Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T91480
(Former ID: TTDS00331)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
ATP-binding cassette transporter C8 (ABCC8)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Sulfonylurea receptor 1; SUR1-type K(ATP) channel; SUR1; Kir6.2/SUR1; ATPbinding cassette subfamily C member 8; ABCC8
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ABCC8
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Acute diabete complication [ICD-11: 5A2Y] | |||||
| 2 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||||
| Function |
Putative subunit of the beta-cell ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP). Regulator of ATP-sensitive K(+) channels and insulin release.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
ABC transporter
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MPLAFCGSENHSAAYRVDQGVLNNGCFVDALNVVPHVFLLFITFPILFIGWGSQSSKVHI
HHSTWLHFPGHNLRWILTFMLLFVLVCEIAEGILSDGVTESHHLHLYMPAGMAFMAAVTS VVYYHNIETSNFPKLLIALLVYWTLAFITKTIKFVKFLDHAIGFSQLRFCLTGLLVILYG MLLLVEVNVIRVRRYIFFKTPREVKPPEDLQDLGVRFLQPFVNLLSKGTYWWMNAFIKTA HKKPIDLRAIGKLPIAMRALTNYQRLCEAFDAQVRKDIQGTQGARAIWQALSHAFGRRLV LSSTFRILADLLGFAGPLCIFGIVDHLGKENDVFQPKTQFLGVYFVSSQEFLANAYVLAV LLFLALLLQRTFLQASYYVAIETGINLRGAIQTKIYNKIMHLSTSNLSMGEMTAGQICNL VAIDTNQLMWFFFLCPNLWAMPVQIIVGVILLYYILGVSALIGAAVIILLAPVQYFVATK LSQAQRSTLEYSNERLKQTNEMLRGIKLLKLYAWENIFRTRVETTRRKEMTSLRAFAIYT SISIFMNTAIPIAAVLITFVGHVSFFKEADFSPSVAFASLSLFHILVTPLFLLSSVVRST VKALVSVQKLSEFLSSAEIREEQCAPHEPTPQGPASKYQAVPLRVVNRKRPAREDCRGLT GPLQSLVPSADGDADNCCVQIMGGYFTWTPDGIPTLSNITIRIPRGQLTMIVGQVGCGKS SLLLAALGEMQKVSGAVFWSSLPDSEIGEDPSPERETATDLDIRKRGPVAYASQKPWLLN ATVEENIIFESPFNKQRYKMVIEACSLQPDIDILPHGDQTQIGERGINLSGGQRQRISVA RALYQHANVVFLDDPFSALDIHLSDHLMQAGILELLRDDKRTVVLVTHKLQYLPHADWII AMKDGTIQREGTLKDFQRSECQLFEHWKTLMNRQDQELEKETVTERKATEPPQGLSRAMS SRDGLLQDEEEEEEEAAESEEDDNLSSMLHQRAEIPWRACAKYLSSAGILLLSLLVFSQL LKHMVLVAIDYWLAKWTDSALTLTPAARNCSLSQECTLDQTVYAMVFTVLCSLGIVLCLV TSVTVEWTGLKVAKRLHRSLLNRIILAPMRFFETTPLGSILNRFSSDCNTIDQHIPSTLE CLSRSTLLCVSALAVISYVTPVFLVALLPLAIVCYFIQKYFRVASRDLQQLDDTTQLPLL SHFAETVEGLTTIRAFRYEARFQQKLLEYTDSNNIASLFLTAANRWLEVRMEYIGACVVL IAAVTSISNSLHRELSAGLVGLGLTYALMVSNYLNWMVRNLADMELQLGAVKRIHGLLKT EAESYEGLLAPSLIPKNWPDQGKIQIQNLSVRYDSSLKPVLKHVNALIAPGQKIGICGRT GSGKSSFSLAFFRMVDTFEGHIIIDGIDIAKLPLHTLRSRLSIILQDPVLFSGTIRFNLD PERKCSDSTLWEALEIAQLKLVVKALPGGLDAIITEGGENFSQGQRQLFCLARAFVRKTS IFIMDEATASIDMATENILQKVVMTAFADRTVVTIAHRVHTILSADLVIVLKRGAILEFD KPEKLLSRKDSVFASFVRADK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A00555 ; BADD_A06316 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 6 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Acetohexamide | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Glibenclamide | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [4], [5] | |
| 3 | Gliclazide | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [6] | |
| 4 | Glimepiride | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [7], [8] | |
| 5 | Repaglinide | Drug Info | Approved | Diabetic complication | [9], [10] | |
| 6 | Tolbutamide | Drug Info | Approved | Non-insulin dependent diabetes | [11] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NN-414 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-1 diabetes | [12] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 4 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Acetohexamide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 2 | Glibenclamide | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 3 | NN-414 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 4 | NS-11757 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| Blocker | [+] 4 Blocker drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Gliclazide | Drug Info | [15], [16] | |||
| 2 | Glimepiride | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | Repaglinide | Drug Info | [16], [17], [18] | |||
| 4 | Tolbutamide | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | HBR-985 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Cryo-EM structure of human KATP bound to ATP and ADP in quatrefoil form | PDB:6C3O | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.90 Å | Mutation | No | [23] |
| PDB Sequence |
PLAFCGSENH
11 SAAYRVDQGV21 LNNGCFVDAL31 NVVPHVFLLF41 ITFPILFIGW51 GFPGHNLRWI 76 LTFMLLFVLV86 CEIAEGILSD96 GVTESHHLHL106 YMPAGMAFMA116 AVTSVVYYHN 126 IETSNFPKLL136 IALLVYWTLA146 FITKTIKFVK156 FLDHAIGFSQ166 LRFCLTGLLV 176 ILYGMLLLVE186 VNVIRVNYQR265 LCEAFDAQVR275 KDAIWQALSH293 AFGRRLVLSS 303 TFRILADLLG313 FAGPLCIFGI323 VDHLGKANAY356 VLAVLLFLAL366 LLQRTFLQAS 376 YYVAIETGIN386 LRGAIQTKIY396 NKIMHLSTSN406 LSMGEMTAGQ416 ICNLVAIDTN 426 QLMWFFFLCP436 NLWAMPVQII446 VGVILLYYIL456 GVSALIGAAV466 IILLAPVQYF 476 VATKLSQAQR486 STLEYSNERL496 KQTNEMLRGI506 KLLKLYAWEN516 IFRTRVETTR 526 RKEMTSLRAF536 AIYTSISIFM546 NTAIPIAAVL556 ITFVGHVPSV575 AFASLSLFHI 585 LVTPLFLLSS595 VVRSTVKALV605 SVQKLSEFLS615 SAEIRCCVQI681 MGGYFTWTPD 691 GIPTLSNITI701 RIPRGQLTMI711 VGQVGCGKSS721 LLLAALGEMQ731 KVSGAVFWSR 766 GPVAYASQKP776 WLLNATVEEN786 IIFESPFNKQ796 RYKMVIEACS806 LQPDIDILPH 816 GDQTQIGERG826 INLSGGQRQR836 ISVARALYQH846 ANVVFLDDPF856 SALDIHLSDH 866 LMQAGILELL876 RDDKRTVVLV886 THKLQYLPHA896 DWIIAMKDGT906 IQREGTLKDF 916 QRSECQLFEH926 WKTLEIPWRA999 CAKYLSSAGI1009 LLLSLLVFSQ1019 LLKHMVLVAI 1029 DYWLAKWTDT1061 VYAMVFTVLC1071 SLGIVLCLVT1081 SVTVEWTGLK1091 VAKRLHRSLL 1101 NRIILAPMRF1111 FETTPLGSIL1121 NRFSSDCNTI1131 DQHIPSTLEC1141 LSRSTLLCVS 1151 ALAVISYVTP1161 VFLVALLPLA1171 IVCYFIQKYF1181 RVASRDLQQL1191 DDTTQLPLLS 1201 HFAETVEGLT1211 TIRAFRYEAR1221 FQQKLLEYTD1231 SNNIASLFLT1241 AANRWLEVRM 1251 EYIGACVVLI1261 AAVTSISNSL1271 HRELSAGLVG1281 LGLTYALMVS1291 NYLNWMVRNL 1301 ADMELQLGAV1311 KRIHGLLKTE1321 AESYEGLLAP1331 SLIPKNWPDQ1341 GKIQIQNLSV 1351 RYDSSLKPVL1361 KHVNALIAPG1371 QKIGICGRTG1381 SGKSSFSLAF1391 FRMVDTFEGH 1401 IIIDGIDIAK1411 LPLHTLRSRL1421 SIILQDPVLF1431 SGTIRFNLDP1441 ERKCSDSTLW 1451 EALEIAQLKL1461 VVKALPGGLD1471 AIITEGGENF1481 SQGQRQLFCL1491 ARAFVRKTSI 1501 FIMDEATASI1511 DMATENILQK1521 VVMTAFADRT1531 VVTIAHRVHT1541 ILSADLVIVL 1551 KRGAILEFDK1561 PEKLLSRKDS1571 VFASFVRADK1581
|
|||||
|
|
SER408
3.400
MET409
3.493
TRP688
3.108
THR695
4.154
GLN714
3.722
VAL715
3.215
GLY716
2.343
CYS717
3.071
GLY718
3.027
LYS719
3.136
SER720
2.482
SER721
2.486
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: adenosine diphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Cryo-EM structure of human KATP bound to ATP and ADP in quatrefoil form | PDB:6C3O | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.90 Å | Mutation | No | [23] |
| PDB Sequence |
PLAFCGSENH
11 SAAYRVDQGV21 LNNGCFVDAL31 NVVPHVFLLF41 ITFPILFIGW51 GFPGHNLRWI 76 LTFMLLFVLV86 CEIAEGILSD96 GVTESHHLHL106 YMPAGMAFMA116 AVTSVVYYHN 126 IETSNFPKLL136 IALLVYWTLA146 FITKTIKFVK156 FLDHAIGFSQ166 LRFCLTGLLV 176 ILYGMLLLVE186 VNVIRVNYQR265 LCEAFDAQVR275 KDAIWQALSH293 AFGRRLVLSS 303 TFRILADLLG313 FAGPLCIFGI323 VDHLGKANAY356 VLAVLLFLAL366 LLQRTFLQAS 376 YYVAIETGIN386 LRGAIQTKIY396 NKIMHLSTSN406 LSMGEMTAGQ416 ICNLVAIDTN 426 QLMWFFFLCP436 NLWAMPVQII446 VGVILLYYIL456 GVSALIGAAV466 IILLAPVQYF 476 VATKLSQAQR486 STLEYSNERL496 KQTNEMLRGI506 KLLKLYAWEN516 IFRTRVETTR 526 RKEMTSLRAF536 AIYTSISIFM546 NTAIPIAAVL556 ITFVGHVPSV575 AFASLSLFHI 585 LVTPLFLLSS595 VVRSTVKALV605 SVQKLSEFLS615 SAEIRCCVQI681 MGGYFTWTPD 691 GIPTLSNITI701 RIPRGQLTMI711 VGQVGCGKSS721 LLLAALGEMQ731 KVSGAVFWSR 766 GPVAYASQKP776 WLLNATVEEN786 IIFESPFNKQ796 RYKMVIEACS806 LQPDIDILPH 816 GDQTQIGERG826 INLSGGQRQR836 ISVARALYQH846 ANVVFLDDPF856 SALDIHLSDH 866 LMQAGILELL876 RDDKRTVVLV886 THKLQYLPHA896 DWIIAMKDGT906 IQREGTLKDF 916 QRSECQLFEH926 WKTLEIPWRA999 CAKYLSSAGI1009 LLLSLLVFSQ1019 LLKHMVLVAI 1029 DYWLAKWTDT1061 VYAMVFTVLC1071 SLGIVLCLVT1081 SVTVEWTGLK1091 VAKRLHRSLL 1101 NRIILAPMRF1111 FETTPLGSIL1121 NRFSSDCNTI1131 DQHIPSTLEC1141 LSRSTLLCVS 1151 ALAVISYVTP1161 VFLVALLPLA1171 IVCYFIQKYF1181 RVASRDLQQL1191 DDTTQLPLLS 1201 HFAETVEGLT1211 TIRAFRYEAR1221 FQQKLLEYTD1231 SNNIASLFLT1241 AANRWLEVRM 1251 EYIGACVVLI1261 AAVTSISNSL1271 HRELSAGLVG1281 LGLTYALMVS1291 NYLNWMVRNL 1301 ADMELQLGAV1311 KRIHGLLKTE1321 AESYEGLLAP1331 SLIPKNWPDQ1341 GKIQIQNLSV 1351 RYDSSLKPVL1361 KHVNALIAPG1371 QKIGICGRTG1381 SGKSSFSLAF1391 FRMVDTFEGH 1401 IIIDGIDIAK1411 LPLHTLRSRL1421 SIILQDPVLF1431 SGTIRFNLDP1441 ERKCSDSTLW 1451 EALEIAQLKL1461 VVKALPGGLD1471 AIITEGGENF1481 SQGQRQLFCL1491 ARAFVRKTSI 1501 FIMDEATASI1511 DMATENILQK1521 VVMTAFADRT1531 VVTIAHRVHT1541 ILSADLVIVL 1551 KRGAILEFDK1561 PEKLLSRKDS1571 VFASFVRADK1581
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC transporters | hsa02010 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Membrane transport | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |
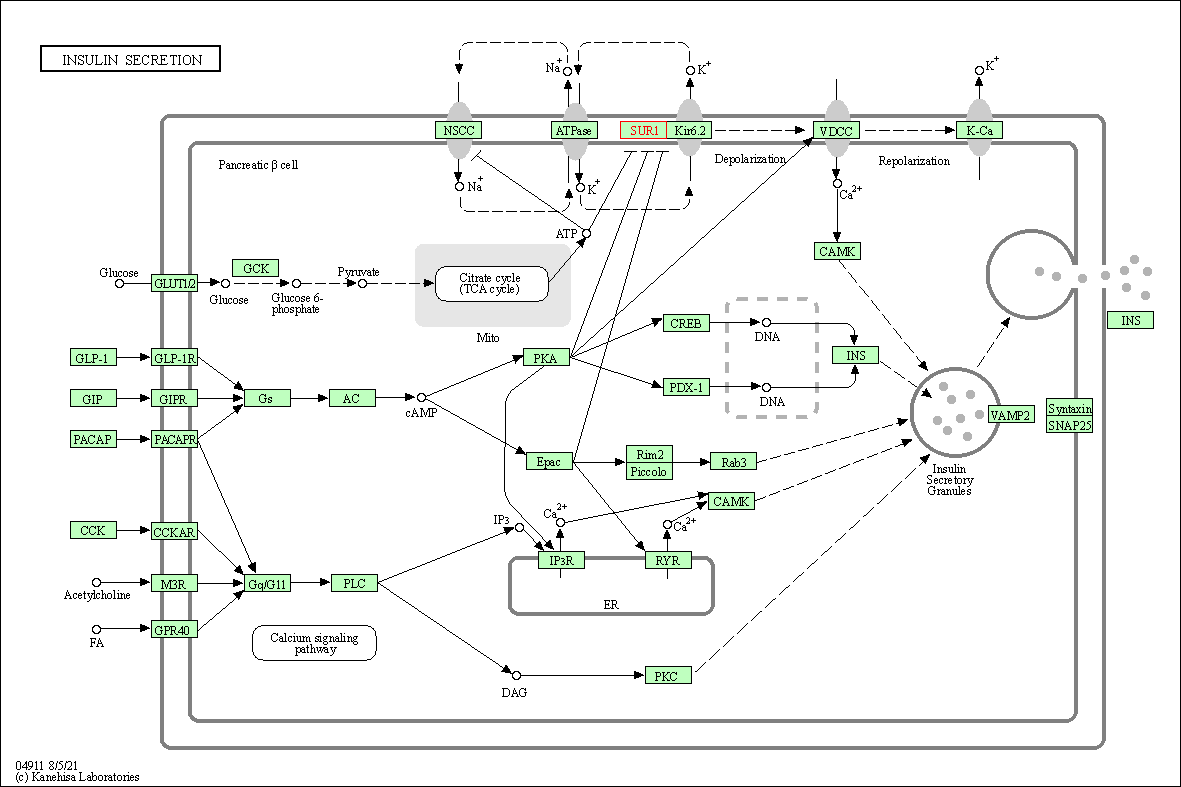
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 2.99E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.78E-01 | Radiality | 1.29E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 9.00E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.78E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ABC transporters | |||||
| 2 | Insulin secretion | |||||
| 3 | Type II diabetes mellitus | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 2 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Muscle/Heart Contraction | |||||
| 2 | Pancreas Function | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | FOXA2 and FOXA3 transcription factor networks | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ABC-family proteins mediated transport | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of insulin secretion | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Potassium Channels | |||||
| 2 | Integration of energy metabolism | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Mechanism of disopyramide-induced hypoglycaemia in a patient with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2009 Jan;26(1):76-8. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6793). | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 071893. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2414). | |||||
| REF 5 | Emerging drug candidates of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) inhibitor class for the treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Curr Drug Targets. 2009 Jan;10(1):71-87. | |||||
| REF 6 | Cefradine - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6820). | |||||
| REF 8 | Clinical utilization of combined rosiglitazone and glimepiride in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Orv Hetil. 2007 Dec 9;148(49):2331-5. | |||||
| REF 9 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6841). | |||||
| REF 10 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 077571. | |||||
| REF 11 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00400283) A Study Looking Into the Effect of NNC 55-0414 in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | Diabetes and insulin secretion: the ATP-sensitive K+ channel (K ATP) connection.Diabetes.2005 Nov;54(11):3065-72. | |||||
| REF 14 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 15 | Structural basis for the interference between nicorandil and sulfonylurea action. Diabetes. 2001 Oct;50(10):2253-9. | |||||
| REF 16 | Pharmacological modulation of K(ATP) channels. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Apr;30(2):333-9. | |||||
| REF 17 | Metformin/Repaglinide (PrandiMet) for type 2 diabetes. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2009 Jun 1;51(1313):41-3. | |||||
| REF 18 | Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repaglinide. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(7):471-83. | |||||
| REF 19 | Expression of an activating mutation in the gene encoding the KATP channel subunit Kir6.2 in mouse pancreatic beta cells recapitulates neonatal diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2009 Jan;119(1):80-90. | |||||
| REF 20 | Attenuation of hyperinsulinemia by NN414, a SUR1/Kir6.2 selective K-adenosine triphosphate channel opener, improves glucose tolerance and lipid profile in obese Zucker rats.Metabolism.2004 Apr;53(4):441-7. | |||||
| REF 21 | Cardioselective K(ATP) channel blockers derived from a new series of m-anisamidoethylbenzenesulfonylthioureas. J Med Chem. 2001 Mar 29;44(7):1085-98. | |||||
| REF 22 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2944). | |||||
| REF 23 | Molecular structure of human KATP in complex with ATP and ADP. Elife. 2017 Dec 29;6:e32481. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

