Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T86271
(Former ID: TTDI03308)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Calcium-activated potassium channel KCa2.2 (KCNN2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 2; SKCa2; SKCa 2; SK2; KCa2.2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KCNN2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Myelopathy [ICD-11: 8B42] | |||||
| Function |
Forms a voltage-independent potassium channel activated by intracellular calcium. Activation is followed by membrane hyperpolarization. Thought to regulate neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic afterhyperpolarization. The channel is blocked by apamin.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Voltage-gated ion channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MSSCRYNGGVMRPLSNLSASRRNLHEMDSEAQPLQPPASVGGGGGASSPSAAAAAAAAVS
SSAPEIVVSKPEHNNSNNLALYGTGGGGSTGGGGGGGGSGHGSSSGTKSSKKKNQNIGYK LGHRRALFEKRKRLSDYALIFGMFGIVVMVIETELSWGAYDKASLYSLALKCLISLSTII LLGLIIVYHAREIQLFMVDNGADDWRIAMTYERIFFICLEILVCAIHPIPGNYTFTWTAR LAFSYAPSTTTADVDIILSIPMFLRLYLIARVMLLHSKLFTDASSRSIGALNKINFNTRF VMKTLMTICPGTVLLVFSISLWIIAAWTVRACERYHDQQDVTSNFLGAMWLISITFLSIG YGDMVPNTYCGKGVCLLTGIMGAGCTALVVAVVARKLELTKAEKHVHNFMMDTQLTKRVK NAAANVLRETWLIYKNTKLVKKIDHAKVRKHQRKFLQAIHQLRSVKMEQRKLNDQANTLV DLAKTQNIMYDMISDLNERSEDFEKRIVTLETKLETLIGSIHALPGLISQTIRQQQRDFI EAQMESYDKHVTYNAERSRSSSRRRRSSSTAPPTSSESS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | dequalinium | Drug Info | Clinical trial | Myelopathy | [2] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | zoxazolamine | Drug Info | Terminated | Multiple myeloma | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Blocker (channel blocker) | [+] 5 Blocker (channel blocker) drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | dequalinium | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | apamin | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | UCL1684 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 4 | UCL1848 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 5 | [14C]TEA | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Activator | [+] 4 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | zoxazolamine | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | CyPPA | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | DC-EBIO | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 4 | EBIO | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Riluzole | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | A positive allosteric modulator binding pocket in SK2 ion channels is shared by Riluzole and CyPPA | PDB:5V02 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.78 Å | Mutation | No | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
GRKLELTKAD
413 TQLTKRVKNA423 AANVLRETWL433 IYKNTKLVKK443 IDHAKVRKHQ453 RKFLQAIHQL 463 RSVKMEQRKL473 NDQANTLVDL483 AKTQLEH
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: (3Z)-6-bromo-3-(hydroxyimino)-5-methyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structural insights into the potency of SK/IK channel positive modulators | PDB:5WBX | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | Yes | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
GRKLELTKAE
404 KHVHAFMMDT414 QLTKRVKNAA424 ANVLRETWLI434 YKNTKLVKKI444 DHAKVRKHQR 454 KFLQAIHQLR464 SVKMEQRKLN474 DQANTLVDLA484 KTQLE
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
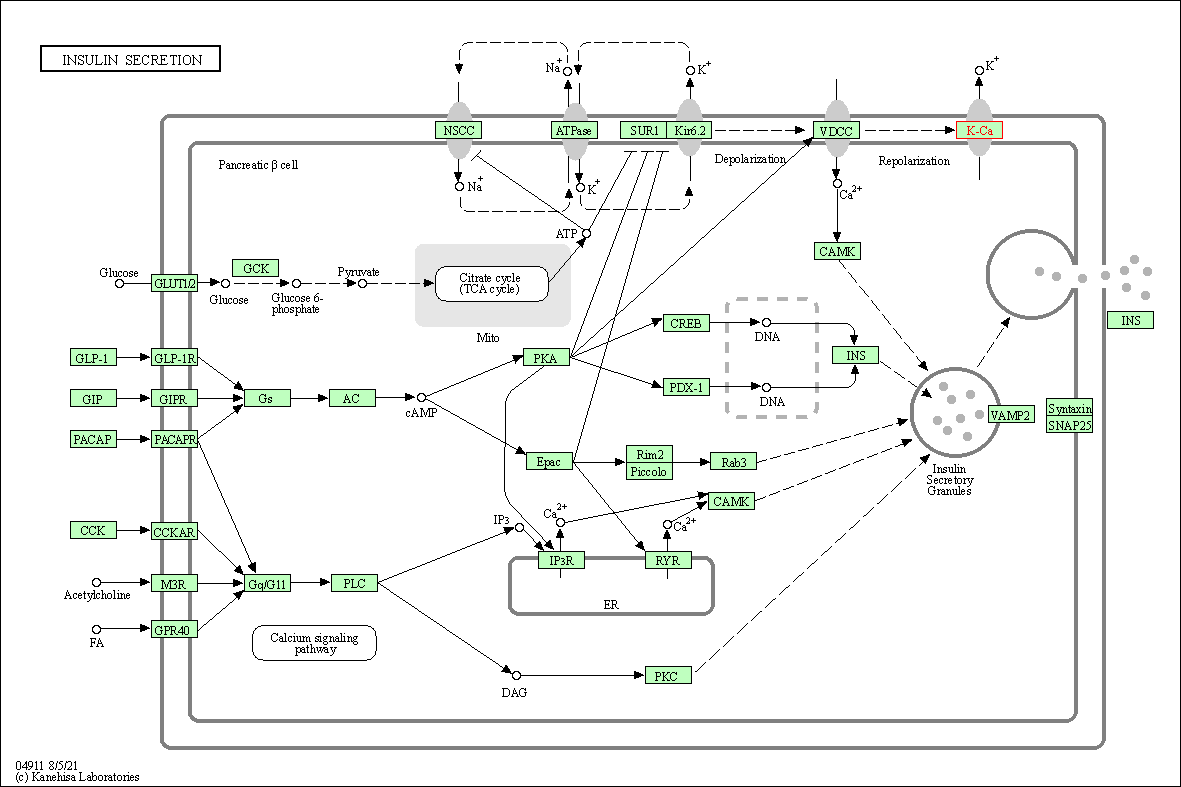
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
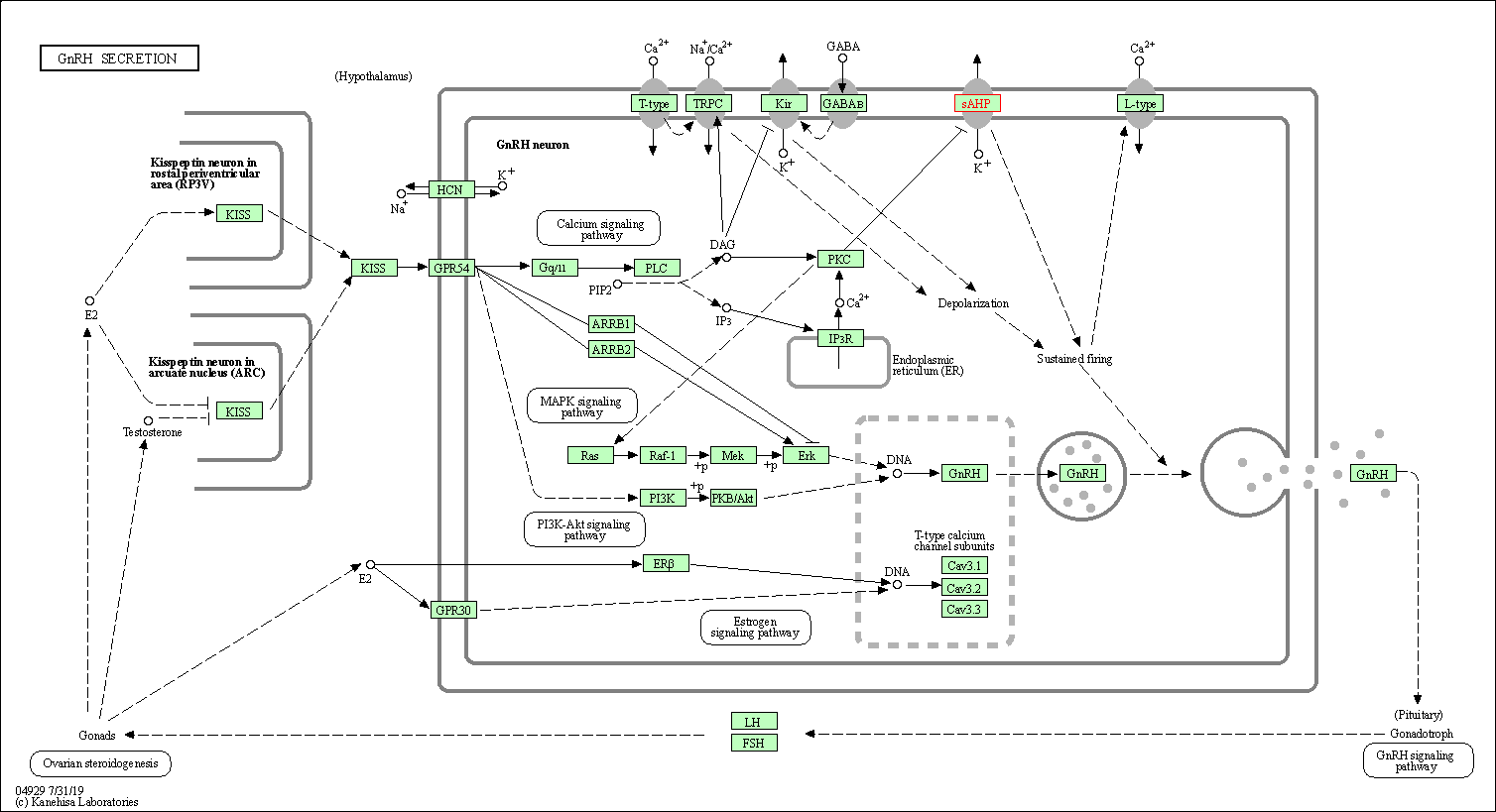
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
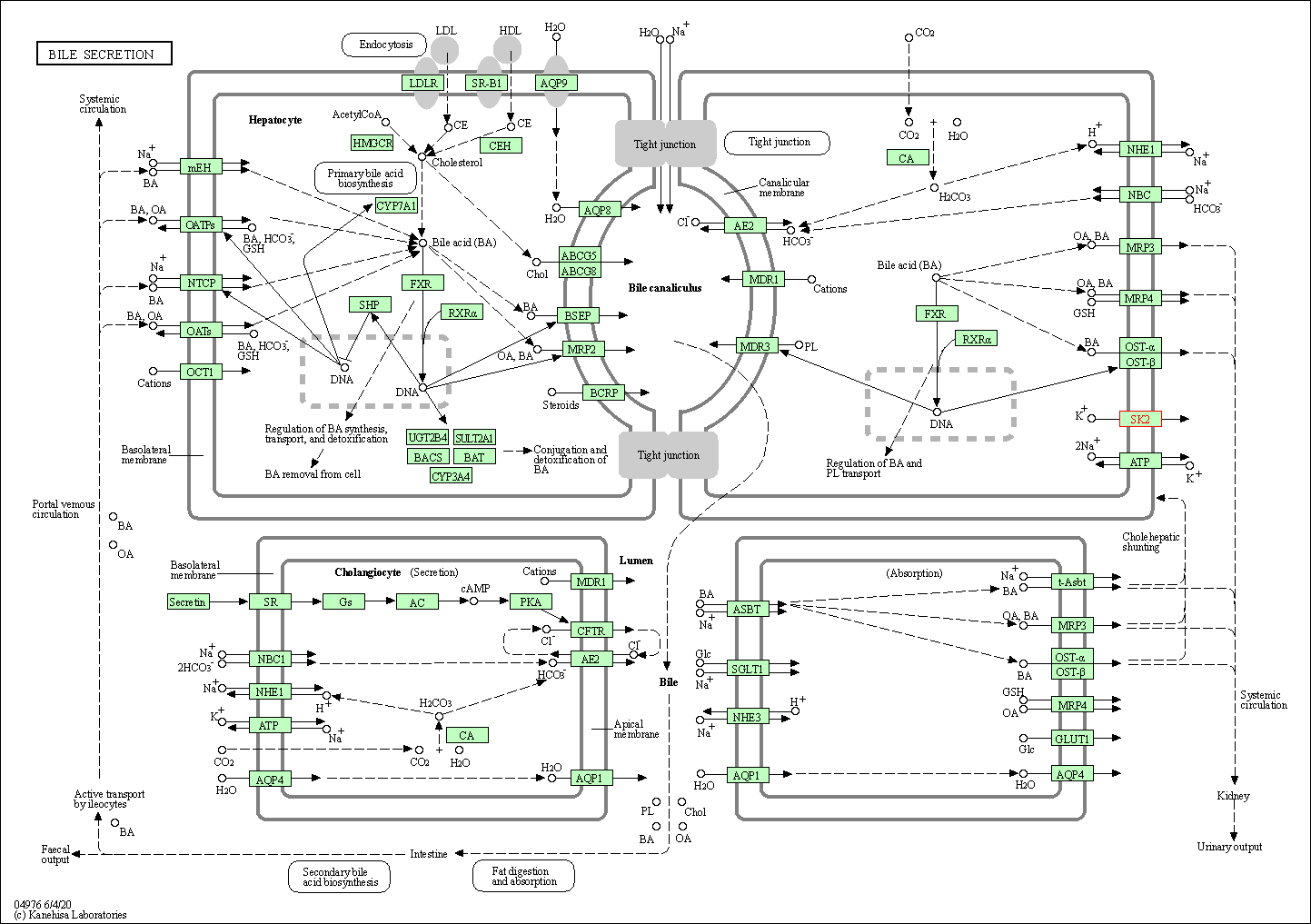
| Bile secretion | hsa04976 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Block of rat brain recombinant SK channels by tricyclic antidepressants and related compounds. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jul 28;401(1):1-7. | |||||
| REF 2 | Pharmacological characterisation of the human small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel hSK3 reveals sensitivity to tricyclic antidepressants and antipsychotic phenothiazines. Neuropharmacology. 2001 May;40(6):772-83. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2327). | |||||
| REF 4 | Modulation of recombinant small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels by the muscle relaxant chlorzoxazone and structurally related compounds. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Mar;296(3):683-9. | |||||
| REF 5 | SK2 encodes the apamin-sensitive Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels in the human leukemic T cell line, Jurkat. FEBS Lett. 2000 Mar 10;469(2-3):196-202. | |||||
| REF 6 | Selective positive modulation of the SK3 and SK2 subtypes of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;151(5):655-65. | |||||
| REF 7 | Specific enhancement of SK channel activity selectively potentiates the afterhyperpolarizing current I(AHP) and modulates the firing properties of ... J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 16;280(50):41404-11. | |||||
| REF 8 | Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels: from structure to function. Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Jul;91(3):242-55. | |||||
| REF 9 | Pharmacological characterization of small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels stably expressed in HEK 293 cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(5):991-9. | |||||
| REF 10 | Calcium-activated potassium channels sustain calcium signaling in T lymphocytes. Selective blockers and manipulated channel expression levels. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 13;276(15):12249-56. | |||||
| REF 11 | An Intracellular Allosteric Modulator Binding Pocket in SK2 Ion Channels Is Shared by Multiple Chemotypes. Structure. 2018 Apr 3;26(4):533-544.e3. | |||||
| REF 12 | Structural insights into the potency of SK channel positive modulators. Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 7;7(1):17178. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

