Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T70977
(Former ID: TTDC00162)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3B)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase GSK3B; GSK-3 beta
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
GSK3B
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Myotonic disorder [ICD-11: 8C71] | |||||
| Function |
Requires primed phosphorylation of the majority of its substrates. In skeletal muscle, contributes to insulin regulation of glycogen synthesis by phosphorylating and inhibiting GYS1 activity and hence glycogen synthesis. May also mediate the development of insulin resistance by regulating activation of transcription factors. Regulates protein synthesis by controlling the activity of initiation factor 2B (EIF2BE/EIF2B5) in the same manner as glycogen synthase. In Wnt signaling, GSK3B forms a multimeric complex with APC, AXIN1 and CTNNB1/beta-catenin and phosphorylates the N-terminus of CTNNB1 leading to its degradation mediated by ubiquitin/proteasomes. Phosphorylates JUN at sites proximal to its DNA-binding domain, thereby reducing its affinity for DNA. Phosphorylates NFATC1/NFATC on conserved serine residues promoting NFATC1/NFATC nuclear export, shutting off NFATC1/NFATC gene regulation, and thereby opposing the action of calcineurin. Phosphorylates MAPT/TAU on 'Thr-548', decreasing significantly MAPT/TAU ability to bind and stabilize microtubules. MAPT/TAU is the principal component of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease. Plays an important role in ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. Phosphorylates MACF1, inhibiting its binding to microtubules which is critical for its role in bulge stem cell migration and skin wound repair. Probably regulates NF-kappa-B (NFKB1) at the transcriptional level and is required for the NF-kappa-B-mediated anti-apoptotic response to TNF-alpha (TNF/TNFA). Negatively regulates replication in pancreatic beta-cells, resulting in apoptosis, loss of beta-cells and diabetes. Through phosphorylation of the anti-apoptotic protein MCL1, may control cell apoptosis in response to growth factors deprivation. Phosphorylates MUC1 in breast cancer cells, decreasing the interaction of MUC1 with CTNNB1/beta-catenin. Is necessary for the establishment of neuronal polarity and axon outgrowth. Phosphorylates MARK2, leading to inhibit its activity. Phosphorylates SIK1 at 'Thr-182', leading to sustain its activity. Phosphorylates ZC3HAV1 which enhances its antiviral activity. Phosphorylates SNAI1, leading to its BTRC-triggered ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylates SFPQ at 'Thr-687' upon T-cell activation. Phosphorylates NR1D1 st 'Ser-55' and 'Ser-59' and stabilizes it by protecting it from proteasomal degradation. Regulates the circadian clock via phosphorylation of the major clock components including ARNTL/BMAL1, CLOCK and PER2. Phosphorylates CLOCK AT 'Ser-427' and targets it for proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylates ARNTL/BMAL1 at 'Ser-17' and 'Ser-21' and primes it for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylates OGT at 'Ser-3' or 'Ser-4' which positively regulates its activity. Phosphorylates MYCN in neuroblastoma cells which may promote its degradation. Regulates the circadian rhythmicity of hippocampal long-term potentiation and ARNTL/BMLA1 and PER2 expression. Acts as a regulator of autophagy by mediating phosphorylation of KAT5/TIP60 under starvation conditions, leading to activate KAT5/TIP60 acetyltransferase activity and promote acetylation of key autophagy regulators, such as ULK1 and RUBCNL/Pacer. Constitutively active protein kinase that acts as a negative regulator in the hormonal control of glucose homeostasis, Wnt signaling and regulation of transcription factors and microtubules, by phosphorylating and inactivating glycogen synthase (GYS1 or GYS2), EIF2B, CTNNB1/beta-catenin, APC, AXIN1, DPYSL2/CRMP2, JUN, NFATC1/NFATC, MAPT/TAU and MACF1.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.26
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSGRPRTTSFAESCKPVQQPSAFGSMKVSRDKDGSKVTTVVATPGQGPDRPQEVSYTDTK
VIGNGSFGVVYQAKLCDSGELVAIKKVLQDKRFKNRELQIMRKLDHCNIVRLRYFFYSSG EKKDEVYLNLVLDYVPETVYRVARHYSRAKQTLPVIYVKLYMYQLFRSLAYIHSFGICHR DIKPQNLLLDPDTAVLKLCDFGSAKQLVRGEPNVSYICSRYYRAPELIFGATDYTSSIDV WSAGCVLAELLLGQPIFPGDSGVDQLVEIIKVLGTPTREQIREMNPNYTEFKFPQIKAHP WTKVFRPRTPPEAIALCSRLLEYTPTARLTPLEACAHSFFDELRDPNVKLPNGRDTPALF NFTTQELSSNPPLATILIPPHARIQAAASTPTNATAASDANTGDRGQTNNAASASASNST Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A02564 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T82ALJ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 6 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AMO-02 | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Myotonic dystrophy | [2] | |
| 2 | 9-ING-41 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Myelofibrosis | [3] | |
| 3 | Lithium | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Fragile X syndrome | [4] | |
| 4 | LY2090314 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [5], [6] | |
| 5 | Tideglusib | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Osteosarcoma | [1] | |
| 6 | Neu-120 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Parkinson disease | [7] | |
| Patented Agent(s) | [+] 3 Patented Agents | + | ||||
| 1 | AR-A014418 | Drug Info | Patented | Ovarian cancer | [8] | |
| 2 | CHIR-99021 | Drug Info | Patented | Graft rejection | [8] | |
| 3 | TDZD-8 | Drug Info | Patented | Malignant glioma | [8] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AZD-1080 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Alzheimer disease | [9], [10] | |
| 2 | SAN-61 | Drug Info | Terminated | Alzheimer disease | [11] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 84 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AMO-02 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 2 | 9-ING-41 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 3 | Lithium | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 4 | Tideglusib | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | AR-A014418 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 6 | CHIR-99021 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 7 | KENPAULLONE | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 8 | PMID26161698-Compound-18 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 9 | TDZD-8 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 10 | RO-320432 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 11 | SAN-61 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 12 | (2'Z,3'E)-7-Azaindirubin-3'-oxime | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 13 | (E)-N-(6-(prop-1-enyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 14 | 12,13-DEHYDRO-8-O-ACETYLMANZAMINE A | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 15 | 12,13-DEHYDROMANZAMINE A | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 16 | 3-(6-(phenylamino)-9H-purin-8-yl)benzonitrile | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 17 | 3-phenyl-4-(phenylamino)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 18 | 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 19 | 4-(5-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-amine | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 20 | 4-[(3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)diazenyl]phenol | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 21 | 6-deoxymanzamine X | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 22 | 8-O-(4-bromobenzenesulfonyl)manzamine F | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 23 | 8-O-(4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)manzamine F | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 24 | 8-O-(4-toluenesulfonyl)manzamine A | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 25 | 8-OH-MANZAMINE A | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 26 | 9-N-ETHYL-8-ETHOXY-MANZAMINE A | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 27 | 9-N-METHYL-8-METHOXY-MANZAMINE A | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 28 | alsterpaullone 2-cyanoethyl | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 29 | AMP-PNP | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 30 | AS-601245 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 31 | AZAKENPAULLONE | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 32 | Bisindolylmaleimide-I | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 33 | BX-795 | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 34 | BX-912 | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 35 | CHIR-98014 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 36 | CHIR-98023 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 37 | CI-1040 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 38 | CP-70949 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 39 | CT-98024 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 40 | ELLAGIC ACID | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 41 | GSK-3beta inhibitor II | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 42 | GSK-3beta inhibitor XI | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 43 | I-5 | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 44 | IM-12 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 45 | indirubin deriv. 8a | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 46 | K00244 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 47 | L-779450 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 48 | LEUCETTAMINE B | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 49 | MANZAMINE A | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 50 | Manzamine E | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 51 | Manzamine Y | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 52 | N,8-diphenyl-9H-purin-6-amine | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 53 | N-(6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 54 | N-(6-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 55 | N-(6-(4-aminophenyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 56 | N-(6-(4-fluorophenyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 57 | N-(6-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 58 | N-(6-(furan-3-yl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 59 | N-(6-(pyridin-3-yl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 60 | N-(6-(pyridin-4-yl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 61 | N-(6-(thiophen-3-yl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 62 | N-(6-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 63 | N-(6-benzyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 64 | N-(6-bromo-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 65 | N-(6-chloro-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 66 | N-(6-chloro-5-p-tolyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 67 | N-(6-chloro-5-phenyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 68 | N-(6-phenethyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 69 | N-(6-phenyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)butyramide | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 70 | N-(8-(3-cyanophenyl)-9H-purin-6-yl)pentanamide | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 71 | Neo-kauluamine | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 72 | NU-6102 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 73 | PAULLONE | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 74 | PF-228 | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 75 | PMID19115845C89S | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 76 | PYRAZOLOPYRIDAZINE 1 | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 77 | PYRAZOLOPYRIDAZINE 2 | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 78 | Quinoxaline1 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 79 | RGB-286147 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 80 | Ro31-8220 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 81 | SB-415286 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 82 | STAUROSPORINONE | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 83 | Thieno analogue of kenpaullone | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 84 | TWS-119 | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LY2090314 | Drug Info | [8], [15] | |||
| 2 | Neu-120 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | AZD-1080 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: adenosine diphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Binary complex structure of human tau protein kinase I with ADP | PDB:1J1C | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.10 Å | Mutation | No | [55] |
| PDB Sequence |
SKVTTVVATP
44 GQGPDRPQEV54 SYTDTKVIGN64 GSFGVVYQAK74 LCDSGELVAI84 KKVLQDKRFK 94 NRELQIMRKL104 DHCNIVRLRY114 FFYSSGEKKD124 EVYLNLVLDY134 VPETVYRVAR 144 HYSRAKQTLP154 VIYVKLYMYQ164 LFRSLAYIHS174 FGICHRDIKP184 QNLLLDPDTA 194 VLKLCDFGSA204 KQLVRGEPNV214 SYICSRYYRA224 PELIFGATDY234 TSSIDVWSAG 244 CVLAELLLGQ254 PIFPGDSGVD264 QLVEIIKVLG274 TPTREQIREM284 NPNYTEFKFP 294 QIKAHPWTKV304 FRPRTPPEAI314 ALCSRLLEYT324 PTARLTPLEA334 CAHSFFDELR 344 DPNVKLPNGR354 DTPALFNFTT364 QELSSNPPLA374 TILIPPHARI384 QAAA |
|||||
|
|
ILE62
3.818
GLY63
4.799
ASN64
3.995
GLY65
2.916
SER66
3.885
PHE67
3.748
VAL70
3.674
ALA83
3.513
LYS85
2.925
GLU97
4.956
VAL110
3.481
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: CHIR-99021 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Co-structure of human glycogen synthase kinase beta with a selective (5-imidazol-2-yl-4-phenylpyrimidin-2-yl)[2-(2-pyridylamino)ethyl]amine inhibitor | PDB:6B8J | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [56] |
| PDB Sequence |
VTTVVATPGQ
46 GPDRPQEVSY56 TDTKVIGNGS66 FGVVYQAKLC76 DSGELVAIKK86 VLQDKRFKNR 96 ELQIMRKLDH106 CNIVRLRYFF116 YSSGDEVYLN129 LVLDYVPETV139 YRVARHYSRA 149 KQTLPVIYVK159 LYMYQLFRSL169 AYIHSFGICH179 RDIKPQNLLL189 DPDTAVLKLC 199 DFGSAKQLVR209 GEPNVSICSR220 YYRAPELIFG230 ATDYTSSIDV240 WSAGCVLAEL 250 LLGQPIFPGD260 SGVDQLVEII270 KVLGTPTREQ280 IREMNPNYTE290 FKFPQIKAHP 300 WTKVFRPRTP310 PEAIALCSRL320 LEYTPTARLT330 PLEACAHSFF340 DELRDPNVKL 350 PNGRDTPALF360 NFTTQELSSN370 PPLATILIPP380 HARI
|
|||||
|
|
ILE62
3.385
GLY63
3.603
ASN64
3.491
PHE67
3.381
VAL70
3.665
ALA83
3.636
LYS85
4.740
VAL110
4.287
LEU132
3.441
ASP133
3.309
TYR134
3.270
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
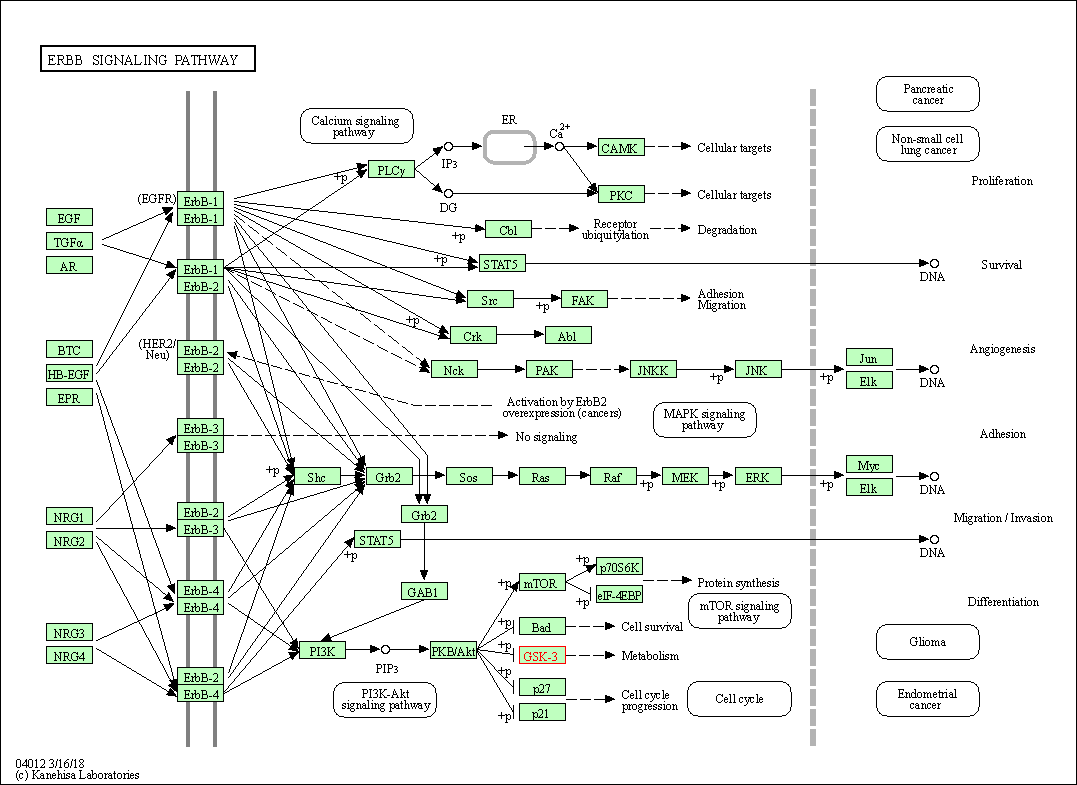
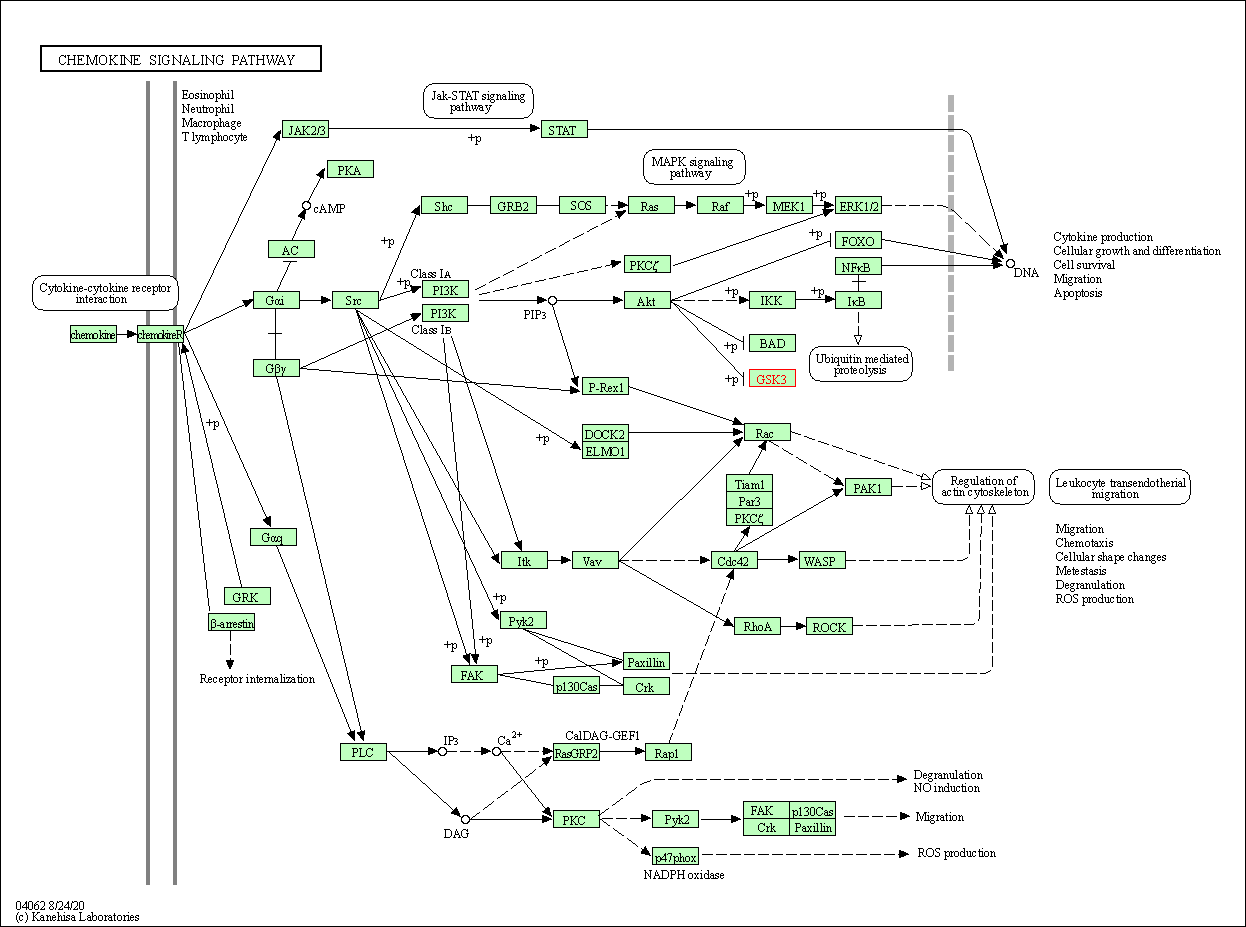
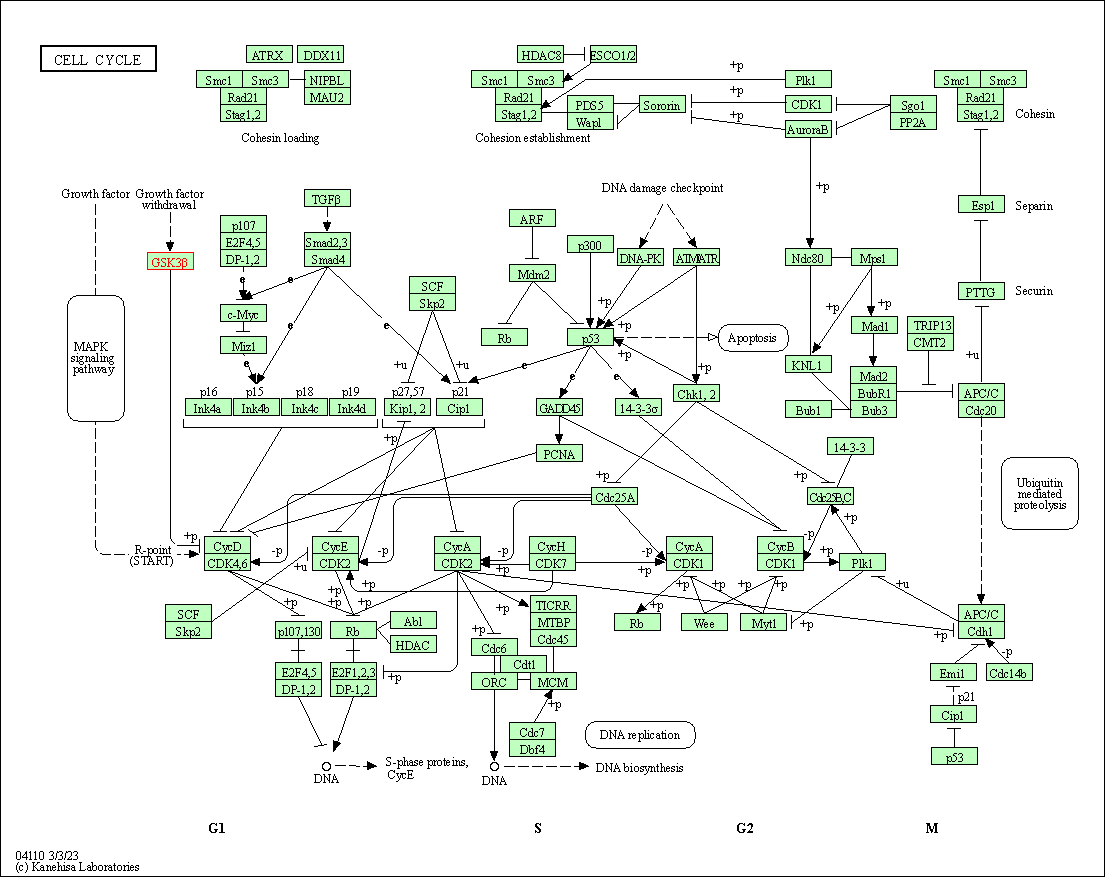
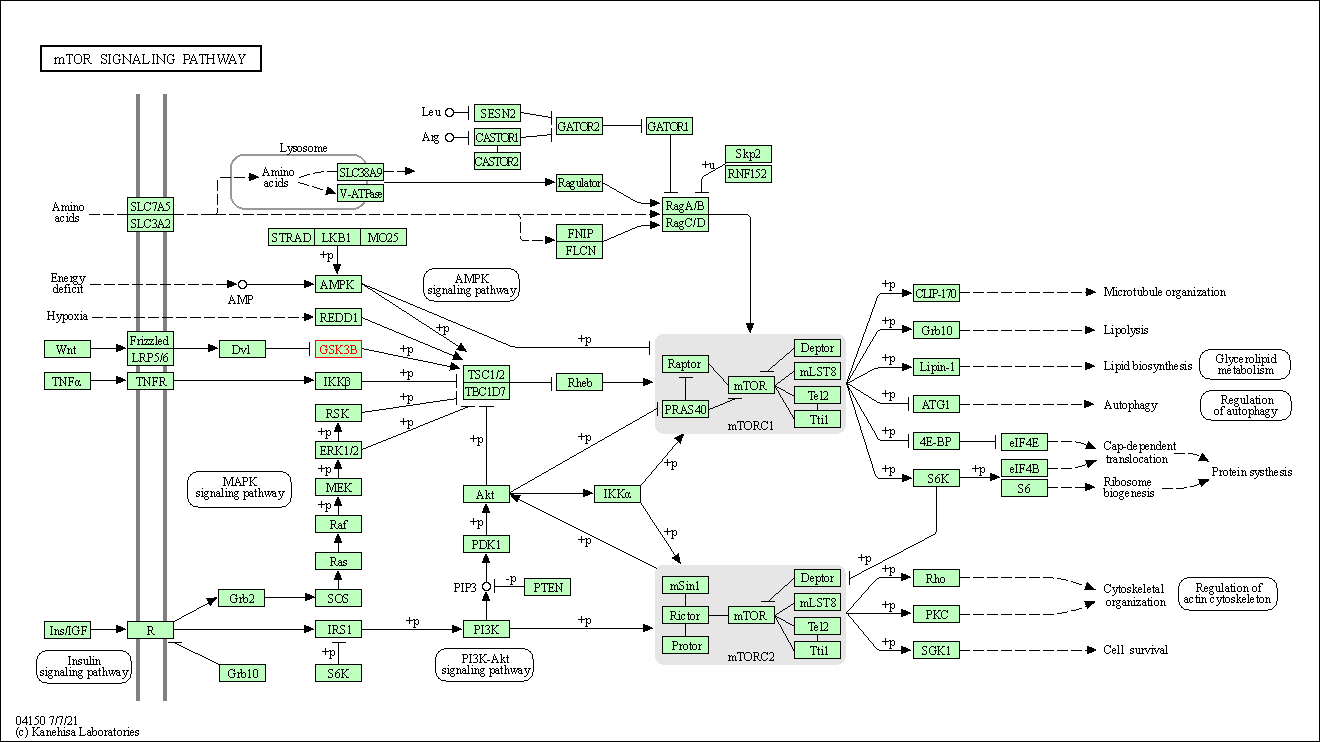
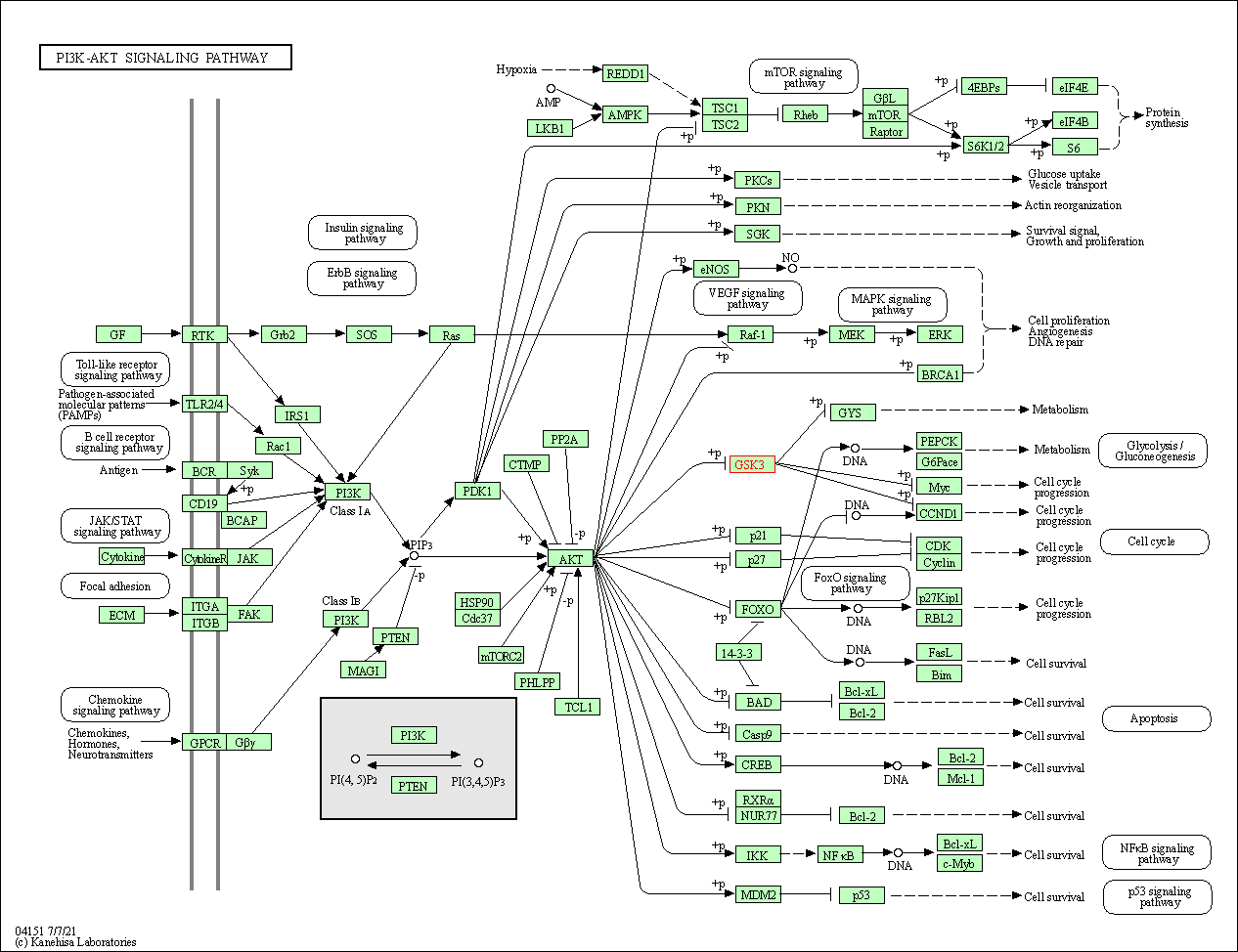
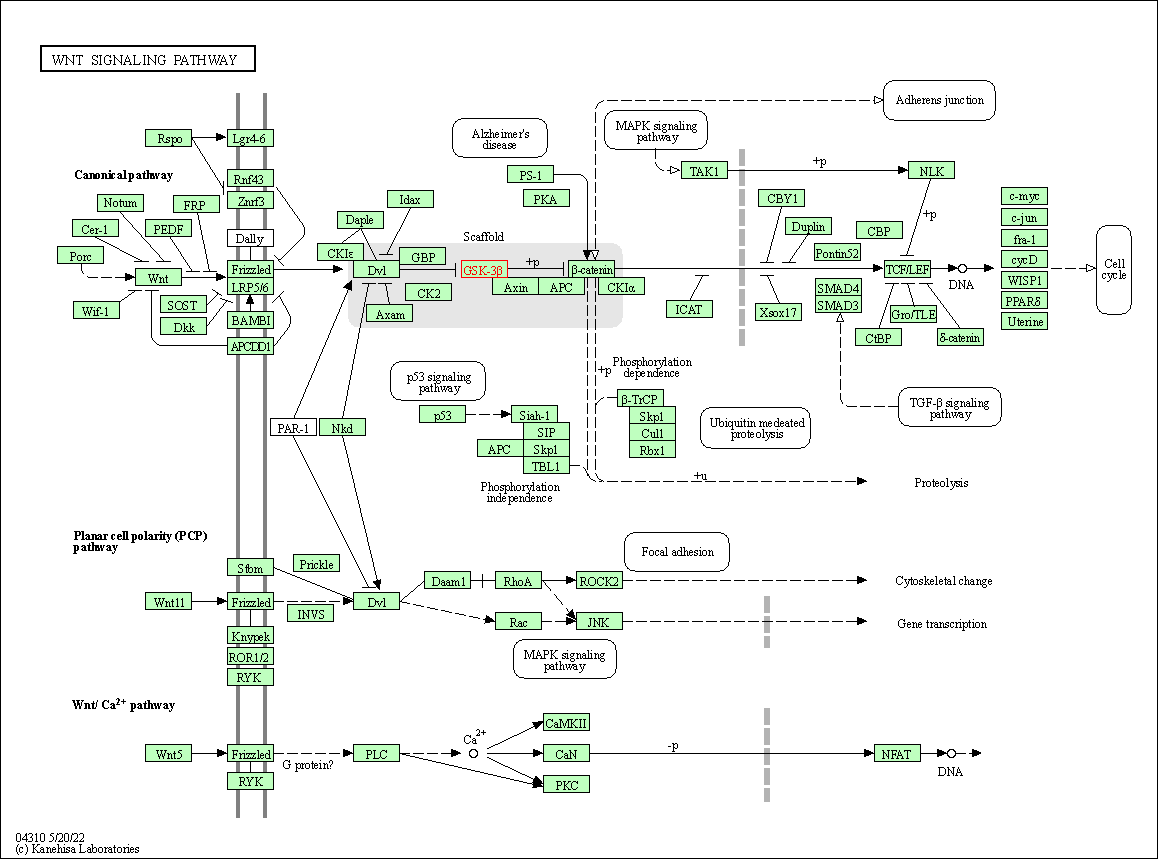
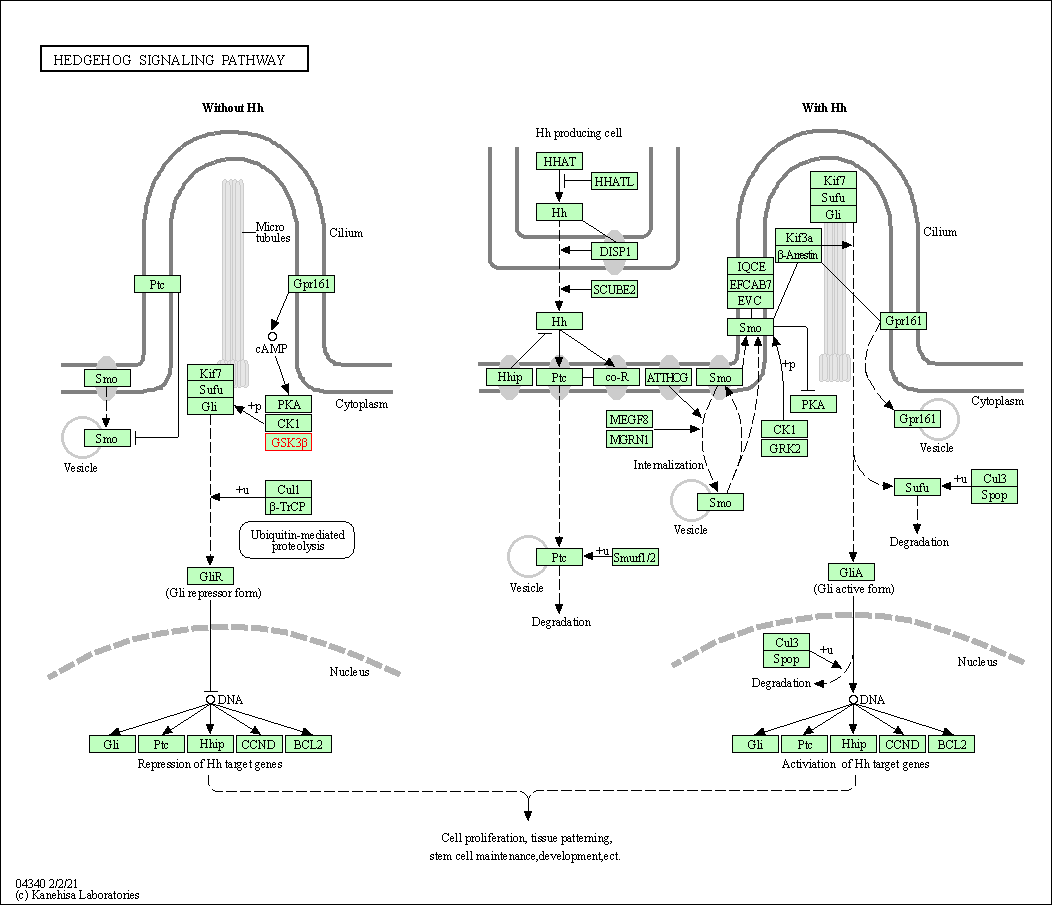
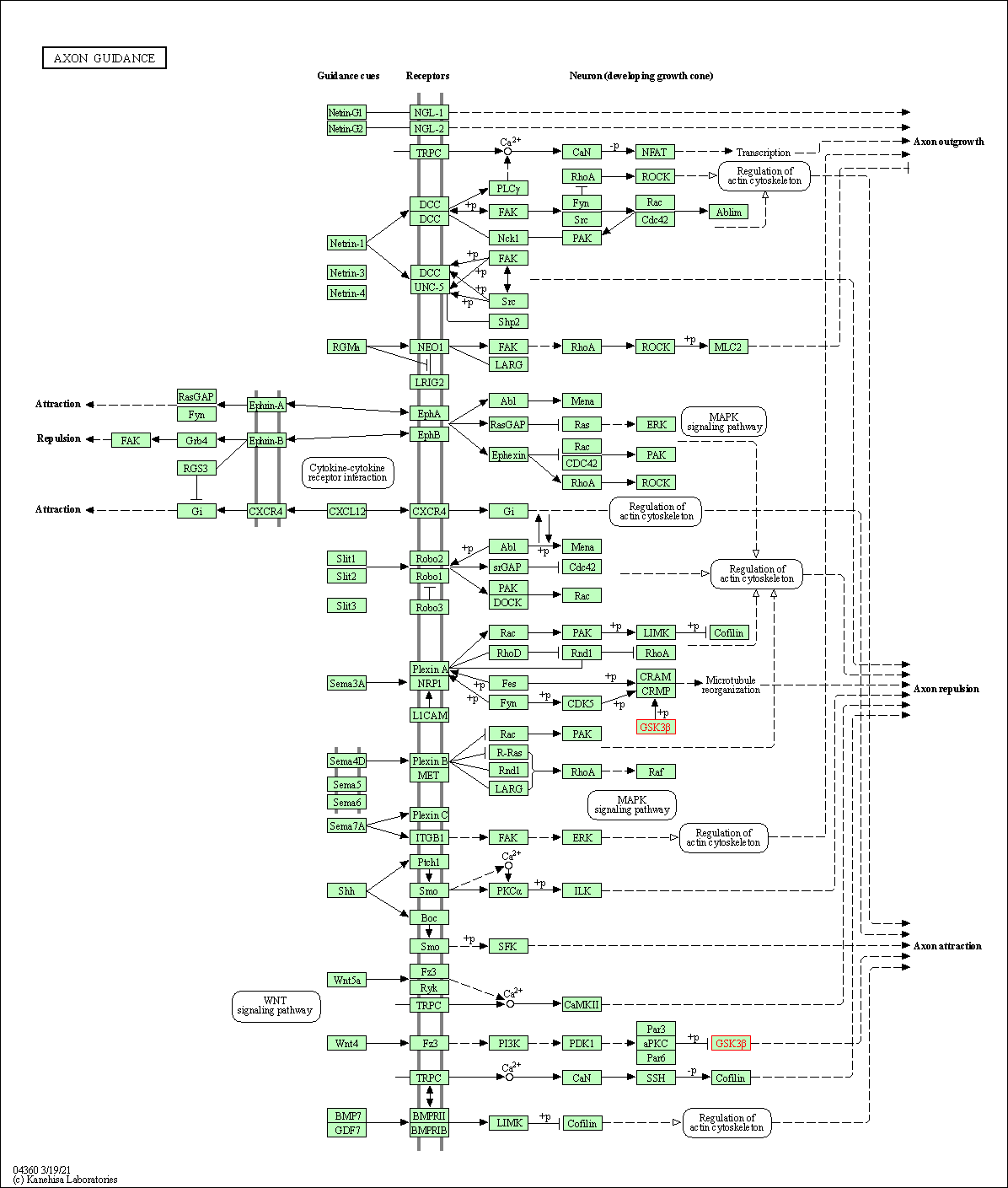
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | hsa04340 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Melanogenesis | hsa04916 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 43 | Degree centrality | 4.62E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 5.84E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.63E-01 | Radiality | 1.45E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.34E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.43E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.27E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Evidence for irreversible inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta by tideglusib. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 6;287(2):893-904. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03692312) Efficacy and Safety of Tideglusib in Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04218071) Actuate 1901: 9-ING-41 in Myelofibrosis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | Open-label treatment trial of lithium to target the underlying defect in fragile X syndrome. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2008 Aug;29(4):293-302. | |||||
| REF 5 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7958). | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01214603) A Study in Participants With Acute Leukemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00607451) Safety, Tolerability, PK and PD Study of Neu-120 in the Treatment of Levodopa-induced Dyskinesia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitors: a patent update (2014-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Jun;27(6):657-666. | |||||
| REF 9 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7819). | |||||
| REF 10 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021264) | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800029796) | |||||
| REF 12 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 13 | 9-ING-41, a small molecule inhibitor of GSK-3beta, potentiates the effects of anticancer therapeutics in bladder cancer. Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):19977. | |||||
| REF 14 | The GSK3 kinase inhibitor lithium produces unexpected hyperphosphorylation of -catenin, a GSK3 substrate, in human glioblastoma cells. Biol Open. 2018 Jan 26;7(1):bio030874. | |||||
| REF 15 | Activating the Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway for the Treatment of Melanoma--Application of LY2090314, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3. PLoS One. 2015 Apr 27;10(4):e0125028. | |||||
| REF 16 | Company report (Neurim Pharmaceuticals) | |||||
| REF 17 | Fragment and knowledge-based design of selective GSK-3beta inhibitors using virtual screening models. Eur J Med Chem. 2009 Jun;44(6):2361-71. | |||||
| REF 18 | Selective glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors potentiate insulin activation of glucose transport and utilization in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes. 2003 Mar;52(3):588-95. | |||||
| REF 19 | 1-Azakenpaullone is a selective inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Jan 19;14(2):413-6. | |||||
| REF 20 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy: a patent review (2009 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(9):953-70. | |||||
| REF 21 | Identification of novel scaffold of benzothiazepinones as non-ATP competitive glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibitors through virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Dec 1;22(23):7232-6. | |||||
| REF 22 | AZD1080, a novel GSK3 inhibitor, rescues synaptic plasticity deficits in rodent brain and exhibits peripheral target engagement in humans.J Neurochem.2013 May;125(3):446-56. | |||||
| REF 23 | Discovery of potent and bioavailable GSK-3beta inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Mar 1;20(5):1693-6. | |||||
| REF 24 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800029796) | |||||
| REF 25 | Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of 7-azaindirubin-3'-oxime, a 7-aza isostere of the natural indirubin pharmacophore. J Nat Prod. 2009 Dec;72(12):2199-202. | |||||
| REF 26 | Rational design of potent GSK3beta inhibitors with selectivity for Cdk1 and Cdk2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Mar 15;20(6):1985-9. | |||||
| REF 27 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) inhibitory activity and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies of the manzamine alkaloids. Potential for ... J Nat Prod. 2007 Sep;70(9):1397-405. | |||||
| REF 28 | Novel 8-arylated purines as inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase. Eur J Med Chem. 2010 Aug;45(8):3389-93. | |||||
| REF 29 | Novel GSK-3beta inhibitors from sequential virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jan 15;16(2):636-43. | |||||
| REF 30 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 31 | 4-arylazo-3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazole CDK inhibitors: SAR study, crystal structure in complex with CDK2, selectivity, and cellular effects. J Med Chem. 2006 Nov 2;49(22):6500-9. | |||||
| REF 32 | Manzamine B and E and ircinal A related alkaloids from an Indonesian Acanthostrongylophora sponge and their activity against infectious, tropical p... J Nat Prod. 2006 Jul;69(7):1034-40. | |||||
| REF 33 | A systematic interaction map of validated kinase inhibitors with Ser/Thr kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 18;104(51):20523-8. | |||||
| REF 34 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 35 | The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J. 2007 Dec 15;408(3):297-315. | |||||
| REF 36 | Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105. | |||||
| REF 37 | Novel small molecule inhibitors of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. J Biol Chem. 2005 May 20;280(20):19867-74. | |||||
| REF 38 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2030). | |||||
| REF 39 | Identification of ellagic acid as potent inhibitor of protein kinase CK2: a successful example of a virtual screening application. J Med Chem. 2006 Apr 20;49(8):2363-6. | |||||
| REF 40 | Scaffold hopping and optimization towards libraries of glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2002 Jun 3;12(11):1525-8. | |||||
| REF 41 | Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel 7-azaindolyl-heteroaryl-maleimides as potent and selective glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004 Jun 15;12(12):3167-85. | |||||
| REF 42 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 43 | Novel indolylmaleimide acts as GSK-3beta inhibitor in human neural progenitor cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Sep 15;18(18):6785-95. | |||||
| REF 44 | Structural basis for the synthesis of indirubins as potent and selective inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 and cyclin-dependent kinases. J Med Chem. 2004 Feb 12;47(4):935-46. | |||||
| REF 45 | The discovery of the potent aurora inhibitor MK-0457 (VX-680). Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jul 1;19(13):3586-92. | |||||
| REF 46 | The identification of potent and selective imidazole-based inhibitors of B-Raf kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Jan 15;16(2):378-81. | |||||
| REF 47 | Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of new derivatives of the marine alkaloid leucettamine B as kinase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2010 Feb;45(2):805-10. | |||||
| REF 48 | 2-N-Methyl modifications and SAR studies of manzamine A. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jul 15;16(14):6702-6. | |||||
| REF 49 | Design of potent and selective GSK3beta inhibitors with acceptable safety profile and pharmacokinetics. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Apr 1;20(7):2344-9. | |||||
| REF 50 | Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines as novel CDK2 inhibitors: protein structure-guided design and SAR. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Mar 1;16(5):1353-7. | |||||
| REF 51 | Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2007 May 18;282(20):14845-52. | |||||
| REF 52 | First Cdc7 kinase inhibitors: pyrrolopyridinones as potent and orally active antitumor agents. 2. Lead discovery. J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 22;52(2):293-307. | |||||
| REF 53 | N-Phenyl-4-pyrazolo[1,5-b]pyridazin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-amines as potent and selective inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3 with good cellular effi... J Med Chem. 2004 Sep 9;47(19):4716-30. | |||||
| REF 54 | Diversity-oriented synthesis: exploring the intersections between chemistry and biology. Nat Chem Biol. 2005 Jul;1(2):74-84. | |||||
| REF 55 | Structural insight into nucleotide recognition in tau-protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004 Mar;60(Pt 3):439-46. | |||||
| REF 56 | Synthesis, Binding Mode, and Antihyperglycemic Activity of Potent and Selective (5-Imidazol-2-yl-4-phenylpyrimidin-2-yl)[2-(2-pyridylamino)ethyl]amine Inhibitors of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3. J Med Chem. 2017 Oct 26;60(20):8482-8514. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

