Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T91696
(Former ID: TTDC00012)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Fibronectin (FN1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
FN; Cold-insoluble globulin; CIG
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
FN1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Vitreous body disorder [ICD-11: 9B8Z] | |||||
| Function |
Fibronectins bind cell surfaces and various compounds including collagen, fibrin, heparin, DNA, and actin. Fibronectins are involved in cell adhesion, cell motility, opsonization, wound healing, and maintenance of cell shape. Involved in osteoblast compaction through the fibronectin fibrillogenesis cell-mediated matrix assembly process, essential for osteoblast mineralization. Participates in the regulation of type I collagen deposition by osteoblasts.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Fibronectin protein
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MLRGPGPGLLLLAVQCLGTAVPSTGASKSKRQAQQMVQPQSPVAVSQSKPGCYDNGKHYQ
INQQWERTYLGNALVCTCYGGSRGFNCESKPEAEETCFDKYTGNTYRVGDTYERPKDSMI WDCTCIGAGRGRISCTIANRCHEGGQSYKIGDTWRRPHETGGYMLECVCLGNGKGEWTCK PIAEKCFDHAAGTSYVVGETWEKPYQGWMMVDCTCLGEGSGRITCTSRNRCNDQDTRTSY RIGDTWSKKDNRGNLLQCICTGNGRGEWKCERHTSVQTTSSGSGPFTDVRAAVYQPQPHP QPPPYGHCVTDSGVVYSVGMQWLKTQGNKQMLCTCLGNGVSCQETAVTQTYGGNSNGEPC VLPFTYNGRTFYSCTTEGRQDGHLWCSTTSNYEQDQKYSFCTDHTVLVQTRGGNSNGALC HFPFLYNNHNYTDCTSEGRRDNMKWCGTTQNYDADQKFGFCPMAAHEEICTTNEGVMYRI GDQWDKQHDMGHMMRCTCVGNGRGEWTCIAYSQLRDQCIVDDITYNVNDTFHKRHEEGHM LNCTCFGQGRGRWKCDPVDQCQDSETGTFYQIGDSWEKYVHGVRYQCYCYGRGIGEWHCQ PLQTYPSSSGPVEVFITETPSQPNSHPIQWNAPQPSHISKYILRWRPKNSVGRWKEATIP GHLNSYTIKGLKPGVVYEGQLISIQQYGHQEVTRFDFTTTSTSTPVTSNTVTGETTPFSP LVATSESVTEITASSFVVSWVSASDTVSGFRVEYELSEEGDEPQYLDLPSTATSVNIPDL LPGRKYIVNVYQISEDGEQSLILSTSQTTAPDAPPDTTVDQVDDTSIVVRWSRPQAPITG YRIVYSPSVEGSSTELNLPETANSVTLSDLQPGVQYNITIYAVEENQESTPVVIQQETTG TPRSDTVPSPRDLQFVEVTDVKVTIMWTPPESAVTGYRVDVIPVNLPGEHGQRLPISRNT FAEVTGLSPGVTYYFKVFAVSHGRESKPLTAQQTTKLDAPTNLQFVNETDSTVLVRWTPP RAQITGYRLTVGLTRRGQPRQYNVGPSVSKYPLRNLQPASEYTVSLVAIKGNQESPKATG VFTTLQPGSSIPPYNTEVTETTIVITWTPAPRIGFKLGVRPSQGGEAPREVTSDSGSIVV SGLTPGVEYVYTIQVLRDGQERDAPIVNKVVTPLSPPTNLHLEANPDTGVLTVSWERSTT PDITGYRITTTPTNGQQGNSLEEVVHADQSSCTFDNLSPGLEYNVSVYTVKDDKESVPIS DTIIPEVPQLTDLSFVDITDSSIGLRWTPLNSSTIIGYRITVVAAGEGIPIFEDFVDSSV GYYTVTGLEPGIDYDISVITLINGGESAPTTLTQQTAVPPPTDLRFTNIGPDTMRVTWAP PPSIDLTNFLVRYSPVKNEEDVAELSISPSDNAVVLTNLLPGTEYVVSVSSVYEQHESTP LRGRQKTGLDSPTGIDFSDITANSFTVHWIAPRATITGYRIRHHPEHFSGRPREDRVPHS RNSITLTNLTPGTEYVVSIVALNGREESPLLIGQQSTVSDVPRDLEVVAATPTSLLISWD APAVTVRYYRITYGETGGNSPVQEFTVPGSKSTATISGLKPGVDYTITVYAVTGRGDSPA SSKPISINYRTEIDKPSQMQVTDVQDNSISVKWLPSSSPVTGYRVTTTPKNGPGPTKTKT AGPDQTEMTIEGLQPTVEYVVSVYAQNPSGESQPLVQTAVTNIDRPKGLAFTDVDVDSIK IAWESPQGQVSRYRVTYSSPEDGIHELFPAPDGEEDTAELQGLRPGSEYTVSVVALHDDM ESQPLIGTQSTAIPAPTDLKFTQVTPTSLSAQWTPPNVQLTGYRVRVTPKEKTGPMKEIN LAPDSSSVVVSGLMVATKYEVSVYALKDTLTSRPAQGVVTTLENVSPPRRARVTDATETT ITISWRTKTETITGFQVDAVPANGQTPIQRTIKPDVRSYTITGLQPGTDYKIYLYTLNDN ARSSPVVIDASTAIDAPSNLRFLATTPNSLLVSWQPPRARITGYIIKYEKPGSPPREVVP RPRPGVTEATITGLEPGTEYTIYVIALKNNQKSEPLIGRKKTDELPQLVTLPHPNLHGPE ILDVPSTVQKTPFVTHPGYDTGNGIQLPGTSGQQPSVGQQMIFEEHGFRRTTPPTTATPI RHRPRPYPPNVGEEIQIGHIPREDVDYHLYPHGPGLNPNASTGQEALSQTTISWAPFQDT SEYIISCHPVGTDEEPLQFRVPGTSTSATLTGLTRGATYNVIVEALKDQQRHKVREEVVT VGNSVNEGLNQPTDDSCFDPYTVSHYAVGDEWERMSESGFKLLCQCLGFGSGHFRCDSSR WCHDNGVNYKIGEKWDRQGENGQMMSCTCLGNGKGEFKCDPHEATCYDDGKTYHVGEQWQ KEYLGAICSCTCFGGQRGWRCDNCRRPGGEPSPEGTTGQSYNQYSQRYHQRTNTNVNCPI ECFMPLDVQADREDSRE Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A02399 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T04WT7 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ocriplasmin | Drug Info | Approved | Symptomatic vitreomacular adhesion | [2], [3] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | L19-TNF-alpha | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Colorectal cancer | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Ocriplasmin | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titin (TTN) | 23.014 (336/1460) | 1.57E-25 | |
| Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 7 (FNDC7) | 23.344 (141/604) | 1.65E-09 | |
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
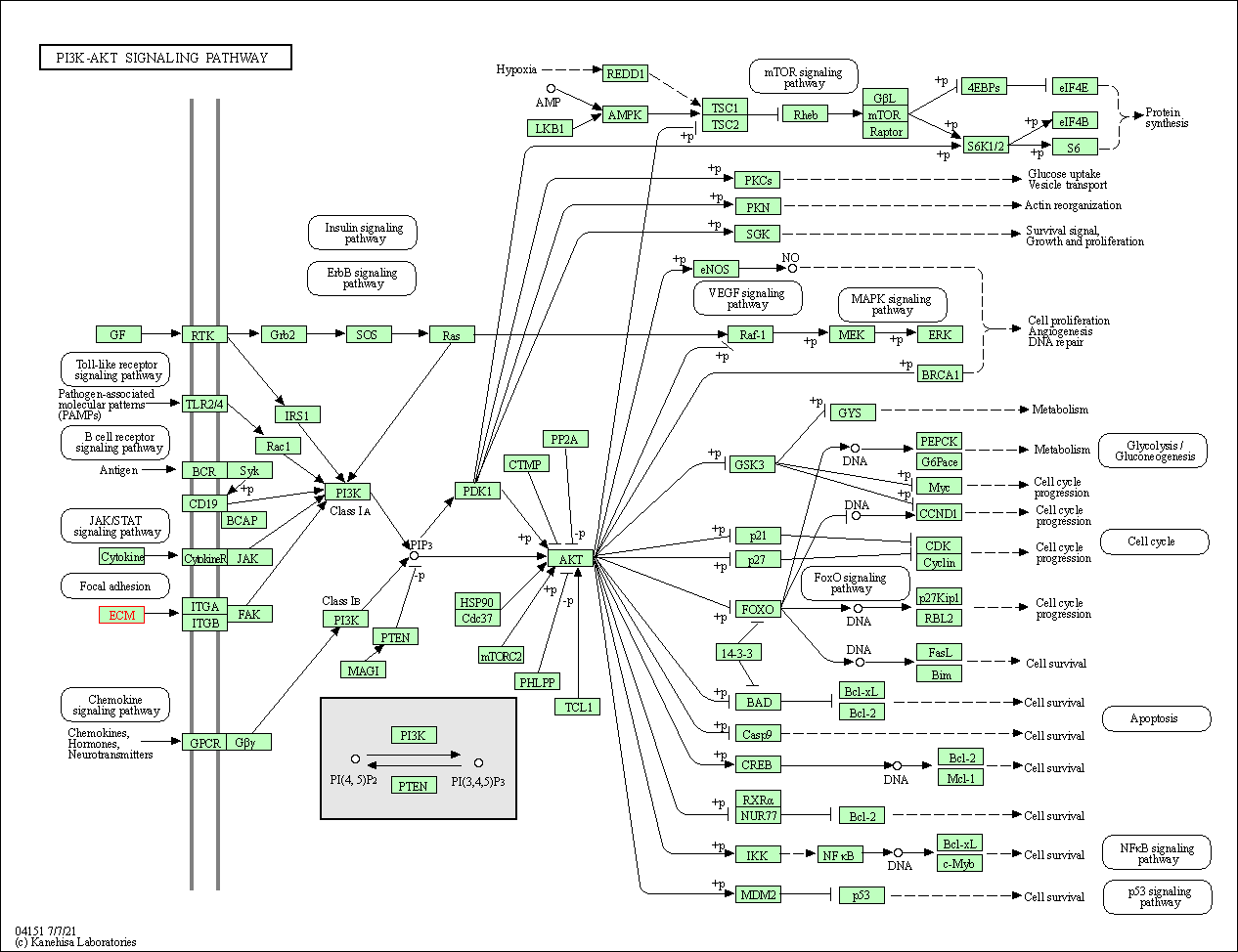
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
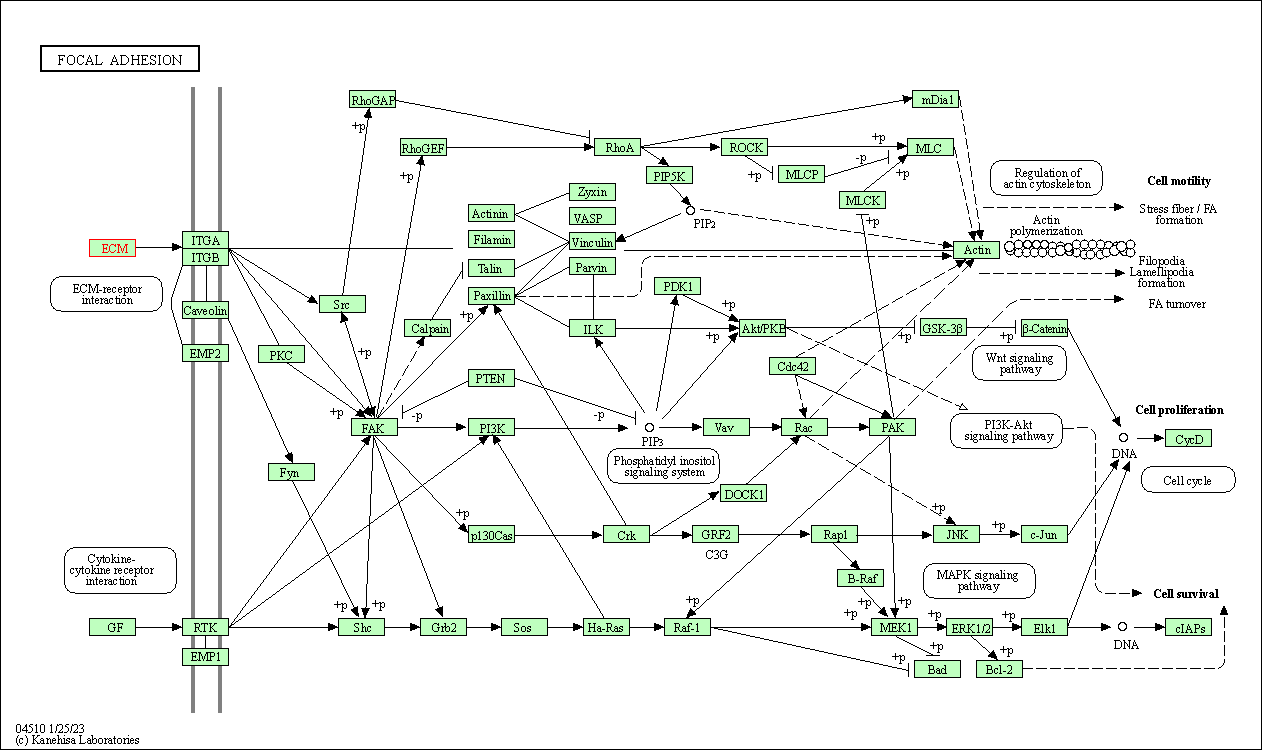
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ECM-receptor interaction | hsa04512 | Affiliated Target |
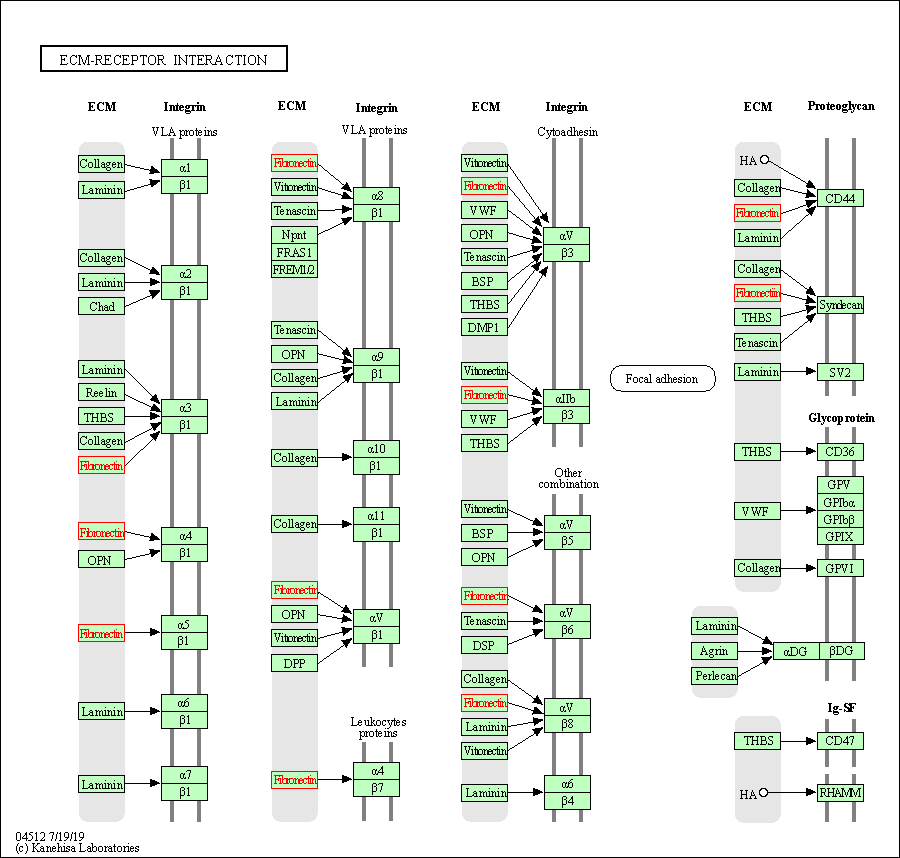
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |
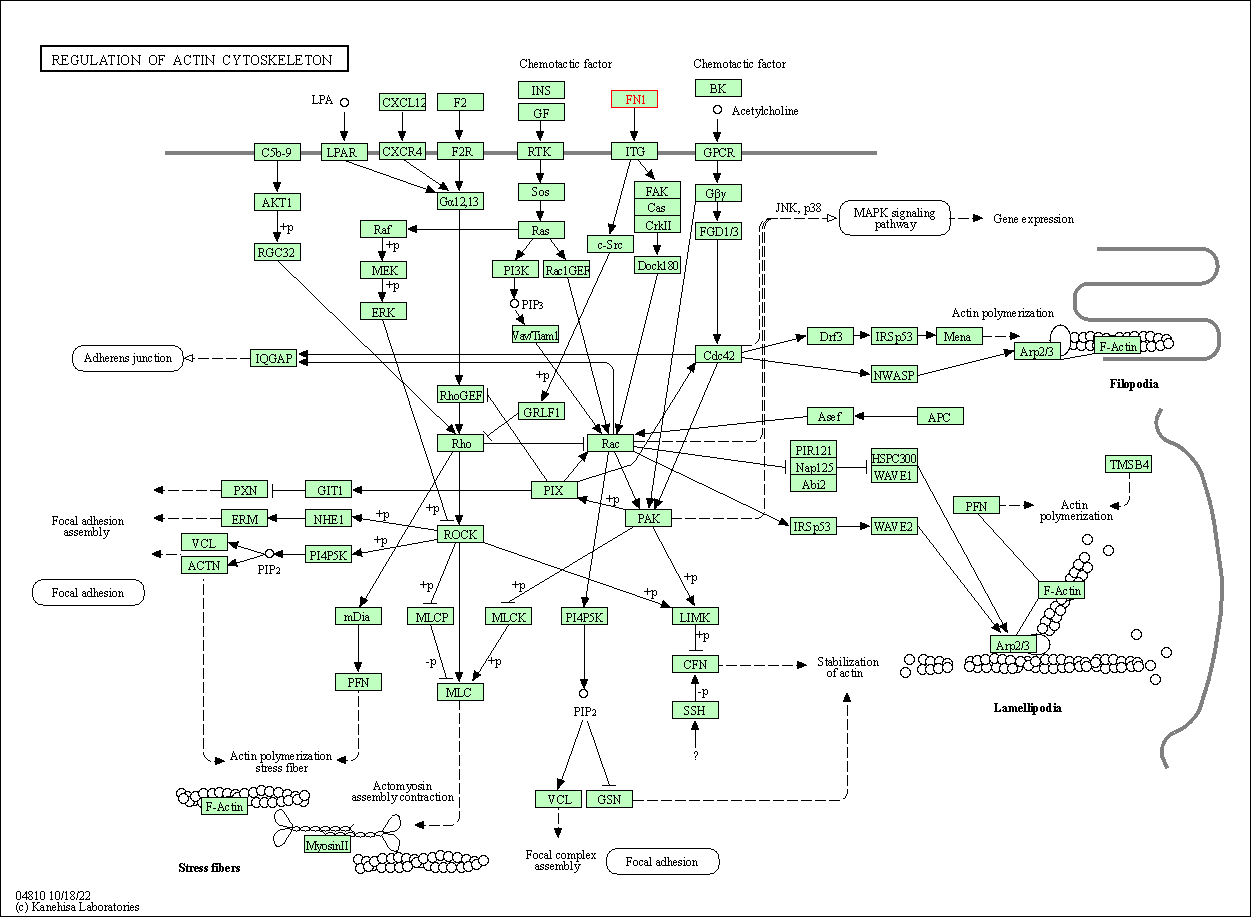
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 63 | Degree centrality | 6.77E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.03E-02 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.54E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 7.53E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.58E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.13E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary (drug id 686947). | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7446). | |||||
| REF 3 | Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Feb;12(2):87-90. | |||||
| REF 4 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026493) | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

