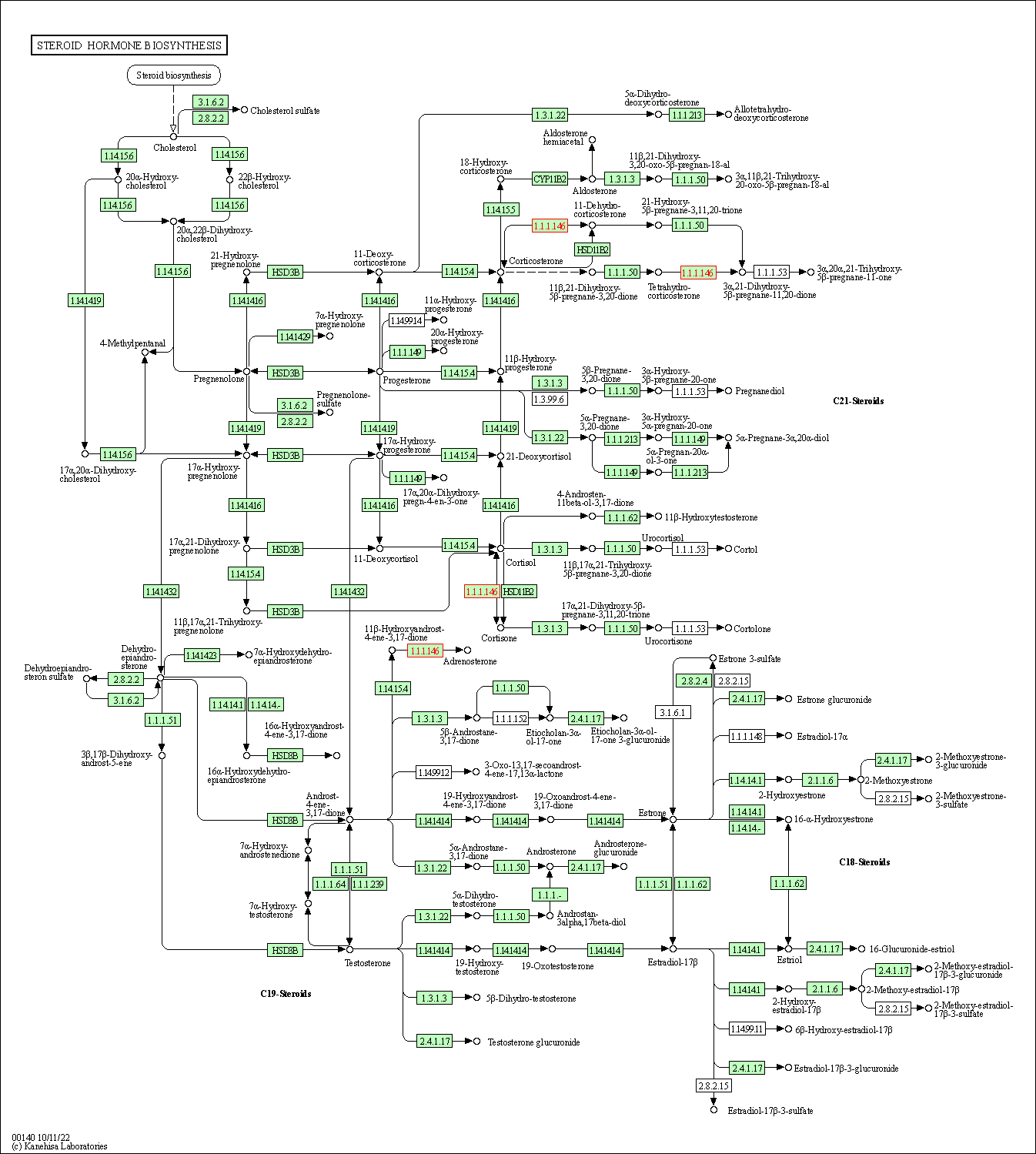
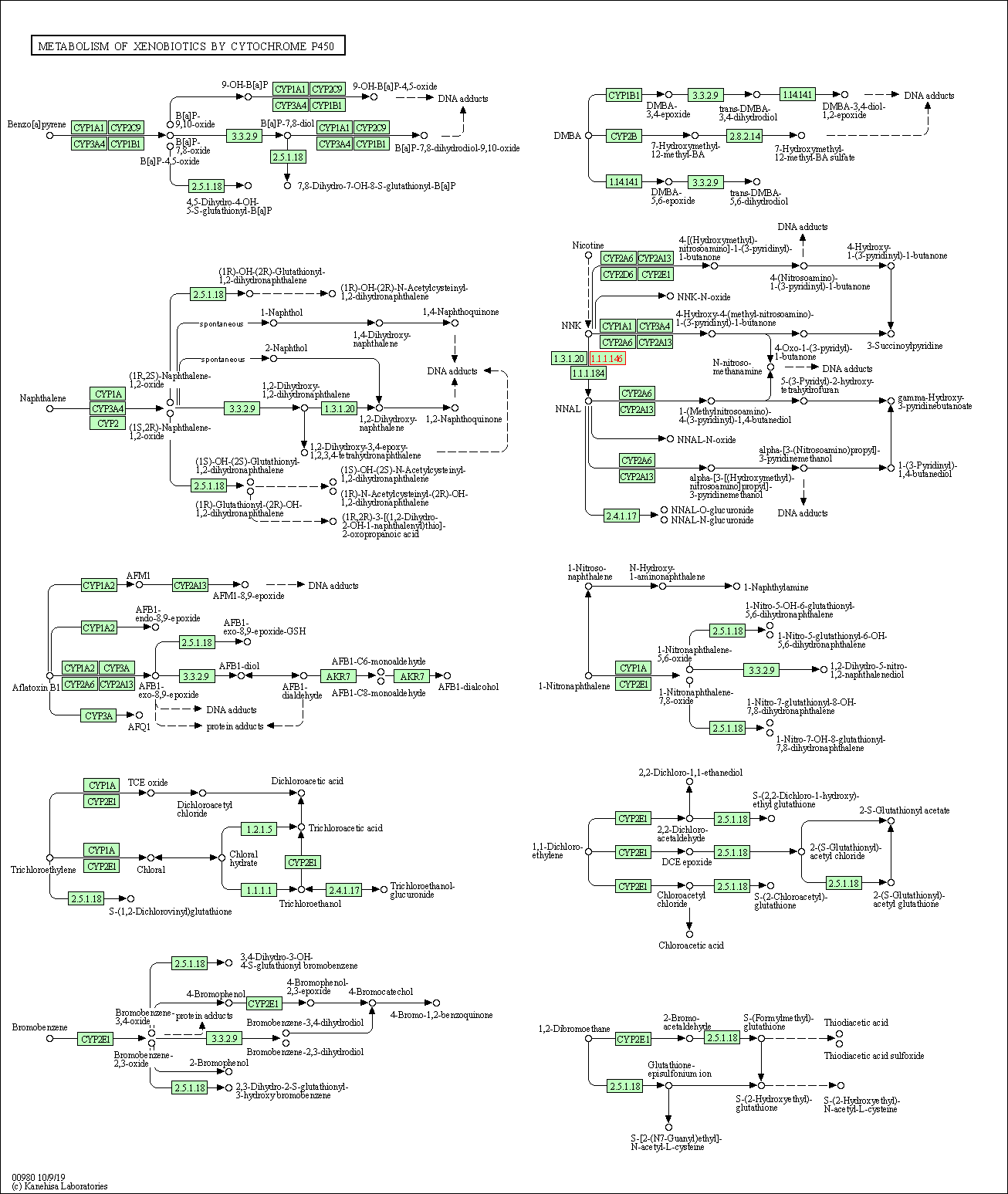
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis | hsa00140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | hsa00980 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 8.40E-07 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.44E-01 | Radiality | 1.17E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 4.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.06E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.95E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Steroid hormone biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | |||||
| 3 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 4 | Chemical carcinogenesis | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 2 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL1 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | FSH Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Steroidogenesis | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glucocorticoid biosynthesis | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Prostaglandin Synthesis and Regulation | |||||
| 2 | Metabolism of steroid hormones and vitamin D | |||||
| 3 | Glucocorticoid & Mineralcorticoid Metabolism | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Selective inhibition of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in hyperglycemic mice strains. Endocrinology. 2003 Nov;144(11):4755-62. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4688). | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01342185) Efficacy of Medical Ozone Therapy in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00698230) Safety and Efficacy of INCB013739 Plus Metformin Compared to Metformin Alone on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetics. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7695). | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01173471) A Phase IIa Study to Assess the Tolerability, Safety, and Efficacy of AZD4017 for Raised Intra-ocular Pressure. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01058083) Safety Study of BMS-770767 in Subjects With Hypercholesterolemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00997152) Efficacy and Safety Study of JTT-654 in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01493271) A Study of RO5093151 in Patients With Ocular Hypertension Or Open Angle Glaucoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 12 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02337933) Effect of Ursolic Acid Administration on Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04983368) XanaMIA-DR A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose Ranging Study to Assess the Efficacy, Pharmacodynamics and Safety of Xanamem? in Healthy Elderly Volunteers. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7715). | |||||
| REF 16 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2011). | |||||
| REF 17 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01282970) Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Multiple Rising Oral Doses of BI 135585 XX in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 18 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00979368) Safety Study of BMS-816336 in Healthy Male Subjects. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 19 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800034519) | |||||
| REF 20 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800017768) | |||||
| REF 21 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025590) | |||||
| REF 22 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800027759) | |||||
| REF 23 | Current and future drug targets in weight management. Pharm Res. 2011 Aug;28(8):1792-818. | |||||
| REF 24 | Discovery of novel dual functional agent as PPARgamma agonist and 11beta-HSD1 inhibitor for the treatment of diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Aug 1;17(15):5722-32. | |||||
| REF 25 | Incyte's Selective Oral Inhibitor Of 11beta-HSD1 Demonstrates Improvements In Insulin Sensitivity And Lowers Cholesterol Levels In Type 2 Diabetics. Incyte. 2008. | |||||
| REF 26 | New Therapeutic Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes: Small Molecule Approaches. 2012. Chapter 5. Page(131). | |||||
| REF 27 | 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 inhibiting constituents from Eriobotrya japonica revealed by bioactivity-guided isolation and computational a... Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Feb 15;18(4):1507-15. | |||||
| REF 28 | Selection and early clinical evaluation of the brain-penetrant 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11beta-HSD1) inhibitor UE2343 (Xanamem?). Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;174(5):396-408. | |||||
| REF 29 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800027626) | |||||
| REF 30 | Repurposing Diabetes Drugs for Brain Insulin Resistance in Alzheimer Disease. before print June 15, 2014. | |||||
| REF 31 | Discovery of a potent, orally active 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitor for clinical study: identification of (S)-2-((1S,2S,4R)-b... J Med Chem. 2010 Jun 10;53(11):4481-7. | |||||
| REF 32 | N-(Pyridin-2-yl) arylsulfonamide inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1: Discovery of PF-915275. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jul 1;19(13):3493-7. | |||||
| REF 33 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800027759) | |||||
| REF 34 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 35 | The discovery of azepane sulfonamides as potent 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Aug 15;19(16):4563-5. | |||||
| REF 36 | beta-Keto sulfones as inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I and the mechanism of action. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Jul 1;15(13):4396-405. | |||||
| REF 37 | Modulation of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 activity by 1,5-substituted 1H-tetrazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jun 1;20(11):3265-71. | |||||
| REF 38 | Discovery of orally active butyrolactam 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Nov 1;16(21):5555-60. | |||||
| REF 39 | Discovery and initial SAR of arylsulfonylpiperazine inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11beta-HSD1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Jun 15;18(12):3513-6. | |||||
| REF 40 | Discovery and biological evaluation of adamantyl amide 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 May 15;17(10):2838-43. | |||||
| REF 41 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 42 | The discovery of 2-anilinothiazolones as 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Nov 15;17(22):6056-61. | |||||
| REF 43 | Oxazolones as potent inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Sep 1;17(17):4837-40. | |||||
| REF 44 | 2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-ones as potent and selective 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors: enzyme-ligand co-crystal structure an... J Med Chem. 2008 May 22;51(10):2933-43. | |||||
| REF 45 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2763). | |||||
| REF 46 | A rapid screening assay for inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (11beta-HSD): flavanone selectively inhibits 11beta-HSD1 reductase activity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2003 Dec 30;212(1-2):41-9. | |||||
| REF 47 | Selective inhibition of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 by 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid but not 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009 Feb;113(3-5):248-52. | |||||
| REF 48 | Mediators of mineralocorticoid receptor-induced profibrotic inflammatory responses in the heart. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009 May;116(9):731-9. | |||||
| REF 49 | Rapid hepatic metabolism of 7-ketocholesterol by 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1: species-specific differences between the rat, human, a... J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 30;279(18):18415-24. | |||||
| REF 50 | 4-Methyl-5-phenyl triazoles as selective inhibitors of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type I. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Jun 1;18(11):3405-11. | |||||
| REF 51 | Azabicyclic sulfonamides as potent 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Mar 1;20(5):1551-4. | |||||
| REF 52 | The development and SAR of pyrrolidine carboxamide 11beta-HSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 May 1;20(9):2897-902. | |||||
| REF 53 | Discovery and optimization of adamantyl carbamate inhibitors of 11-HSD1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Nov 15;20(22):6725-9. | |||||
| REF 54 | Discovery of Clinical Candidate BMS-823778 as an Inhibitor of Human 11beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 (11beta-HSD-1). ACS Med Chem Lett. 2018 Nov 13;9(12):1170-1174. | |||||
| REF 55 | Discovery of a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable acidic 11-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11-HSD1) inhibitor: discovery of 2-[(3S)-1-[5-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)-6-propylsulfanylpyridin-2-yl]-3-piperidyl]acetic acid (AZD4017). J Med Chem. 2012 Jun 28;55(12):5951-64. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

