Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T04388
(Former ID: TTDI03309)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Calcium-activated potassium channel KCa2.3 (KCNN3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 3; SKCa3; SKCa 3; SK3; KCa2.3; K3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KCNN3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Myelopathy [ICD-11: 8B42] | |||||
| Function |
Forms a voltage-independent potassium channel activated by intracellular calcium. Activation is followed by membrane hyperpolarization. Thought to regulate neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic afterhyperpolarization. The channel is blocked by apamin.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Voltage-gated ion channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MDTSGHFHDSGVGDLDEDPKCPCPSSGDEQQQQQQQQQQQQPPPPAPPAAPQQPLGPSLQ
PQPPQLQQQQQQQQQQQQQQPPHPLSQLAQLQSQPVHPGLLHSSPTAFRAPPSSNSTAIL HPSSRQGSQLNLNDHLLGHSPSSTATSGPGGGSRHRQASPLVHRRDSNPFTEIAMSSCKY SGGVMKPLSRLSASRRNLIEAETEGQPLQLFSPSNPPEIVISSREDNHAHQTLLHHPNAT HNHQHAGTTASSTTFPKANKRKNQNIGYKLGHRRALFEKRKRLSDYALIFGMFGIVVMVI ETELSWGLYSKDSMFSLALKCLISLSTIILLGLIIAYHTREVQLFVIDNGADDWRIAMTY ERILYISLEMLVCAIHPIPGEYKFFWTARLAFSYTPSRAEADVDIILSIPMFLRLYLIAR VMLLHSKLFTDASSRSIGALNKINFNTRFVMKTLMTICPGTVLLVFSISLWIIAAWTVRV CERYHDQQDVTSNFLGAMWLISITFLSIGYGDMVPHTYCGKGVCLLTGIMGAGCTALVVA VVARKLELTKAEKHVHNFMMDTQLTKRIKNAAANVLRETWLIYKHTKLLKKIDHAKVRKH QRKFLQAIHQLRSVKMEQRKLSDQANTLVDLSKMQNVMYDLITELNDRSEDLEKQIGSLE SKLEHLTASFNSLPLLIADTLRQQQQQLLSAIIEARGVSVAVGTTHTPISDSPIGVSSTS FPTPYTSSSSC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | dequalinium | Drug Info | Clinical trial | Myelopathy | [1] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Blocker (channel blocker) | [+] 5 Blocker (channel blocker) drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | dequalinium | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | apamin | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 3 | UCL1684 | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 4 | UCL1848 | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 5 | [14C]TEA | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Activator | [+] 3 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CyPPA | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 2 | DC-EBIO | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | EBIO | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
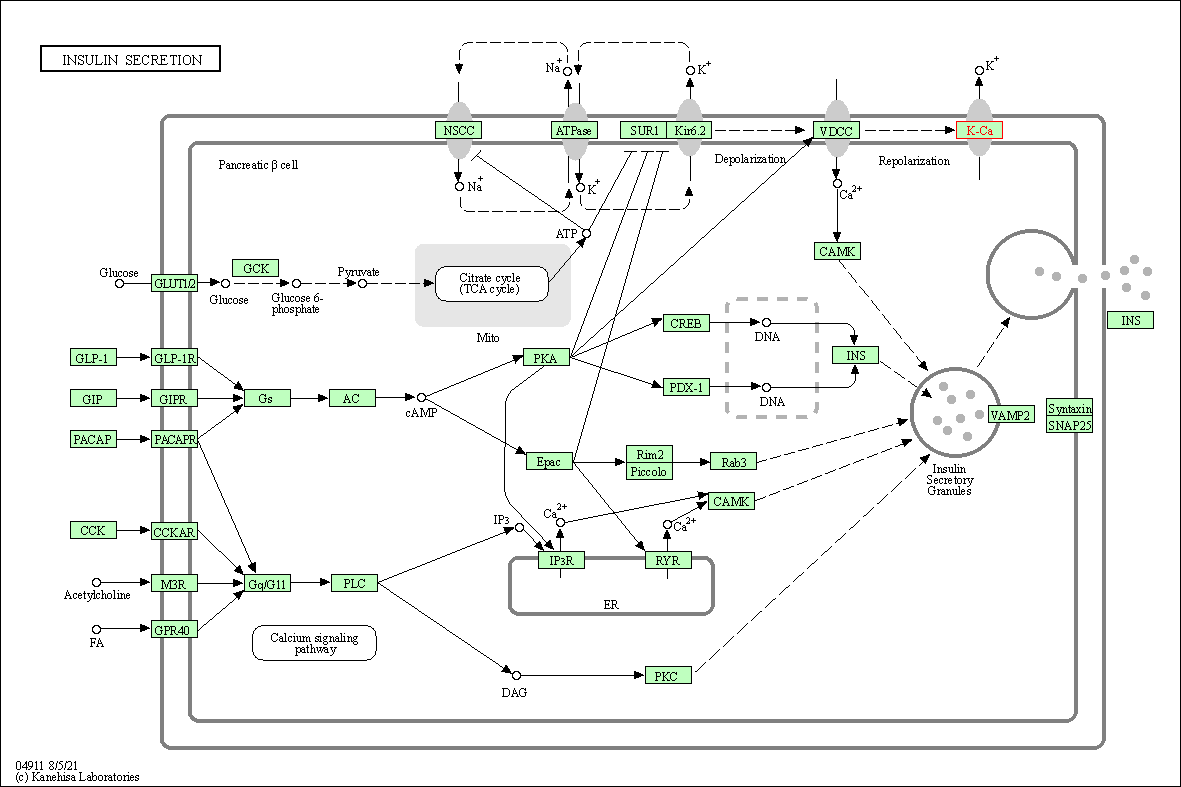
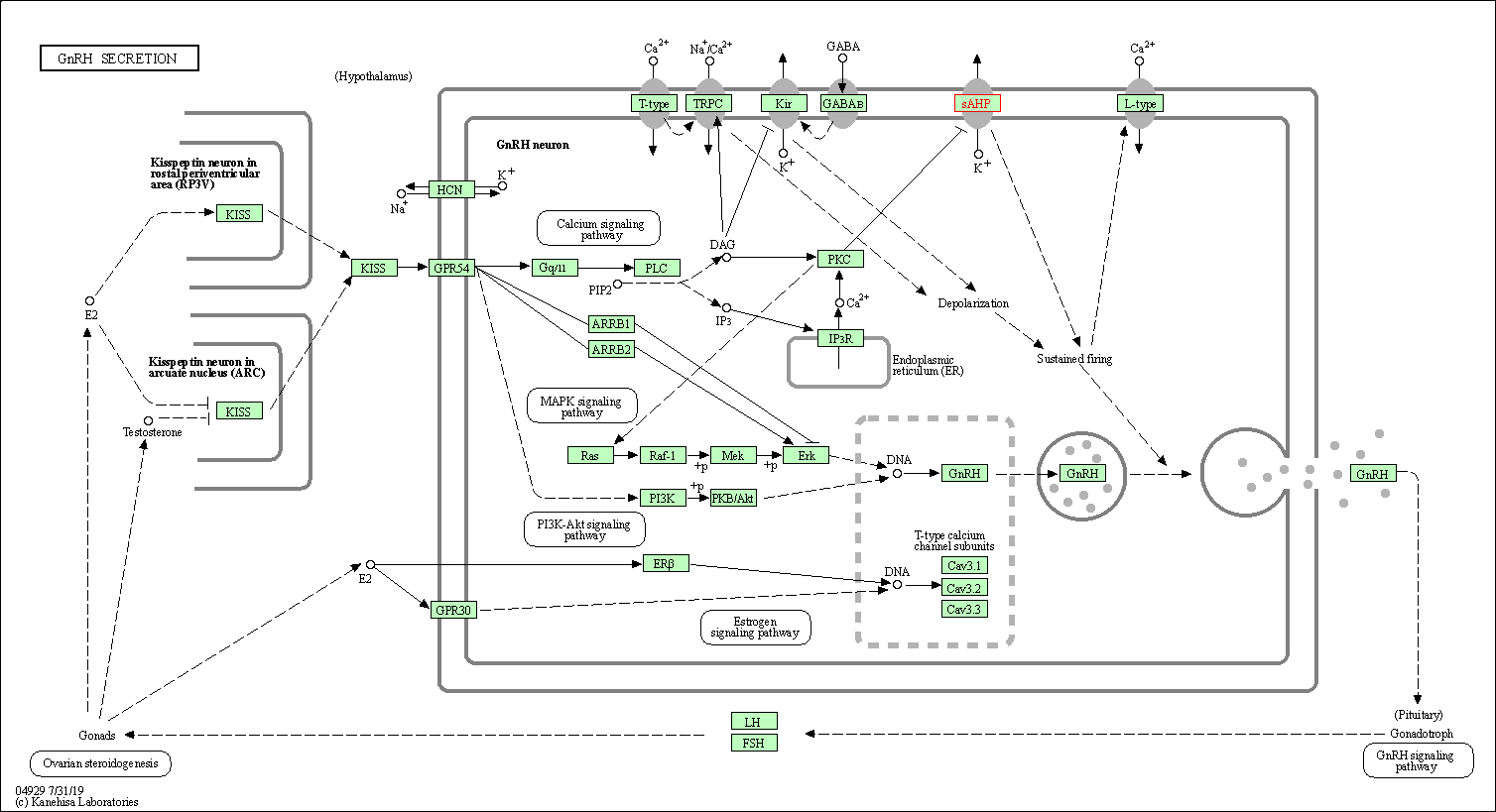
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.21E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.75E-01 | Radiality | 1.28E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.33E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.33E+00 | Topological coefficient | 4.00E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Pharmacological characterisation of the human small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel hSK3 reveals sensitivity to tricyclic antidepressants and antipsychotic phenothiazines. Neuropharmacology. 2001 May;40(6):772-83. | |||||
| REF 2 | SK3 is an important component of K(+) channels mediating the afterhyperpolarization in cultured rat SCG neurones. J Physiol. 2001 Sep 1;535(Pt 2):323-34. | |||||
| REF 3 | Selective positive modulation of the SK3 and SK2 subtypes of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;151(5):655-65. | |||||
| REF 4 | Modulators of small- and intermediate-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels and their therapeutic indications. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(13):1437-57. | |||||
| REF 5 | Small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels: from structure to function. Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Jul;91(3):242-55. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

