Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T86385
(Former ID: TTDC00019)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Cathepsin G (CTSG)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
CG
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CTSG
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ICD-11: CA22] | |||||
| Function |
Cleaves complement C3. Has antibacterial activity against the Gram-negative bacterium P. aeruginosa, antibacterial activity is inhibited by LPS from P. aeruginosa, Z-Gly-Leu-Phe-CH2Cl and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Serine protease with trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like specificity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Peptidase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.4.21.20
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MQPLLLLLAFLLPTGAEAGEIIGGRESRPHSRPYMAYLQIQSPAGQSRCGGFLVREDFVL
TAAHCWGSNINVTLGAHNIQRRENTQQHITARRAIRHPQYNQRTIQNDIMLLQLSRRVRR NRNVNPVALPRAQEGLRPGTLCTVAGWGRVSMRRGTDTLREVQLRVQRDRQCLRIFGSYD PRRQICVGDRRERKAAFKGDSGGPLLCNNVAHGIVSYGKSSGVPPEVFTRVSSFLPWIRT TMRSFKLLDQMETPL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T36BW3 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | JNJ-10311795 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [2] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Aloxistatin | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 3 | Neurological disorder | [3] | |
| 2 | Dermolastin | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Atopic dermatitis | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 15 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | JNJ-10311795 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Peptide analog 55 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | Peptide analog 56 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 4 | Peptide analog 57 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | Peptide analog 58 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 6 | Peptide analog 59 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 7 | Peptide analog 60 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 8 | Peptide analog 61 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 9 | Peptide analog 62 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 10 | Peptide analog 70 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 11 | Aloxistatin | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 12 | Dermolastin | Drug Info | [7], [8], [9], [10] | |||
| 13 | 1,3-Dibenzyl-[1,3]diazetidine-2,4-dione | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 14 | Bis-Napthyl Beta-Ketophosphonic Acid | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 15 | PMID22595175C4g | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Bis-Napthyl Beta-Ketophosphonic Acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Cathepsin-G | PDB:1KYN | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.50 Å | Mutation | No | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
IIGGRESRPH
25 SRPYMAYLQI35 QSPAGQSRCG43 GFLVREDFVL53 TAAHCWGSNI64 NVTLGAHNIQ 74 RRENTQQHIT84 ARRAIRHPQY94 NQRTIQNDIM104 LLQLSRRVRR114 NRNVNPVALP 124 RAQEGLRPGT134 LCTVAGWGRV144 SMRRGTDTLR156 EVQLRVQRDR166 QCLRIFGSYD 176 PRRQICVGDR185 RERKAAFKGD194 SGGPLLCNNV204 AHGIVSYGKS218 SGVPPEVFTR 230 VSSFLPWIRT240 TMR
|
|||||
|
|
SER40
4.449
ARG41
4.802
CYS42
3.509
HIS57
3.284
CYS58
4.004
TYR94
3.832
ILE99
4.804
ASP102
4.841
ALA190
3.438
PHE191
3.524
LYS192
3.672
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: N-(3-Carboxypropanoyl)-L-Valyl-N-{(1r)-1-[(S)-Hydroxy(Oxido)phosphanyl]-2-Phenylethyl}-L-Prolinamide | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human cathepsin G | PDB:1CGH | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.80 Å | Mutation | No | [15] |
| PDB Sequence |
IIGGRESRPH
25 SRPYMAYLQI35 QSPAGQSRCG43 GFLVREDFVL53 TAAHCWGSNI64 NVTLGAHNIQ 74 RRENTQQHIT84 ARRAIRHPQY94 NQRTIQNDIM104 LLQLSRRVRR114 NRNVNPVALP 124 RAQEGLRPGT134 LCTVAGWGRV144 SMRRGTDTLR156 EVQLRVQRDR166 QCLRIFGSYD 176 PRRQICVGDR185 RERKAAFKGD194 SGGPLLCNNV204 AHGIVSYGKS218 SGVPPEVFTR 230 VSSFLPWIRT240 TMRS
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
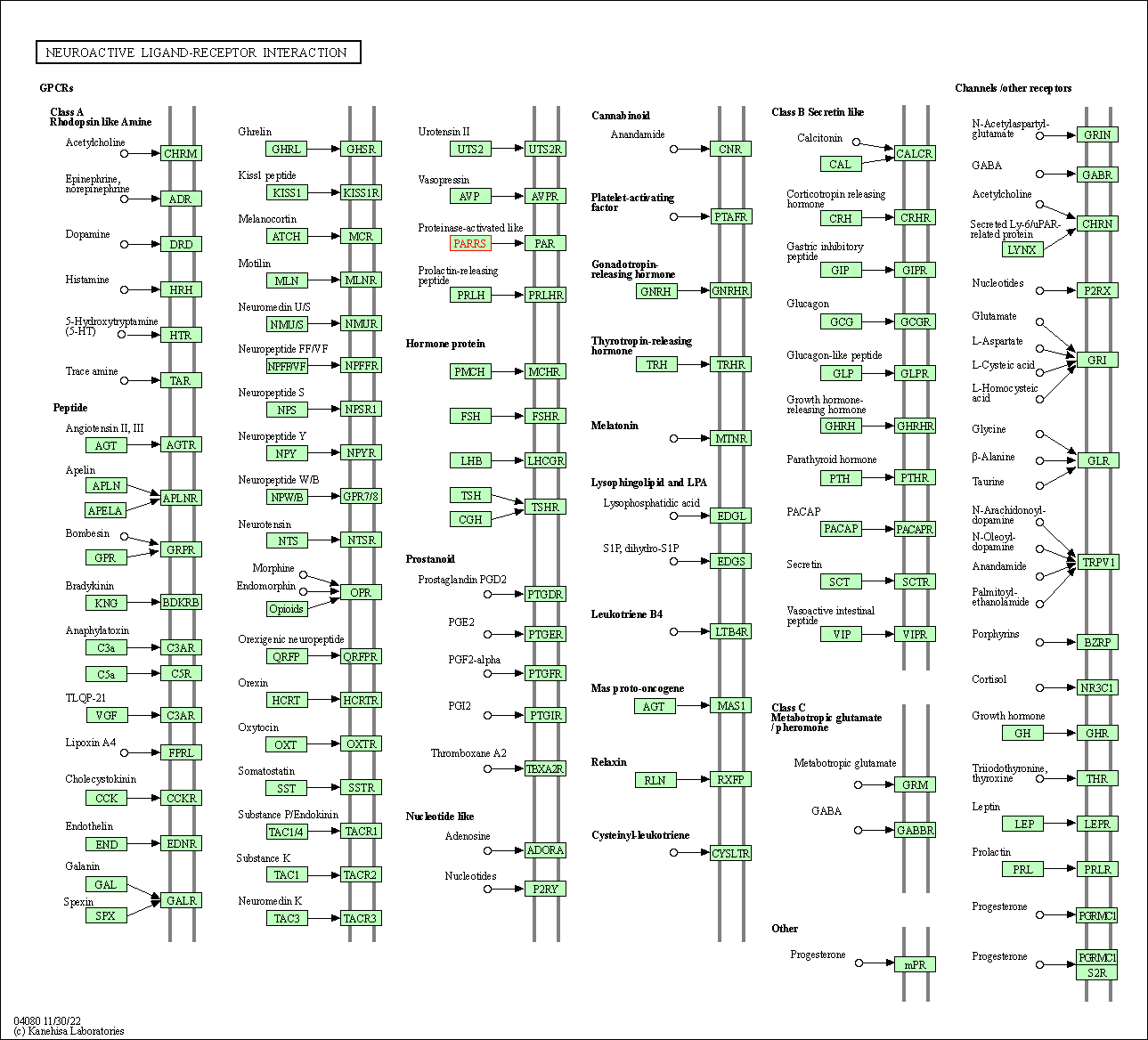
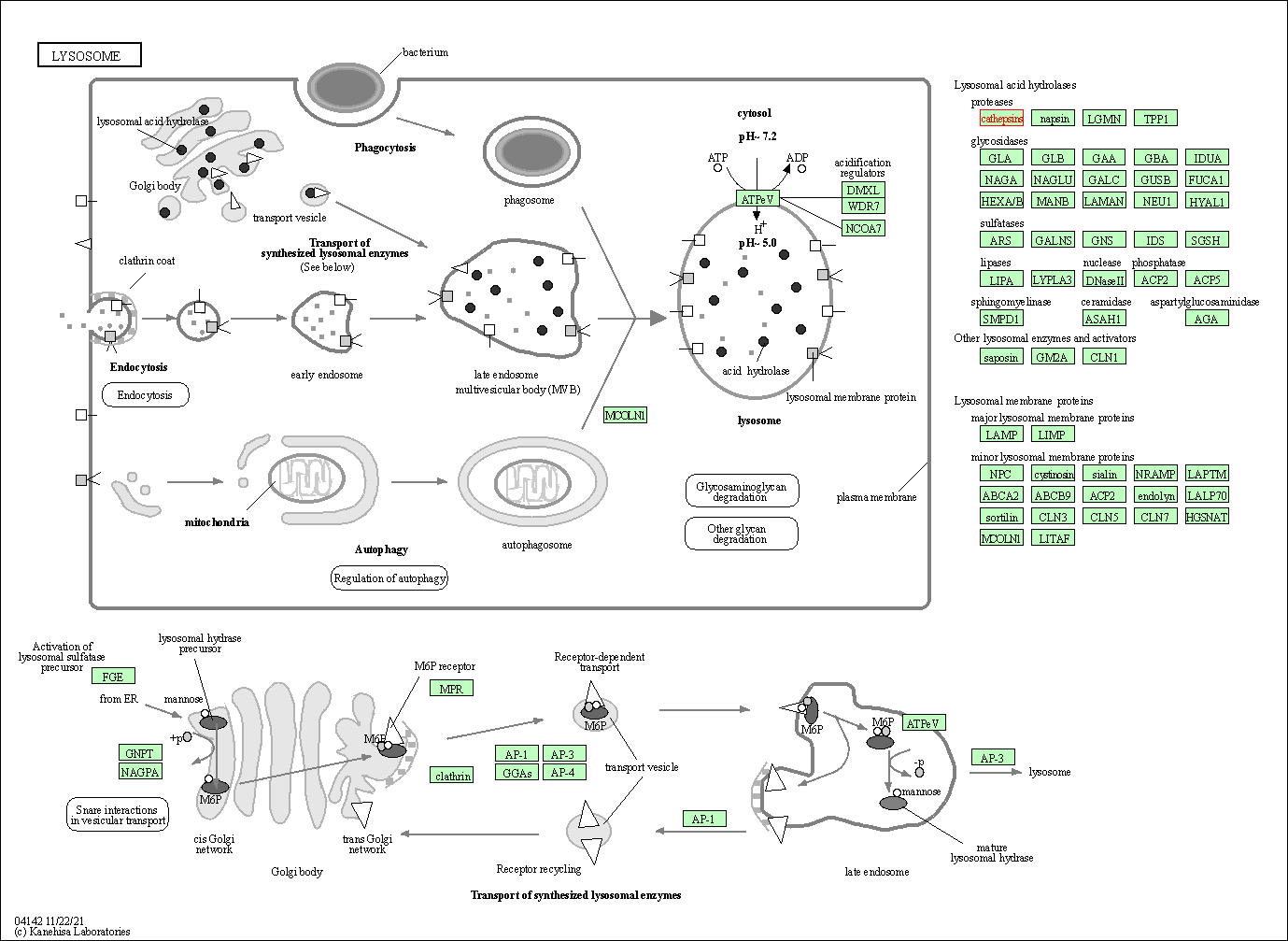
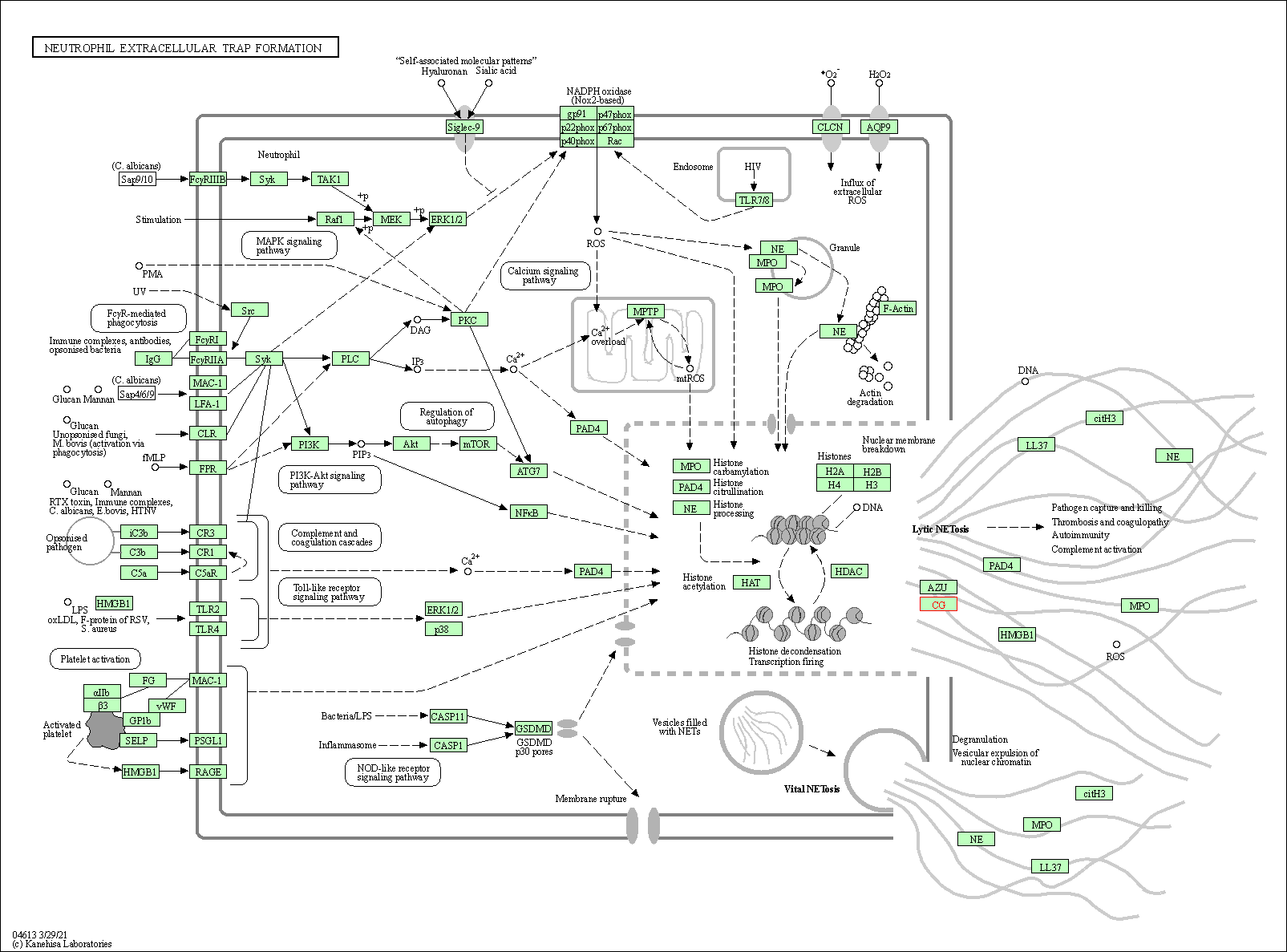
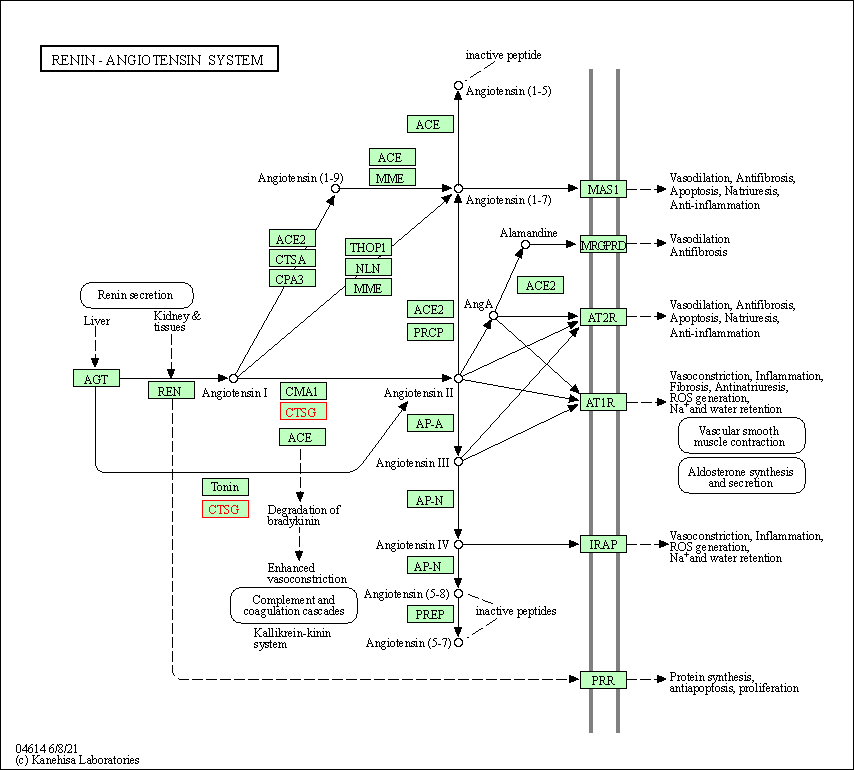
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Lysosome | hsa04142 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Renin-angiotensin system | hsa04614 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 6.35E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.05E-01 | Radiality | 1.36E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.30E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.03E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | Lysosome | |||||
| 3 | Renin-angiotensin system | |||||
| 4 | Amoebiasis | |||||
| 5 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and uPAR-mediated signaling | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 4 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Degradation of the extracellular matrix | |||||
| 2 | Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | |||||
| 3 | Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins | |||||
| 4 | Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ACE Inhibitor Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) Transport and Uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Discovery of potent, selective, orally active, nonpeptide inhibitors of human mast cell chymase. J Med Chem. 2007 Apr 19;50(8):1727-30. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6563). | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002441) | |||||
| REF 4 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800018071) | |||||
| REF 5 | Neutrophil elastase inhibitors: a patent review and potential applications for inflammatory lung diseases (2010 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(10):1145-58. | |||||
| REF 6 | Inhibition of the activation of multiple serine proteases with a cathepsin C inhibitor requires sustained exposure to prevent pro-enzyme processing. J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 20;282(29):20836-46. | |||||
| REF 7 | Arriva-ProMetic recombinant alpha 1-antitrypsin (rAAT) moves into the clinic for dermatology applications. ProMetic Life Sciences. 2009. | |||||
| REF 8 | rAAt (inhaled) Arriva/Hyland Immuno. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2006 Feb;8(1):76-82. | |||||
| REF 9 | Optimization of the bioprocessing conditions for scale-up of transient production of a heterologous protein in plants using a chemically inducible viral amplicon expression system. Biotechnol Prog. 2009 May-Jun;25(3):722-34. | |||||
| REF 10 | Bioreactor strategies for improving production yield and functionality of a recombinant human protein in transgenic tobacco cell cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009 Feb 1;102(2):508-20. | |||||
| REF 11 | Inhibition of serine proteases: activity of 1,3-diazetidine-2,4-diones. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Jul 9;11(13):1691-4. | |||||
| REF 12 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 13 | N-Acyl and N-sulfonyloxazolidine-2,4-diones are pseudo-irreversible inhibitors of serine proteases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jun 15;22(12):3993-7. | |||||
| REF 14 | Nonpeptide inhibitors of cathepsin G: optimization of a novel beta-ketophosphonic acid lead by structure-based drug design. J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Apr 17;124(15):3810-1. | |||||
| REF 15 | The 1.8 A crystal structure of human cathepsin G in complex with Suc-Val-Pro-PheP-(OPh)2: a Janus-faced proteinase with two opposite specificities. EMBO J. 1996 Oct 15;15(20):5481-91. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

