Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T20333
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Proto-oncogene c-Fms; M-CSF-R; FMS; CSF-1R; CSF-1-R; CSF-1 receptor; CD115
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CSF1R
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Bone/articular cartilage neoplasm [ICD-11: 2F7B] | |||||
| Function |
Promotes the release of proinflammatory chemokines in response to IL34 and CSF1, and thereby plays an important role in innate immunity and in inflammatory processes. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoclast proliferation and differentiation, the regulation of bone resorption, and is required for normal bone and tooth development. Required for normal male and female fertility, and for normal development of milk ducts and acinar structures in the mammary gland during pregnancy. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, regulates formation of membrane ruffles, cell adhesion and cell migration, and promotes cancer cell invasion. Activates several signaling pathways in response to ligand binding. Phosphorylates PIK3R1, PLCG2, GRB2, SLA2 and CBL. Activation of PLCG2 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, that then lead to the activation of protein kinase C family members, especially PRKCD. Phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leads to activation of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Activated CSF1R also mediates activation of the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1, and of the SRC family kinases SRC, FYN and YES1. Activated CSF1R transmits signals both via proteins that directly interact with phosphorylated tyrosine residues in its intracellular domain, or via adapter proteins, such as GRB2. Promotes activation of STAT family members STAT3, STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Promotes tyrosine phosphorylation of SHC1 and INPP5D/SHIP-1. Receptor signaling is down-regulated by protein phosphatases, such as INPP5D/SHIP-1, that dephosphorylate the receptor and its downstream effectors, and by rapid internalization of the activated receptor. Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for CSF1 and IL34 and plays an essential role in the regulation of survival, proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic precursor cells, especially mononuclear phagocytes, such as macrophages and monocytes.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MGPGVLLLLLVATAWHGQGIPVIEPSVPELVVKPGATVTLRCVGNGSVEWDGPPSPHWTL
YSDGSSSILSTNNATFQNTGTYRCTEPGDPLGGSAAIHLYVKDPARPWNVLAQEVVVFED QDALLPCLLTDPVLEAGVSLVRVRGRPLMRHTNYSFSPWHGFTIHRAKFIQSQDYQCSAL MGGRKVMSISIRLKVQKVIPGPPALTLVPAELVRIRGEAAQIVCSASSVDVNFDVFLQHN NTKLAIPQQSDFHNNRYQKVLTLNLDQVDFQHAGNYSCVASNVQGKHSTSMFFRVVESAY LNLSSEQNLIQEVTVGEGLNLKVMVEAYPGLQGFNWTYLGPFSDHQPEPKLANATTKDTY RHTFTLSLPRLKPSEAGRYSFLARNPGGWRALTFELTLRYPPEVSVIWTFINGSGTLLCA ASGYPQPNVTWLQCSGHTDRCDEAQVLQVWDDPYPEVLSQEPFHKVTVQSLLTVETLEHN QTYECRAHNSVGSGSWAFIPISAGAHTHPPDEFLFTPVVVACMSIMALLLLLLLLLLYKY KQKPKYQVRWKIIESYEGNSYTFIDPTQLPYNEKWEFPRNNLQFGKTLGAGAFGKVVEAT AFGLGKEDAVLKVAVKMLKSTAHADEKEALMSELKIMSHLGQHENIVNLLGACTHGGPVL VITEYCCYGDLLNFLRRKAEAMLGPSLSPGQDPEGGVDYKNIHLEKKYVRRDSGFSSQGV DTYVEMRPVSTSSNDSFSEQDLDKEDGRPLELRDLLHFSSQVAQGMAFLASKNCIHRDVA ARNVLLTNGHVAKIGDFGLARDIMNDSNYIVKGNARLPVKWMAPESIFDCVYTVQSDVWS YGILLWEIFSLGLNPYPGILVNSKFYKLVKDGYQMAQPAFAPKNIYSIMQACWALEPTHR PTFQQICSFLQEQAQEDRRERDYTNLPSSSRSGGSGSSSSELEEESSSEHLTCCEQGDIA QPLLQPNNYQFC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pexidartinib | Drug Info | Approved | Tenosynovial giant cell tumour | [2] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 14 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sulfatinib | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Neuroendocrine cancer | [3] | |
| 2 | AMB-05X | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | [4] | |
| 3 | ARRY-382 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [1] | |
| 4 | BLZ-945 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | [5] | |
| 5 | Cabiralizumab | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [1], [6] | |
| 6 | DCC-3014 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [7] | |
| 7 | FPA-008 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Autoimmune diabetes | [8] | |
| 8 | ABSK021 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [9] | |
| 9 | Axatilamab | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [10] | |
| 10 | DCC-3014 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Haematological malignancy | [1] | |
| 11 | EI1071 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [11] | |
| 12 | PLX7486 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Pancreatic cancer | [12] | |
| 13 | SNDX-6352 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [1], [6] | |
| 14 | TPX-0022 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [13] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 15 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pexidartinib | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 2 | Sulfatinib | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | ARRY-382 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 4 | DCC-3014 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 5 | ABSK021 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 6 | DCC-3014 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 7 | EI1071 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 8 | PLX7486 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 9 | TPX-0022 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 10 | PMID28270010-Compound-Figure24-a | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 11 | Pyridine derivative 18 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 12 | Pyridine derivative 19 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 13 | Pyridine derivative 20 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 14 | Pyridine derivative 21 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 15 | Pyridine derivative 22 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 4 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BLZ-945 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Cabiralizumab | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 3 | Axatilamab | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 4 | SNDX-6352 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Imatinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of FMS kinase domain with a small molecular inhibitor, GLEEVEC | PDB:4R7I | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.75 Å | Mutation | Yes | [23] |
| PDB Sequence |
TQLPYNEKWE
576 FPRNNLQFGK586 TLGAGAFGKV596 VEATAFGLGK606 EDAVLKVAVK616 MLKSTAHADE 626 KEALMSELKI636 MSHLGQHENI646 VNLLGACTHG656 GPVLVITEYC666 TYGDLLNFLR 676 RKAEAMLGPS686 LSGRPLELRD754 LLHFSSQVAQ764 GMAFLASKNC774 IHRDVAARNV 784 LLTNGHVAKI794 GDFGLARDIM804 NDSNYIVKGN814 ARLPVKWMAP824 ESIFDSVYTV 834 QSDVWSYGIL844 LWEIFSLGLN854 PYPGILVNSK864 FYKLVKDGYQ874 MAQPAFAPKN 884 IYSIMQACWA894 LEPTHRPTFQ904 QITSFLQEQA914
|
|||||
|
|
LEU588
3.904
VAL596
3.512
ALA614
3.781
VAL615
4.110
LYS616
3.473
GLU633
2.983
ILE636
4.242
MET637
3.600
LEU640
4.354
VAL647
3.814
VAL661
3.834
THR663
3.028
GLU664
4.110
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Pexidartinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of FMS KINASE domain with a small molecular inhibitor, PLX3397 | PDB:4R7H | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.80 Å | Mutation | Yes | [23] |
| PDB Sequence |
PKYQVRWKII
553 ESYTFIDPTQ568 LPYNEKWEFP578 RNNLQFGKTL588 GAGAFGKVVE598 ATAFGLGKED 608 AVLKVAVKML618 KSTAHADEKE628 ALMSELKIMS638 HLGQHENIVN648 LLGACTHGGP 658 VLVITEYCTY668 GDLLNFLRRK678 AEAMLGPSLG747 RPLELRDLLH757 FSSQVAQGMA 767 FLASKNCIHR777 DVAARNVLLT787 NGHVAKIGDF797 GLARDIMNDS807 NYIVKGNARL 817 PVKWMAPESI827 FDSVYTVQSD837 VWSYGILLWE847 IFSLGLNPYP857 GILVNSKFYK 867 LVKDGYQMAQ877 PAFAPKNIYS887 IMQACWALEP897 THRPTFQQIT907 SFLQEQAQ |
|||||
|
|
VAL548
4.225
ARG549
3.782
TRP550
2.699
LEU588
3.694
VAL596
3.980
ALA614
3.361
LYS616
3.909
SER632
4.469
GLU633
3.016
ILE636
3.612
MET637
3.473
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
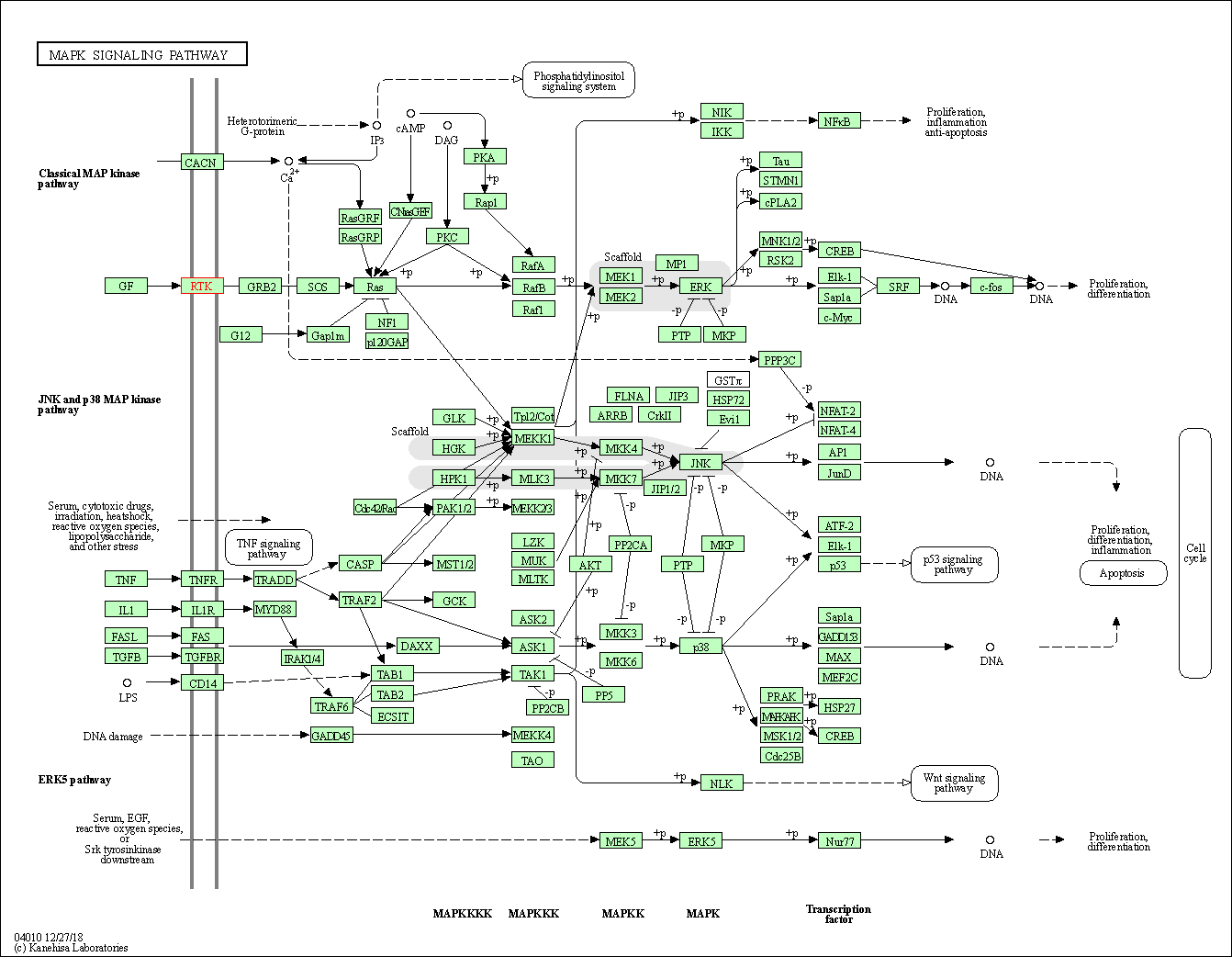
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
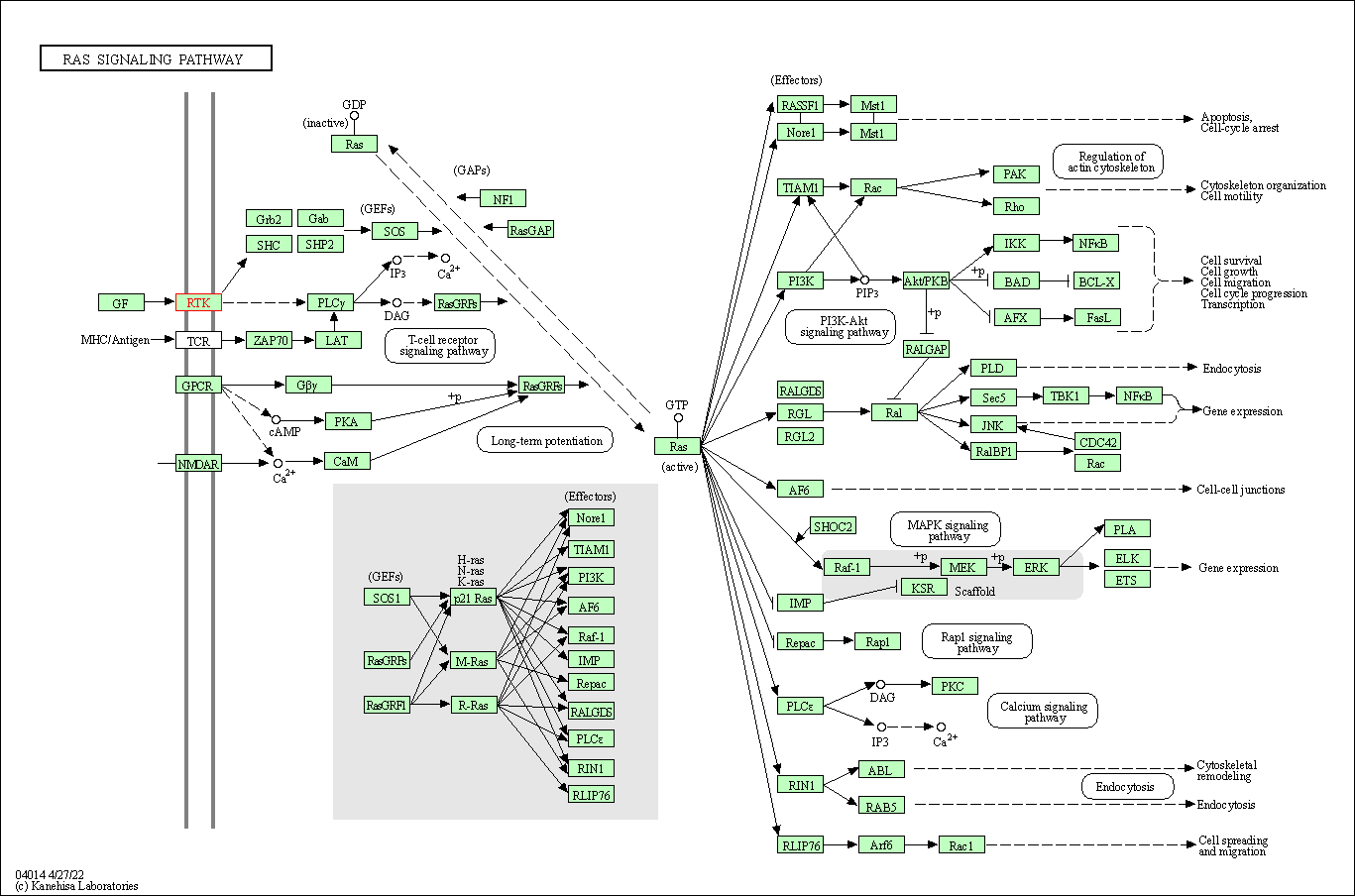
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |
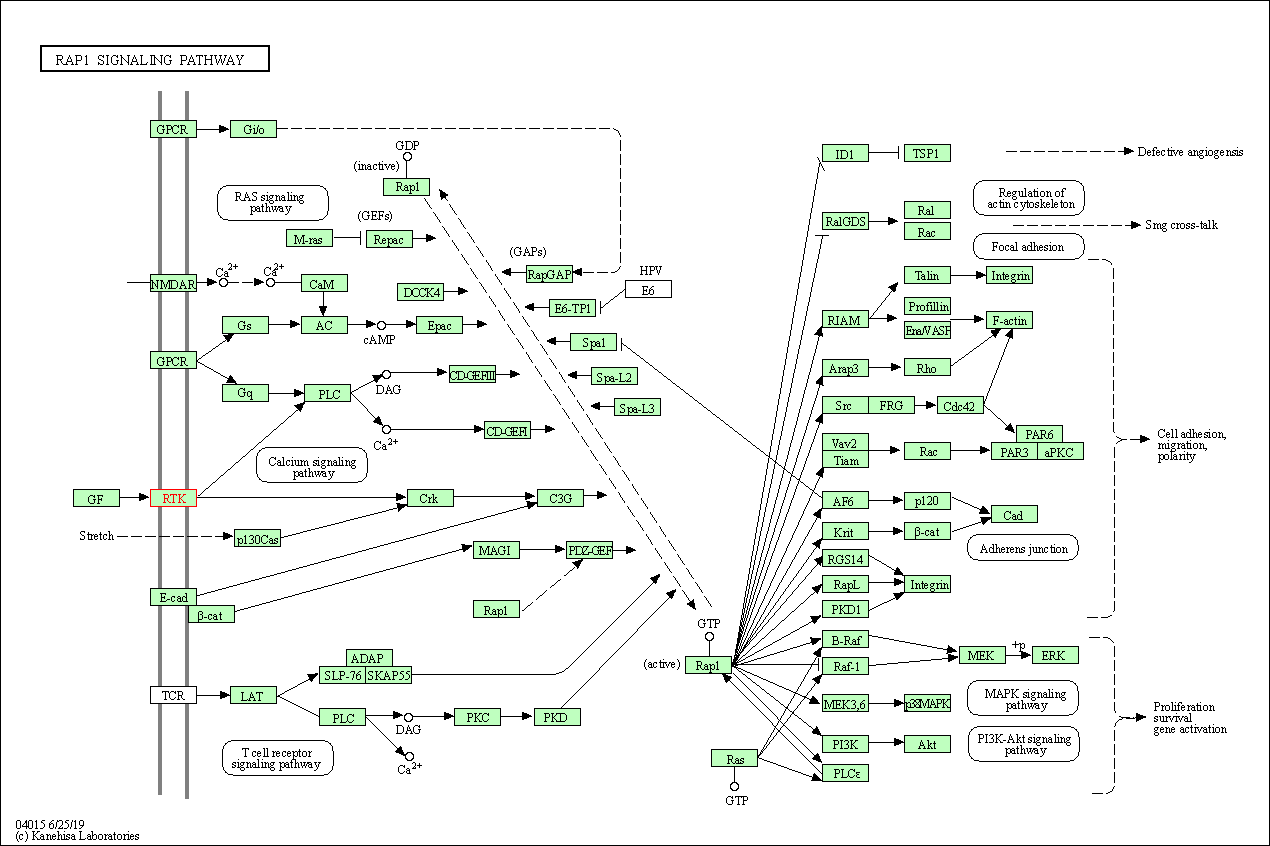
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |
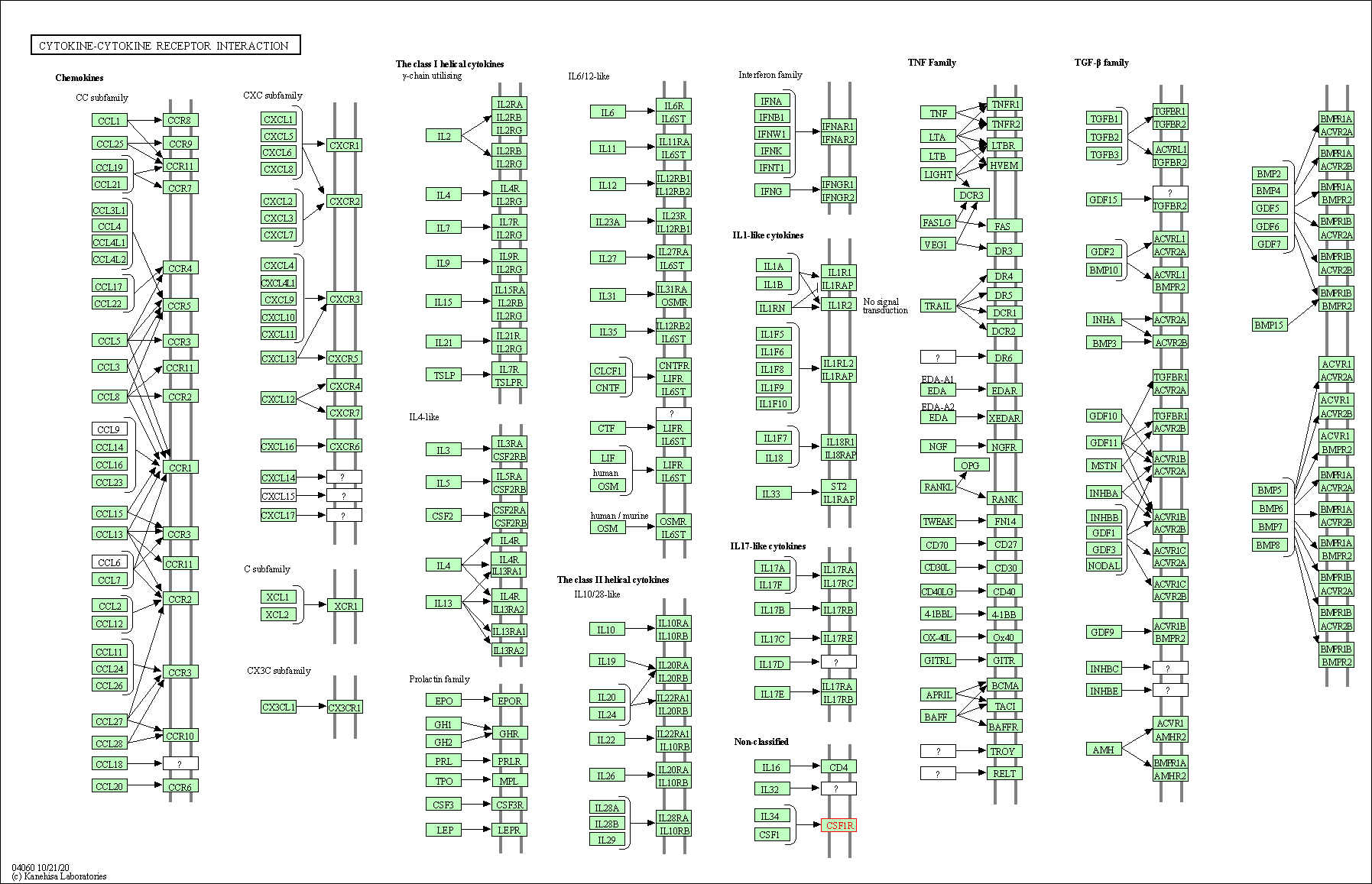
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | hsa04061 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | hsa04640 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 4.60E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.29E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.97E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.71E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 11 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | MAPK signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Ras signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Rap1 signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 5 | Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor | |||||
| 6 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 7 | Osteoclast differentiation | |||||
| 8 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | |||||
| 9 | Pathways in cancer | |||||
| 10 | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | |||||
| 11 | Acute myeloid leukemia | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health Human Services. 2019 | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02589821) Phase III Study of Surufatinib in Treating Advanced Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05349760) A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Preliminary Efficacy of AMB-05X in Subjects With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04066244) Study of Safety and of the Mechanism of BLZ945 in ALS Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03069469) Study of DCC-3014 in Patients With Advanced Tumors and Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800039179) | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04192344) A Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of ABSK021 in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumor. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03238027) A Phase 1 Study to Investigate SNDX-6352 Alone or in Combination With Durvalumab in Patients With Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04238364) A Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability and Amount of Drug Levels in Blood of EI1071 in Healthy Volunteers. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800038879) | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03993873) Phase 1 Study of TPX-0022, a MET/CSF1R/SRC Inhibitor, in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors Harboring Genetic Alterations in MET. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AmMax Bio | |||||
| REF 15 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Deciphera Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 16 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 17 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Abbisko Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 18 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Syndax Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 19 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Elixiron Immunotherapeutics. | |||||
| REF 20 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Turning Point Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 21 | Tropomyosin receptor kinase inhibitors: an updated patent review for 2010-2016 - Part I.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Jun;27(6):733-751. | |||||
| REF 22 | RET kinase inhibitors: a review of recent patents (2012-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Jan;27(1):91-99. | |||||
| REF 23 | Structure-Guided Blockade of CSF1R Kinase in Tenosynovial Giant-Cell Tumor. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 30;373(5):428-37. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

