Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T67619
(Former ID: TTDI00350)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
RAC-PK-alpha; RAC; Proto-oncogene c-Akt; Protein kinase B alpha; PKB alpha
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
AKT1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C6Y] | |||||
| Function |
AKT1 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development. Phosphorylates STK4/MST1 at 'Thr-120' and 'Thr-387' leading to inhibition of its: kinase activity, nuclear translocation, autophosphorylation and ability to phosphorylate FOXO3. Phosphorylates STK3/MST2 at 'Thr-117' and 'Thr-384' leading to inhibition of its: cleavage, kinase activity, autophosphorylation at Thr-180, binding to RASSF1 and nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates SRPK2 and enhances its kinase activity towards SRSF2 and ACIN1 and promotes its nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-259' and negatively regulates its activity. Phosphorylation of BAD stimulates its pro-apoptotic activity. Phosphorylates KAT6A at 'Thr-369' and this phosphorylation inhibits the interaction of KAT6A with PML and negatively regulates its acetylation activity towards p53/TP53.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSDVAIVKEGWLHKRGEYIKTWRPRYFLLKNDGTFIGYKERPQDVDQREAPLNNFSVAQC
QLMKTERPRPNTFIIRCLQWTTVIERTFHVETPEEREEWTTAIQTVADGLKKQEEEEMDF RSGSPSDNSGAEEMEVSLAKPKHRVTMNEFEYLKLLGKGTFGKVILVKEKATGRYYAMKI LKKEVIVAKDEVAHTLTENRVLQNSRHPFLTALKYSFQTHDRLCFVMEYANGGELFFHLS RERVFSEDRARFYGAEIVSALDYLHSEKNVVYRDLKLENLMLDKDGHIKITDFGLCKEGI KDGATMKTFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGRAVDWWGLGVVMYEMMCGRLPFYNQDHEKLFEL ILMEEIRFPRTLGPEAKSLLSGLLKKDPKQRLGGGSEDAKEIMQHRFFAGIVWQHVYEKK LSPPFKPQVTSETDTRYFDEEFTAQMITITPPDQDDSMECVDSERRPHFPQFSYSASGTA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A03237 ; BADD_A05675 ; BADD_A06952 ; BADD_A08298 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T88TDZ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Capivasertib | Drug Info | Approved | Breast cancer | [1] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 12 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Enzastaurin | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Non-hodgkin lymphoma | [2], [3], [4] | |
| 2 | GDC-0068 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Breast cancer | [5] | |
| 3 | ARQ 092 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Proteus syndrome | [6] | |
| 4 | CI-1033 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Lymphoma | [7], [8] | |
| 5 | CMX-2043 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Myocardial reperfusion injury | [9] | |
| 6 | GSK2110183 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | leukaemia | [10] | |
| 7 | PTX-200 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Parkinson disease | [11] | |
| 8 | RX-0201 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [12] | |
| 9 | Trametinib + 2141795 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [13] | |
| 10 | Triciribine prodrug | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [14] | |
| 11 | ARQ 751 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [5] | |
| 12 | M2698 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [15] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Squalestatin 1 | Drug Info | Terminated | Arteriosclerosis | [16], [17] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 36 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Capivasertib | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Enzastaurin | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | GDC-0068 | Drug Info | [5], [18] | |||
| 4 | ARQ 092 | Drug Info | [5], [19] | |||
| 5 | CI-1033 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 6 | PTX-200 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 7 | RX-0201 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 8 | Triciribine prodrug | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 9 | ARQ 751 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 10 | BMS-754807 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 11 | M2698 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 12 | PMID28460551-Compound-6 | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 13 | Squalestatin 1 | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 14 | (Z)-3-((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)indolin-2-one | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 15 | 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 16 | 4,5,6-trihydroxy-3-methylphthalide | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 17 | 4-[(3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)diazenyl]phenol | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 18 | A-443654 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 19 | A-674563 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 20 | Akt inhibitor VIII | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 21 | ALM-301 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 22 | Bisindolylmaleimide-I | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 23 | BMS-536924 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 24 | BX-517 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 25 | CI-1040 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 26 | Inositol 1,3,4,5-Tetrakisphosphate | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 27 | KN-62 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 28 | Lactoquinomycin | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 29 | LD-101 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 30 | MYRIOCIN | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 31 | PMID20005102C1 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 32 | RO-316233 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 33 | Ro31-8220 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 34 | SB-747651A | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 35 | STAUROSPORINONE | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 36 | VLI-27 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CMX-2043 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 2 | GSK2110183 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 3 | Trametinib + 2141795 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: GDC-0068 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Akt1 with GDC0068 | PDB:4EKL | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | Yes | [40] |
| PDB Sequence |
RVTMNEFEYL
153 KLLGKGTFGK163 VILVKEKATG173 RYYAMKILKK183 EVIVAKDEVA193 HTLTENRVLQ 203 NSRHPFLTAL213 KYSFQTHDRL223 CFVMEYANGG233 ELFFHLSRER243 VFSEDRARFY 253 GAEIVSALDY263 LHSEKNVVYR273 DLKLENLMLD283 KDGHIKITDF293 GLCKEGIKDG 303 ATMKFCGTPE314 YLAPEVLEDN324 DYGRAVDWWG334 LGVVMYEMMC344 GRLPFYNQDH 354 EKLFELILME364 EIRFPRTLGP374 EAKSLLSGLL384 KKDPKQRLGG394 GSEDAKEIMQ 404 HRFFAGIVWQ414 HVYEKKLSPP424 FKPQVTSETD434 TRYFDEEFTA444 QMITITPSME 459 CVDSERRPHF469 PQFDYSASS
|
|||||
|
|
LEU156
3.661
GLY157
3.365
LYS158
3.338
GLY159
3.098
GLY162
3.619
LYS163
3.738
VAL164
3.625
ALA177
3.458
LYS179
3.800
LEU181
4.170
THR211
3.818
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: AZD5363 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | PKB alpha in complex with AZD5363 | PDB:4GV1 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.49 Å | Mutation | No | [41] |
| PDB Sequence |
SRVTMNEFEY
152 LKLLGKGTFG162 KVILVKEKAT172 GRYYAMKILK182 KEVIVAKDEV192 AHTLTENRVL 202 QNSRHPFLTA212 LKYSFQTHDR222 LCFVMEYANG232 GELFFHLSRE242 RVFSEDRARF 252 YGAEIVSALD262 YLHSEKNVVY272 RDLKLENLML282 DKDGHIKITD292 FGLCKEGIKD 302 GATMKFCGTP313 EYLAPEVLED323 NDYGRAVDWW333 GLGVVMYEMM343 CGRLPFYNQD 353 HEKLFELILM363 EEIRFPRTLG373 PEAKSLLSGL383 LKKDPKQRLG393 GGSEDAKEIM 403 QHRFFAGIVW413 QHVYEKKLSP423 PFKPQVTSET433 DTRYFDEEFT443 AQMITITPSM 458 ECVDSERRPH468 FPQFDYSAS
|
|||||
|
|
LEU156
3.868
GLY157
3.658
LYS158
3.689
GLY159
3.642
PHE161
4.723
GLY162
3.385
LYS163
3.493
VAL164
3.563
ALA177
3.373
LYS179
3.523
ILE180
4.883
LEU181
3.692
THR211
3.873
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|



| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | hsa04213 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
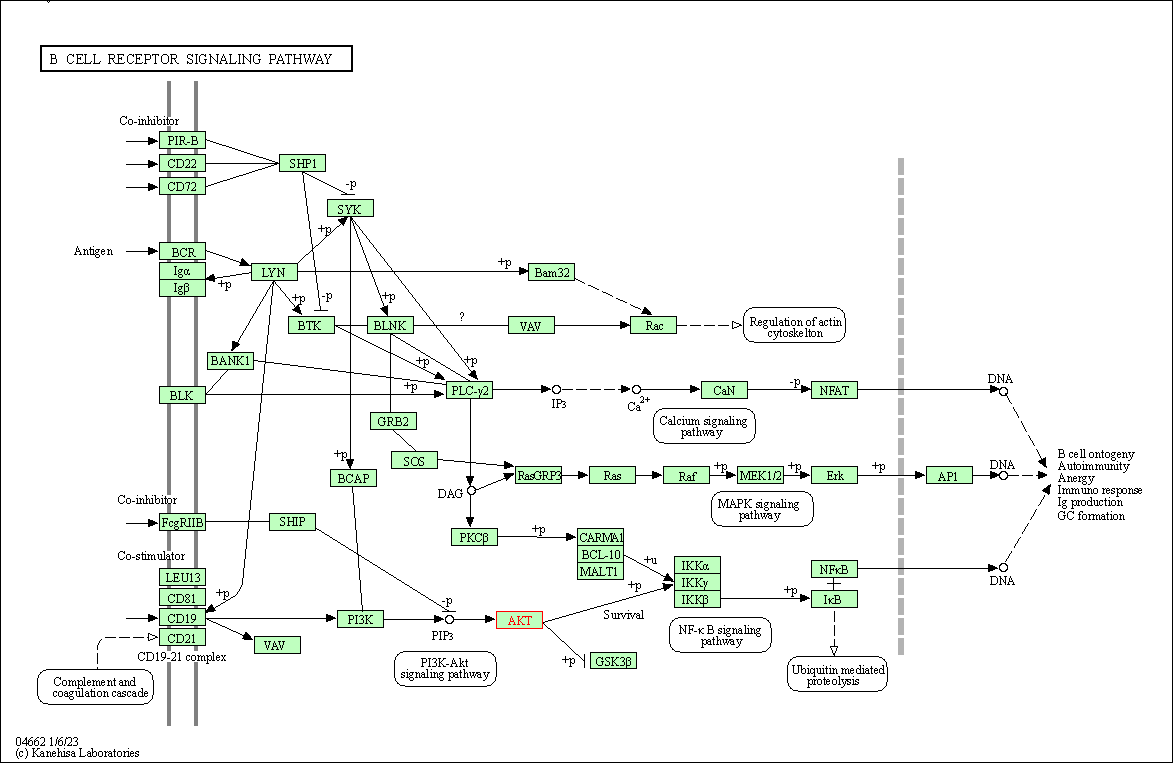
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
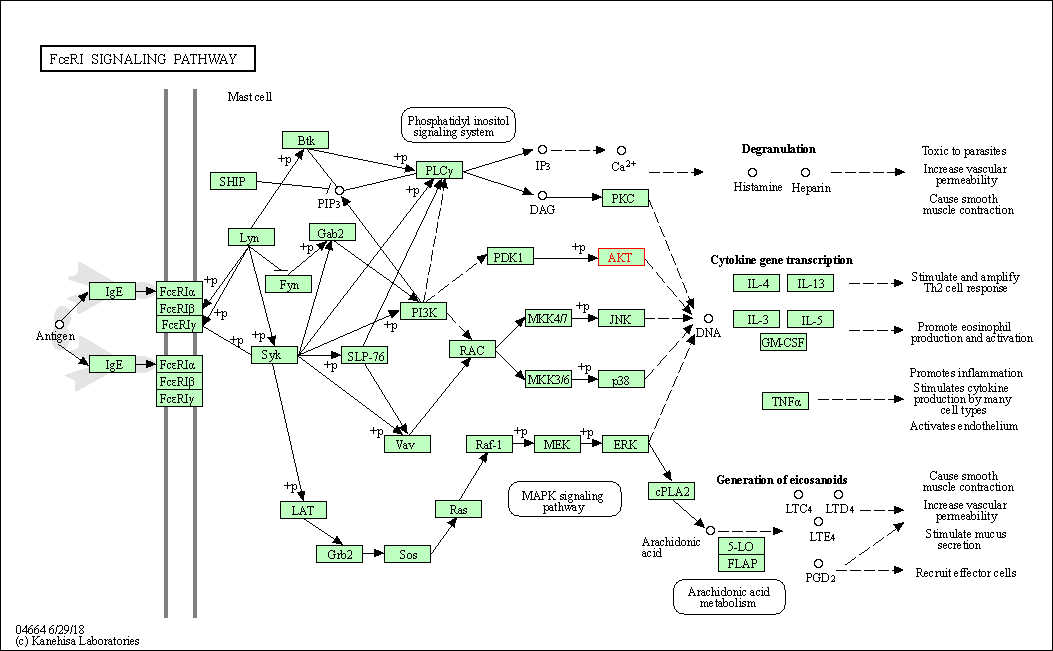
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
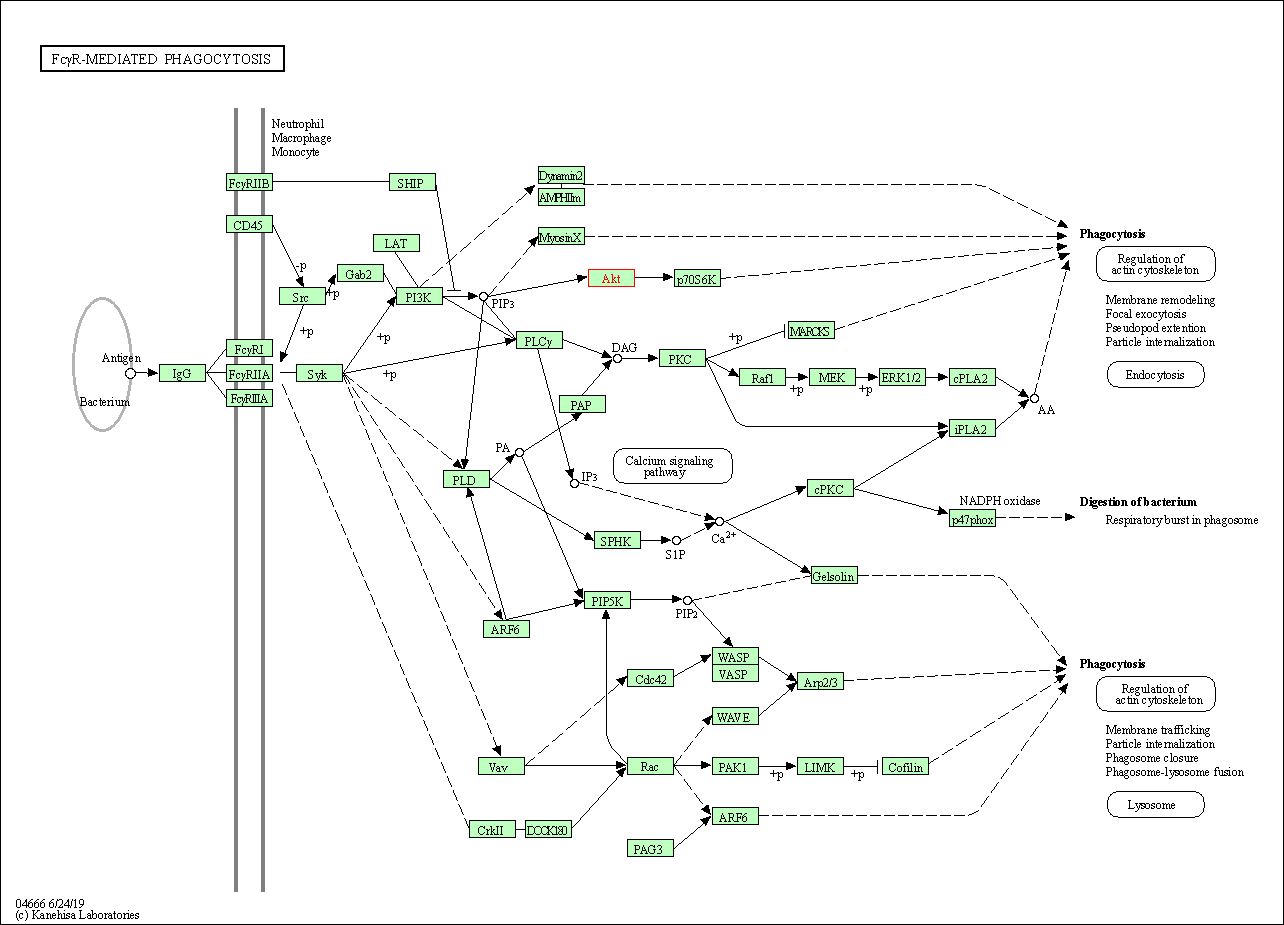
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
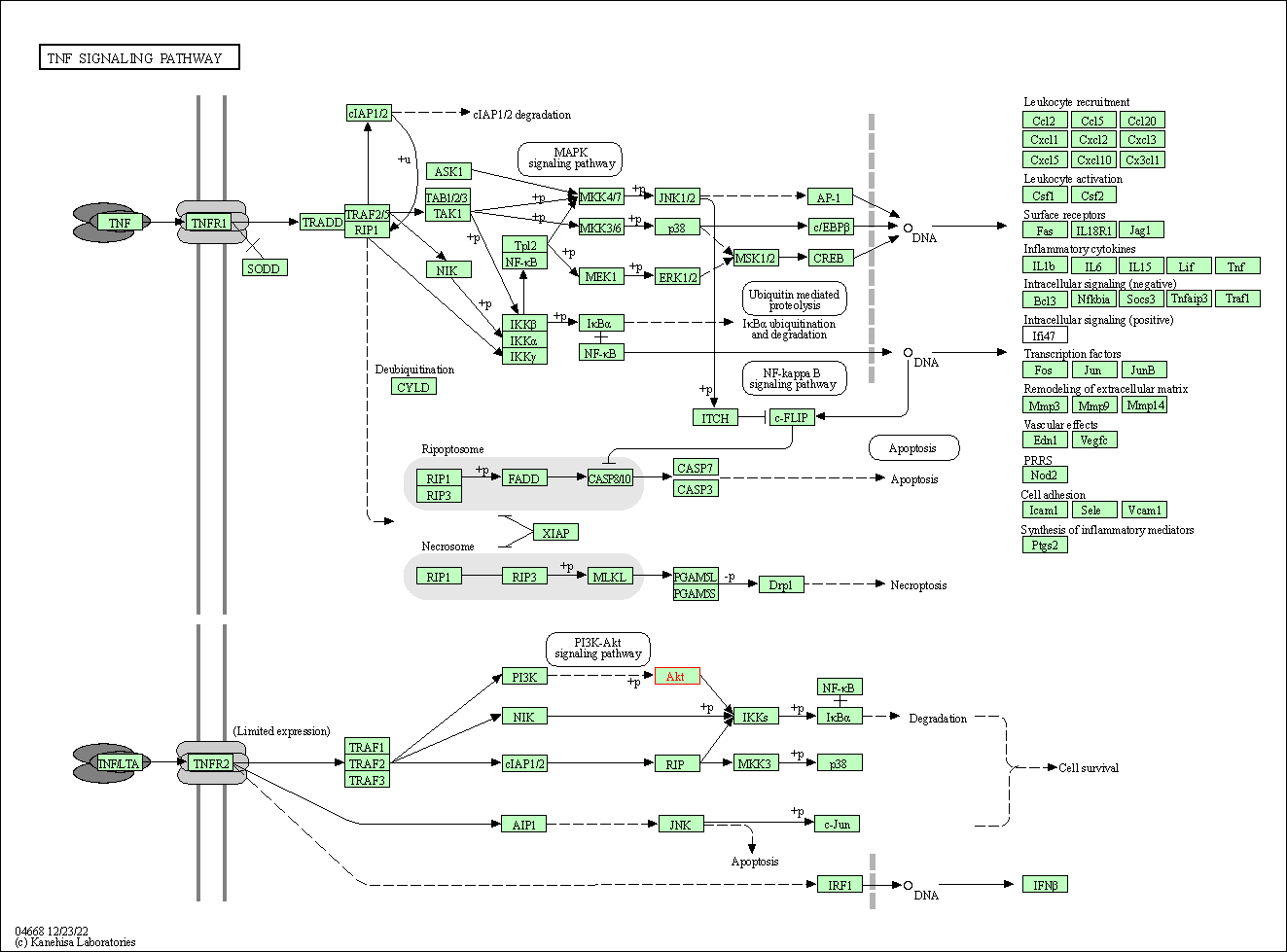
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | hsa04923 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Carbohydrate digestion and absorption | hsa04973 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 165 | Degree centrality | 1.77E-02 | Betweenness centrality | 4.69E-02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.97E-01 | Radiality | 1.49E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 5.23E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.74E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.76E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2023. Application Number: 218197 | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5693). | |||||
| REF 3 | The oral protein-kinase C beta inhibitor enzastaurin (LY317615) suppresses signalling through the AKT pathway, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008 Jul;49(7):1374-83. | |||||
| REF 4 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | |||||
| REF 5 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04316546) ARQ 092 (Miransertib) in Proteus Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5675). | |||||
| REF 8 | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 17. Irreversible inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor: 4-(phenylamino)quinazoline- and 4-(phenylamino)pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidine-6-acrylamides bearing additional solubilizing functions. J Med Chem. 2000 Apr 6;43(7):1380-97. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02103959) Safety and Efficacy of CMX-2043 for Protection of the Heart and Kidneys in Subjects Undergoing Coronary Angiography. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01445587) A Study of GSK2110183 in Subjects With Proteasome Inhibitor Refractory Multiple Myeloma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | PTX-200 Phase 1b/2 clinical trial update. Prescient Therapeutics. 26 August 2015. | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01028495) A Safety and Efficacy Study of RX-0201 Plus Gemcitabine in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01941927) Trametinib With GSK2141795 in BRAF Wild-type Melanoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01690468) Triciribine and Carboplatin in Ovarian Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01971515) First-in-Human Dose Escalation Trial in Subjects With Advanced Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 16 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3057). | |||||
| REF 17 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002681) | |||||
| REF 18 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Genentech (2011). | |||||
| REF 19 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 20 | A comparison of physicochemical property profiles of marketed oral drugs and orally bioavailable anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors in clinical development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(14):1408-22. | |||||
| REF 21 | Pre-clinical and Clinical Safety Studies of CMX-2043: a cytoprotective lipoic acid analogue for ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014 Nov;115(5):456-64. | |||||
| REF 22 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1479). | |||||
| REF 23 | CenterWatch. Drugs in Clinical Trials Database. CenterWatch. 2008. | |||||
| REF 24 | Discovery of a 2,4-disubstituted pyrrolo[1,2-f][1,2,4]triazine inhibitor (BMS-754807) of insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1R) kinase in cli... J Med Chem. 2009 Dec 10;52(23):7360-3. | |||||
| REF 25 | Cancer stem cell (CSC) inhibitors: a review of recent patents (2012-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Jul;27(7):753-761. | |||||
| REF 26 | Raft nanodomains contribute to Akt/PKB plasma membrane recruitment and activation. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Sep;4(9):538-47. | |||||
| REF 27 | Indolinone based phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1) inhibitors. Part 1: design, synthesis and biological activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Jul 15;17(14):3814-8. | |||||
| REF 28 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 29 | A phthalide with in vitro growth inhibitory activity from an oidiodendron strain. J Nat Prod. 2004 Dec;67(12):2086-9. | |||||
| REF 30 | 4-arylazo-3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazole CDK inhibitors: SAR study, crystal structure in complex with CDK2, selectivity, and cellular effects. J Med Chem. 2006 Nov 2;49(22):6500-9. | |||||
| REF 31 | Syntheses of potent, selective, and orally bioavailable indazole-pyridine series of protein kinase B/Akt inhibitors with reduced hypotension. J Med Chem. 2007 Jun 28;50(13):2990-3003. | |||||
| REF 32 | Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat Biotechnol. 2011 Oct 30;29(11):1046-51. | |||||
| REF 33 | Allosteric Akt (PKB) inhibitors: discovery and SAR of isozyme selective inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Feb 1;15(3):761-4. | |||||
| REF 34 | Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105. | |||||
| REF 35 | Discovery of a (1H-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyridin-2-one (BMS-536924) inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor I receptor kinase with in vivo antitum... J Med Chem. 2005 Sep 8;48(18):5639-43. | |||||
| REF 36 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 37 | The PI3K/Akt pathway as a target in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2009 Jun;9(5):550-9. | |||||
| REF 38 | 2,3,5-Trisubstituted pyridines as selective AKT inhibitors. Part II: Improved drug-like properties and kinase selectivity from azaindazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):679-83. | |||||
| REF 39 | Identification of 4-(2-(4-amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-7-{[(3S)-3-piperidinylmethyl]oxy}-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-yl)-2-methyl-3-butyn-2-o... J Med Chem. 2008 Sep 25;51(18):5663-79. | |||||
| REF 40 | An ATP-site on-off switch that restricts phosphatase accessibility of Akt. Sci Signal. 2012 May 8;5(223):ra37. | |||||
| REF 41 | Discovery of 4-amino-N-[(1S)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-1-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)piperidine-4-carboxamide (AZD5363), an orally bioavailable, potent inhibitor of Akt kinases. J Med Chem. 2013 Mar 14;56(5):2059-73. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

