Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T85799
(Former ID: TTDC00165)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
PSK-J3; Cell division protein kinase 4
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CDK4
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C6Y] | |||||
| 2 | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||||
| 3 | Psoriasis [ICD-11: EA90] | |||||
| Function |
Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complexes and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. Also phosphorylates SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and represses its transcriptional activity. Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. Ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.22
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MATSRYEPVAEIGVGAYGTVYKARDPHSGHFVALKSVRVPNGGGGGGGLPISTVREVALL
RRLEAFEHPNVVRLMDVCATSRTDREIKVTLVFEHVDQDLRTYLDKAPPPGLPAETIKDL MRQFLRGLDFLHANCIVHRDLKPENILVTSGGTVKLADFGLARIYSYQMALTPVVVTLWY RAPEVLLQSTYATPVDMWSVGCIFAEMFRRKPLFCGNSEADQLGKIFDLIGLPPEDDWPR DVSLPRGAFPPRGPRPVQSVVPEMEESGAQLLLEMLTFNPHKRISAFRALQHSYLHKDEG NPE Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T10S5F | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 5 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Apremilast | Drug Info | Approved | Psoriasis vulgaris | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | LY2835219 | Drug Info | Approved | Breast cancer | [4] | |
| 3 | Palbociclib | Drug Info | Approved | Breast cancer | [5] | |
| 4 | Ribociclib Succinate | Drug Info | Approved | Hormone receptor positive and HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer | [6] | |
| 5 | Trilaciclib | Drug Info | Approved | Small-cell lung cancer | [7] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 16 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LEE011 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Solid tumour/cancer | [8], [9] | |
| 2 | G1T38 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Breast cancer | [10] | |
| 3 | P-276 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Breast cancer | [11], [12] | |
| 4 | P276-00 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Mantle cell lymphoma | [13] | |
| 5 | Ro 31-7453 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [14] | |
| 6 | FCN-437 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Breast cancer | [15] | |
| 7 | GLR2007 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Non-small-cell lung cancer | [16] | |
| 8 | NUV-422 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Malignant glioma | [17] | |
| 9 | AG-024322 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [18] | |
| 10 | FN-1501 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [19] | |
| 11 | G1T28-1 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [20] | |
| 12 | P1446A-05 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [21] | |
| 13 | PF-07220060 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Prostate cancer | [22] | |
| 14 | PHA-793887 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [23] | |
| 15 | RGB-286638 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Haematological malignancy | [24], [25] | |
| 16 | RGT-419B | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Breast cancer | [26] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 5 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BAY 10-00394 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Small-cell lung cancer | [27], [28] | |
| 2 | R547 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Advanced solid tumour | [29], [30] | |
| 3 | ZK 304709 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Advanced solid tumour | [31] | |
| 4 | CYC-103 | Drug Info | Terminated | Solid tumour/cancer | [33] | |
| 5 | PD-0183812 | Drug Info | Terminated | Retinoblastoma | [34] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | INOC-005 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Solid tumour/cancer | [32] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 57 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Apremilast | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Trilaciclib | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 3 | G1T38 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 4 | P-276 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 5 | P276-00 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 6 | Ro 31-7453 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 7 | FCN-437 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 8 | GLR2007 | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 9 | NUV-422 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 10 | AG-024322 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 11 | FN-1501 | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 12 | P1446A-05 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 13 | PF-07220060 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 14 | PHA-793887 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 15 | RGB-286638 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 16 | RGT-419B | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 17 | Imidazo pyridine derivative 3 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 18 | Indole-based analog 13 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 19 | Isoquinoline 1,3-dione derivative 1 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 20 | Oxazolyl methylthiothiazole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 21 | Palbociclib/ribociclib analog 1 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 22 | PMID25726713-Compound-47 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 23 | PMID25726713-Compound-48 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 24 | PMID25726713-Compound-49 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 25 | PMID25726713-Compound-50 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 26 | PMID25726713-Compound-51 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 27 | PMID25991433-Compound-A1 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 28 | PMID26161698-Compound-17 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 29 | Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivative 10 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 30 | Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivative 9 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 31 | BAY 10-00394 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 32 | R547 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 33 | ZK 304709 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 34 | INOC-005 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 35 | CYC-103 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 36 | PD-0183812 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 37 | 1-(1H-Indazol-6-yl)-3-pyridin-2-yl-urea | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 38 | 1-(7-Hydroxy-naphthalen-1-yl)-3-pyridin-2-yl-urea | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 39 | 1-(9-Oxo-9H-fluoren-4-yl)-3-pyridin-2-yl-urea | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 40 | 1-Pyridin-2-yl-3-quinolin-5-yl-urea | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 41 | 10-hydroxy-18-methoxybetaenone | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 42 | 3,4-di-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 43 | 3,4-diphenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 44 | 3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 45 | 3-(indole-3-yl)-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 46 | 4-[(3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)diazenyl]phenol | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| 47 | Cdk4 inhibitor III | Drug Info | [51] | |||
| 48 | Fascaplysin | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 49 | K00024 | Drug Info | [52] | |||
| 50 | N-(2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)ethyl)biphenyl-4-carboxamide | Drug Info | [53] | |||
| 51 | NSC-625987 | Drug Info | [54] | |||
| 52 | NU-6102 | Drug Info | [55] | |||
| 53 | NU6140 | Drug Info | [56] | |||
| 54 | PMID18986805C9b | Drug Info | [57] | |||
| 55 | PYRAZOLOPYRIDAZINE 1 | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| 56 | PYRAZOLOPYRIDAZINE 2 | Drug Info | [58] | |||
| 57 | Ro-0505124 | Drug Info | [59] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 5 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LY2835219 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 2 | Palbociclib | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | Ribociclib Succinate | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 4 | LEE011 | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 5 | G1T28-1 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Abemaciclib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of CDK4-Cyclin D3 bound to abemaciclib | PDB:7SJ3 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.51 Å | Mutation | Yes | [60] |
| PDB Sequence |
ATSRYEPVAE
11 IGVGAYGTVY21 KARDPHSGHF31 VALKSVRGGG48 LPISTVREVA58 LLRRLEAFEH 68 PNVVRLMDVC78 ATSDREIKVT90 LVFEHVDQDL100 RTYLDKAPAE115 TIKDLMRQFL 125 RGLDFLHANC135 IVHRDLKPEN145 ILVTSGGTVK155 LADFGLARIY165 SYQMALPVVV 176 TLWYRAPEVL186 LQSTYATPVD196 MWSVGCIFAE206 MFRRKPLFCG216 NSEADQLGKI 226 FDLIGLPPED236 DWPRDVSLPR246 GAFPPRGPRP262 EMEESGAQLL272 LEMLTFNPHK 282 RISAFRALQH292 SYL
|
|||||
|
|
GLU11
4.190
ILE12
3.216
GLY13
4.193
TYR17
3.521
VAL20
3.911
ALA33
3.710
LYS35
3.057
GLU56
3.769
VAL72
3.871
PHE93
3.102
GLU94
3.344
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Phosphonothreonine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of CDK4-Cyclin D3 bound to abemaciclib | PDB:7SJ3 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.51 Å | Mutation | Yes | [60] |
| PDB Sequence |
ATSRYEPVAE
11 IGVGAYGTVY21 KARDPHSGHF31 VALKSVRGGG48 LPISTVREVA58 LLRRLEAFEH 68 PNVVRLMDVC78 ATSDREIKVT90 LVFEHVDQDL100 RTYLDKAPAE115 TIKDLMRQFL 125 RGLDFLHANC135 IVHRDLKPEN145 ILVTSGGTVK155 LADFGLARIY165 SYQMALPVVV 176 TLWYRAPEVL186 LQSTYATPVD196 MWSVGCIFAE206 MFRRKPLFCG216 NSEADQLGKI 226 FDLIGLPPED236 DWPRDVSLPR246 GAFPPRGPRP262 EMEESGAQLL272 LEMLTFNPHK 282 RISAFRALQH292 SYL
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
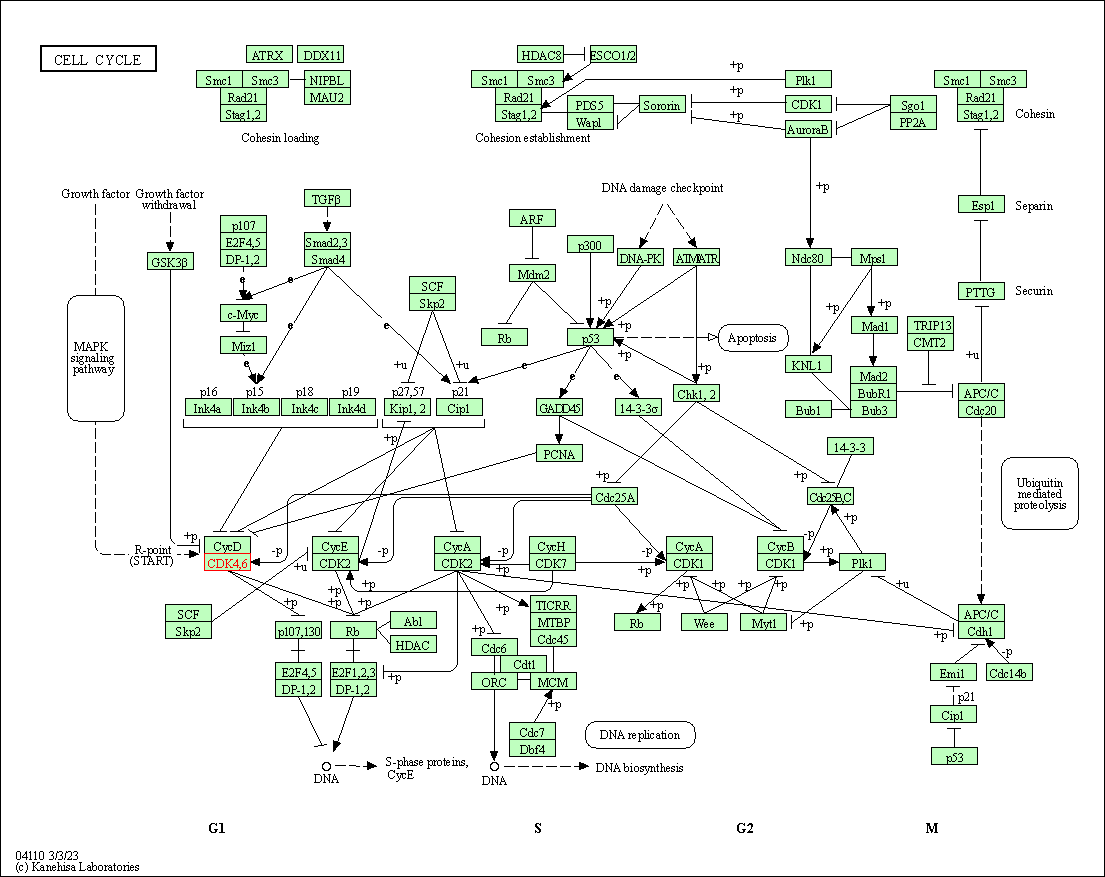
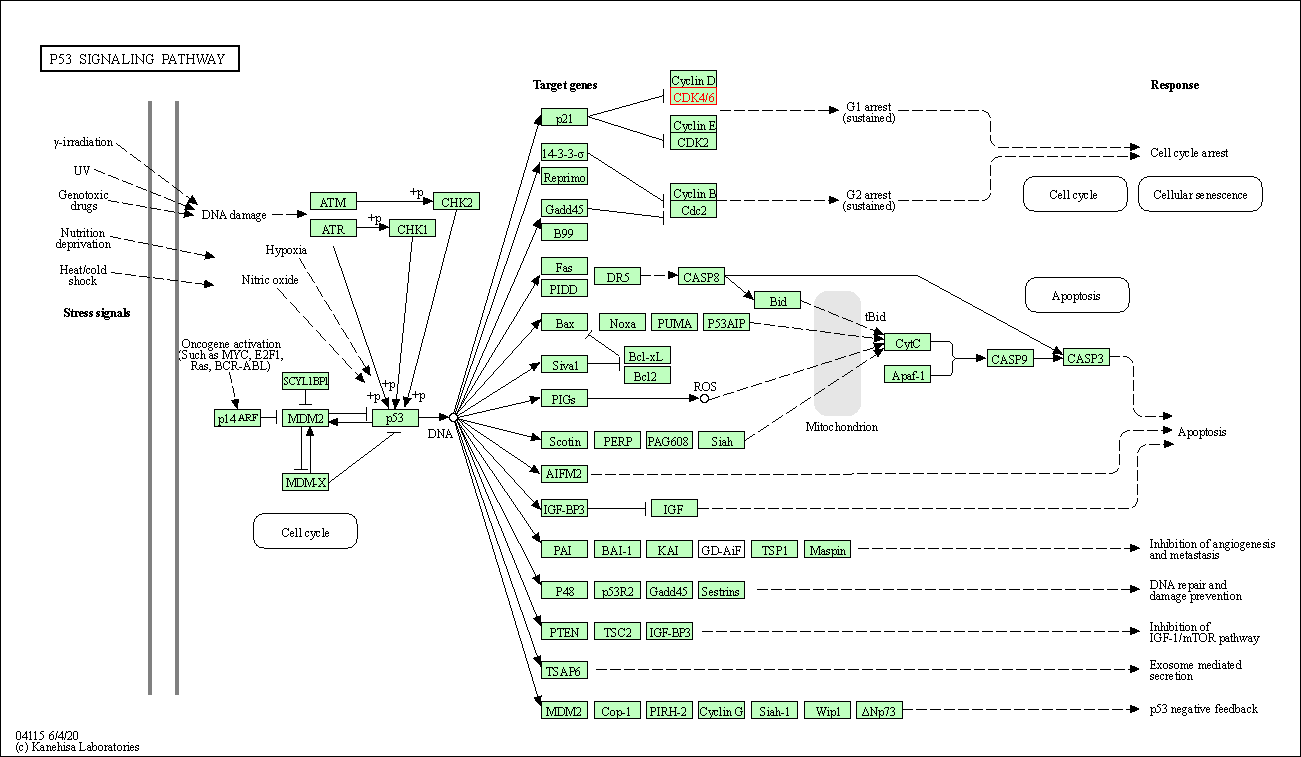
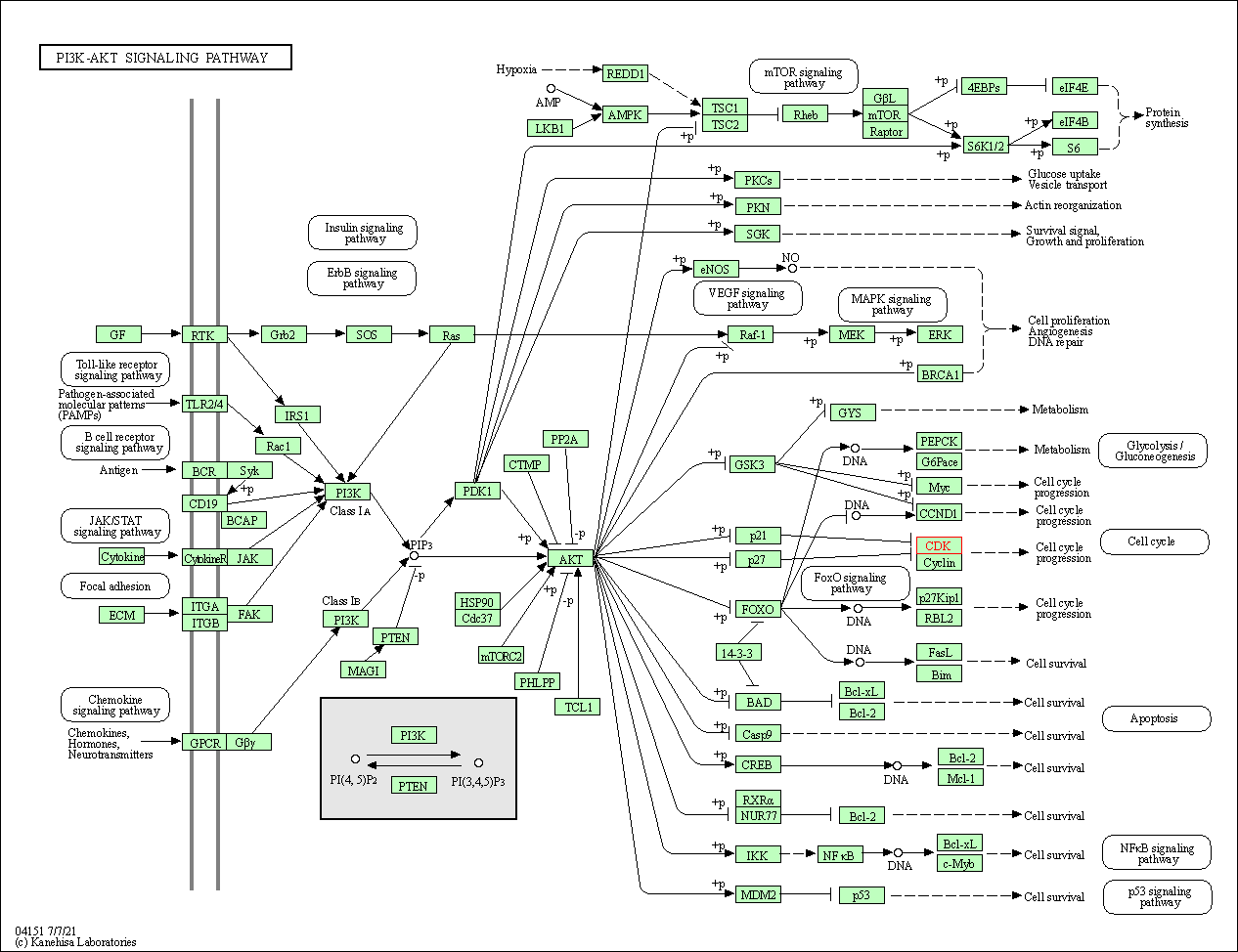
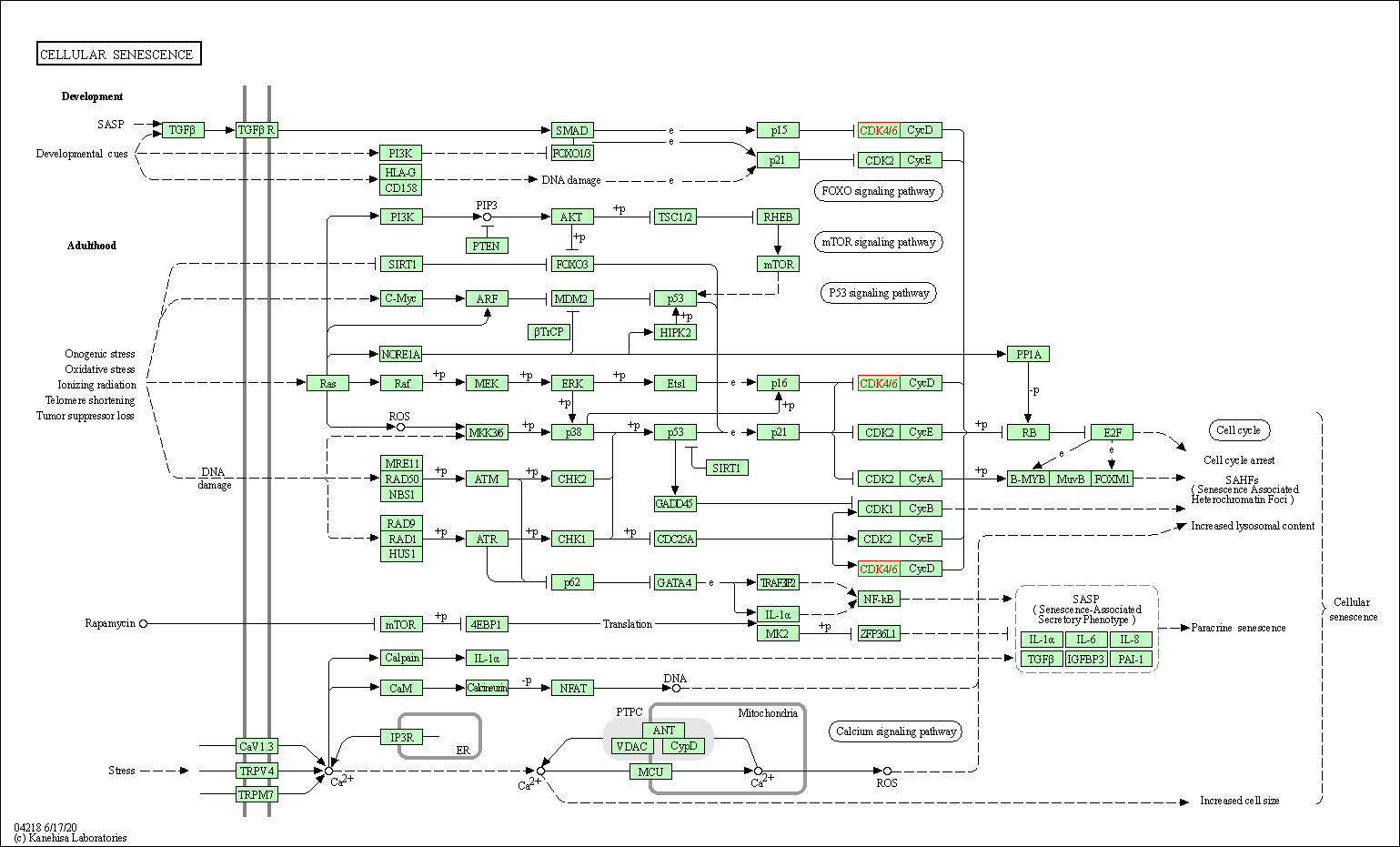
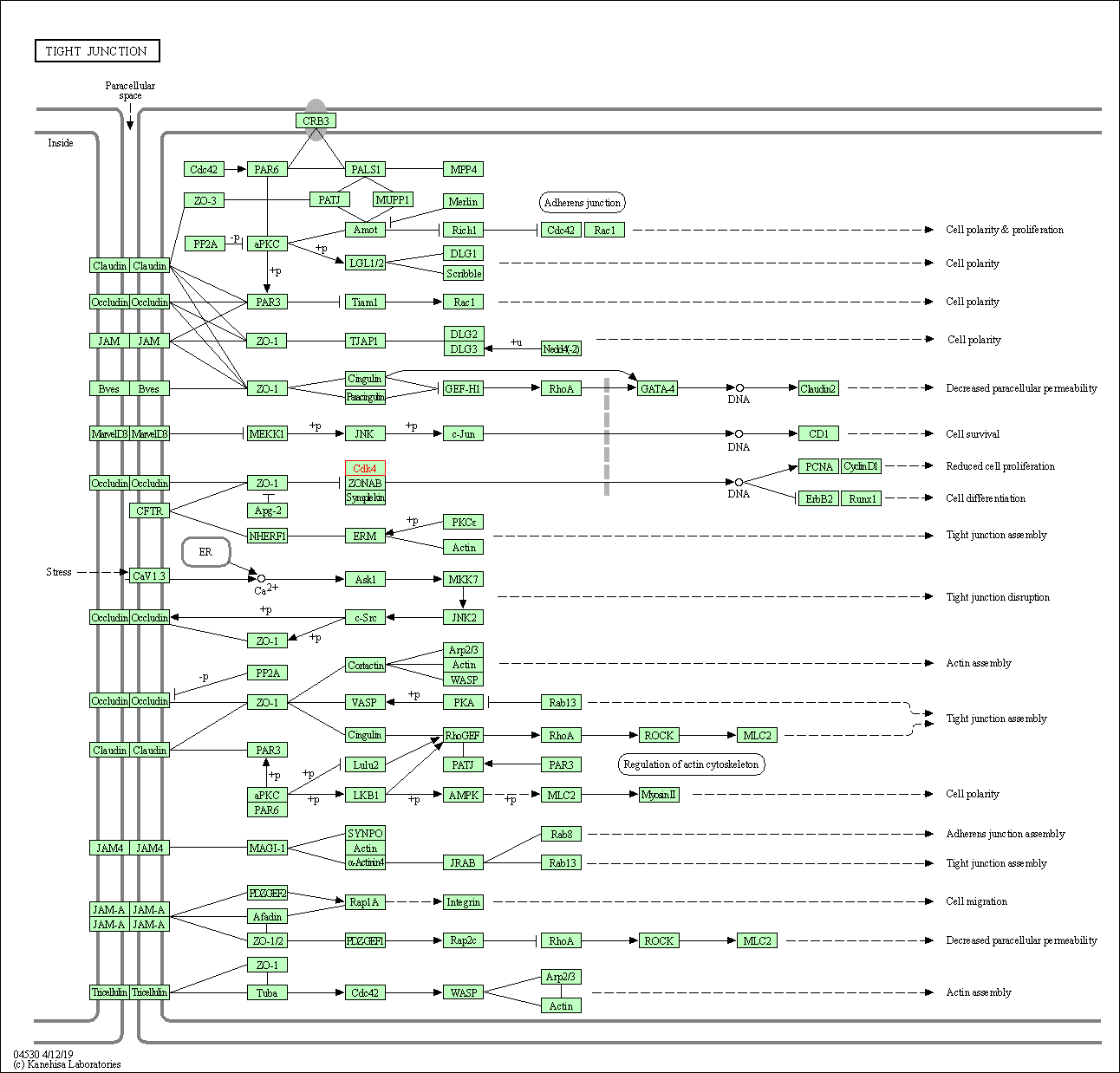
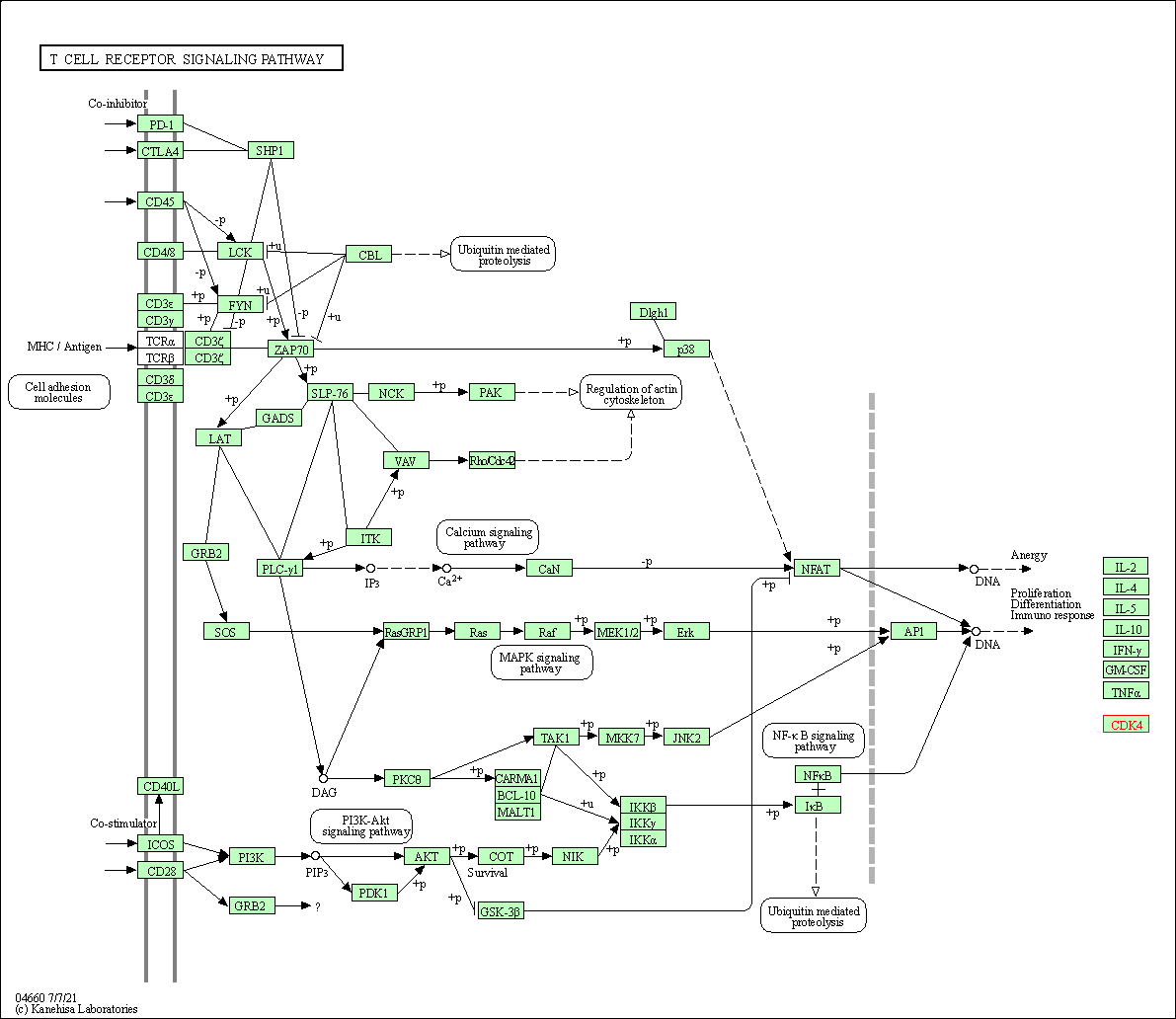
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell cycle | hsa04110 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Tight junction | hsa04530 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 41 | Degree centrality | 4.40E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.54E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.53E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.30E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.37E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.42E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Agreement signed with Prostagenics to develop prostate cancer treatment. Innovate Oncology, Inc. 2005. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7372). | |||||
| REF 3 | Emerging drugs for psoriasis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):145-63. | |||||
| REF 4 | 2017 FDA drug approvals.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Feb;17(2):81-85. | |||||
| REF 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2017 | |||||
| REF 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2018 | |||||
| REF 7 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2021 | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7383). | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01958021) Study of Efficacy and Safety of LEE011 in Postmenopausal Women With Advanced Breast Cancer.(MONALEESA-2). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 11 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7934). | |||||
| REF 12 | P276-00, a novel cyclin-dependent inhibitor induces G1-G2 arrest, shows antitumor activity on cisplatin-resistant cells and significant in vivo efficacy in tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):926-34. | |||||
| REF 13 | A phase II, single-arm, open-label, multicenter study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of P276-00, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015 Jul;15(7):392-7. | |||||
| REF 14 | A phase 2 study of oral MKC-1, an inhibitor of importin-beta, tubulin, and the mTOR pathway in patients with unresectable or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Invest New Drugs. 2012 Aug;30(4):1614-20. | |||||
| REF 15 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04488107) Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Antitumor Activity of FCN-437c. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04444427) Evaluation of GLR2007 for Advanced Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04541225) Phase 1/2 Dose Escalation, Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Efficacy Study of NUV-422 in Adults With Recurrent or Refractory High-grade Gliomas and Solid Tumors. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 18 | Cell cycle kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009 Jul;8(7):547-66. | |||||
| REF 19 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03690154) A Phase 1 Study to Evaluate FN-1501 Monotherapy in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors and R/R AML. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 20 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02243150) Safety, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of the CDK 4/6 Inhibitor G1T28-1. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 21 | Liposarcoma: molecular genetics and therapeutics. Sarcoma. 2011;2011:483154. | |||||
| REF 22 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04557449) Study to Test the Safety and Tolerability of PF-07220060 in Participants With Advance Solid Tumors (CDK4). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 23 | A first in man, phase I dose-escalation study of PHA-793887, an inhibitor of multiple cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK2, 1 and 4) reveals unexpected h... Cell Cycle. 2011 Mar 15;10(6):963-70. | |||||
| REF 24 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7744). | |||||
| REF 25 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01168882) Safety and Tolerability of RGB-286638 in Patients With Selected, Relapsed or Refractory Hematological Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 26 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05304962) First-in-Human, Escalating Oral Dose Study of RGT-419B Given Alone and With Endocrine Therapy in Subjects With Hormone Receptor Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Negative Advanced/Metastatic Breast Cancer. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 27 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7874). | |||||
| REF 28 | BAY 1000394, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, with potent antitumor activity in mono- and in combination treatment upon oral application. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Oct;11(10):2265-73. | |||||
| REF 29 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5707). | |||||
| REF 30 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800018924) | |||||
| REF 31 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800022386) | |||||
| REF 32 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800022337) | |||||
| REF 33 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800015455) | |||||
| REF 34 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800014130) | |||||
| REF 35 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 36 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 37 | Dual CDK4/CDK6 inhibition induces cell-cycle arrest and senescence in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;19(22):6173-82. | |||||
| REF 38 | A comparison of physicochemical property profiles of marketed oral drugs and orally bioavailable anti-cancer protein kinase inhibitors in clinical development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(14):1408-22. | |||||
| REF 39 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Fochon Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 40 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 41 | Discovery of 4-((7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)-N-(4-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)phenyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide (FN-1501), an FLT3- and CDK-Kinase Inhibitor with Potentially High Efficiency against Acute Myelocytic Leukemia. J Med Chem. 2018 Feb 22;61(4):1499-1518. | |||||
| REF 42 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Regor Therapeutics | |||||
| REF 43 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy: a patent review (2009 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(9):953-70. | |||||
| REF 44 | Hedgehog inhibitors: a patent review (2013 - present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 May;25(5):549-65. | |||||
| REF 45 | c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors: a patent review (2010 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(8):849-72. | |||||
| REF 46 | Pharmacological inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002 Sep;23(9):417-25. | |||||
| REF 47 | Structure-based generation of a new class of potent Cdk4 inhibitors: new de novo design strategy and library design. J Med Chem. 2001 Dec 20;44(26):4615-27. | |||||
| REF 48 | Anthraquinones and betaenone derivatives from the sponge-associated fungus Microsphaeropsis species: novel inhibitors of protein kinases. J Nat Prod. 2000 Jun;63(6):739-45. | |||||
| REF 49 | Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 3,4-diarylmaleimides as angiogenesis inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2006 Feb 23;49(4):1271-81. | |||||
| REF 50 | 4-arylazo-3,5-diamino-1H-pyrazole CDK inhibitors: SAR study, crystal structure in complex with CDK2, selectivity, and cellular effects. J Med Chem. 2006 Nov 2;49(22):6500-9. | |||||
| REF 51 | 5-Arylamino-2-methyl-4,7-dioxobenzothiazoles as inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and cytotoxic agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2000 Mar 6;10(5):461-4. | |||||
| REF 52 | Synthesis, structure-activity relationship, and biological studies of indolocarbazoles as potent cyclin D1-CDK4 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2003 May 22;46(11):2027-30. | |||||
| REF 53 | Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new tryptamine and tetrahydro-beta-carboline-based selective inhibitors of CDK4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Aug 15;16(16):7728-39. | |||||
| REF 54 | The p16 status of tumor cell lines identifies small molecule inhibitors specific for cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Clin Cancer Res. 1999 Dec;5(12):4279-86. | |||||
| REF 55 | Dissecting the determinants of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor selectivity. J Med Chem. 2006 Sep 7;49(18):5470-7. | |||||
| REF 56 | Potentiation of paclitaxel-induced apoptosis by the novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor NU6140: a possible role for survivin down-regulation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Sep;4(9):1328-37. | |||||
| REF 57 | Imidazole pyrimidine amides as potent, orally bioavailable cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Dec 15;18(24):6486-9. | |||||
| REF 58 | N-Phenyl-4-pyrazolo[1,5-b]pyridazin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-amines as potent and selective inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3 with good cellular effi... J Med Chem. 2004 Sep 9;47(19):4716-30. | |||||
| REF 59 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1976). | |||||
| REF 60 | Structure of CDK4-Cyclin D3 bound to abemaciclib | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

