Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T36557
(Former ID: TTDC00069)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARD)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Peroxisomeproliferator-activated receptor beta; Peroxisomeproliferator activated receptor beta/delta; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta; PPARdelta; PPARB; PPAR-delta; PPAR-beta; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 2; Nuclear hormone receptor 1; NUCI; NUC1; NR1C2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PPARD
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92] | |||||
| 2 | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B80-5B81] | |||||
| Function |
Receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Has a preference for poly-unsaturated fatty acids, such as gamma-linoleic acid and eicosapentanoic acid. Once activated by a ligand, the receptor binds to promoter elements of target genes. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the acyl-CoA oxidase gene. Decreases expression of NPC1L1 once activated by a ligand. Ligand-activated transcription factor.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Nuclear hormone receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MEQPQEEAPEVREEEEKEEVAEAEGAPELNGGPQHALPSSSYTDLSRSSSPPSLLDQLQM
GCDGASCGSLNMECRVCGDKASGFHYGVHACEGCKGFFRRTIRMKLEYEKCERSCKIQKK NRNKCQYCRFQKCLALGMSHNAIRFGRMPEAEKRKLVAGLTANEGSQYNPQVADLKAFSK HIYNAYLKNFNMTKKKARSILTGKASHTAPFVIHDIETLWQAEKGLVWKQLVNGLPPYKE ISVHVFYRCQCTTVETVRELTEFAKSIPSFSSLFLNDQVTLLKYGVHEAIFAMLASIVNK DGLLVANGSGFVTREFLRSLRKPFSDIIEPKFEFAVKFNALELDDSDLALFIAAIILCGD RPGLMNVPRVEAIQDTILRALEFHLQANHPDAQYLFPKLLQKMADLRQLVTEHAQMMQRI KKTETETSLHPLLQEIYKDMY Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T74WWP | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 7 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GFT-505 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis | [2] | |
| 2 | MBX-8025 | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Obesity | [3] | |
| 3 | T3D-959 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Alzheimer disease | [4] | |
| 4 | T3D-959 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Alzheimer disease | [5] | |
| 5 | CER-002 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Dyslipidemia | [6] | |
| 6 | KD3010 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Obesity | [7] | |
| 7 | SAR351034 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Dyslipidemia | [8] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 5 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GW-501516 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 4 | Type-1 diabetes | [9], [10] | |
| 2 | GSK-677954 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | [11] | |
| 3 | Indeglitazar | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [12] | |
| 4 | Sodelglitazar | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [13] | |
| 5 | CS-204 | Drug Info | Terminated | Metabolic disorder | [14] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | KD-3020 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | [11] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 5 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GFT-505 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 2 | T3D-959 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 3 | SAR351034 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 4 | GW-501516 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | SAVX-1 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 15 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MBX-8025 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 2 | T3D-959 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 3 | CER-002 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 4 | KD3010 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 5 | PMID25416646-Compound-Figure5-C | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 6 | GSK-677954 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 7 | Indeglitazar | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 8 | Sodelglitazar | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 9 | KD-3020 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 10 | CS-204 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 11 | DB-900 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 12 | GW0742X | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 13 | GW2433 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 14 | L-165041 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 15 | L-783483 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 6 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | (11E)-OCTADEC-11-ENOIC ACID | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 2 | GSK-0660 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 3 | GSK-3787 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 4 | Heptyl-Beta-D-Glucopyranoside | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 5 | L-165461 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 6 | L-796449 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Pemafibrate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | X-ray structure of human PPAR delta ligand binding domain-pemafibrate co-crystals obtained by co-crystallization | PDB:7WGN | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.81 Å | Mutation | No | [33] |
| PDB Sequence |
ADLKAFSKHI
182 YNAYLKNFNM192 TKKKARSILT202 GKTAPFVIHD215 IETLWQAEKG225 LVWGLPPYKE 240 ISVHVFYRCQ250 CTTVETVREL260 TEFAKSIPSF270 SSLFLNDQVT280 LLKYGVHEAI 290 FAMLASIVNK300 DGLLVANGSG310 FVTREFLRSL320 RKPFSDIIEP330 KFEFAVKFNA 340 LELDDSDLAL350 FIAAIILCGD360 RPGLMNVPRV370 EAIQDTILRA380 LEFHLQANHP 390 DAQYLFPKLL400 QKMADLRQLV410 TEHAQMMQRI420 KKTETETSLH430 PLLQEIYKDM 440 Y
|
|||||
|
|
MET192
3.330
ILE213
3.567
LEU219
3.066
GLU223
4.315
TRP228
2.743
HIS244
4.449
VAL245
3.026
PHE246
2.660
ARG248
3.322
CYS249
2.715
GLN250
3.142
THR252
3.314
THR253
2.269
THR256
4.232
HIS287
2.825
ALA289
4.891
ILE290
2.775
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Bezafibrate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | X-ray structure of human PPAR delta ligand binding domain-bezafibrate co-crystals obtained by co-crystallization | PDB:7WGL | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.09 Å | Mutation | No | [33] |
| PDB Sequence |
DLKAFSKHIY
183 NAYLKNFNMT193 KKKARSILTG203 KAPFVIHDIE217 TLWQAEKGLV227 WLPPYKEISV 243 HVFYRCQCTT253 VETVRELTEF263 AKSIPSFSSL273 FLNDQVTLLK283 YGVHEAIFAM 293 LASIVNKDGL303 LVANGSGFVT313 REFLRSLRKP323 FSDIIEPKFE333 FAVKFNALEL 343 DDSDLALFIA353 AIILCGDRPG363 LMNVPRVEAI373 QDTILRALEF383 HLQANHPDAQ 393 YLFPKLLQKM403 ADLRQLVTEH413 AQMMQRIKKT423 ETETSLHPLL433 QEIYKDM |
|||||
|
|
TRP228
3.738
VAL245
3.711
PHE246
2.967
ARG248
3.248
CYS249
3.038
GLN250
2.815
THR252
2.591
THR253
2.415
HIS287
2.801
ILE290
4.134
PHE291
3.211
LEU294
3.249
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPAR signaling pathway | hsa03320 | Affiliated Target |
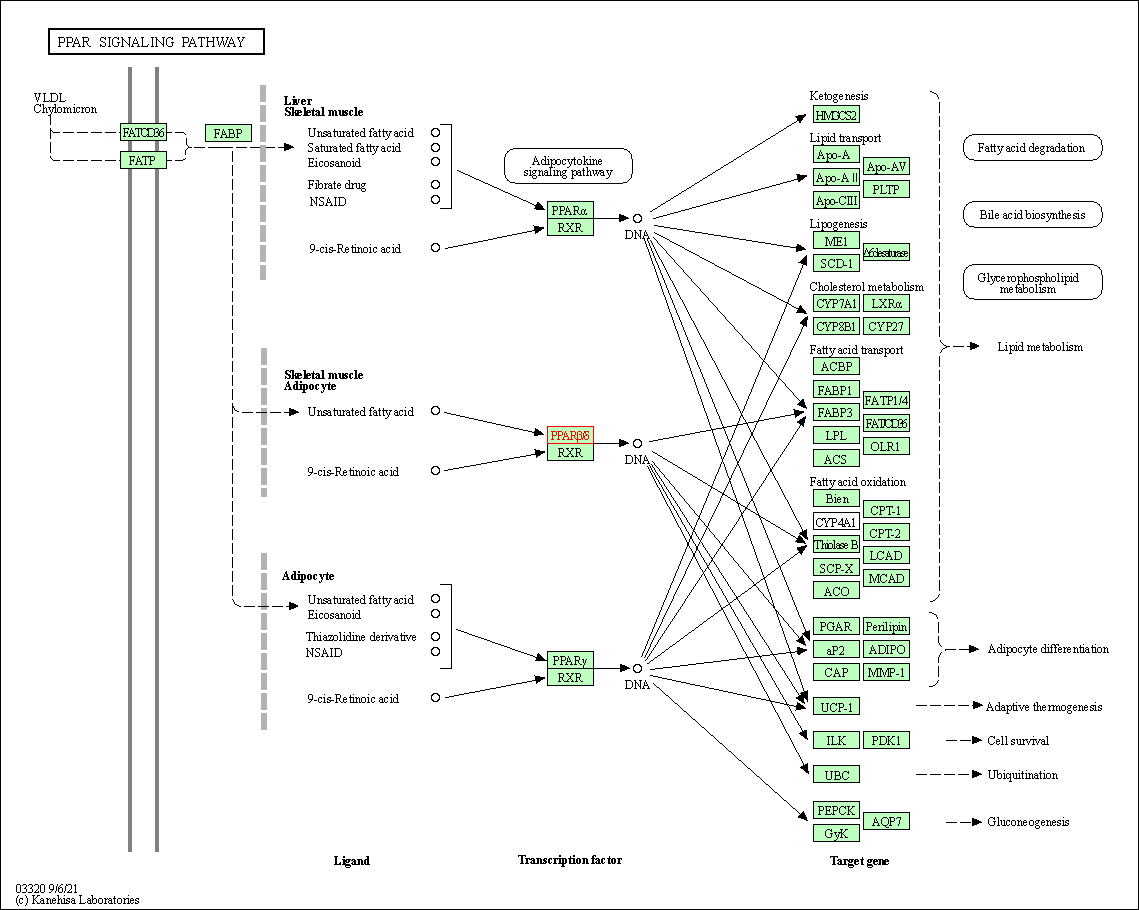
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |
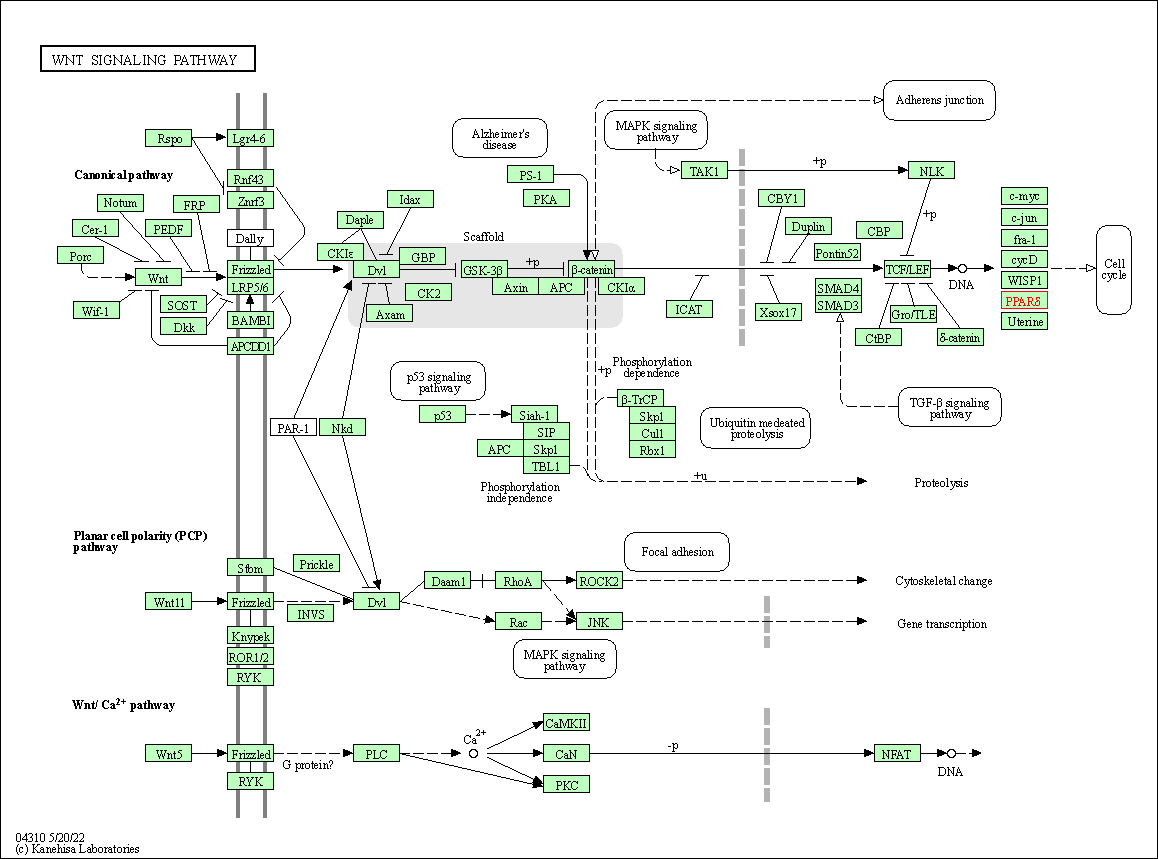
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.68E-06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.17E-01 | Radiality | 1.38E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.33E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.57E+01 | Topological coefficient | 4.05E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | PPAR signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Wnt signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Pathways in cancer | |||||
| 4 | Acute myeloid leukemia | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Wnt signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 2 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Presenilin action in Notch and Wnt signaling | |||||
| 2 | RXR and RAR heterodimerization with other nuclear receptor | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Import of palmitoyl-CoA into the mitochondrial matrix | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex | |||||
| 3 | Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 8 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Wnt Signaling Pathway and Pluripotency | |||||
| 2 | Nuclear Receptors in Lipid Metabolism and Toxicity | |||||
| 3 | NRF2 pathway | |||||
| 4 | Nuclear Receptors Meta-Pathway | |||||
| 5 | Vitamin D Receptor Pathway | |||||
| 6 | Ectoderm Differentiation | |||||
| 7 | Adipogenesis | |||||
| 8 | Nuclear Receptors | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Lipid effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- agonist GW501516 in subjects with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol: characteristics of metabolic syndrome.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2012 Sep;32(9):2289-94. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02704403) Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Elafibranor Versus Placebo in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) (RESOLVE-IT). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800024671) | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04251182) A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multi-Center Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Three Dose Strengths of T3D-959 in Subjects With Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer's Disease. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02560753) Feasibility Study in Subjects With Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease. | |||||
| REF 6 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800028321) | |||||
| REF 7 | Kalypsys nearing completion of phase Ia study of KD3010 for metabolic disorders. Kalypsys. 2007. | |||||
| REF 8 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800029833) | |||||
| REF 9 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2687). | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00841217) Regulation of Lipoprotein Transport in Metabolic Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | Emerging drugs for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Mar;13(1):145-58. | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800022483) | |||||
| REF 13 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800018093) | |||||
| REF 14 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026847) | |||||
| REF 15 | Dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor / agonist GFT505 improves hepatic and peripheral insulin sensitivity in abdominally obese subjects.Diabetes Care.2013 Oct;36(10):2923-30. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00701883) Safety and Benefit of MBX-8025 With and Without Commonly Used Statins in Moderately Overweight Patients With High Cholesterol. U. S. National Institute of Health. 2008. | |||||
| REF 17 | T3D-959: A Multi-Faceted Disease Remedial Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;51(1):123-38. | |||||
| REF 18 | Phrma report (2013 Alzheimers disease) | |||||
| REF 19 | Fibrates, glitazones, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 May; 30(5): 894-899. | |||||
| REF 20 | Addressing Unmet Medical Needs in Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review of Drugs under Development. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2015 March; 11(1): 17-31. | |||||
| REF 21 | PPAR ligands and their therapeutic applications: a patent review (2008 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Feb;25(2):175-91. | |||||
| REF 22 | Scaffold-based discovery of indeglitazar, a PPAR pan-active anti-diabetic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 6;106(1):262-7. | |||||
| REF 23 | Docking and molecular dynamics simulations of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors interacting with pan agonist sodelglitazar. Protein Pept Lett. 2011 Oct;18(10):1021-7. | |||||
| REF 24 | Peroxisome Proliferators-Activated Receptor (PPAR) Modulators and Metabolic Disorders. PPAR Res. 2008; 2008: 679137. | |||||
| REF 25 | DrugBank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for 'omics' research on drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D1035-41. | |||||
| REF 26 | CN patent application no. 102459215, 3-(4-aminophenyl)-2-furancarboxylic acid derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. | |||||
| REF 27 | Identification and characterization of 4-chloro-N-(2-{[5-trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyl]sulfonyl}ethyl)benzamide (GSK3787), a selective and irreversibl... J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 25;53(4):1857-61. | |||||
| REF 28 | Novel selective small molecule agonists for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARdelta)--synthesis and biological activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 May 5;13(9):1517-21. | |||||
| REF 29 | Identification of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands from a biased chemical library. Chem Biol. 1997 Dec;4(12):909-18. | |||||
| REF 30 | Novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma and PPARdelta ligands produce distinct biological effects. J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 5;274(10):6718-25. | |||||
| REF 31 | Phenylacetic acid derivatives as hPPAR agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Apr 7;13(7):1277-80. | |||||
| REF 32 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 594). | |||||
| REF 33 | Functional and Structural Insights into Human PPARAlpha/Delta/Gamma Subtype Selectivity of Bezafibrate, Fenofibric Acid, and Pemafibrate. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 25;23(9):4726. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

