Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T99397
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel 1 (VDAC1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Porin 31HM; Porin 31HL; Plasmalemmal porin; Outer mitochondrial membrane protein porin 1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
VDAC1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Epidermal dysplasias [ICD-11: EK90] | |||||
| Function |
Forms a channel through the mitochondrial outer membrane and also the plasma membrane. The channel at the outer mitochondrial membrane allows diffusion of small hydrophilic molecules; in the plasma membrane it is involved in cell volume regulation and apoptosis. It adopts an open conformation at low or zero membrane potential and a closed conformation at potentials above 30-40 mV. The open state has a weak anion selectivity whereas the closed state is cation-selective (PubMed:11845315, PubMed:18755977, PubMed:20230784, PubMed:8420959). May participate in the formation of the permeability transition pore complex (PTPC) responsible for the release of mitochondrial products that triggers apoptosis (PubMed:15033708, PubMed:25296756).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Eukaryotic mitochondrial porin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAVPPTYADLGKSARDVFTKGYGFGLIKLDLKTKSENGLEFTSSGSANTETTKVTGSLET
KYRWTEYGLTFTEKWNTDNTLGTEITVEDQLARGLKLTFDSSFSPNTGKKNAKIKTGYKR EHINLGCDMDFDIAGPSIRGALVLGYEGWLAGYQMNFETAKSRVTQSNFAVGYKTDEFQL HTNVNDGTEFGGSIYQKVNKKLETAVNLAWTAGNSNTRFGIAAKYQIDPDACFSAKVNNS SLIGLGYTQTLKPGIKLTLSALLDGKNVNAGGHKLGLGLEFQA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T11FY2 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | VDA-1102 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Actinic keratosis | [1] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | VDA-1102 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: NADH | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | NOE based model of hVDAC-1 bound to beta-NADH in detergent micelles | PDB:6TIR | ||||
| Method | Solution NMR | Resolution | N.A. | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
MAVPPTYADL
10 GKSARDVFTK20 GYGFGLIKLD30 LKTKSENGLE40 FTSSGSANTE50 TTKVTGSLET 60 KYRWTEYGLT70 FTEKWNTDNT80 LGTEITVEDQ90 LARGLKLTFD100 SSFSPNTGKK 110 NAKIKTGYKR120 EHINLGCDMD130 FDIAGPSIRG140 ALVLGYEGWL150 AGYQMNFETA 160 KSRVTQSNFA170 VGYKTDEFQL180 HTNVNDGTEF190 GGSIYQKVNK200 KLETAVNLAW 210 TAGNSNTRFG220 IAAKYQIDPD230 ACFSAKVNNS240 SLIGLGYTQT250 LKPGIKLTLS 260 ALLDGKNVNA270 GGHKLGLGLE280 FQALE
|
|||||
|
|
ARG15
2.341
VAL17
4.472
PHE18
2.190
THR19
2.473
LYS20
2.254
TYR22
2.596
GLN154
4.681
ASN168
4.890
ASN183
3.428
ASN185
2.660
GLU189
4.856
ASN207
3.244
ARG218
1.945
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Spermidine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (hVDAC1) in C222 space group | PDB:5XDO | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
MAVPPTYADL
10 GKSARDVFTK20 GYGFGLIKLD30 LKTKSENGLE40 FTSSGSANTE50 TTKVTGSLET 60 KYRWTEYGLT70 FTEKWNTDNT80 LGTEITVEDQ90 LARGLKLTFD100 SSFSPNTGKK 110 NAKIKTGYKR120 EHINLGCDMD130 FDIAGPSIRG140 ALVLGYEGWL150 AGYQMNFETA 160 KSRVTQSNFA170 VGYKTDEFQL180 HTNVNDGTEF190 GGSIYQKVNK200 KLETAVNLAW 210 TAGNSNTRFG220 IAAKYQIDPD230 ACFSAKVNNS240 SLIGLGYTQT250 LKPGIKLTLS 260 ALLDGKNVNA270 GGHKLGLGLE280 FQA
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
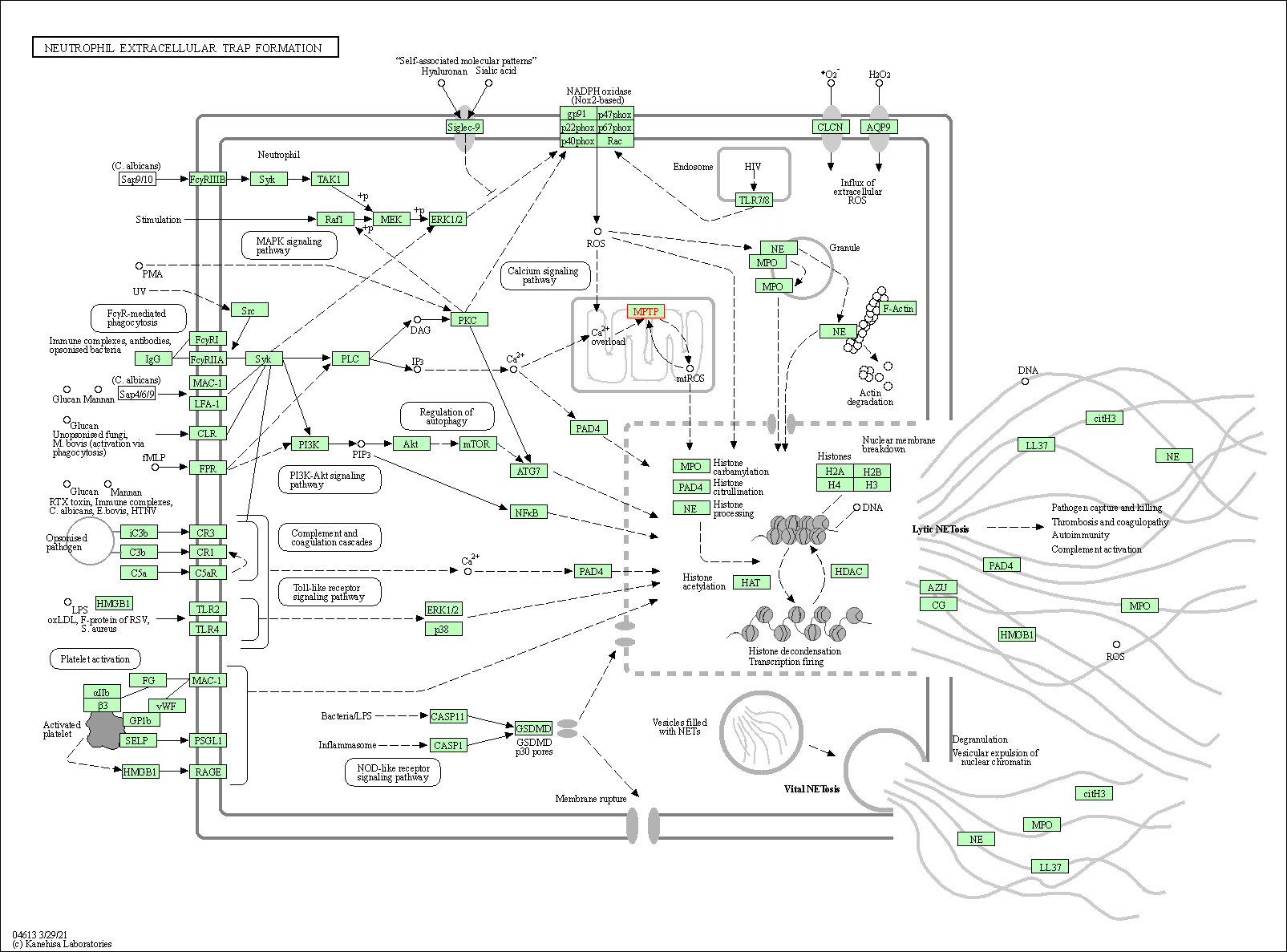
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
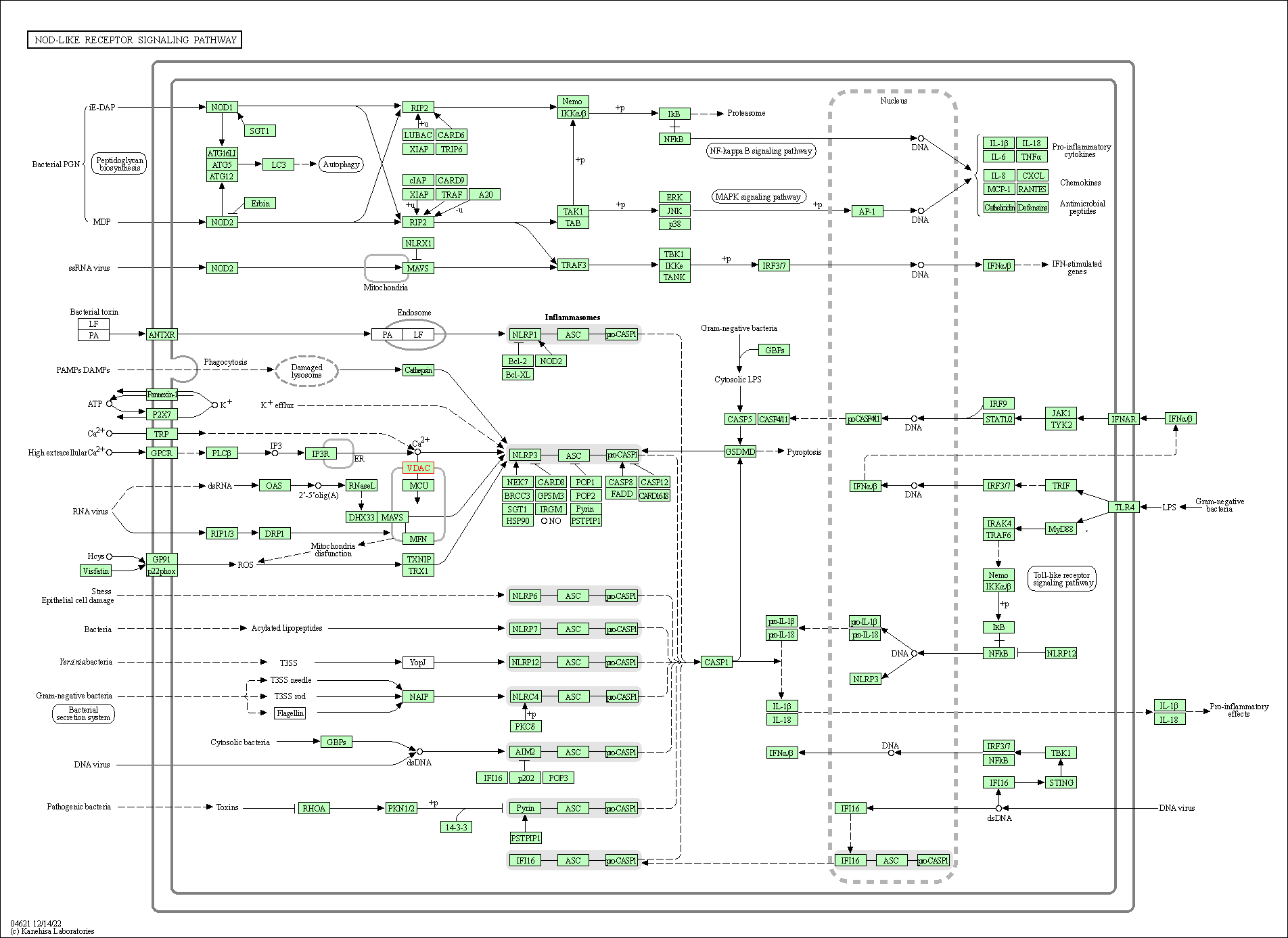
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholesterol metabolism | hsa04979 | Affiliated Target |
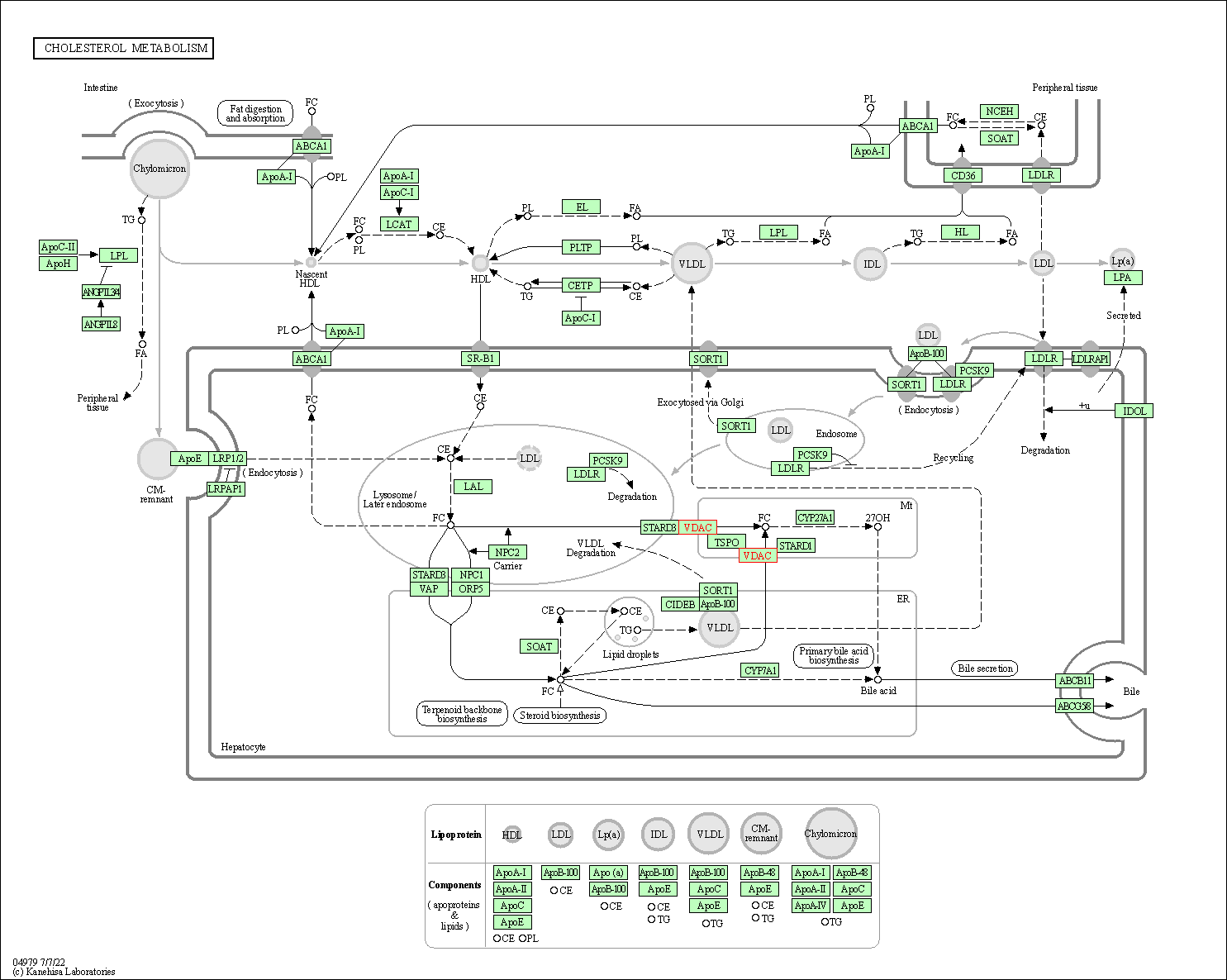
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 28 | Degree centrality | 3.01E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.92E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.27E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.14E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.68E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.15E-02 | Eccentricity | 10 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 10 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Necroptosis | |||||
| 4 | Cellular senescence | |||||
| 5 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 6 | Cholesterol metabolism | |||||
| 7 | Parkinson disease | |||||
| 8 | Huntington disease | |||||
| 9 | Influenza A | |||||
| 10 | Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | The Structural Basis for Low Conductance in the Membrane Protein VDAC upon beta-NADH Binding and Voltage Gating. Structure. 2020 Feb 4;28(2):206-214.e4. | |||||
| REF 3 | Crystal structural characterization reveals novel oligomeric interactions of human voltage-dependent anion channel 1. Protein Sci. 2017 Sep;26(9):1749-1758. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

