Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T94621
(Former ID: TTDI00101)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
RAC-PK-beta; Protein kinase B beta; Protein kinase Akt-2; PKB beta
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
AKT2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
AKT2 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MNEVSVIKEGWLHKRGEYIKTWRPRYFLLKSDGSFIGYKERPEAPDQTLPPLNNFSVAEC
QLMKTERPRPNTFVIRCLQWTTVIERTFHVDSPDEREEWMRAIQMVANSLKQRAPGEDPM DYKCGSPSDSSTTEEMEVAVSKARAKVTMNDFDYLKLLGKGTFGKVILVREKATGRYYAM KILRKEVIIAKDEVAHTVTESRVLQNTRHPFLTALKYAFQTHDRLCFVMEYANGGELFFH LSRERVFTEERARFYGAEIVSALEYLHSRDVVYRDIKLENLMLDKDGHIKITDFGLCKEG ISDGATMKTFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGRAVDWWGLGVVMYEMMCGRLPFYNQDHERLFE LILMEEIRFPRTLSPEAKSLLAGLLKKDPKQRLGGGPSDAKEVMEHRFFLSINWQDVVQK KLLPPFKPQVTSEVDTRYFDDEFTAQSITITPPDRYDSLGLLELDQRTHFPQFSYSASIR E Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T96ZVQ | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: GSK690693 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human Akt2 in complex with GSK690693 | PDB:3D0E | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | Yes | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
KVTMNDFDYL
155 KLLGKGTFGK165 VILVREKATG175 RYYAMKILRK185 EVIIAKDEVA195 HTVTESRVLQ 205 NTRHPFLTAL215 KYAFQTHDRL225 CFVMEYANGG235 ELFFHLSRER245 VFTEERARFY 255 GAEIVSALEY265 LHSRDVVYRD275 IKLENLMLDK285 DGHIKITDFG295 LCKEGISDGA 305 TMKFCGTPEY316 LAPEVLEDND326 YGRAVDWWGL336 GVVMYEMMCG346 RLPFYNQDHE 356 RLFELILMEE366 IRFPRTLSPE376 AKSLLAGLLK386 KDPKQRLGGG396 PSDAKEVMEH 406 RFFLSINWQD416 VVQKKLLPPF426 KPQVTSEVDT436 RYFDDEFTAQ446 SITIPPDQRT 468 HFPQFDYSAS478 IR
|
|||||
|
|
LEU158
3.786
GLY159
3.902
LYS160
3.806
PHE163
3.889
VAL166
3.427
ALA179
3.654
LYS181
3.401
GLU200
2.650
LEU204
3.464
THR213
4.112
LEU215
4.585
PHE227
3.627
MET229
3.404
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: A-443654 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | STRUCTURE OF PKB-BETA (AKT2) COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR A-443654 | PDB:2JDR | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | No | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
KVTMNDFDYL
155 KLLGKGTFGK165 VILVREKATG175 RYYAMKILRK185 EVIIAKDEVA195 HTVTESRVLQ 205 NTRHPFLTAL215 KYAFQTHDRL225 CFVMEYANGG235 ELFFHLSRER245 VFTEERARFY 255 GAEIVSALEY265 LHSRDVVYRD275 IKLENLMLDK285 DGHIKITDFG295 LCKEGISDGA 305 TMKFCGTPEY316 LAPEVLEDND326 YGRAVDWWGL336 GVVMYEMMCG346 RLPFYNQDHE 356 RLFELILMEE366 IRFPRTLSPE376 AKSLLAGLLK386 KDPKQRLGGG396 PSDAKEVMEH 406 RFFLSINWQD416 VVQKKLLPPF426 KPQVTSEVDT436 RYFDDEFTAQ446 SITQEMFEDF 473 DYIADW
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | hsa04072 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |
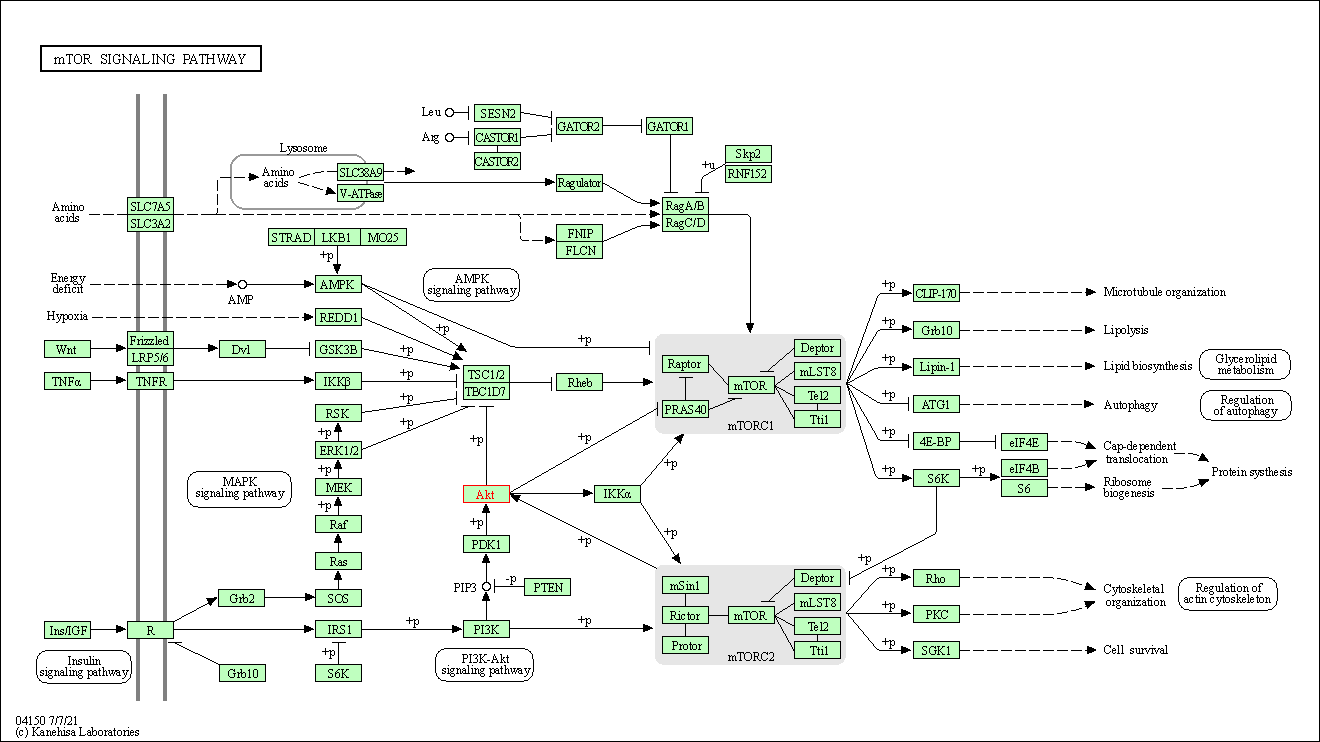
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
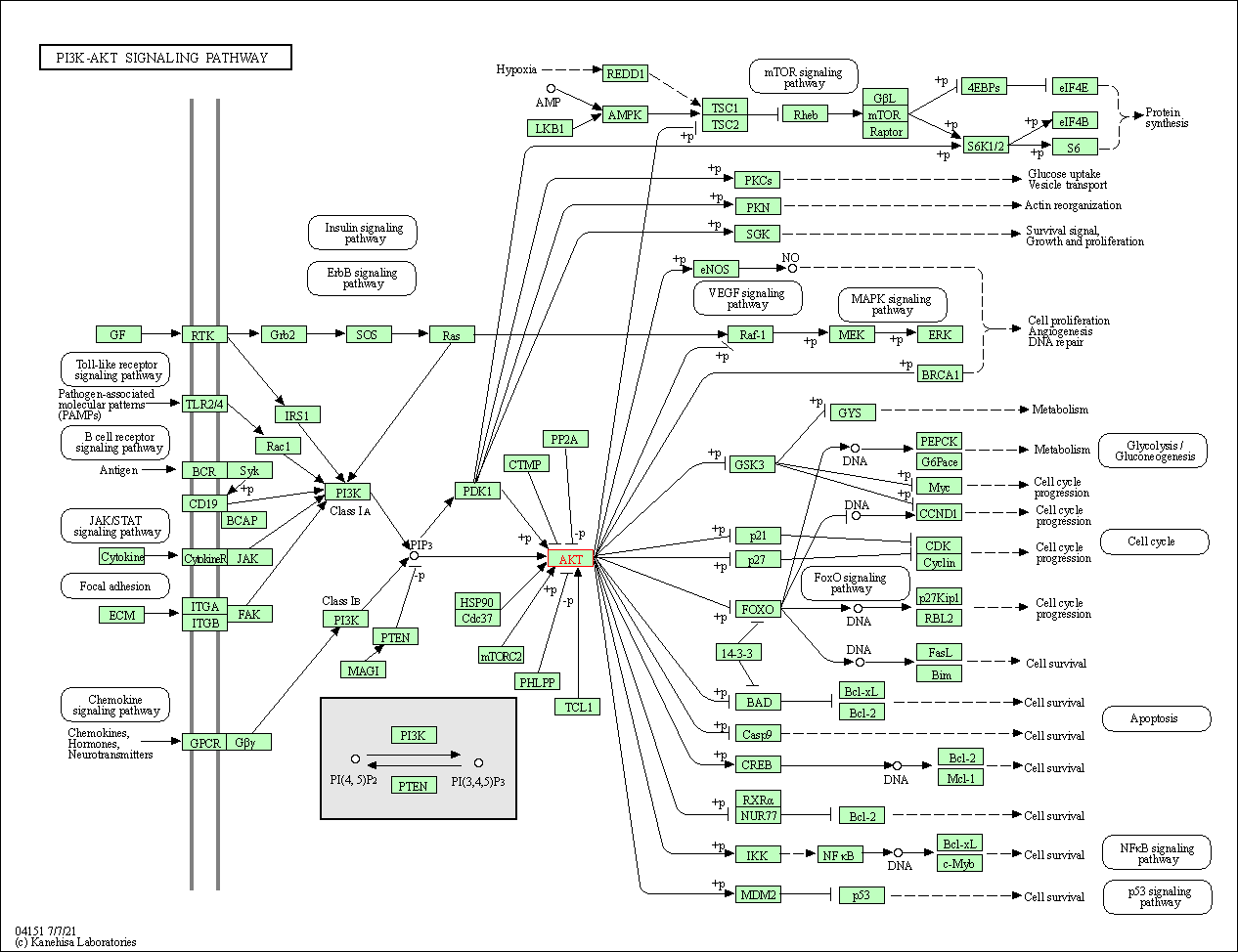
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |
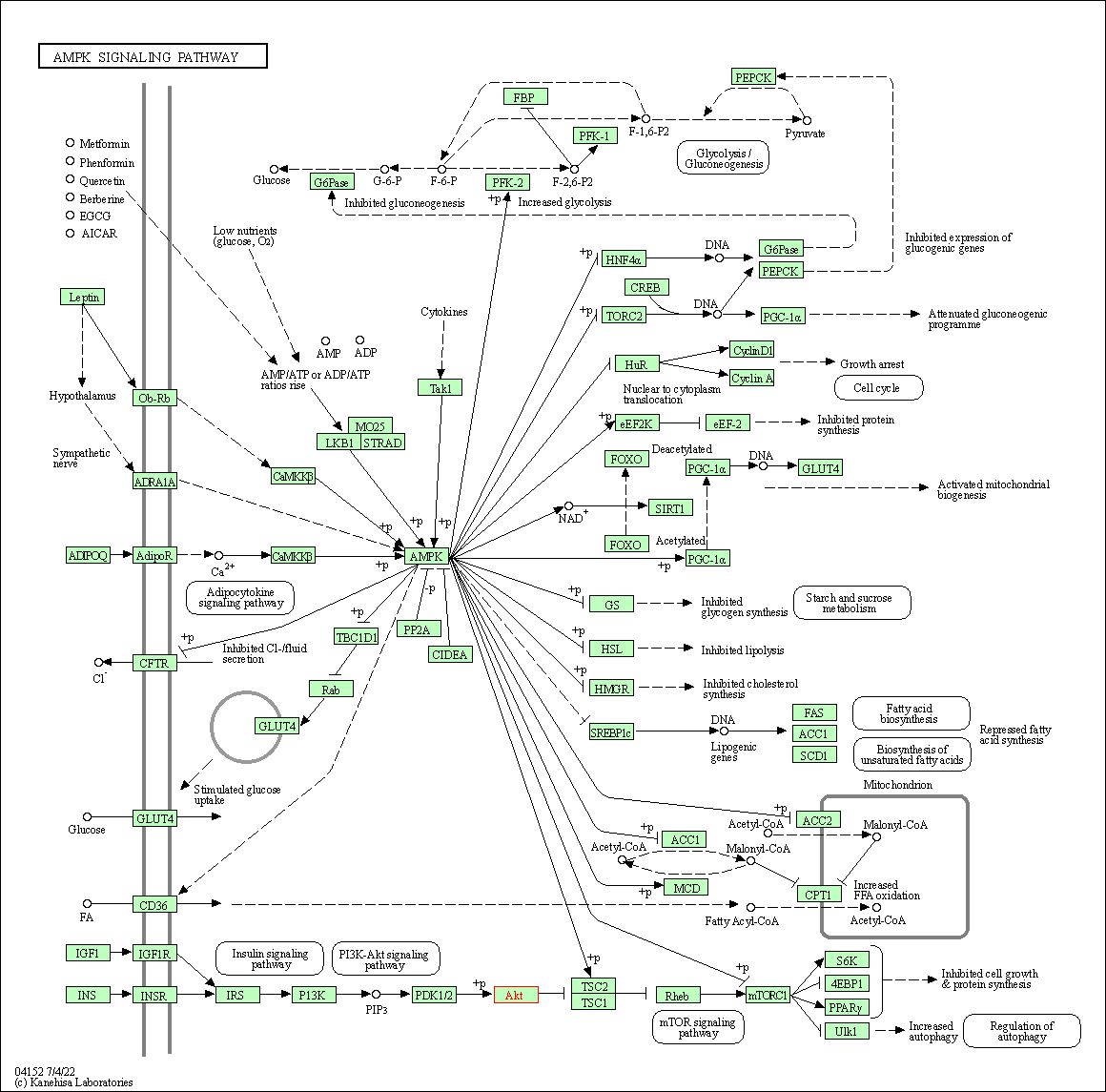
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |
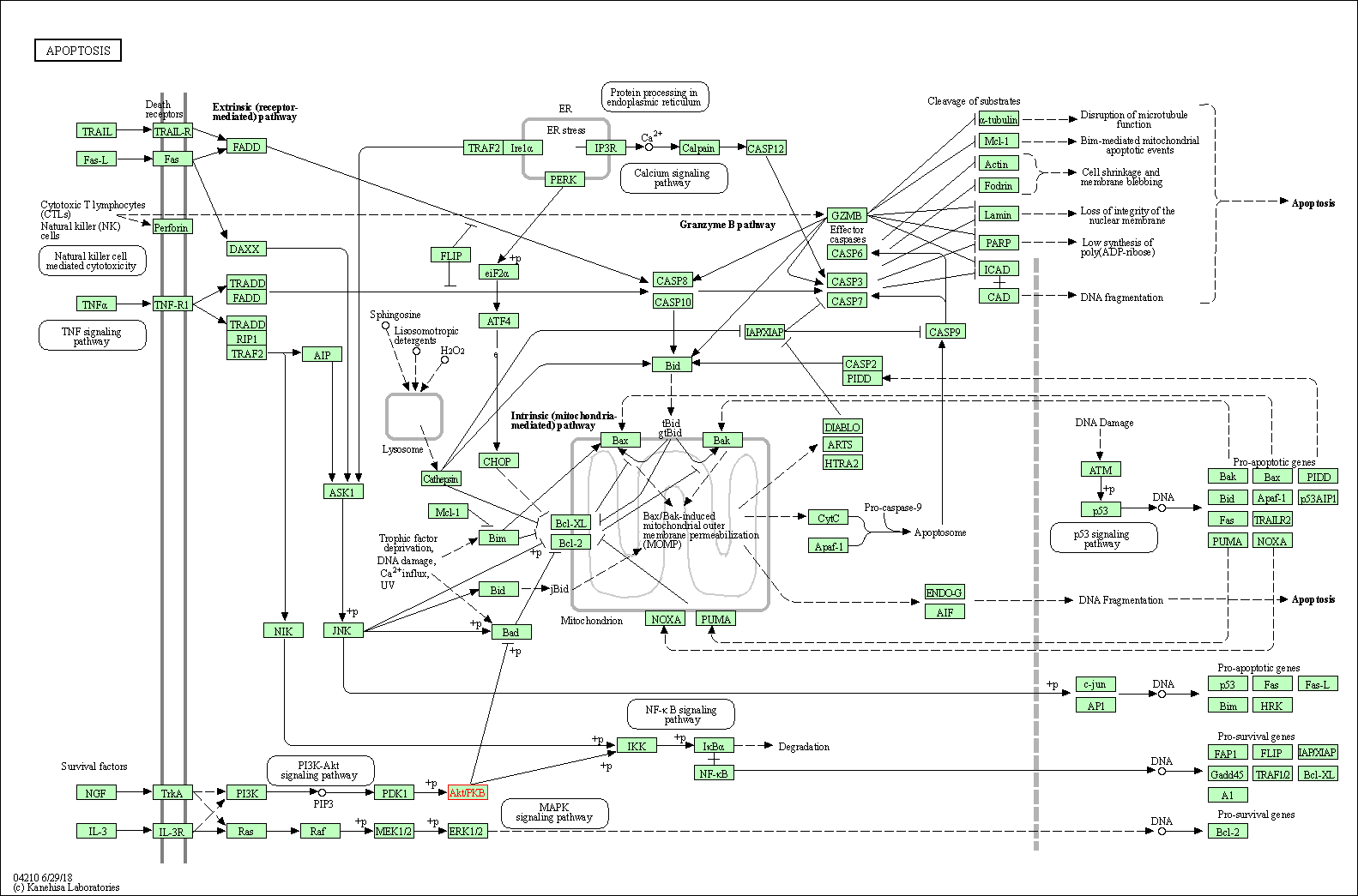
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway | hsa04211 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | hsa04213 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Aging | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
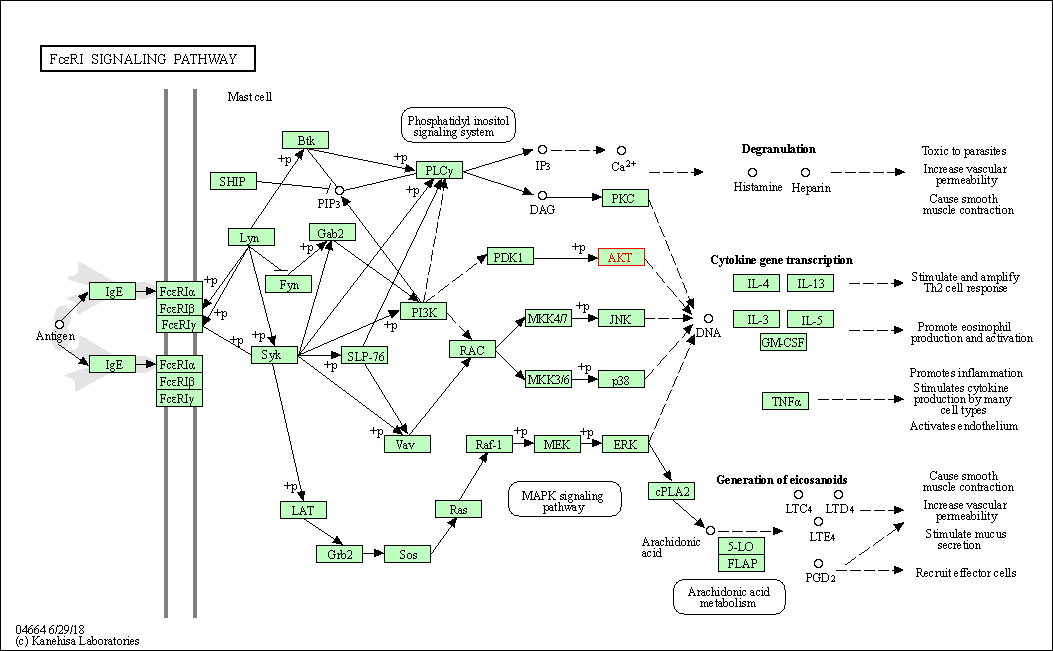
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |
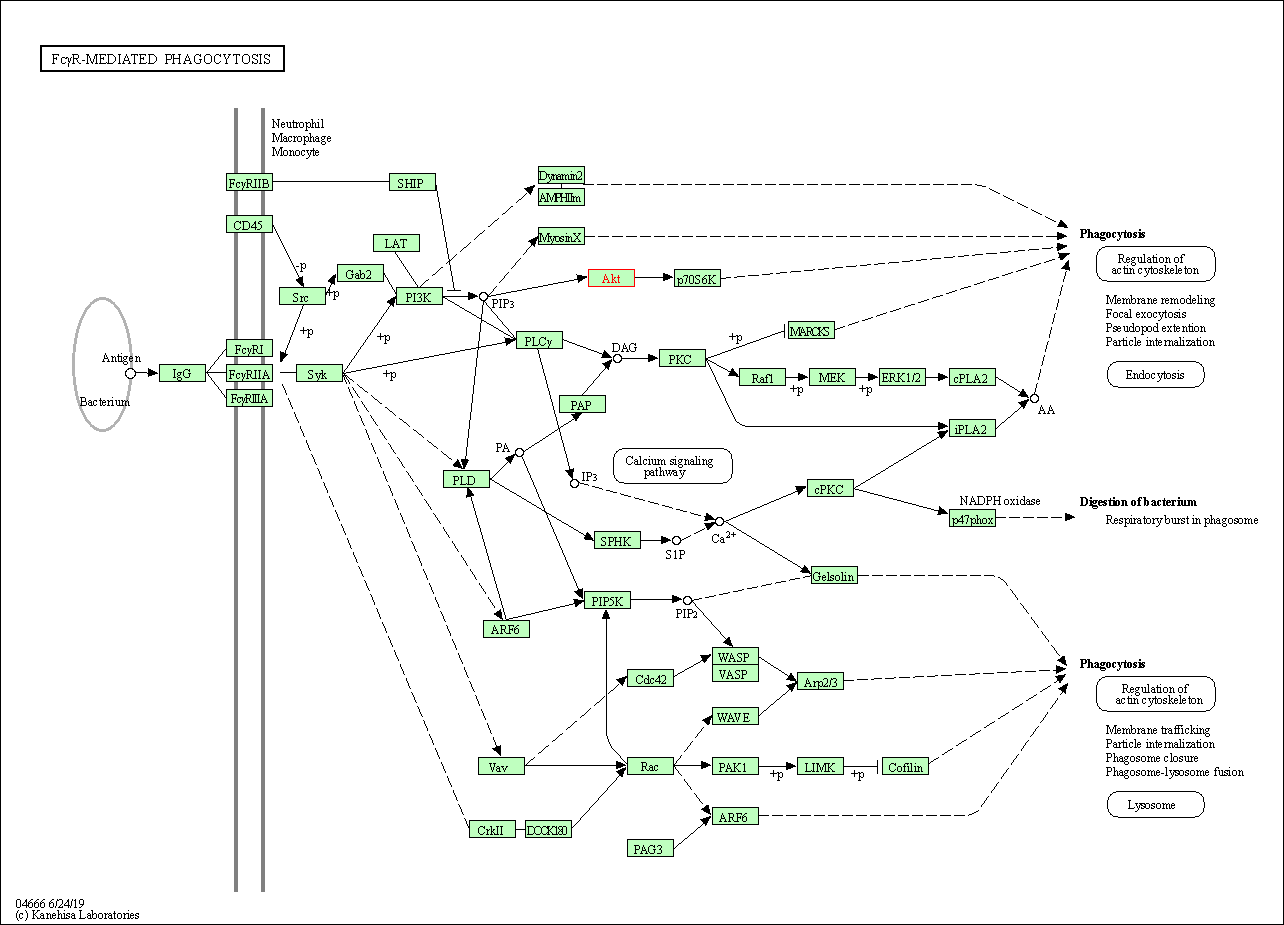
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
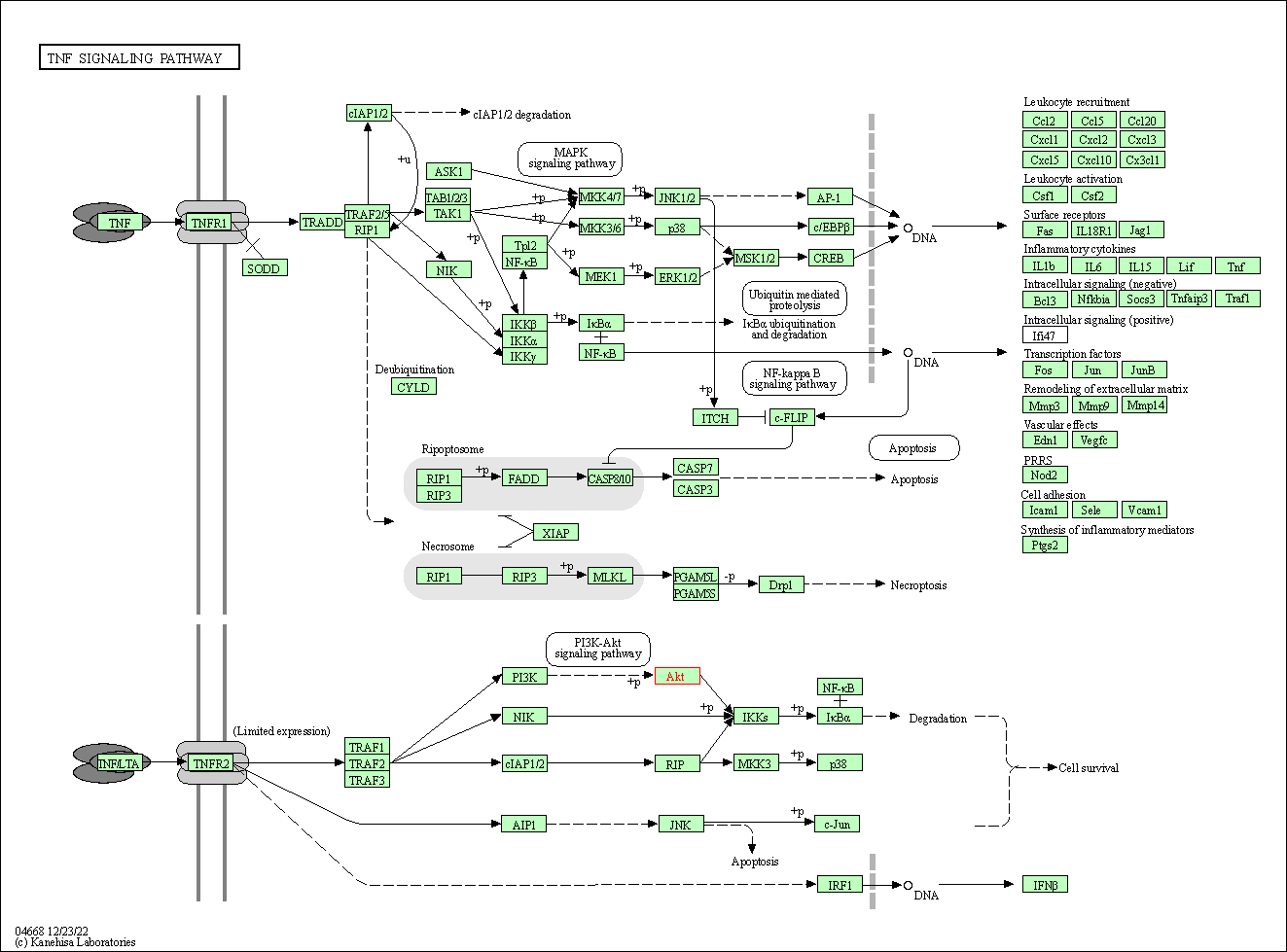
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
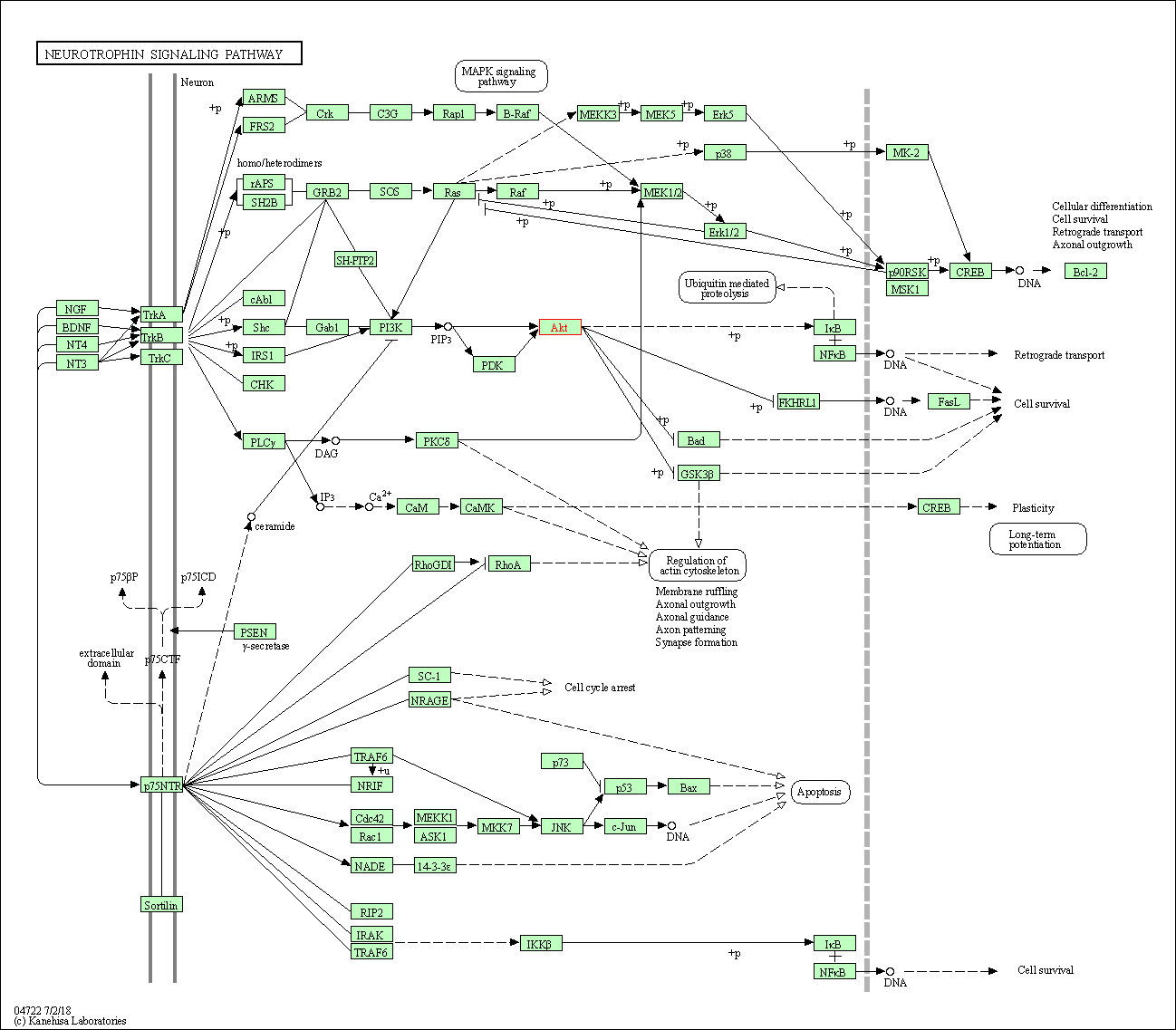
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cholinergic synapse | hsa04725 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | hsa04919 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | hsa04923 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Carbohydrate digestion and absorption | hsa04973 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 22 | Degree centrality | 2.36E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.79E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.55E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.08E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.44E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.62E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Molecular pharmacology and antitumor activity of PHT-427, a novel Akt/phosphatidylinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 pleckstrin homology domain inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Mar;9(3):706-17. | |||||
| REF 2 | Allosteric Akt (PKB) inhibitors: discovery and SAR of isozyme selective inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Feb 1;15(3):761-4. | |||||
| REF 3 | 2,3,5-Trisubstituted pyridines as selective AKT inhibitors. Part II: Improved drug-like properties and kinase selectivity from azaindazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):679-83. | |||||
| REF 4 | Identification of 4-(2-(4-amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1-ethyl-7-{[(3S)-3-piperidinylmethyl]oxy}-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-yl)-2-methyl-3-butyn-2-o... J Med Chem. 2008 Sep 25;51(18):5663-79. | |||||
| REF 5 | A structural comparison of inhibitor binding to PKB, PKA and PKA-PKB chimera. J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 30;367(3):882-94. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

