Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T75243
(Former ID: TTDS00265)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR (mTOR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Target of rapamycin; TOR kinase; Rapamycin target protein 1; Rapamycin target protein; Rapamycin and FKBP12 target 1; RAPT1; RAFT1; Mechanistic target of rapamycin; Mammalian target of rapamycin; FRAP2; FRAP1; FRAP; FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein; FKBP-rapamycin associated protein; FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MTOR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 6 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Arteries/arterioles disorder [ICD-11: BD52] | |||||
| 2 | Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A40] | |||||
| 3 | Multiple myeloma [ICD-11: 2A83] | |||||
| 4 | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||||
| 5 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 6 | Transplant rejection [ICD-11: NE84] | |||||
| Function |
MTOR directly or indirectly regulates the phosphorylation of at least 800 proteins. Functions as part of 2 structurally and functionally distinct signaling complexes mTORC1 and mTORC2 (mTOR complex 1 and 2). Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. This includes phosphorylation of EIF4EBP1 and release of its inhibition toward the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). Moreover, phosphorylates and activates RPS6KB1 and RPS6KB2 that promote protein synthesis by modulating the activity of their downstream targets including ribosomal protein S6, eukaryotic translation initiation factor EIF4B, and the inhibitor of translation initiation PDCD4. Stimulates the pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway, both by acute regulation through RPS6KB1-mediated phosphorylation of the biosynthetic enzyme CAD, and delayed regulation, through transcriptional enhancement of the pentose phosphate pathway which produces 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP), an allosteric activator of CAD at a later step in synthesis, this function is dependent on the mTORC1 complex. Regulates ribosome synthesis by activating RNA polymerase III-dependent transcription through phosphorylation and inhibition of MAF1 an RNA polymerase III-repressor. In parallel to protein synthesis, also regulates lipid synthesis through SREBF1/SREBP1 and LPIN1. To maintain energy homeostasis mTORC1 may also regulate mitochondrial biogenesis through regulation of PPARGC1A. mTORC1 also negatively regulates autophagy through phosphorylation of ULK1. Under nutrient sufficiency, phosphorylates ULK1 at 'Ser-758', disrupting the interaction with AMPK and preventing activation of ULK1. Also prevents autophagy through phosphorylation of the autophagy inhibitor DAP. Also prevents autophagy by phosphorylating RUBCNL/Pacer under nutrient-rich conditions. mTORC1 exerts a feedback control on upstream growth factor signaling that includes phosphorylation and activation of GRB10 a INSR-dependent signaling suppressor. Among other potential targets mTORC1 may phosphorylate CLIP1 and regulate microtubules. As part of the mTORC2 complex MTOR may regulate other cellular processes including survival and organization of the cytoskeleton. Plays a critical role in the phosphorylation at 'Ser-473' of AKT1, a pro-survival effector of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, facilitating its activation by PDK1. mTORC2 may regulate the actin cytoskeleton, through phosphorylation of PRKCA, PXN and activation of the Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors RHOA and RAC1A or RAC1B. mTORC2 also regulates the phosphorylation of SGK1 at 'Ser-422'. Regulates osteoclastogenesis by adjusting the expression of CEBPB isoforms. Plays an important regulatory role in the circadian clock function; regulates period length and rhythm amplitude of the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and liver clocks. Serine/threonine protein kinase which is a central regulator of cellular metabolism, growth and survival in response to hormones, growth factors, nutrients, energy and stress signals.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MLGTGPAAATTAATTSSNVSVLQQFASGLKSRNEETRAKAAKELQHYVTMELREMSQEES
TRFYDQLNHHIFELVSSSDANERKGGILAIASLIGVEGGNATRIGRFANYLRNLLPSNDP VVMEMASKAIGRLAMAGDTFTAEYVEFEVKRALEWLGADRNEGRRHAAVLVLRELAISVP TFFFQQVQPFFDNIFVAVWDPKQAIREGAVAALRACLILTTQREPKEMQKPQWYRHTFEE AEKGFDETLAKEKGMNRDDRIHGALLILNELVRISSMEGERLREEMEEITQQQLVHDKYC KDLMGFGTKPRHITPFTSFQAVQPQQSNALVGLLGYSSHQGLMGFGTSPSPAKSTLVESR CCRDLMEEKFDQVCQWVLKCRNSKNSLIQMTILNLLPRLAAFRPSAFTDTQYLQDTMNHV LSCVKKEKERTAAFQALGLLSVAVRSEFKVYLPRVLDIIRAALPPKDFAHKRQKAMQVDA TVFTCISMLARAMGPGIQQDIKELLEPMLAVGLSPALTAVLYDLSRQIPQLKKDIQDGLL KMLSLVLMHKPLRHPGMPKGLAHQLASPGLTTLPEASDVGSITLALRTLGSFEFEGHSLT QFVRHCADHFLNSEHKEIRMEAARTCSRLLTPSIHLISGHAHVVSQTAVQVVADVLSKLL VVGITDPDPDIRYCVLASLDERFDAHLAQAENLQALFVALNDQVFEIRELAICTVGRLSS MNPAFVMPFLRKMLIQILTELEHSGIGRIKEQSARMLGHLVSNAPRLIRPYMEPILKALI LKLKDPDPDPNPGVINNVLATIGELAQVSGLEMRKWVDELFIIIMDMLQDSSLLAKRQVA LWTLGQLVASTGYVVEPYRKYPTLLEVLLNFLKTEQNQGTRREAIRVLGLLGALDPYKHK VNIGMIDQSRDASAVSLSESKSSQDSSDYSTSEMLVNMGNLPLDEFYPAVSMVALMRIFR DQSLSHHHTMVVQAITFIFKSLGLKCVQFLPQVMPTFLNVIRVCDGAIREFLFQQLGMLV SFVKSHIRPYMDEIVTLMREFWVMNTSIQSTIILLIEQIVVALGGEFKLYLPQLIPHMLR VFMHDNSPGRIVSIKLLAAIQLFGANLDDYLHLLLPPIVKLFDAPEAPLPSRKAALETVD RLTESLDFTDYASRIIHPIVRTLDQSPELRSTAMDTLSSLVFQLGKKYQIFIPMVNKVLV RHRINHQRYDVLICRIVKGYTLADEEEDPLIYQHRMLRSGQGDALASGPVETGPMKKLHV STINLQKAWGAARRVSKDDWLEWLRRLSLELLKDSSSPSLRSCWALAQAYNPMARDLFNA AFVSCWSELNEDQQDELIRSIELALTSQDIAEVTQTLLNLAEFMEHSDKGPLPLRDDNGI VLLGERAAKCRAYAKALHYKELEFQKGPTPAILESLISINNKLQQPEAAAGVLEYAMKHF GELEIQATWYEKLHEWEDALVAYDKKMDTNKDDPELMLGRMRCLEALGEWGQLHQQCCEK WTLVNDETQAKMARMAAAAAWGLGQWDSMEEYTCMIPRDTHDGAFYRAVLALHQDLFSLA QQCIDKARDLLDAELTAMAGESYSRAYGAMVSCHMLSELEEVIQYKLVPERREIIRQIWW ERLQGCQRIVEDWQKILMVRSLVVSPHEDMRTWLKYASLCGKSGRLALAHKTLVLLLGVD PSRQLDHPLPTVHPQVTYAYMKNMWKSARKIDAFQHMQHFVQTMQQQAQHAIATEDQQHK QELHKLMARCFLKLGEWQLNLQGINESTIPKVLQYYSAATEHDRSWYKAWHAWAVMNFEA VLHYKHQNQARDEKKKLRHASGANITNATTAATTAATATTTASTEGSNSESEAESTENSP TPSPLQKKVTEDLSKTLLMYTVPAVQGFFRSISLSRGNNLQDTLRVLTLWFDYGHWPDVN EALVEGVKAIQIDTWLQVIPQLIARIDTPRPLVGRLIHQLLTDIGRYHPQALIYPLTVAS KSTTTARHNAANKILKNMCEHSNTLVQQAMMVSEELIRVAILWHEMWHEGLEEASRLYFG ERNVKGMFEVLEPLHAMMERGPQTLKETSFNQAYGRDLMEAQEWCRKYMKSGNVKDLTQA WDLYYHVFRRISKQLPQLTSLELQYVSPKLLMCRDLELAVPGTYDPNQPIIRIQSIAPSL QVITSKQRPRKLTLMGSNGHEFVFLLKGHEDLRQDERVMQLFGLVNTLLANDPTSLRKNL SIQRYAVIPLSTNSGLIGWVPHCDTLHALIRDYREKKKILLNIEHRIMLRMAPDYDHLTL MQKVEVFEHAVNNTAGDDLAKLLWLKSPSSEVWFDRRTNYTRSLAVMSMVGYILGLGDRH PSNLMLDRLSGKILHIDFGDCFEVAMTREKFPEKIPFRLTRMLTNAMEVTGLDGNYRITC HTVMEVLREHKDSVMAVLEAFVYDPLLNWRLMDTNTKGNKRSRTRTDSYSAGQSVEILDG VELGEPAHKKTGTTVPESIHSFIGDGLVKPEALNKKAIQIINRVRDKLTGRDFSHDDTLD VPTQVELLIKQATSHENLCQCYIGWCPFW Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A06952 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T74QXI | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 6 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Everolimus | Drug Info | Approved | Renal cell carcinoma | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Novolimus | Drug Info | Approved | Artery stenosis | [4], [5] | |
| 3 | PF-04449913 | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia | [6] | |
| 4 | Sirolimus | Drug Info | Approved | Organ transplant rejection | [7], [8] | |
| 5 | Temsirolimus | Drug Info | Approved | Renal cell carcinoma | [1], [9] | |
| 6 | Zotarolimus | Drug Info | Approved | Solid tumour/cancer | [10], [11], [12] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 26 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ridaforolimus | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Sarcoma | [13], [14] | |
| 2 | ABI-009 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [15] | |
| 3 | AZD2014 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [16], [17] | |
| 4 | BEZ235 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [18], [19] | |
| 5 | GDC-0980/RG7422 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [20] | |
| 6 | INK128 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Breast cancer | [21] | |
| 7 | LY3023414 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [22] | |
| 8 | MM-141 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [23] | |
| 9 | OSI-027 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Renal cell carcinoma | [24] | |
| 10 | PF-04691502 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Endometrial cancer | [25], [26] | |
| 11 | PF-05212384 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [21], [27], [28] | |
| 12 | PQR309 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Squamous head and neck cell carcinom | [29] | |
| 13 | Salirasib | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Lung cancer | [30], [31] | |
| 14 | SAR245409 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [32] | |
| 15 | SF1126 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Head and neck cancer | [21] | |
| 16 | BGT226 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [33], [34] | |
| 17 | CC-223 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [35] | |
| 18 | ME-344 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Breast cancer | [21] | |
| 19 | BI 860585 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [36] | |
| 20 | CERC 006 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lymphatic malformation | [37] | |
| 21 | DS-3078 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lymphoma | [38] | |
| 22 | DS-7423 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [39] | |
| 23 | GDC-0349 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [40] | |
| 24 | LAM-001 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lymphangioleiomyomatosis | [41] | |
| 25 | PWT-33597 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [42] | |
| 26 | VS-5584 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [43], [44] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 3 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AZD8055 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1/2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [45], [46] | |
| 2 | TAFA-93 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Transplant rejection | [47] | |
| 3 | SCR-44001 | Drug Info | Terminated | Solid tumour/cancer | [48] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 57 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Everolimus | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 2 | Novolimus | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 3 | PF-04449913 | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 4 | Sirolimus | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 5 | Temsirolimus | Drug Info | [1], [11] | |||
| 6 | Ridaforolimus | Drug Info | [54], [55] | |||
| 7 | ABI-009 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 8 | AZD2014 | Drug Info | [56] | |||
| 9 | INK128 | Drug Info | [59] | |||
| 10 | MM-141 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 11 | OSI-027 | Drug Info | [61] | |||
| 12 | PQR309 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 13 | SAR245409 | Drug Info | [50], [63] | |||
| 14 | SF1126 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 15 | ME-344 | Drug Info | [65] | |||
| 16 | BI 860585 | Drug Info | [66] | |||
| 17 | CERC 006 | Drug Info | [67] | |||
| 18 | GDC-0349 | Drug Info | [70] | |||
| 19 | LAM-001 | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 20 | PMID25726713-Compound-47 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 21 | PMID25726713-Compound-48 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 22 | PMID25726713-Compound-49 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 23 | PMID25726713-Compound-50 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 24 | PMID25726713-Compound-51 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 25 | AZD8055 | Drug Info | [73] | |||
| 26 | TAFA-93 | Drug Info | [74] | |||
| 27 | SCR-44001 | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 28 | (4-(6-morpholino-9H-purin-2-yl)phenyl)methanol | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 29 | 2-(2-Methyl-morpholin-4-yl)-benzo[h]chromen-4-one | Drug Info | [77] | |||
| 30 | 2-(6-morpholino-9H-purin-2-yl)phenol | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 31 | 2-chloro-N-(6-cyanopyridin-3-yl)propanamide | Drug Info | [78] | |||
| 32 | 2-Morpholin-4-yl-pyrimido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one | Drug Info | [77] | |||
| 33 | 3-(6-morpholino-9H-purin-2-yl)phenol | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 34 | 4-(2-(1H-indol-6-yl)-9H-purin-6-yl)morpholine | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 35 | 4-(2-(thiophen-2-yl)-9H-purin-6-yl)morpholine | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 36 | 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)-9H-purin-6-yl)morpholine | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 37 | 4-(6-morpholino-9H-purin-2-yl)phenol | Drug Info | [76] | |||
| 38 | AP-21967 | Drug Info | [79] | |||
| 39 | AR-mTOR-26 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 40 | C-16-(S)-3-methylindolerapamycin | Drug Info | [79] | |||
| 41 | CU-906 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 42 | EC-0565 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 43 | EM-101 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 44 | Ethyl 1-[(1H-benzimidazol-2(3H)one-5-yl)sulfonyl]-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate | Drug Info | [77] | |||
| 45 | HM-5016699 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 46 | OXA-01 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 47 | P-2281 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 48 | P-6915 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 49 | PF-03772304 | Drug Info | [80] | |||
| 50 | PF-05094037 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 51 | PP-242 | Drug Info | [81] | |||
| 52 | PP121 | Drug Info | [81] | |||
| 53 | Rapamycin complexed with immunophilin FKBP12 | Drug Info | [82] | |||
| 54 | SB-2280 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 55 | torin 1 | Drug Info | [83] | |||
| 56 | Torin2 | Drug Info | [84] | |||
| 57 | X-387 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 15 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Zotarolimus | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 2 | BEZ235 | Drug Info | [57] | |||
| 3 | GDC-0980/RG7422 | Drug Info | [50], [58] | |||
| 4 | LY3023414 | Drug Info | [60] | |||
| 5 | PF-04691502 | Drug Info | [62] | |||
| 6 | PF-05212384 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 7 | Salirasib | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 8 | BGT226 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 9 | CC-223 | Drug Info | [64] | |||
| 10 | DS-3078 | Drug Info | [68] | |||
| 11 | DS-7423 | Drug Info | [69] | |||
| 12 | PWT-33597 | Drug Info | [71] | |||
| 13 | VS-5584 | Drug Info | [44], [50] | |||
| 14 | EC-0845 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 15 | SX-MTR1 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Sirolimus | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Co-crystal structure of the PPIase domain of FKBP51, Rapamycin and the FRB fragment of mTOR | PDB:4DRI | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.45 Å | Mutation | No | [85] |
| PDB Sequence |
GAMDPEFMEM
2026 WHEGLEEASR2036 LYFGERNVKG2046 MFEVLEPLHA2056 MMERGPQTLK2066 ETSFNQAYGR 2076 DLMEAQEWCR2086 KYMKSGNVKD2096 LTQAWDLYYH2106 VFRRIS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Myo-inositol hexaphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | cryo-EM structure of human mTOR complex 2, focused on one half | PDB:6ZWO | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | No | [86] |
| PDB Sequence |
NPGVINNVLA
800 TIGELAQVSG810 LEMRKWVDEL820 FIIIMDMLQD830 SSLLAKRQVA840 LWTLGQLVAS 850 TGYVVEPYRK860 YPTLLEVLLN870 FLKTEQNQGT880 RREAIRVLGL890 LGALDPYKHK 900 VNISDYSTSE933 MLVNMGNLPL943 DEFYPAVSMV953 ALMRIFRDQS963 LSHHHTMVVQ 973 AITFIFKSLG983 LKCVQFLPQV993 MPTFLNVIRV1003 CDGAIREFLF1013 QQLGMLVSFV 1023 KSHIRPYMDE1033 IVTLMREFWV1043 MNTSIQSTII1053 LLIEQIVVAL1063 GGEFKLYLPQ 1073 LIPHMLRVFM1083 HDNSPGRIVS1093 IKLLAAIQLF1103 GANLDDYLHL1113 LLPPIVKLFD 1123 APEAPLPSRK1133 AALETVDRLT1143 ESLDFTDYAS1153 RIIHPIVRTL1163 DQSPELRSTA 1173 MDTLSSLVFQ1183 LGKKYQIFIP1193 MVNKVLVRHR1203 INHQRYDVLI1213 CRIVKGYTLA 1223 DEEEDPLIYQ1233 HRMLRINLQK1267 AWGAARRVSK1277 DDWLEWLRRL1287 SLELLKDSSS 1297 PSLRSCWALA1307 QAYNPMARDL1317 FNAAFVSCWS1327 ELNEDQQDEL1337 IRSIELALTS 1347 QDIAEVTQTL1357 LNLAEFMEHS1367 DKGPLPLRDD1377 NGIVLLGERA1387 AKCRAYAKAL 1397 HYKELEFQKG1407 PTPAILESLI1417 SINNKLQQPE1427 AAAGVLEYAM1437 KHFGELEIQA 1447 TWYEKLHEWE1457 DALVAYDKKM1467 DTNKDDPELM1477 LGRMRCLEAL1487 GEWGQLHQQC 1497 CEKWTLVNDE1507 TQAKMARMAA1517 AAAWGLGQWD1527 SMEEYTCMIP1537 RDTHDGAFYR 1547 AVLALHQDLF1557 SLAQQCIDKA1567 RDLLDAELTA1577 MAGESYSRAY1587 GAMVSCHMLS 1597 ELEEVIQYKL1607 VPERREIIRQ1617 IWWERLQGCQ1627 RIVEDWQKIL1637 MVRSLVVSPH 1647 EDMRTWLKYA1657 SLCGKSGRLA1667 LAHKTLVLLL1677 GVDPSRQLDH1687 PLPTVHPQVT 1697 YAYMKNMWKS1707 ARKIDAFQHM1717 QHFVQTMQQQ1727 AQHAIATEDQ1737 QHKQELHKLM 1747 ARCFLKLGEW1757 QLNLQGINES1767 TIPKVLQYYS1777 AATEHDRSWY1787 KAWHAWAVMN 1797 FEAVLHYKHQ1807 NQALSKTLLM1879 YTVPAVQGFF1889 RSISLSRGNN1899 LQDTLRVLTL 1909 WFDYGHWPDV1919 NEALVEGVKA1929 IQIDTWLQVI1939 PQLIARIDTP1949 RPLVGRLIHQ 1959 LLTDIGRYHP1969 QALIYPLTVA1979 SKSTTTARHN1989 AANKILKNMC1999 EHSNTLVQQA 2009 MMVSEELIRV2019 AILWHEMWHE2029 GLEEASRLYF2039 GERNVKGMFE2049 VLEPLHAMME 2059 RGPQTLKETS2069 FNQAYGRDLM2079 EAQEWCRKYM2089 KSGNVKDLTQ2099 AWDLYYHVFR 2109 RISKQLPQLT2119 SLELQYVSPK2129 LLMCRDLELA2139 VPGTYDPNQP2149 IIRIQSIAPS 2159 LQVITSKQRP2169 RKLTLMGSNG2179 HEFVFLLKGH2189 EDLRQDERVM2199 QLFGLVNTLL 2209 ANDPTSLRKN2219 LSIQRYAVIP2229 LSTNSGLIGW2239 VPHCDTLHAL2249 IRDYREKKKI 2259 LLNIEHRIML2269 RMAPDYDHLT2279 LMQKVEVFEH2289 AVNNTAGDDL2299 AKLLWLKSPS 2309 SEVWFDRRTN2319 YTRSLAVMSM2329 VGYILGLGDR2339 HPSNLMLDRL2349 SGKILHIDFG 2359 DCFEVAMTRE2369 KFPEKIPFRL2379 TRMLTNAMEV2389 TGLDGNYRIT2399 CHTVMEVLRE 2409 HKDSVMAVLE2419 AFVYDPLLNW2429 RLMDALNKKA2497 IQIINRVRDK2507 LTGRDFSHDD 2517 TLDVPTQVEL2527 LIKQATSHEN2537 LCQCYIGWCP2547 FW
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - other | hsa04136 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
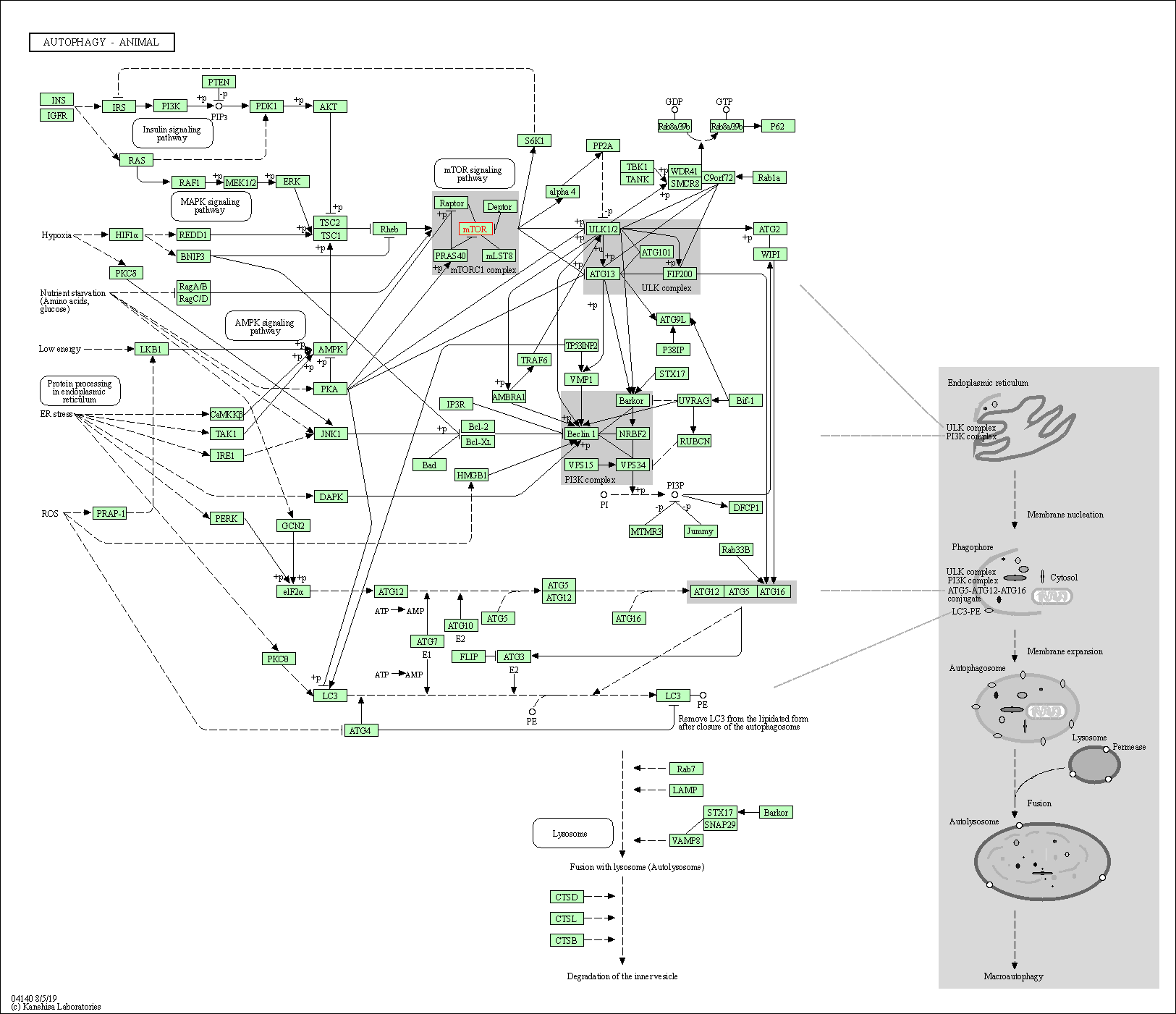
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |
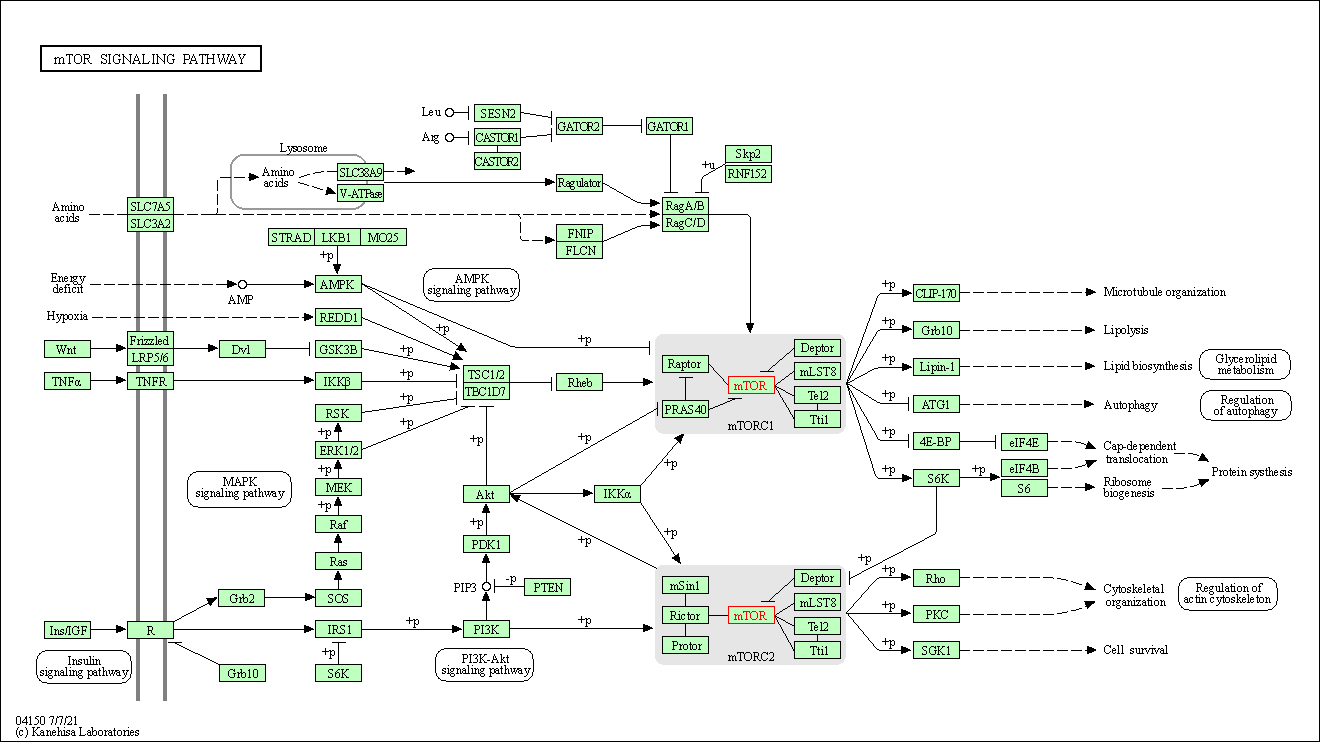
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
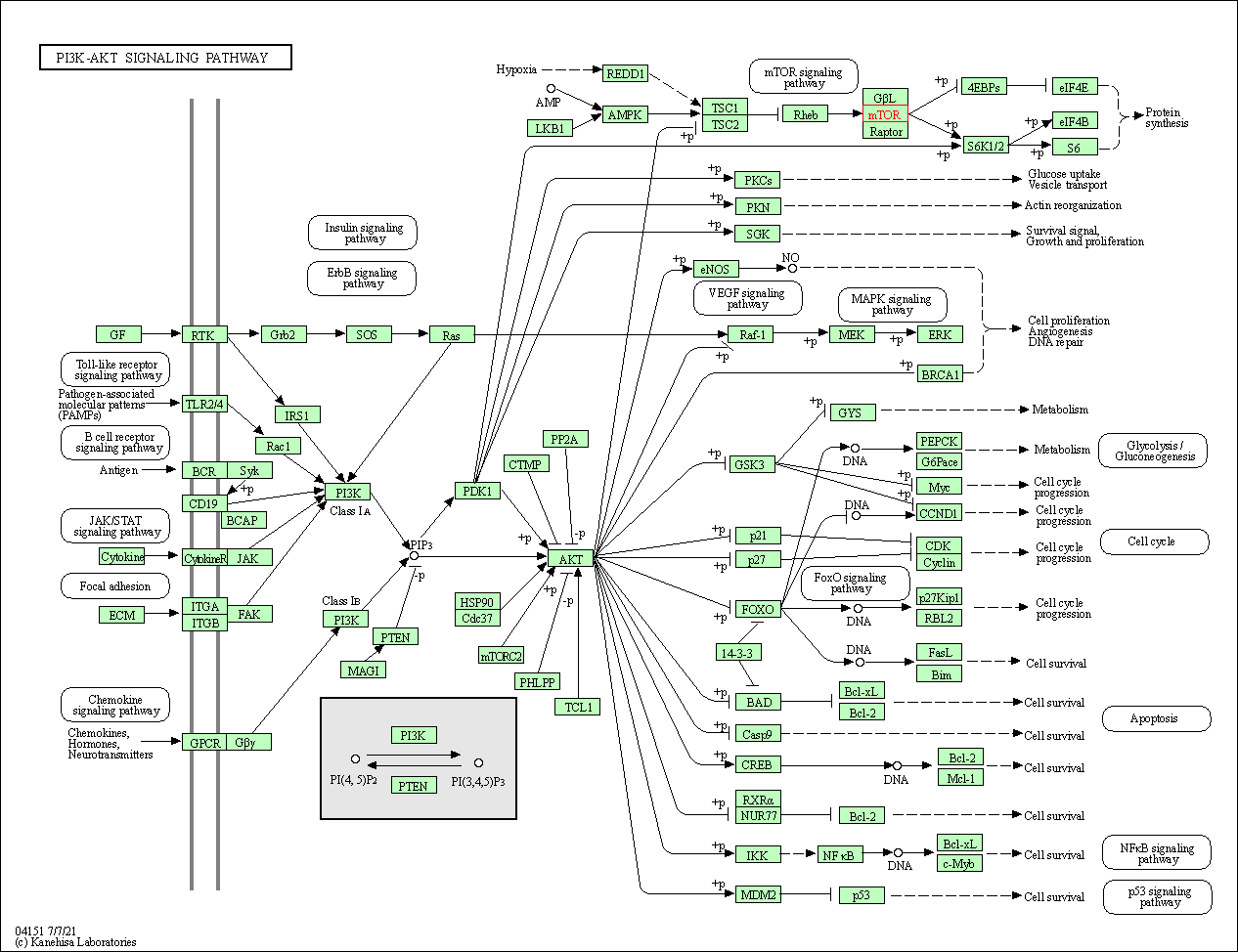
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |
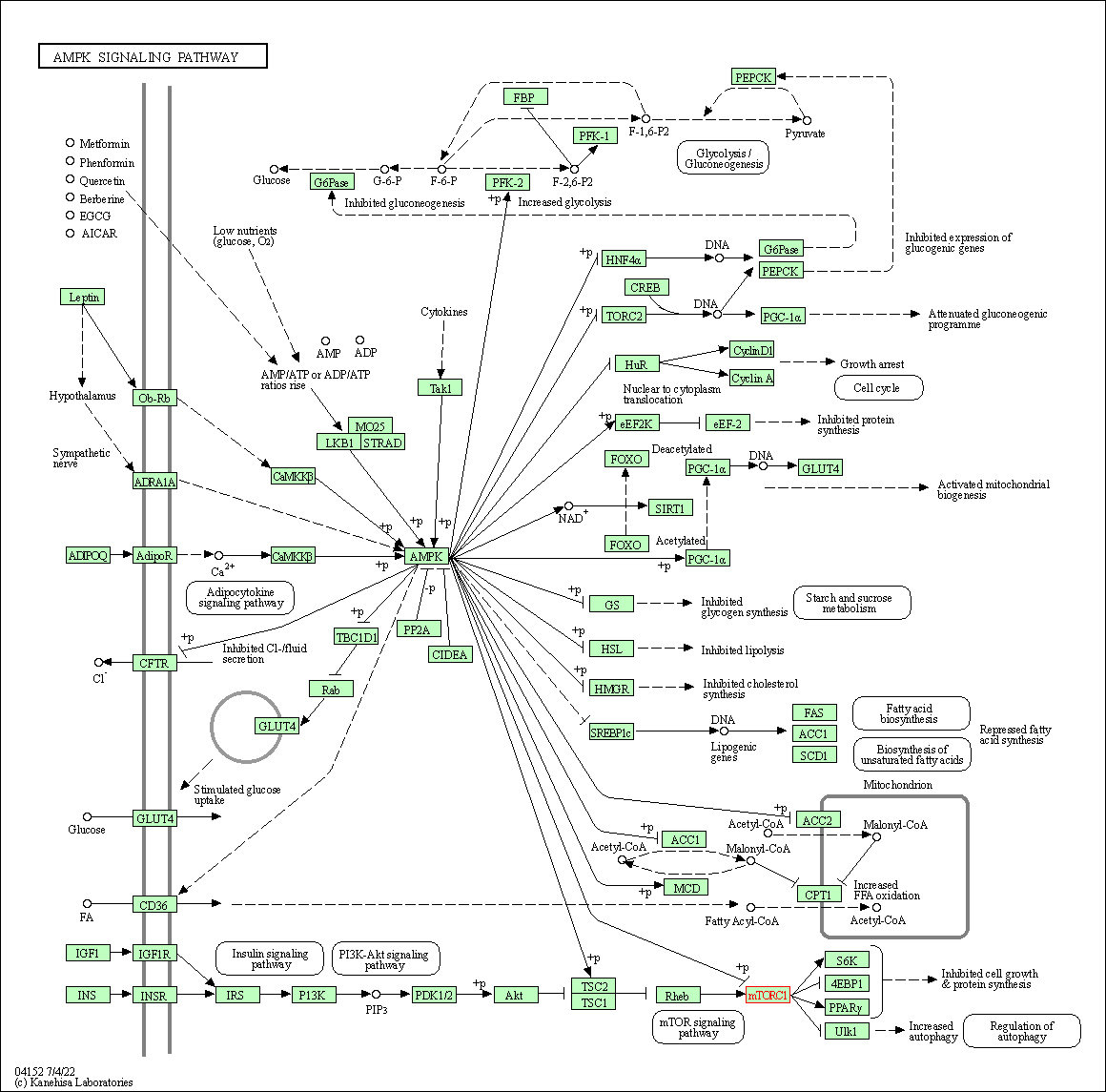
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | hsa04213 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 68 | Degree centrality | 7.31E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.09E-02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.67E-01 | Radiality | 1.46E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.22E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.47E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.19E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Advances in kinase targeting: current clinical use and clinical trials. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014 Nov;35(11):604-20. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5889). | |||||
| REF 3 | Hughes B: 2009 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Feb;9(2):89-92. | |||||
| REF 4 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Elixir. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02009956) EXCELLA Post-Approval Study. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | 2018 FDA drug approvals.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019 Feb;18(2):85-89. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6031). | |||||
| REF 8 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 9 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5892). | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7974). | |||||
| REF 11 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00589927) Triple Versus Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After ABT578-Eluting Stent. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7884). | |||||
| REF 14 | Phase II study of the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor ridaforolimus in patients with advanced bone and soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jan 1;30(1):78-84. | |||||
| REF 15 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02494570) A Phase 2 Study of ABI-009 in Patients With Advanced Malignant PEComa. | |||||
| REF 16 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7699). | |||||
| REF 17 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01793636) A Study Comparing AZD2014 vs Everolimus in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 18 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7950). | |||||
| REF 19 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026094) | |||||
| REF 20 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Roche. | |||||
| REF 21 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 22 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02549989) Study of LY3023414 for the Treatment of Recurrent. | |||||
| REF 23 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02399137) A Phase 2 Study of MM-141 Plus Nab-paclitaxel and Gemcitabine in Front-line Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 24 | Preclinical characterization of OSI-027, a potent and selective inhibitor of mTORC1 and mTORC2: distinct from rapamycin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Aug;10(8):1394-406. | |||||
| REF 25 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7936). | |||||
| REF 26 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01430585) Pre-Operative Study of PF-4691502 With Letrozole Compared To Letrozole Alone In Patients With Early Breast Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 27 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7940). | |||||
| REF 28 | First-in-Human Study of PF-05212384 (PKI-587), a Small-Molecule, Intravenous, Dual Inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Apr 15;21(8):1888-95. | |||||
| REF 29 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03740100) Single-arm Study With Bimiralisib in Patients With HNSCC Harboring NOTCH1 Loss of Function Mutations (HNSCC). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 30 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6281). | |||||
| REF 31 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026972) | |||||
| REF 32 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01936363) Trial of Pimasertib With SAR245409 or Placebo in Ovarian Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 33 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7951). | |||||
| REF 34 | Simultaneous targeting of PI3K and mTOR with NVP-BGT226 is highly effective in multiple myeloma. Anticancer Drugs. 2012 Jan;23(1):131-8. | |||||
| REF 35 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01177397) Study to Assess Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy of Oral CC-223 for Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma or Multiple Myeloma. U.S. NationalInstitutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 36 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800038828) | |||||
| REF 37 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04994002) A Phase 1b, Open-Label, Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic, Safety and Tolerability Study of CERC-006 in Adults (Aged 18-31 Years) With Complex Lymphatic Malformations. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 38 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01588678) A Open-Label, Multiple Ascending Dose Study of DS-3078a, an Oral TORC1/2 Kinase Inhibitor, in Subjects With Advanced Solid Tumors or Lymphomas. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 39 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800034336) | |||||
| REF 40 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01356173) Evaluating the Safety and Tolerability of GDC-0349 in Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors or Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma. U.S. National Institutes ofHealth. | |||||
| REF 41 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 42 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01407380) Study of PWT33597 Mesylate in Subjects With Advanced Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 43 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8382). | |||||
| REF 44 | VS-5584, a novel and highly selective PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Feb;12(2):151-61. | |||||
| REF 45 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7714). | |||||
| REF 46 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800028731) | |||||
| REF 47 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800018935) | |||||
| REF 48 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800022134) | |||||
| REF 49 | Mammalian target of rapamycin, its mode of action and clinical response in metastatic clear cell carcinoma. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2009 Jul;36(7):1076-9. | |||||
| REF 50 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2109). | |||||
| REF 51 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 52 | Knockouts model the 100 best-selling drugs--will they model the next 100 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003 Jan;2(1):38-51. | |||||
| REF 53 | Natural products to drugs: natural product-derived compounds in clinical trials. Nat Prod Rep. 2008 Jun;25(3):475-516. | |||||
| REF 54 | A novel c-Met inhibitor, MK8033, synergizes with carboplatin plus paclitaxel to inhibit ovarian cancer cell growth. Oncol Rep. 2013 May;29(5):2011-8. | |||||
| REF 55 | mTOR: The Mammalian Target of Replication. Merck. Report of Merck. January 20 2008. | |||||
| REF 56 | Dramatic suppression of colorectal cancer cell growth by the dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor AZD-2014. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 10;443(2):406-12. | |||||
| REF 57 | The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 is a potent inhibitor of ATM- and DNA-PKCs-mediated DNA damage responses. Neoplasia. 2012 Jan;14(1):34-43. | |||||
| REF 58 | GDC-0980 is a novel class I PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor with robust activity in cancer models driven by the PI3K pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Dec;10(12):2426-36. | |||||
| REF 59 | 2011 Pipeline of Intellikine. | |||||
| REF 60 | Company report (Lilly) | |||||
| REF 61 | Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Aug;8(8):627-44. | |||||
| REF 62 | PF-04691502, a potent and selective oral inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR kinases with antitumor activity.Mol Cancer Ther.2011 Nov;10(11):2189-99. | |||||
| REF 63 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Sanofi Oncology. | |||||
| REF 64 | CC-223, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of mTOR Kinase: In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Jun;14(6):1295-305. | |||||
| REF 65 | National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary (drug id 728650). | |||||
| REF 66 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of tatcongress. | |||||
| REF 67 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2023. Adis Insight | |||||
| REF 68 | A first-in-human Phase I study of DS-3078a, an oral TORC1/2 inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors: Preliminary results, Mol Cancer Ther November,2013, 12, C173. | |||||
| REF 69 | Antitumor activity and induction of TP53-dependent apoptosis toward ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma by the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor DS-7423. PLoS One. 2014 Feb 4;9(2):e87220. | |||||
| REF 70 | Discovery and Biological Profiling of Potent and Selective mTOR Inhibitor GDC-0349. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Nov 29;4(1):103-7. | |||||
| REF 71 | PIK3CA mutation H1047R is associated with response to PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibitors in early phase clinical trials | |||||
| REF 72 | Hedgehog inhibitors: a patent review (2013 - present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 May;25(5):549-65. | |||||
| REF 73 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2009). | |||||
| REF 74 | EP patent application no. 2275103, Mtor inhibitors in the treatment of endocrine tumors. | |||||
| REF 75 | Early detection of response to experimental chemotherapeutic Top216 with [18F]FLT and [18F]FDG PET in human ovary cancer xenografts in mice. PLoS One. 2010 Sep 24;5(9):e12965. | |||||
| REF 76 | Novel purine and pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of PI3 kinase-alpha: Hit to lead studies. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):636-9. | |||||
| REF 77 | Selective benzopyranone and pyrimido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein kinase: synthesis, structure-activity studies, and... J Med Chem. 2005 Jan 27;48(2):569-85. | |||||
| REF 78 | Synthesis and therapeutic evaluation of pyridyl based novel mTOR inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jun 1;19(11):2949-52. | |||||
| REF 79 | The rapamycin-binding domain of the protein kinase mammalian target of rapamycin is a destabilizing domain. J Biol Chem. 2007 May 4;282(18):13395-401. | |||||
| REF 80 | Discovery of the Highly Potent PI3K/mTOR Dual Inhibitor PF-04979064 through Structure-Based Drug Design. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012 Nov 7;4(1):91-7. | |||||
| REF 81 | Targeted polypharmacology: discovery of dual inhibitors of tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinases. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Nov;4(11):691-9. | |||||
| REF 82 | Selected novel anticancer treatments targeting cell signaling proteins. Oncologist. 2001;6(6):517-37. | |||||
| REF 83 | Discovery of 1-(4-(4-propionylpiperazin-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-9-(quinolin-3-yl)benzo[h][1,6]naphthyridin-2(1H)-one as a highly potent, selective mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. 2010 Oct 14;53(19):7146-55. | |||||
| REF 84 | Torin2 Potentiates Anticancer Effects on Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma by Inhibiting Mammalian Target of Rapamycin. Anticancer Res. 2016 Jan;36(1):95-102. | |||||
| REF 85 | Large FK506-binding proteins shape the pharmacology of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;33(7):1357-67. | |||||
| REF 86 | The 3.2-? resolution structure of human mTORC2. Sci Adv. 2020 Nov 6;6(45):eabc1251. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

