Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T43814
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter (TIRAP)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adapter protein; TIR domain-containing adapter protein; MyD88-2; MyD88 adapter-like protein; MAL; Adaptor protein Wyatt
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TIRAP
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Acts via IRAK2 and TRAF-6, leading to the activation of NF-kappa-B, MAPK1, MAPK3 and JNK, and resulting in cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. Positively regulates the production of TNF-alpha and interleukin-6. Adapter involved in TLR2 and TLR4 signaling pathways in the innate immune response.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MASSTSLPAPGSRPKKPLGKMADWFRQTLLKKPKKRPNSPESTSSDASQPTSQDSPLPPS
LSSVTSPSLPPTHASDSGSSRWSKDYDVCVCHSEEDLVAAQDLVSYLEGSTASLRCFLQL RDATPGGAIVSELCQALSSSHCRVLLITPGFLQDPWCKYQMLQALTEAPGAEGCTIPLLS GLSRAAYPPELRFMYYVDGRGPDGGFRQVKEAVMRYLQTLS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: (2S,3S)-1,4-Dimercaptobutane-2,3-diol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | S180L variant of TIR domain of Mal/TIRAP | PDB:3UB4 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
SSRWSKDYDV
88 CVCHSEEDLV98 AAQDLVSYLE108 GAIVSELCQA136 LSSSHCRVLL146 ITPGFLQDPW 156 CKYQMLQALT166 EAPGAEGCTI176 PLLLGLSRAA186 YPPELRFMYY196 VDGRGPDGGF 206 RQVKEAVMRY216 LQTLS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
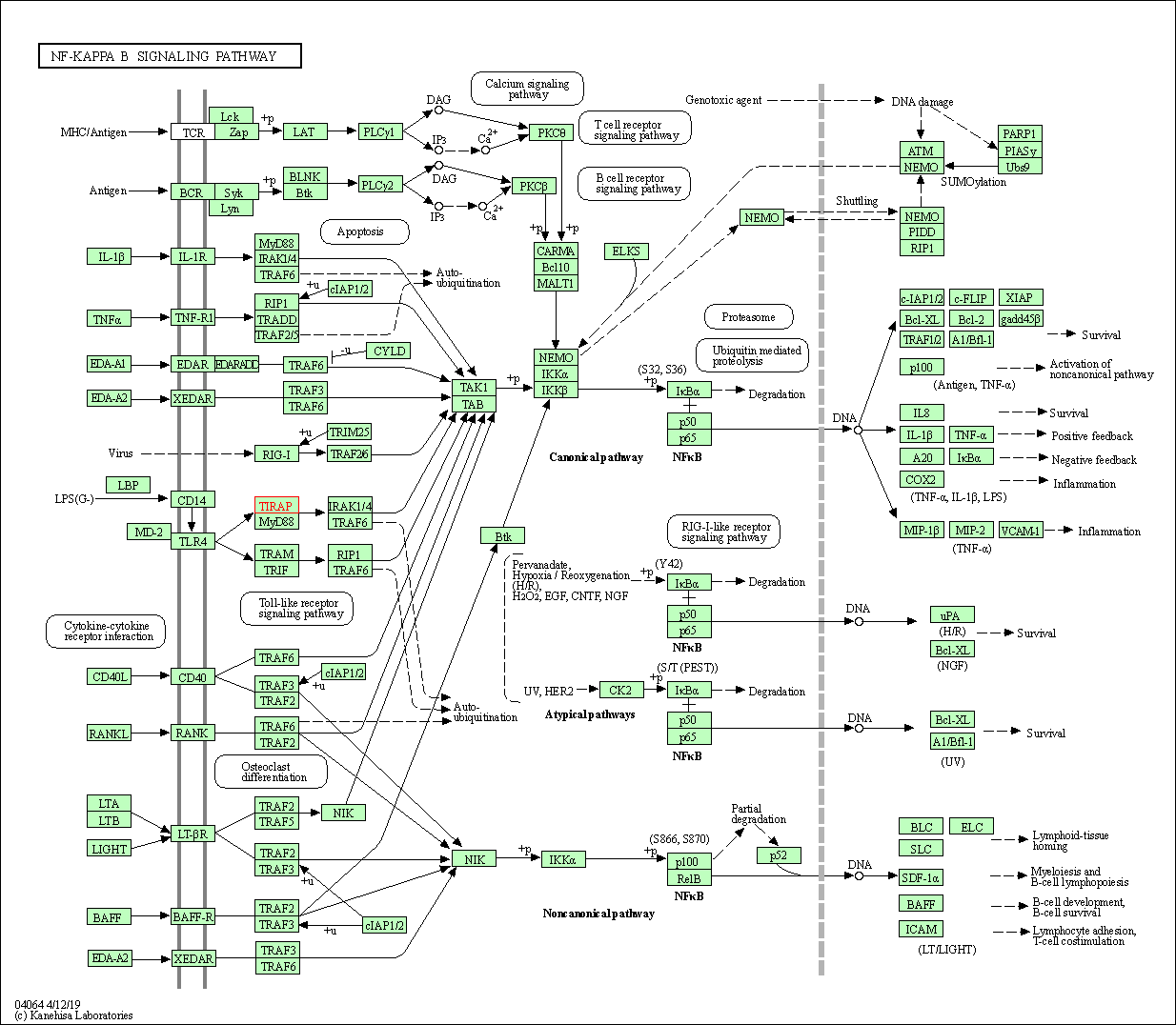
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
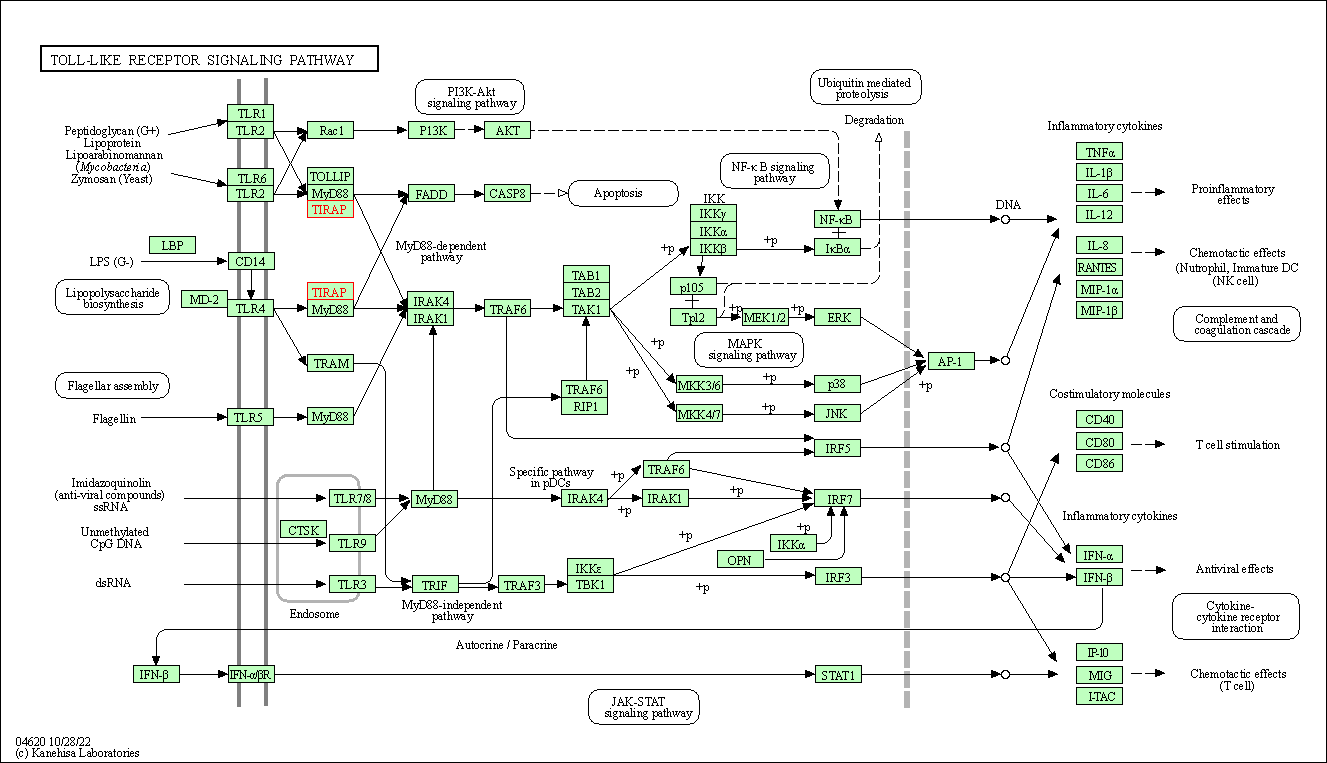
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 11 | Degree centrality | 1.18E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.49E-06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.19E-01 | Radiality | 1.38E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 8.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.91E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.02E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 6 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Pertussis | |||||
| 4 | Tuberculosis | |||||
| 5 | Hepatitis B | |||||
| 6 | PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Aberrant TIRAP and MyD88 expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2013 Jun;51(1):48-55. | |||||
| REF 2 | Structural insights into TIR domain specificity of the bridging adaptor Mal in TLR4 signaling. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34202. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

