Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T02333
(Former ID: TTDS00076)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Growth hormone receptor (GHR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Somatotropin receptor; Serum bindingprotein; GH receptor
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
GHR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Pituitary gland disorder [ICD-11: 5A60-5A61] | |||||
| Function |
On ligand binding, couples to the JAK2/STAT5 pathway. Receptor for pituitary gland growth hormone involved in regulating postnatal body growth.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MDLWQLLLTLALAGSSDAFSGSEATAAILSRAPWSLQSVNPGLKTNSSKEPKFTKCRSPE
RETFSCHWTDEVHHGTKNLGPIQLFYTRRNTQEWTQEWKECPDYVSAGENSCYFNSSFTS IWIPYCIKLTSNGGTVDEKCFSVDEIVQPDPPIALNWTLLNVSLTGIHADIQVRWEAPRN ADIQKGWMVLEYELQYKEVNETKWKMMDPILTTSVPVYSLKVDKEYEVRVRSKQRNSGNY GEFSEVLYVTLPQMSQFTCEEDFYFPWLLIIIFGIFGLTVMLFVFLFSKQQRIKMLILPP VPVPKIKGIDPDLLKEGKLEEVNTILAIHDSYKPEFHSDDSWVEFIELDIDEPDEKTEES DTDRLLSSDHEKSHSNLGVKDGDSGRTSCCEPDILETDFNANDIHEGTSEVAQPQRLKGE ADLLCLDQKNQNNSPYHDACPATQQPSVIQAEKNKPQPLPTEGAESTHQAAHIQLSNPSS LSNIDFYAQVSDITPAGSVVLSPGQKNKAGMSQCDMHPEMVSLCQENFLMDNAYFCEADA KKCIPVAPHIKVESHIQPSLNQEDIYITTESLTTAAGRPGTGEHVPGSEMPVPDYTSIHI VQSPQGLILNATALPLPDKEFLSSCGYVSTDQLNKIMP Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T46HRF | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pegvisomant | Drug Info | Approved | Acromegaly | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Somatropin recombinant | Drug Info | Approved | Growth hormone deficiency | [4] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 6 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | IONIS-GHR-LRx | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Acromegaly | [5] | |
| 2 | PH-794428 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Growth hormone deficiency | [6] | |
| 3 | SKF-110679 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Growth hormone deficiency | [7] | |
| 4 | EP-51216 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Eating disorder | [8] | |
| 5 | EP-51389 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Eating disorder | [8] | |
| 6 | Syntropin | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Dwarfism | [9] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AOD-9604 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Obesity | [10] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BVT-A | Drug Info | Preclinical | Acromegaly | [11] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 4 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 2 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pegvisomant | Drug Info | [1], [12], [13], [14], [15] | |||
| 2 | BVT-A | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Somatropin recombinant | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 4 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PH-794428 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 2 | SKF-110679 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 3 | Syntropin | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 4 | NNC-26-0194 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 3 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | EP-51216 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 2 | EP-51389 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 3 | AOD-9604 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleukin 5 receptor alpha (IL5RA) | 21.402 (58/271) | 2.06E-04 |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
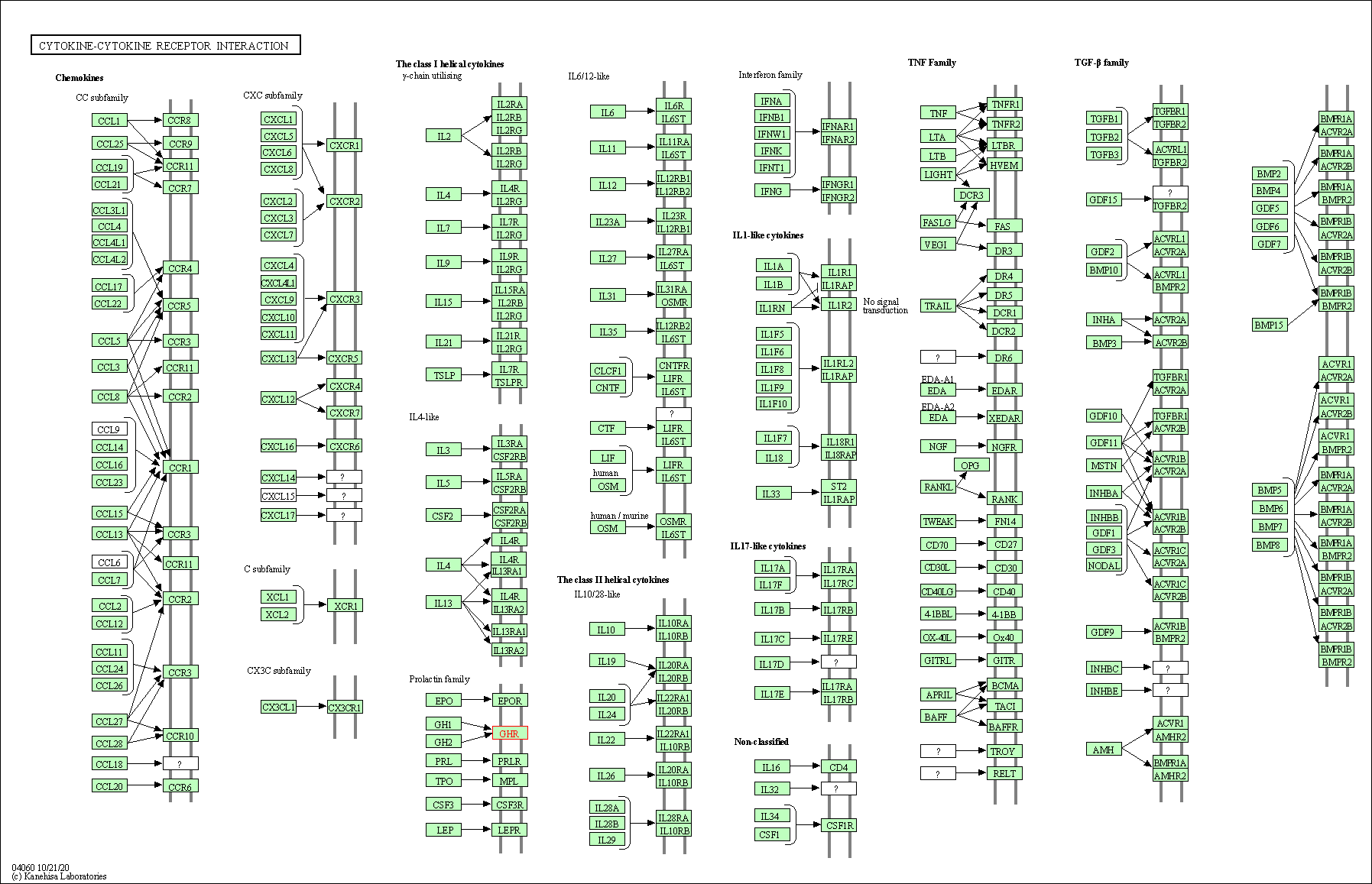
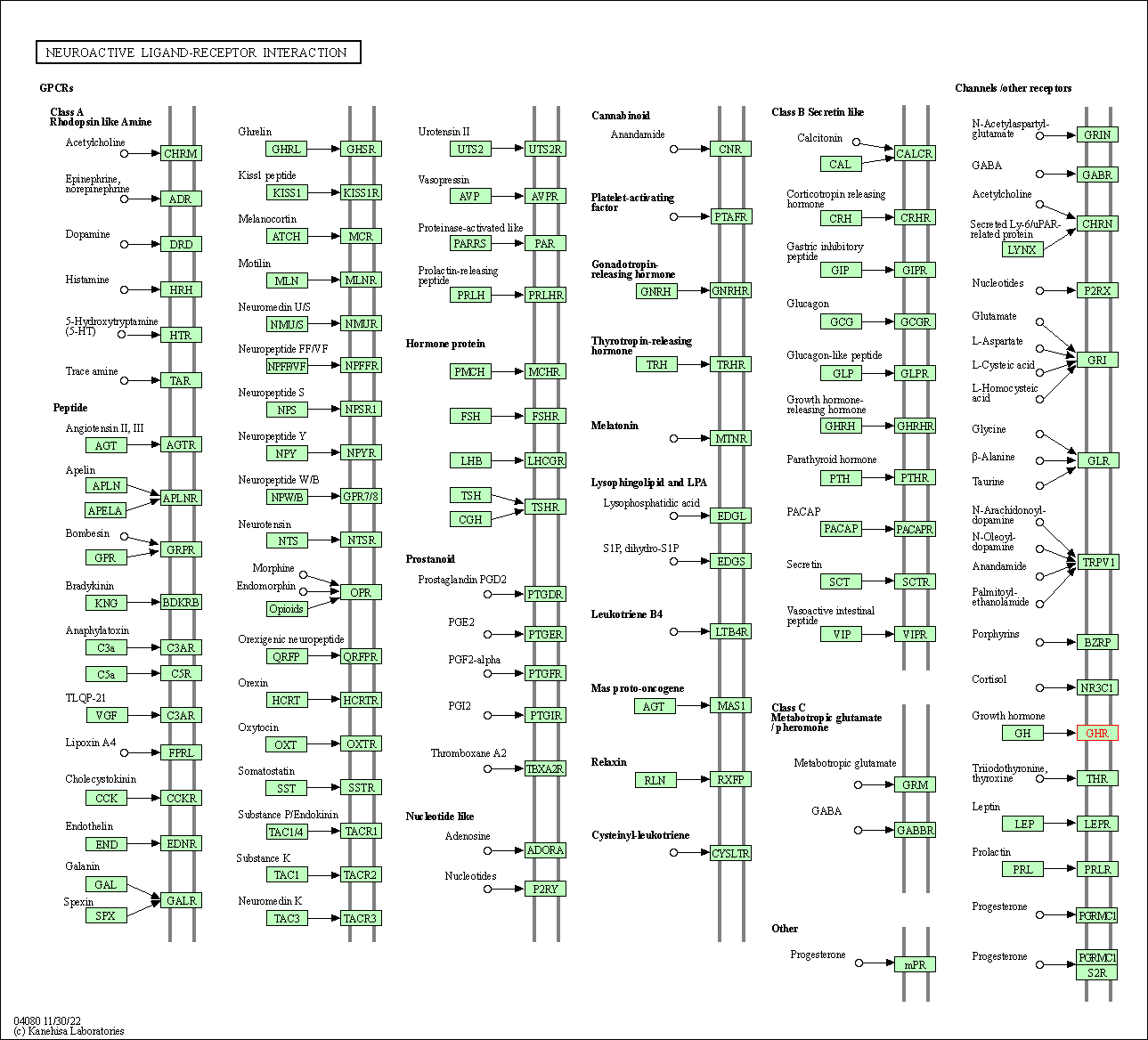
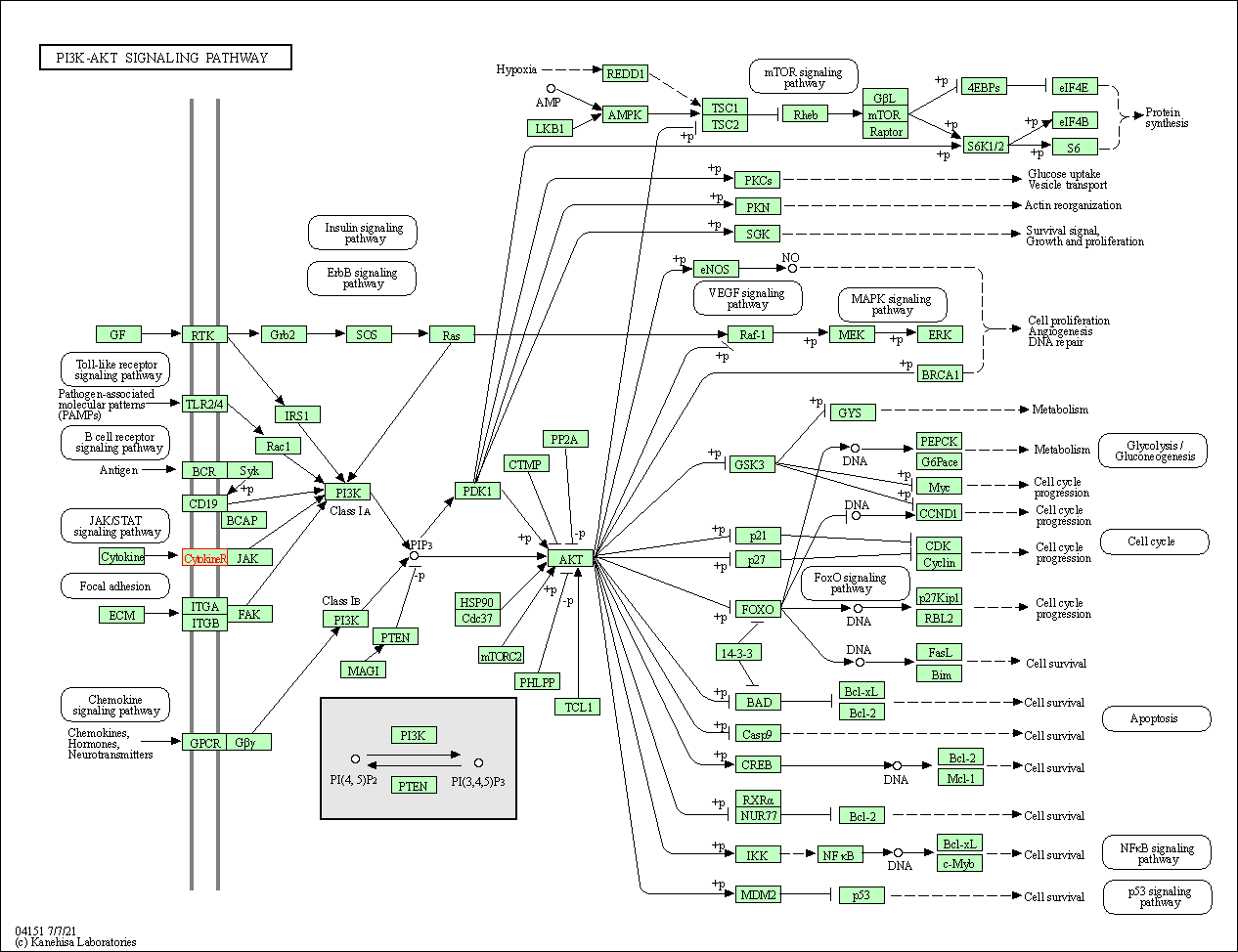
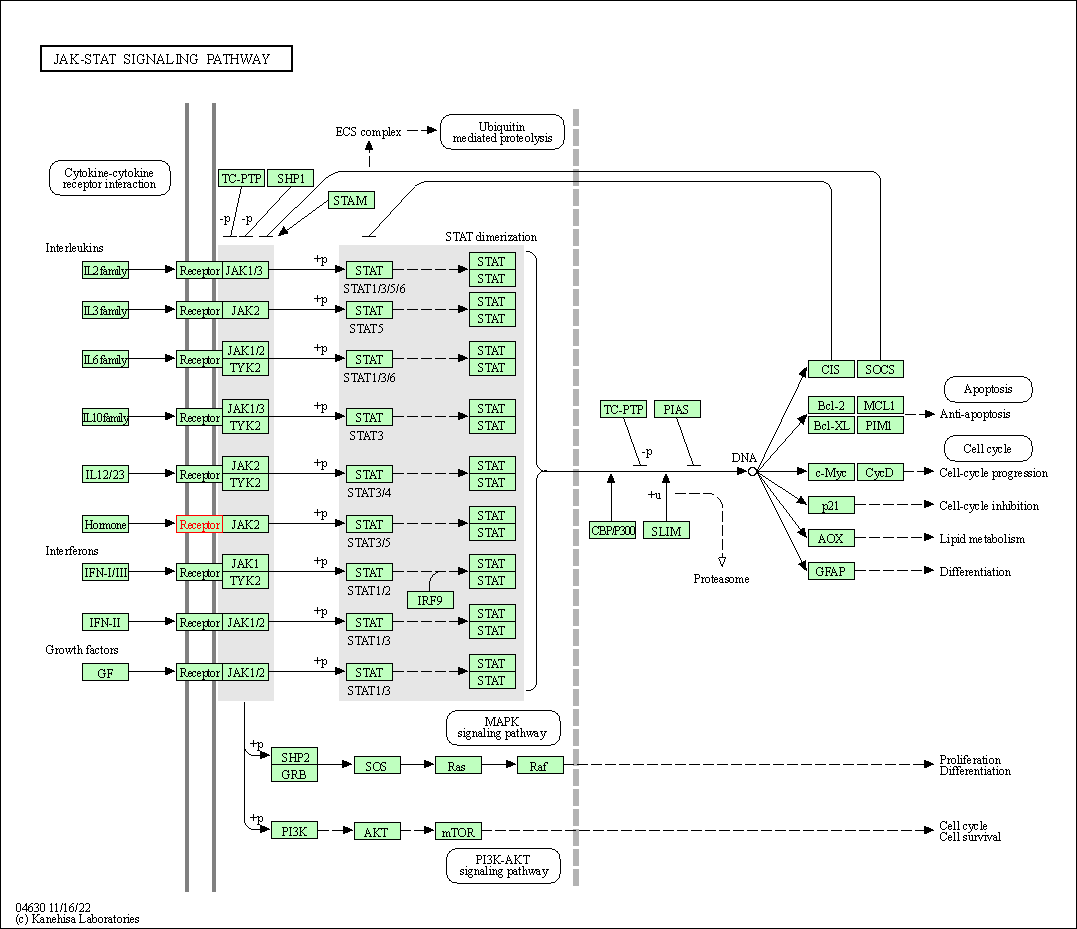
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
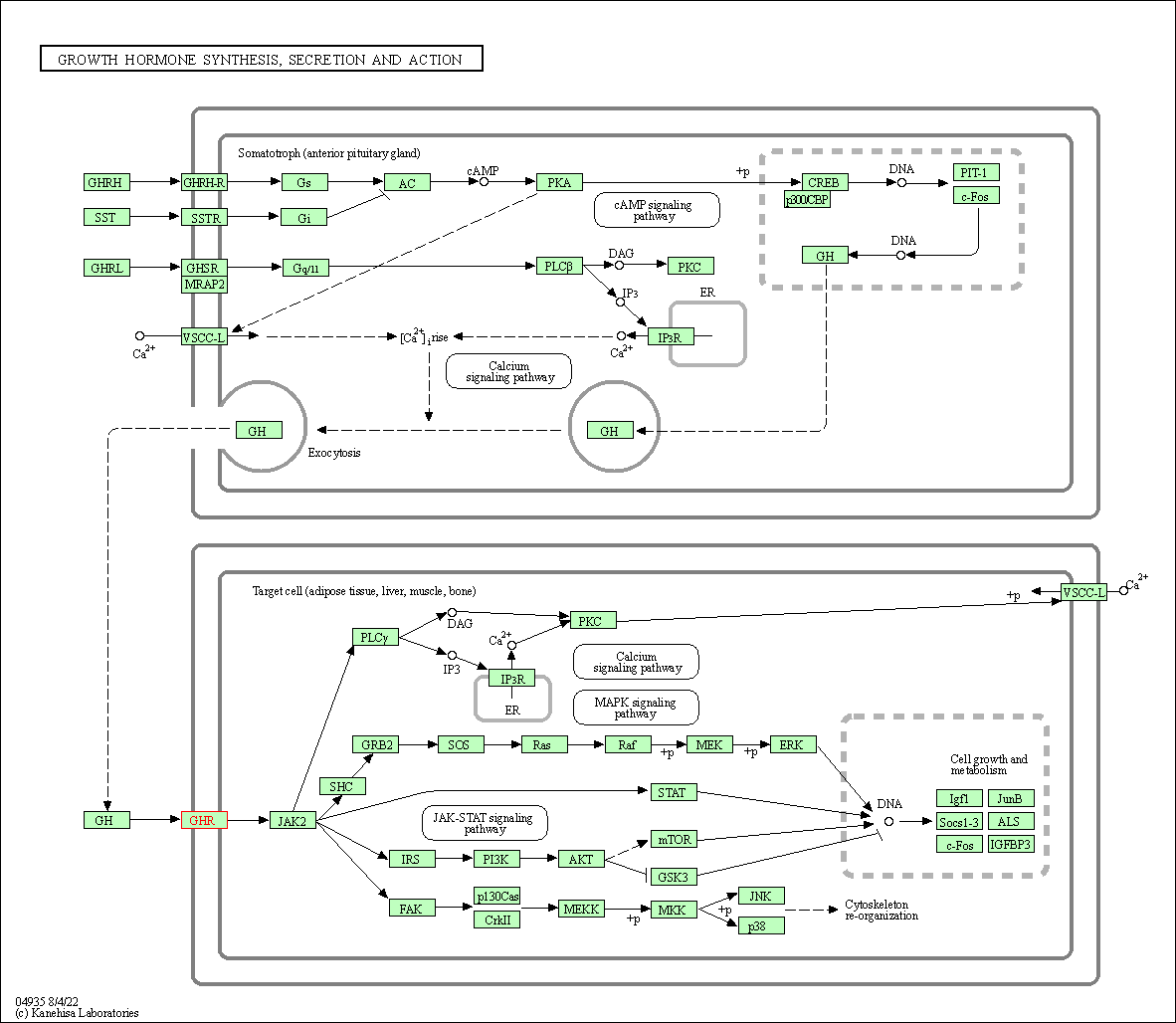
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 7.18E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.10E-01 | Radiality | 1.37E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 4.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.30E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.96E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| 3 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Notch-mediated HES/HEY network | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Prolactin receptor signaling | |||||
| 2 | Growth hormone receptor signaling | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Endochondral Ossification | |||||
| 2 | Prolactin receptor signaling | |||||
| 3 | Growth hormone receptor signaling | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Growth hormone receptor antagonist treatment reduces exercise performance in young males. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Sep;94(9):3265-72. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7485). | |||||
| REF 3 | Treatment strategies for acromegaly. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2005 Nov;10(4):875-90. | |||||
| REF 4 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04522180) An Open Label, Randomized, Phase 2 Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of IONIS-GHR-LRx, an Antisense Inhibitor of the Growth Hormone Receptor, Administered Monthly as Monotherapy in Patients With Acromegaly. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00308464) A Study To Evaluate The Dose Response And Safety Of PHA-794428 In Adults With Growth Hormone Deficiency. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1093). | |||||
| REF 8 | Emerging drugs for eating disorder treatment. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 May;11(2):315-36. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00489294) Safety Study of Syntropin (Human Growth Hormone) for the Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | Emerging drugs for obesity: linking novel biological mechanisms to pharmaceutical pipelines. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2005 Aug;10(3):643-60. | |||||
| REF 11 | Emerging drugs for acromegaly. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2008 Jun;13(2):273-93. | |||||
| REF 12 | Pituitary tumors. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2009 Jul;11(4):287-96. | |||||
| REF 13 | Current therapy and drug pipeline for the treatment of patients with acromegaly. Adv Ther. 2009 Apr;26(4):383-403. | |||||
| REF 14 | Growth hormone receptor antagonists. Minerva Endocrinol. 2002 Dec;27(4):287-98. | |||||
| REF 15 | Growth hormone receptor antagonist improves insulin resistance in acromegaly. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2002 Dec;12(6):418-24. | |||||
| REF 16 | Cost-utility of somatropin (rDNA origin) in the treatment of growth hormone deficiency in children. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006 Feb;22(2):351-7. | |||||
| REF 17 | PEGylation of somatropin (recombinant human growth hormone): impact on its clearance in humans.Xenobiotica.2008 Oct;38(10):1340-51. | |||||
| REF 18 | Late feedback effects of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones in healthy subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1998 May;23(4):371-83. | |||||
| REF 19 | Pharmacokinetic evaluation of ipamorelin and other peptidyl growth hormone secretagogues with emphasis on nasal absorption. Xenobiotica. 1998 Nov;28(11):1083-92. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

