Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T31309
(Former ID: TTDC00319)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 (BCL-2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Bcl-2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
BCL2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 4 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C6Y] | |||||
| 2 | Mature B-cell leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A82] | |||||
| 3 | Motor neuron disease [ICD-11: 8B60] | |||||
| 4 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Regulates cell death by controlling the mitochondrial membrane permeability. Appears to function in a feedback loop system with caspases. Inhibits caspase activity either by preventing the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and/or by binding to the apoptosis-activating factor (APAF-1). May attenuate inflammation by impairing NLRP1-inflammasome activation, hence CASP1 activation and IL1B release. Suppresses apoptosis in a variety of cell systems including factor-dependent lymphohematopoietic and neural cells.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
B-cell lymphoma Bcl-2
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAHAGRTGYDNREIVMKYIHYKLSQRGYEWDAGDVGAAPPGAAPAPGIFSSQPGHTPHPA
ASRDPVARTSPLQTPAAPGAAAGPALSPVPPVVHLTLRQAGDDFSRRYRRDFAEMSSQLH LTPFTARGRFATVVEELFRDGVNWGRIVAFFEFGGVMCVESVNREMSPLVDNIALWMTEY LNRHLHTWIQDNGGWDAFVELYGPSMRPLFDFSWLSLKTLLSLALVGACITLGAYLGHK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05519 ; BADD_A06250 ; BADD_A06535 ; BADD_A08298 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T71K92 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 3 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GDC-0199 | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | [2] | |
| 2 | MCI-186 | Drug Info | Approved | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | [3] | |
| 3 | Taxol | Drug Info | Approved | Solid tumour/cancer | [4] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 19 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ABT-263 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Myelofibrosis | [5] | |
| 2 | Oblimersen | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Multiple myeloma | [6], [7] | |
| 3 | RG7601 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | [8] | |
| 4 | Taxol/Paraplatin/Herceptin | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Breast cancer | [9] | |
| 5 | Thymoquinone | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Polycystic ovarian syndrome | [10] | |
| 6 | Gossypol | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Prostate cancer | [11], [12] | |
| 7 | Obatoclax | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [13] | |
| 8 | PI-88/Taxotere | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [14] | |
| 9 | APG-1252 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Small-cell lung cancer | [15] | |
| 10 | APG-2575 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | [16] | |
| 11 | AZD0466 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Hematologic tumour | [17] | |
| 12 | AI-850 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [18], [19] | |
| 13 | BCL201 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Follicular lymphoma | [20] | |
| 14 | BGB-11417 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [21] | |
| 15 | Irofulven/Taxotere | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [22] | |
| 16 | LOXO-338 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Haematological malignancy | [23] | |
| 17 | LP-108 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [24] | |
| 18 | Pc4 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Psoriasis vulgaris | [25] | |
| 19 | VOB560 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Multiple myeloma | [26] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 5 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 9 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GDC-0199 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 2 | Taxol | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 3 | RG7601 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 4 | Taxol/Paraplatin/Herceptin | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 5 | PI-88/Taxotere | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 6 | AI-850 | Drug Info | [18], [19] | |||
| 7 | Irofulven/Taxotere | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 8 | modified HA14-1 compounds (cancer) | Drug Info | [49] | |||
| 9 | WL-276 | Drug Info | [50] | |||
| Regulator (upregulator) | [+] 1 Regulator (upregulator) drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MCI-186 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 24 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ABT-263 | Drug Info | [28], [29], [30] | |||
| 2 | Oblimersen | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 3 | Thymoquinone | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 4 | Obatoclax | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 5 | APG-1252 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 6 | APG-2575 | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 7 | AZD0466 | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 8 | BCL201 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 9 | BGB-11417 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 10 | LOXO-338 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 11 | VOB560 | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 12 | Indole-based analog 2 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 13 | Indole-based analog 3 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 14 | PMID27744724-Compound-10 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 15 | PMID27744724-Compound-18 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 16 | PMID27744724-Compound-21 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 17 | ABT-737 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| 18 | 2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-isopropyl-N-phenyl-benzamide | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 19 | 4,5-dibenzylbenzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| 20 | 5,10-Dioxy-2-phenyl-benzo[g]pteridin-4-ylamine | Drug Info | [47] | |||
| 21 | Apogossypol | Drug Info | [48] | |||
| 22 | N-phenyl-2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-benzyl-benzamide | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 23 | QEDIIRNIARHLAQVGDSMDR | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| 24 | TW-37 | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| Regulator | [+] 1 Regulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Gossypol | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 1 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pc4 | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: ABT-263 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Bcl_2-Navitoclax (ABT-263) Complex | PDB:4LVT | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.05 Å | Mutation | Yes | [27] |
| PDB Sequence |
YDNREIVMKY
16 IHYKLSQRGY26 EWDASEVVHL92 TLRQAGDDFS102 RRYRRDFAEM112 SSQLHLTPFT 122 ARGRFATVVE132 ELFRDGVNWG142 RIVAFFEFGG152 VMCVESVNRE162 MSPLVDNIAL 172 WMTEYLNRHL182 HTWIQDNGGW192 DAFVELYGP
|
|||||
|
|
ALA97
3.618
ASP100
3.648
PHE101
3.508
ARG104
3.413
TYR105
3.363
ASP108
3.449
PHE109
3.665
MET112
3.730
VAL130
3.803
GLU133
3.975
LEU134
3.729
ASN140
3.557
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: 4-(4-{[4-(4-Chlorophenyl)-5,6-Dihydro-2h-Pyran-3-Yl]methyl}piperazin-1-Yl)-N-{[3-Nitro-4-(Tetrahydro-2h-Pyran-4-Ylamino)phenyl]sulfonyl}benzamide | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Bcl_2-Navitoclax Analog (without Thiophenyl) Complex | PDB:4LXD | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | Yes | [27] |
| PDB Sequence |
RTGYDNREIV
13 MKYIHYKLSQ23 RGYEWDAGSE88 VVHLTLRQAG98 DDFSRRYRRD108 FAEMSSQLHL 118 TPFTARGRFA128 TVVEELFRDG138 VNWGRIVAFF148 EFGGVMCVES158 VNREMSPLVD 168 NIALWMTEYL178 NRHLHTWIQD188 NGGWDAFVEL198 YGP
|
|||||
|
|
ALA97
3.599
ASP100
3.327
PHE101
3.729
TYR105
3.348
ASP108
3.701
PHE109
3.702
MET112
3.687
VAL130
3.641
GLU133
3.567
LEU134
3.585
ASN140
3.349
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
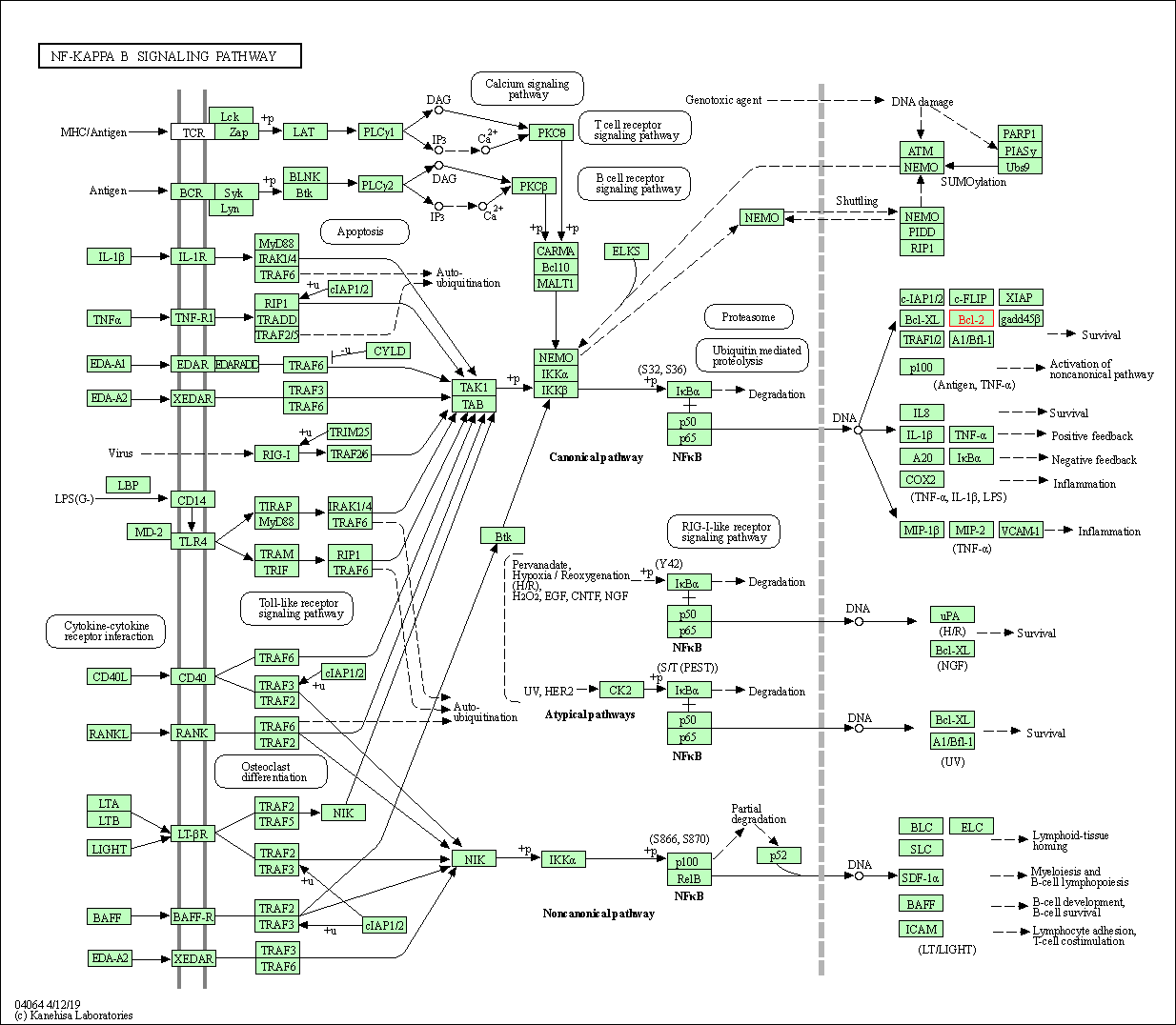
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |
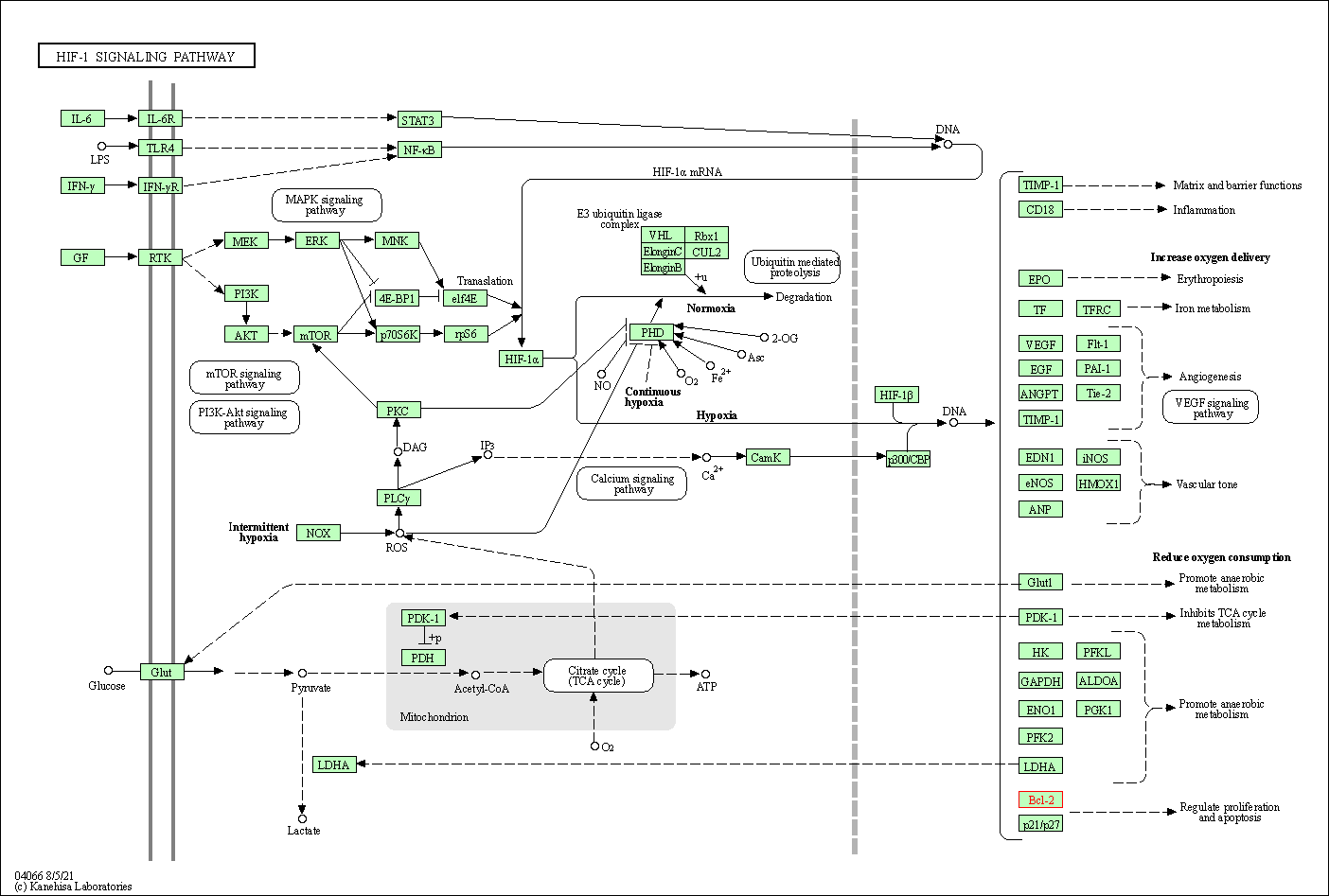
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
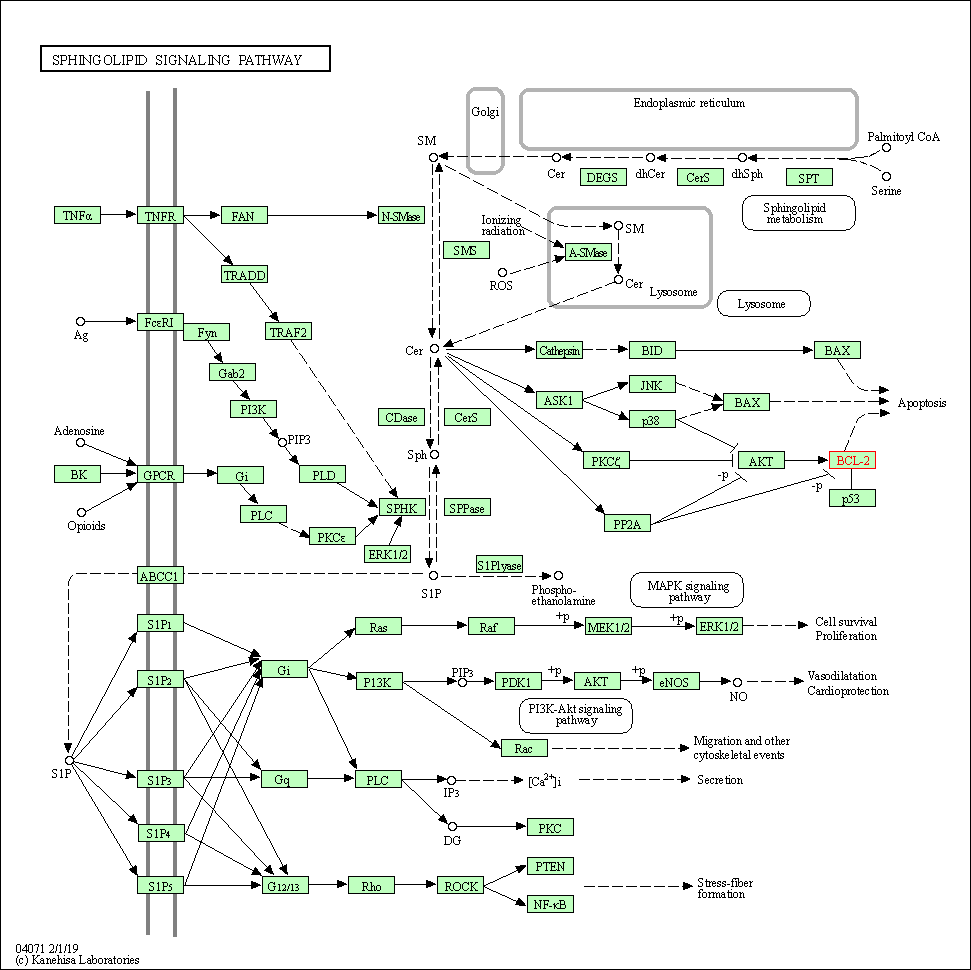
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | Affiliated Target |
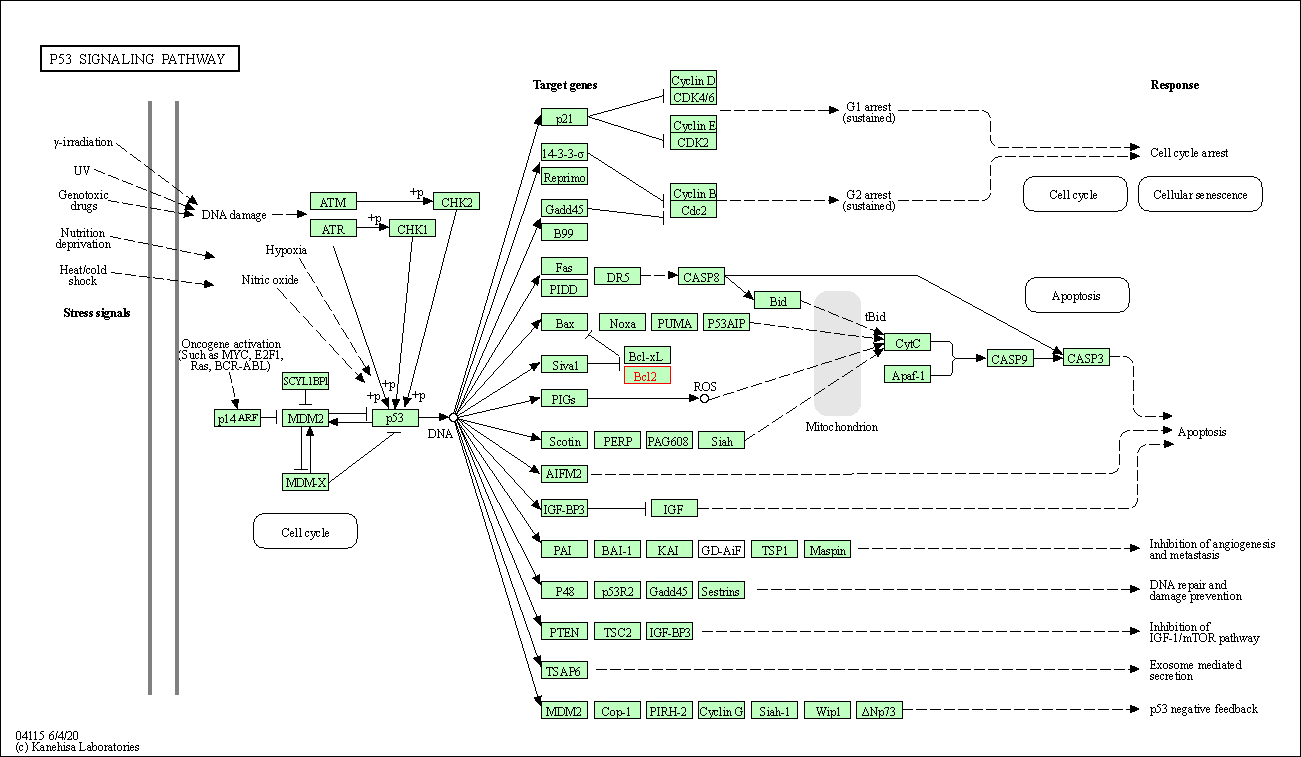
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
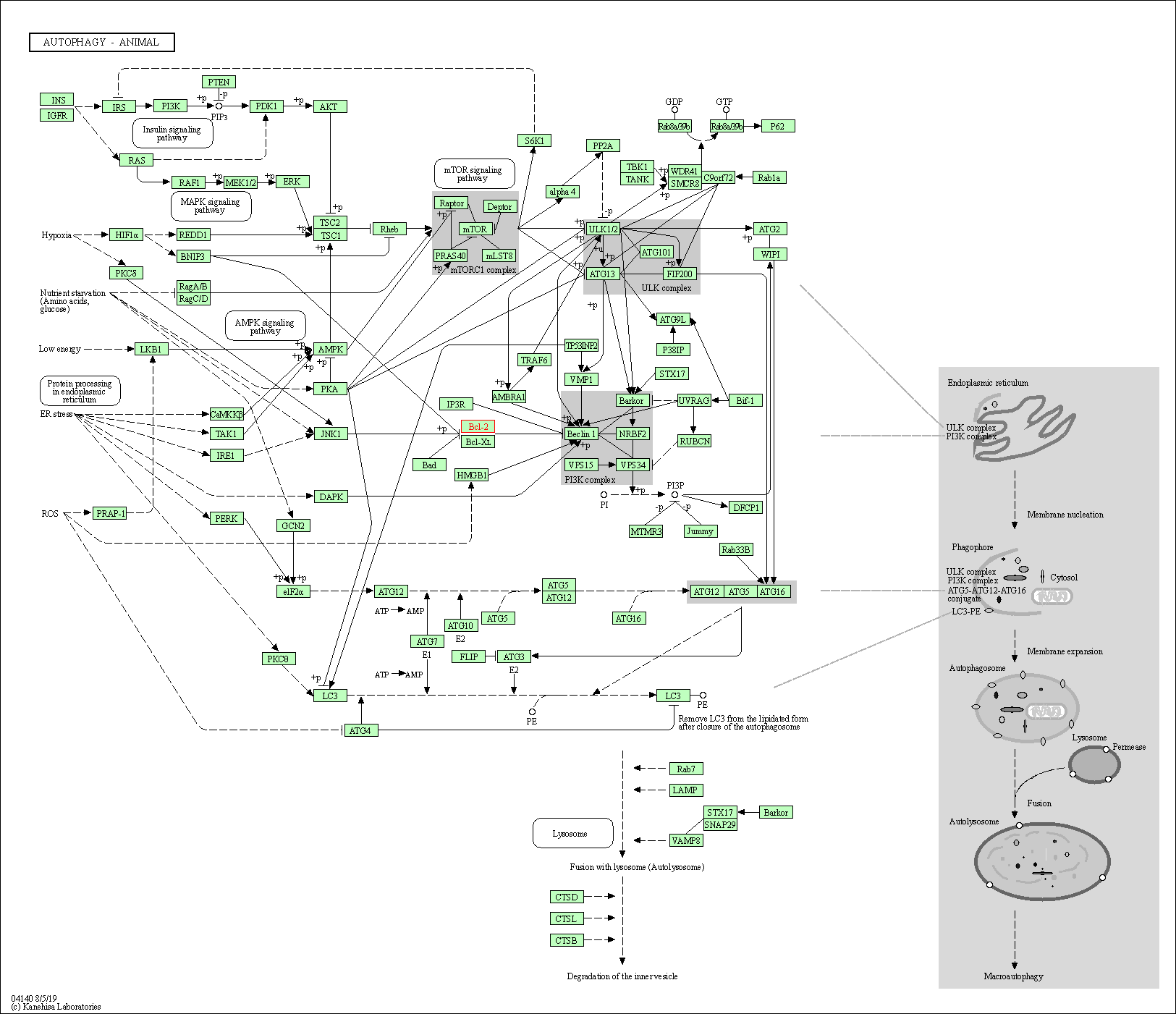
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |
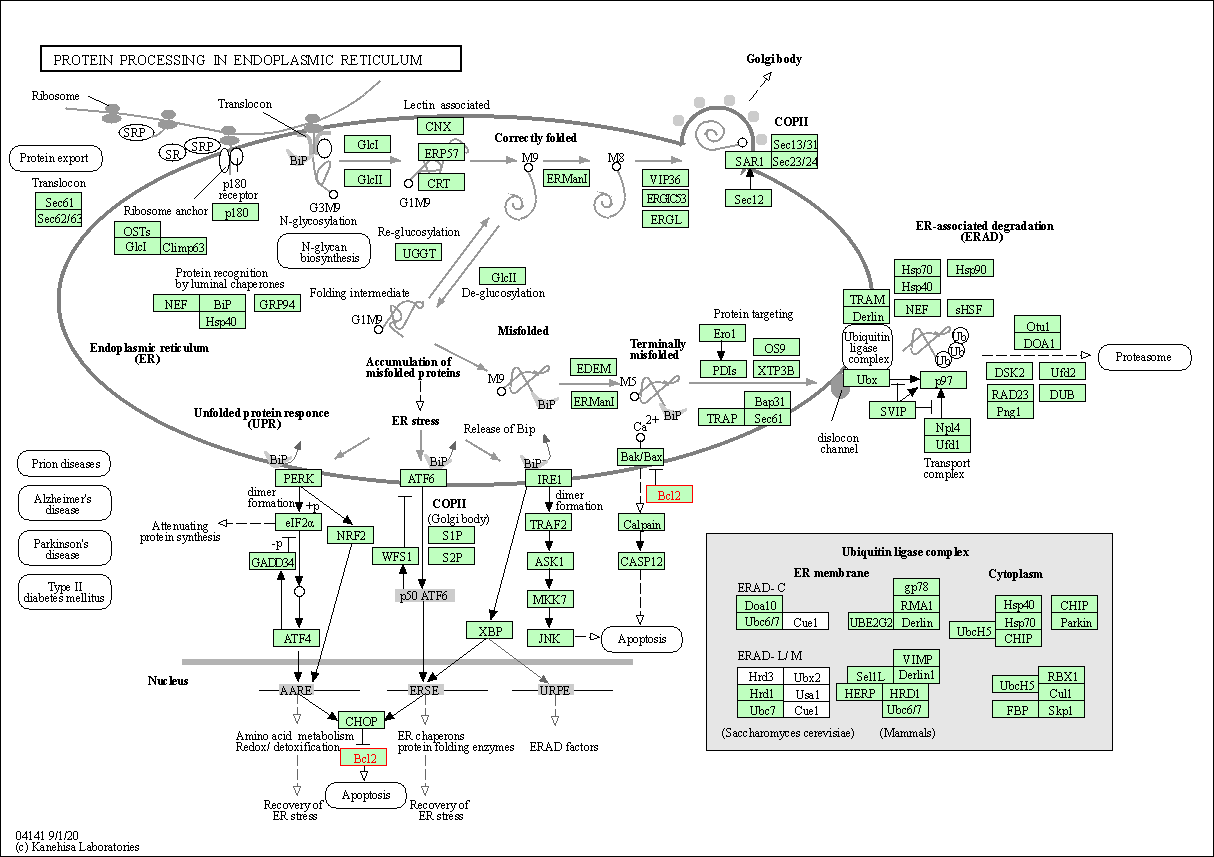
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
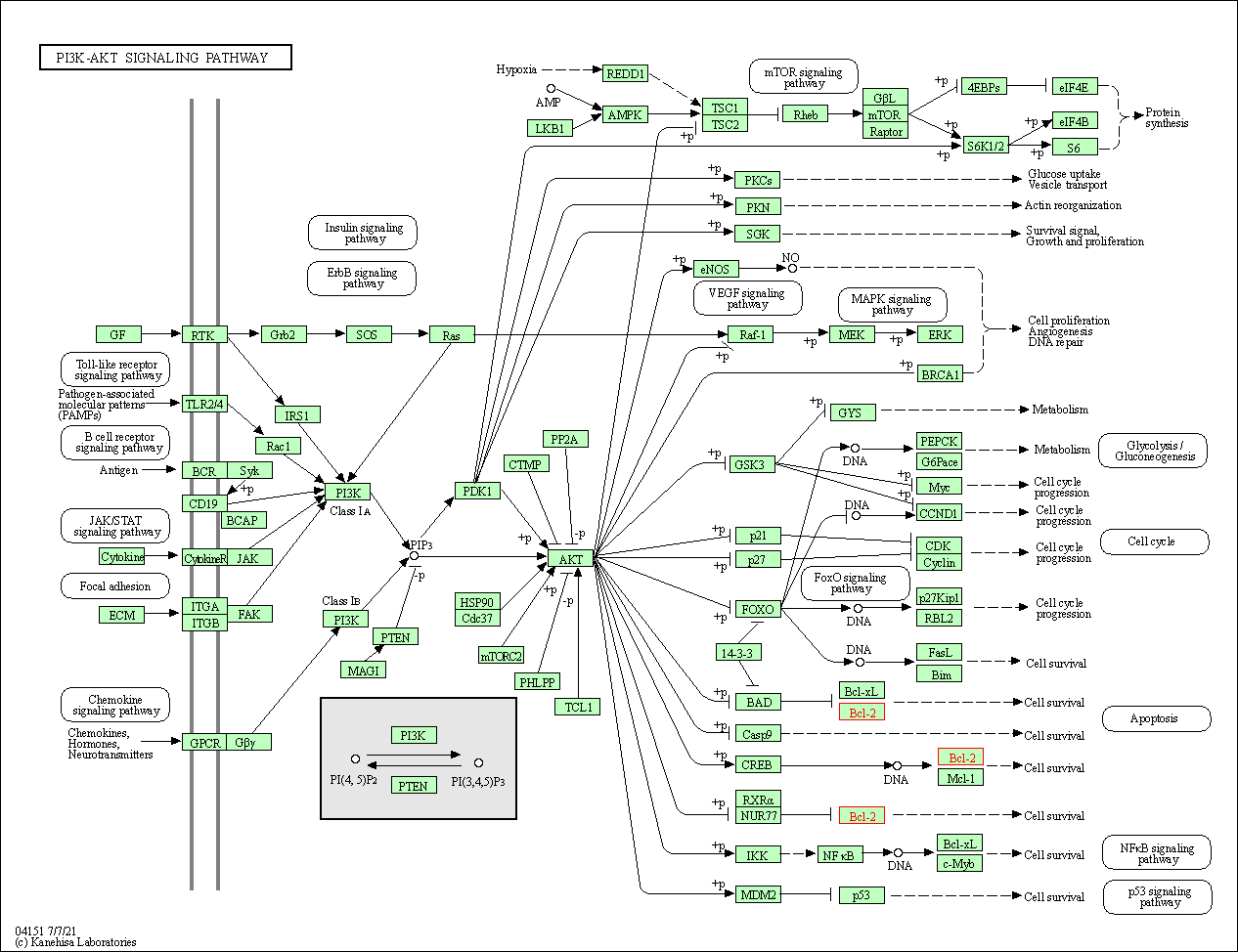
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
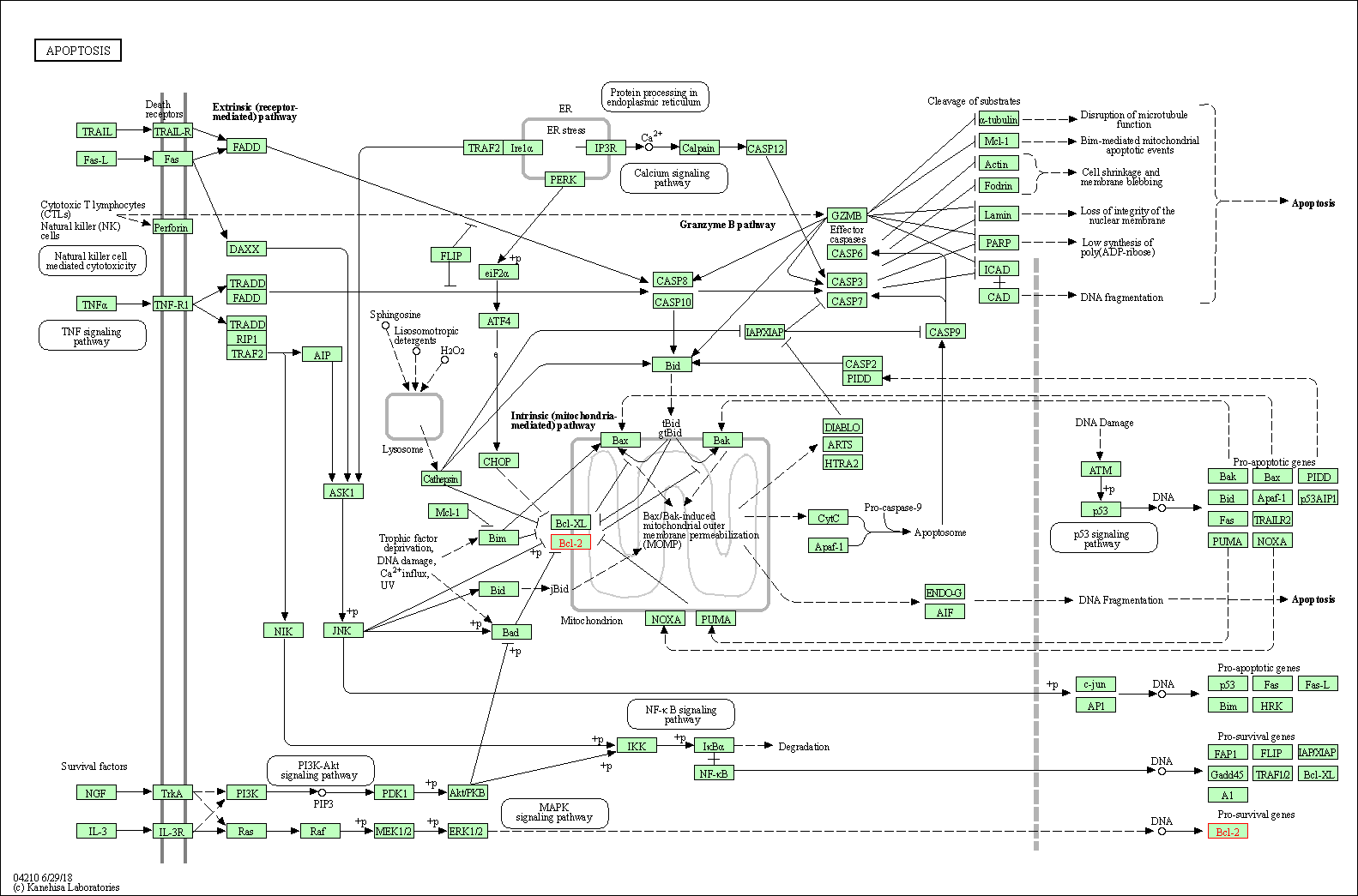
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis - multiple species | hsa04215 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | hsa04340 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04928 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.96E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.44E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.98E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.66E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.59E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging disease-modifying therapies for the treatment of motor neuron disease/amyotropic lateral sclerosis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 May;12(2):229-52. | |||||
| REF 2 | 2016 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Feb 2;16(2):73-76. | |||||
| REF 3 | 2017 FDA drug approvals.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Feb;17(2):81-85. | |||||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04472598) Study of Oral Navitoclax Tablet In Combination With Oral Ruxolitinib Tablet When Compared With Oral Ruxolitinib Tablet To Assess Change In Spleen Volume In Adult Participants With Myelofibrosis (TRANSFORM-1). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8269). | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00024440) Fludarabine and Cyclophosphamide With or Without Oblimersen in Treating Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. U.S. National Institutes ofHealth. | |||||
| REF 8 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800034622) | |||||
| REF 9 | Randomized phase III study of trastuzumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin compared with trastuzumab and paclitaxel in women with HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006 Jun 20;24(18):2786-92. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04852510) Amelioration of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Related Disorders by Supplementation of Thymoquinone and Metformin. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4204). | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00848016) Gossypol Acetic Acid in Treating Patients With Recurrent, Metastatic, or Primary Adrenocortical Cancer That Cannot Be Removed By Surgery. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | Phase II study of obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070), a small-molecule BCL-2 family antagonist, for patients with myelofibrosis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2010 Aug;10(4):285-9. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00268593) Pilot Efficacy Study of PI-88 With Docetaxel to Treat Prostate Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04210037) Study of APG-1252 Plus Paclitaxel in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Small Cell Lung Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04494503) Study of APG2575 Single Agent and Combination Therapy in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory CLL/SLL. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04865419) Study of AZD0466 Monotherapy or in Combination in Patients With Advanced Haematological Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 18 | Intravenous hydrophobic drug delivery: a porous particle formulation of paclitaxel (AI-850). Pharm Res. 2005 Mar;22(3):347-55. | |||||
| REF 19 | Paclitaxel directly binds to Bcl-2 and functionally mimics activity of Nur77. Cancer Res. 2009 Sep 1;69(17):6906-14. | |||||
| REF 20 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 21 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04771130) A Study of BGB-11417 in Participants With Myeloid Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 22 | MGI PHARMA Initiates Drug Combination Trial of Irofulven and Taxotere in Patients With Advanced Cancers; Phase 1 Dose-Escalating Trial to Evaluate Novel Combination Therapy. 2001 Business Wire | |||||
| REF 23 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05024045) A Phase 1 Study of Oral LOXO-338, a Selective BCL-2 Inhibitor, in Patients With Advanced Hematologic Malignancies. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 24 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04139434) Dose-escalation Study of Oral Administration of LP-108 in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS), Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML), or Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 25 | Association between the photodynamic loss of Bcl-2 and the sensitivity to apoptosis caused by phthalocyanine photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol. 2003 Jul;78(1):1-8. | |||||
| REF 26 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04702425) VOB560-MIK665 Combination First in Human Trial in Patients With Hematological Malignancies (Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia, or Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 27 | ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med. 2013 Feb;19(2):202-8. | |||||
| REF 28 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Roche (2009). | |||||
| REF 29 | ABT-263 and rapamycin act cooperatively to kill lymphoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):3265-74. | |||||
| REF 30 | ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008 May 1;68(9):3421-8. | |||||
| REF 31 | Emerging therapies for multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):99-127. | |||||
| REF 32 | Two concurrent phase II trials of paclitaxel/carboplatin/trastuzumab (weekly or every-3-week schedule) as first-line therapy in women with HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: NCCTG study 983252. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005 Dec;6(5):425-32. | |||||
| REF 33 | Apoptosis as a mechanism for the treatment of adult T cell leukemia: promising drugs from benchside to bedside. Drug Discov Today. 2020 Jul;25(7):1189-1197. | |||||
| REF 34 | Opportunities and challenges in antiparasitic drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005 Sep;4(9):727-40. | |||||
| REF 35 | Multicentre phase I/II study of PI-88, a heparanase inhibitor in combination with docetaxel in patients with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010 Jun;21(6):1302-7. | |||||
| REF 36 | Bcl-2/Bcl-xl inhibitor APG-1252-M1 is a promising therapeutic strategy for gastric carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2020 Jun;9(12):4197-4206. | |||||
| REF 37 | A Novel BCL-2 Inhibitor APG-2575 Exerts Synthetic Lethality With BTK or MDM2-p53 Inhibitor in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Oncol Res. 2020 Sep 1;28(4):331-344. | |||||
| REF 38 | Design and optimisation of dendrimer-conjugated Bcl-2/x L inhibitor, AZD0466, with improved therapeutic index for cancer therapy. Commun Biol. 2021 Jan 25;4(1):112. | |||||
| REF 39 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of BeiGene. | |||||
| REF 40 | Antitumor activity of irofulven monotherapy and in combination with mitoxantrone or docetaxel against human prostate cancer models. Prostate. 2004 Apr 1;59(1):22-32. | |||||
| REF 41 | National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary (drug name LP-108). | |||||
| REF 42 | Inhibition of Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins in Preclinical and Clinical Studies: Current Overview in Cancer. Cells. 2020 May 21;9(5):1287. | |||||
| REF 43 | Mcl-1 inhibitors: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Feb;27(2):163-178. | |||||
| REF 44 | Studies leading to potent, dual inhibitors of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. J Med Chem. 2007 Feb 22;50(4):641-62. | |||||
| REF 45 | Structure-based design of potent small-molecule inhibitors of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. J Med Chem. 2006 Oct 19;49(21):6139-42. | |||||
| REF 46 | Vaccinia virus virulence factor N1L is a novel promising target for antiviral therapeutic intervention. J Med Chem. 2010 May 27;53(10):3899-906. | |||||
| REF 47 | Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of Bcl-2 through structure-based computer screening. J Med Chem. 2001 Dec 6;44(25):4313-24. | |||||
| REF 48 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7920). | |||||
| REF 49 | The small-molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor HA14-1 interacts synergistically with flavopiridol to induce mitochondrial injury and apoptosis in human myeloma cells through a free radical-dependent and Jun NH2-terminal kinase-dependent mechanism. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Dec;3(12):1513-24. | |||||
| REF 50 | WL-276, an antagonist against Bcl-2 proteins, overcomes drug resistance and suppresses prostate tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 1;68(11):4377-83. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

