Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T98278
|
|||||
| Target Name |
HUMAN type-1 angiotensin II receptor (AGTR1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type-1 angiotensin II receptor; Angiotensin II type-1 receptor; Angiotensin II receptor 1; Angiotensin 1 receptor; AT2R1B; AT2R1; AT1BR; AT1AR; AT1; AGTR1B; AGTR1A
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
AGTR1
|
|||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00-BA04] | |||||
| Function |
Mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Receptor for angiotensin II.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MILNSSTEDGIKRIQDDCPKAGRHNYIFVMIPTLYSIIFVVGIFGNSLVVIVIYFYMKLK
TVASVFLLNLALADLCFLLTLPLWAVYTAMEYRWPFGNYLCKIASASVSFNLYASVFLLT CLSIDRYLAIVHPMKSRLRRTMLVAKVTCIIIWLLAGLASLPAIIHRNVFFIENTNITVC AFHYESQNSTLPIGLGLTKNILGFLFPFLIILTSYTLIWKALKKAYEIQKNKPRNDDIFK IIMAIVLFFFFSWIPHQIFTFLDVLIQLGIIRDCRIADIVDTAMPITICIAYFNNCLNPL FYGFLGKKFKRYFLQLLKYIPPKAKSHSNLSTKMSTLSYRPSDNVSSSTKKPAPCFEVE Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investigative Agents | [+] 1 | + | ||||
| 1 | Irbesartan | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [2] | |
| Drugs in Phase 3 Trial | [+] 2 | + | ||||
| 1 | Losartan | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [3] | |
| 2 | Telmisartan | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Blocker | [+] 2 Blocker drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Losartan | Drug Info | [5], [6] | |||
| 2 | Telmisartan | Drug Info | [5], [7] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 1 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Irbesartan | Drug Info | [8], [9] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: ZD-7155 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | XFEL structure of human Angiotensin Receptor | PDB:4YAY | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.90 Å | Mutation | Yes | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
DLEDNWETLN
1011 DNLKVIEKAD1021 NAAQVKDALT1031 KMRAAALDAQ1041 KATPPKLEDK1051 SPDSPEMKDF 1061 RHGFDILVGQ1071 IDDALKLANE1081 GKVKEAQAAA1091 EQLKTTRNAY1101 IQKYLILNSS 16 DCPKAGRHNY26 IFVMIPTLYS36 IIFVVGIFGN46 SLVVIVIYFY56 MKLKTVASVF 66 LLNLALADLC76 FLLTLPLWAV86 YTAMEYRWPF96 GNYLCKIASA106 SVSFNLYASV 116 FLLTCLSIDR126 YLAIVHPMKS136 RLRRTMLVAK146 VTCIIIWLLA156 GLASLPAIIH 166 RNVFFIITVC180 AFHYETLPIG194 LGLTKNILGF204 LFPFLIILTS214 YTLIWKALKK 224 NDDIFKIIMA244 IVLFFFFSWI254 PHQIFTFLDV264 LIQLGIIRDC274 RIADIVDTAM 284 PITICIAYFN294 NCLNPLFYGF304 LGKKFKRYFL314 QLL
|
|||||
|
|
ILE31
4.353
TYR35
2.990
PHE77
3.956
LEU81
4.533
TRP84
3.484
TYR87
4.014
THR88
3.264
TYR92
4.774
ALA104
4.937
SER105
3.110
VAL108
3.679
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Cholesterol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of synthetic nanobody-stabilized angiotensin II type 1 receptor bound to TRV026 | PDB:6OS2 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.70 Å | Mutation | Yes | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
IKRIQDDCPK
20 AGRHNYIFVM30 IPTLYSIIFV40 VGIFGNSLVV50 IVIYFYMKLK60 TVASVFLLNL 70 ALADLCFLLT80 LPLWAVYTAM90 EYRWPFGNYL100 CKIASASVSF110 NLYASVFLLT 120 CLSIDRYLAI130 VHPMKSRLRR140 TMLVAKVTCI150 IIWLLAGLAS160 LPAIIHRNVF 170 FIENTNITVC180 AFHYESQNST190 LPIGLGLTKN200 ILGFLFPFLI210 ILTSYTLIWK 220 ALKKAYDLED230 NWETLNDNLK240 VIEKADNAAQ250 VKDALTKMRA260 AALDAQKAHG 289 FDILVGQIDD299 ALKLANEGKV309 KEAQAAAEQL319 KKNKPRNDDI1238 FKIIMAIVLF 1248 FFFSWIPHQI1258 FTFLDVLIQL1268 GIIRDCRIAD1278 IVDTAMPITI1288 CIAYFNNCLN 1298 PLFYGFLGKK1308 FKRYFLQLLK1318
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Renin-angiotensin system | hsa04614 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
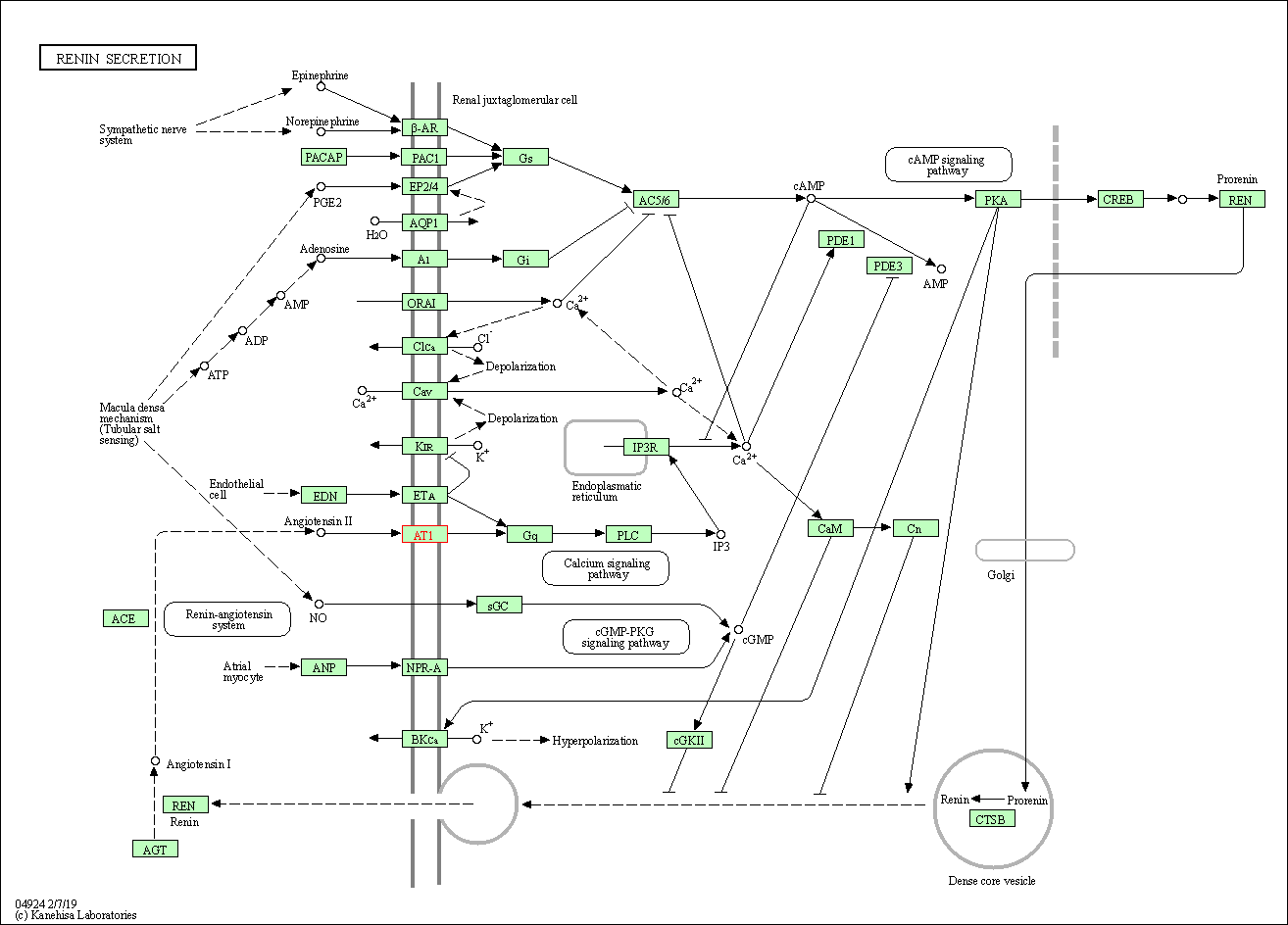
| Renin secretion | hsa04924 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
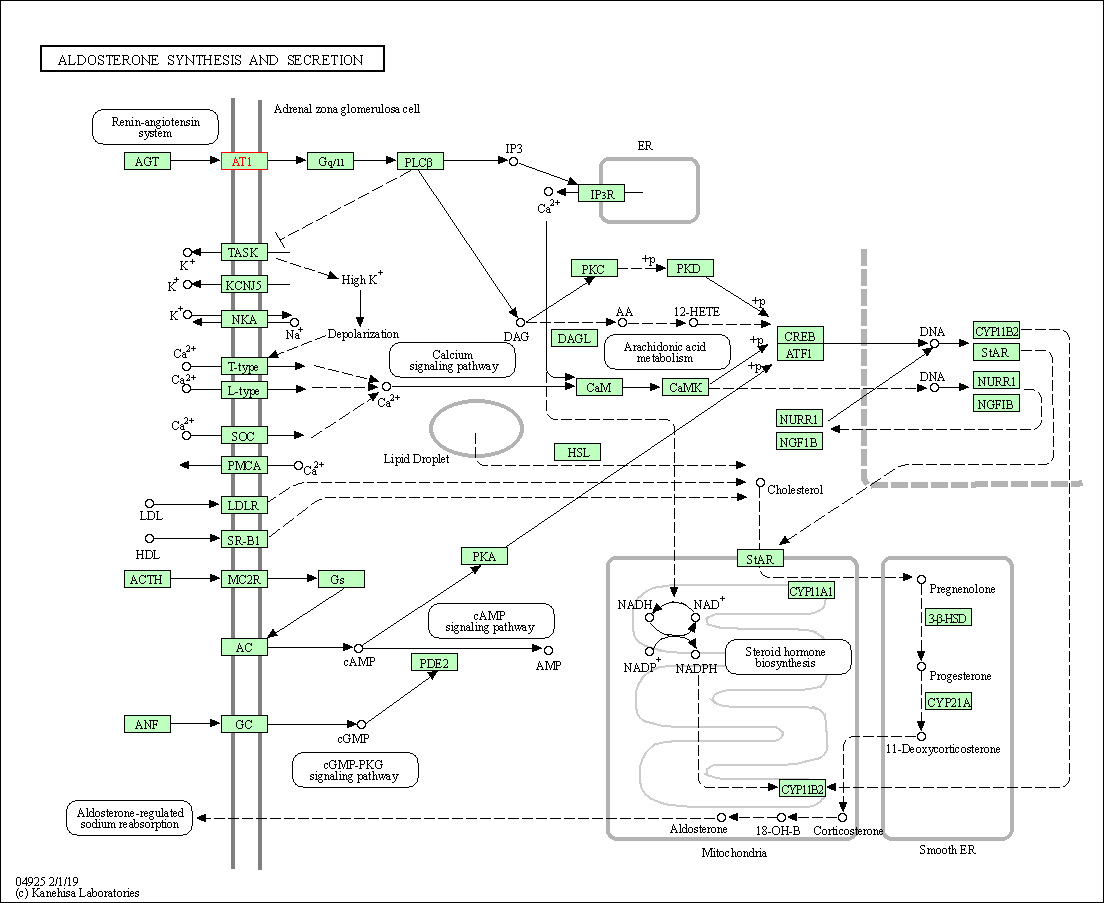
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
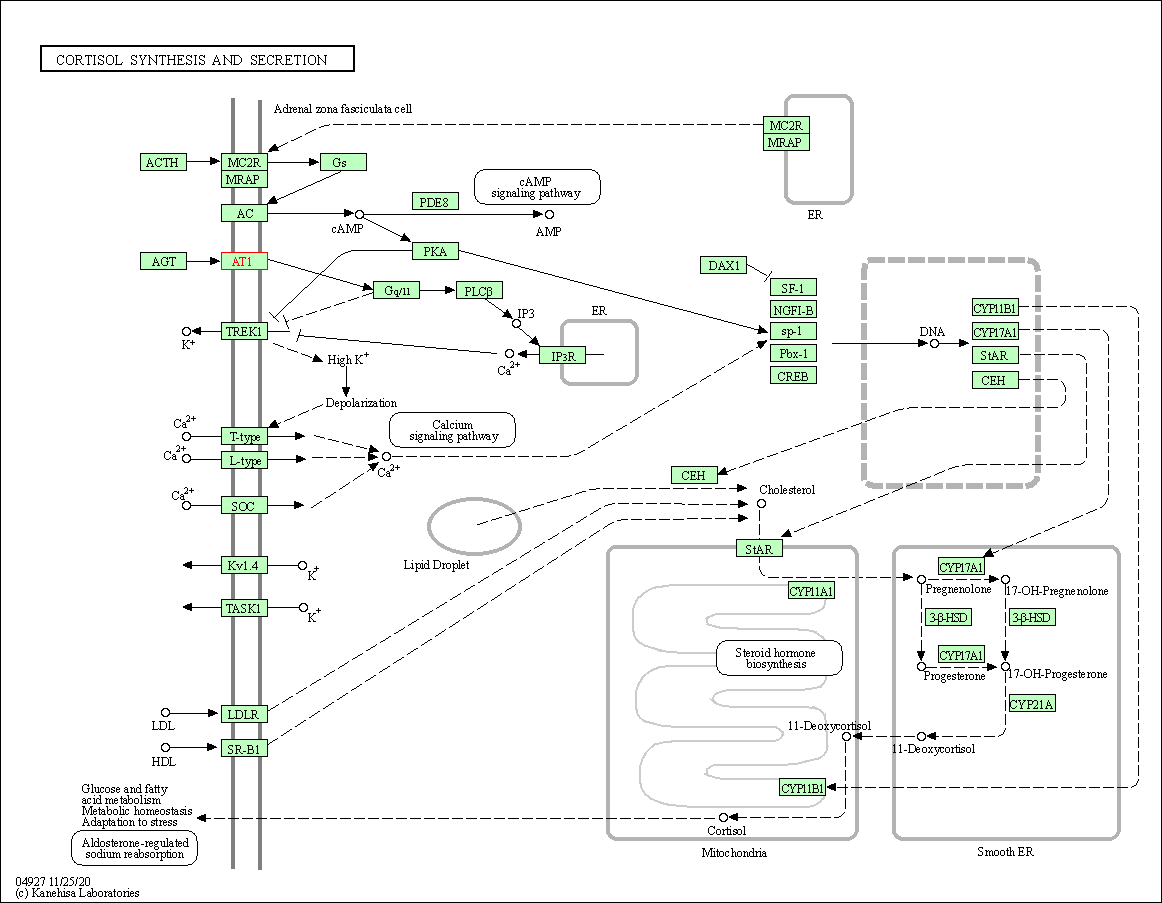
| Cortisol synthesis and secretion | hsa04927 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 10 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 5.66E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.26E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.67E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.48E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.25E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Cardiovascular Disease: A Viewpoint on the Potential Influence of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/Angiotensin Receptor Blockers on Onset and Severity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Apr 7;9(7):e016219. | |||||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (ANDA) 203534. | |||||
| REF 3 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 4 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (ANDA) 203867. | |||||
| REF 5 | Controversies of renin-angiotensin system inhibition during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Apr 3. | |||||
| REF 6 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (NDA) 020386 | |||||
| REF 7 | Telmisartan as tentative angiotensin receptor blocker therapeutic for COVID-19. Drug Dev Res. 2020 May 1. | |||||
| REF 8 | Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics. Drug Dev Res. 2020 Mar 4. | |||||
| REF 9 | Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 20;345(12):851-60. Clinical Trial; | |||||
| REF 10 | Structure of the Angiotensin receptor revealed by serial femtosecond crystallography. Cell. 2015 May 7;161(4):833-44. | |||||
| REF 11 | Angiotensin and biased analogs induce structurally distinct active conformations within a GPCR. Science. 2020 Feb 21;367(6480):888-892. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

