Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T76285
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Phosphodiesterase I beta (ENPP3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Phosphodiesterase I/nucleotide pyrophosphatase 3; PDNP3; PD-Ibeta; NPP3; Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3; E-NPP 3; CD203c
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ENPP3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||||
| Function |
Limits mast cell and basophil responses during inflammation and during the chronic phases of allergic responses by eliminating the extracellular ATP that functions as signaling molecule and activates basophils and mast cells and induces the release of inflammatory cytokines. Metabolizes extracellular ATP in the lumen of the small intestine, and thereby prevents ATP-induced apoptosis of intestinal plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Has also alkaline phosphodiesterase activity. Hydrolase that metabolizes extracellular nucleotides, including ATP, GTP, UTP and CTP.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Phosphoric diester hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MESTLTLATEQPVKKNTLKKYKIACIVLLALLVIMSLGLGLGLGLRKLEKQGSCRKKCFD
ASFRGLENCRCDVACKDRGDCCWDFEDTCVESTRIWMCNKFRCGETRLEASLCSCSDDCL QRKDCCADYKSVCQGETSWLEENCDTAQQSQCPEGFDLPPVILFSMDGFRAEYLYTWDTL MPNINKLKTCGIHSKYMRAMYPTKTFPNHYTIVTGLYPESHGIIDNNMYDVNLNKNFSLS SKEQNNPAWWHGQPMWLTAMYQGLKAATYFWPGSEVAINGSFPSIYMPYNGSVPFEERIS TLLKWLDLPKAERPRFYTMYFEEPDSSGHAGGPVSARVIKALQVVDHAFGMLMEGLKQRN LHNCVNIILLADHGMDQTYCNKMEYMTDYFPRINFFYMYEGPAPRIRAHNIPHDFFSFNS EEIVRNLSCRKPDQHFKPYLTPDLPKRLHYAKNVRIDKVHLFVDQQWLAVRSKSNTNCGG GNHGYNNEFRSMEAIFLAHGPSFKEKTEVEPFENIEVYNLMCDLLRIQPAPNNGTHGSLN HLLKVPFYEPSHAEEVSKFSVCGFANPLPTESLDCFCPHLQNSTQLEQVNQMLNLTQEEI TATVKVNLPFGRPRVLQKNVDHCLLYHREYVSGFGKAMRMPMWSSYTVPQLGDTSPLPPT VPDCLRADVRVPPSESQKCSFYLADKNITHGFLYPPASNRTSDSQYDALITSNLVPMYEE FRKMWDYFHSVLLIKHATERNGVNVVSGPIFDYNYDGHFDAPDEITKHLANTDVPIPTHY FVVLTSCKNKSHTPENCPGWLDVLPFIIPHRPTNVESCPEGKPEALWVEERFTAHIARVR DVELLTGLDFYQDKVQPVSEILQLKTYLPTFETTI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AGS-16C3F | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Renal cell carcinoma | [1], [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AGS-16C3F | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: [3H]alphabeta-meATP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase / phosphodiesterase 3 (ENPP3, NPP3, CD203c), inactive (T205A), N594S, with alpha,beta-methylene-ATP (AMPCPP) | PDB:6C02 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.94 Å | Mutation | Yes | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
GSCRKKCFDA
61 SFRGLENCRC71 DVACKDRGDC81 CWDFEDTCVE91 STRIWMCNKF101 RCGETRLEAS 111 LCSCSDDCLQ121 RKDCCADYKS131 VCQGETSWLE141 ENCDQCPEGF156 DLPPVILFSM 166 DGFRAEYLYT176 WDTLMPNINK186 LKTCGIHSKY196 MRAMYPTKAF206 PNHYTIVTGL 216 YPESHGIIDN226 NMYDVNLNKN236 FSLSSKEQNN246 PAWWHGQPMW256 LTAMYQGLKA 266 ATYFWPGSEV276 AINGSFPSIY286 MPYNGSVPFE296 ERISTLLKWL306 DLPKAERPRF 316 YTMYFEEPDS326 SGHAGGPVSA336 RVIKALQVVD346 HAFGMLMEGL356 KQRNLHNCVN 366 IILLADHGMD376 QTYCNKMEYM386 TDYFPRINFF396 YMYEGPAPRI406 RAHNIPHDFF 416 SFNSEEIVRN426 LSCRKPDQHF436 KPYLTPDLPK446 RLHYAKNVRI456 DKVHLFVDQQ 466 WLAVRSKSNT476 NCGGGNHGYN486 NEFRSMEAIF496 LAHGPSFKEK506 TEVEPFENIE 516 VYNLMCDLLR526 IQPAPNNGTH536 GSLNHLLKVP546 FYEPSHAEEV556 SKFSVCGFAN 566 PLPTESLDCF576 CPHLQNSTQL586 EQVNQMLSLT596 QEEITATVKV606 NLPFGRPRVL 616 QKNVDHCLLY626 HREYVSGFGK636 AMRMPMWSSY646 TVPQLGDTSP656 LPPTVPDCLR 666 ADVRVPPSES676 QKCSFYLADK686 NITHGFLYPP696 ASNRTSDSQY706 DALITSNLVP 716 MYEEFRKMWD726 YFHSVLLIKH736 ATERNGVNVV746 SGPIFDYNYD756 GHFDAPDEIT 766 KHLANTDVPI776 PTHYFVVLTS786 CKNKSHTPEN796 CPGWLDVLPF806 IIPHRPTNVE 816 SCPEGKPEAL826 WVEERFTAHI836 ARVRDVELLT846 GLDFYQDKVQ856 PVSEILQLKT 866 YLPTF
|
|||||
|
|
ASP167
2.557
LYS204
2.466
ALA205
2.372
PHE206
2.833
HIS209
4.899
ASN226
2.015
ASN227
2.949
LEU239
2.753
GLN244
2.738
PHE270
2.966
TRP271
3.484
PRO272
2.728
GLY273
4.094
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | hsa00230 | Affiliated Target |
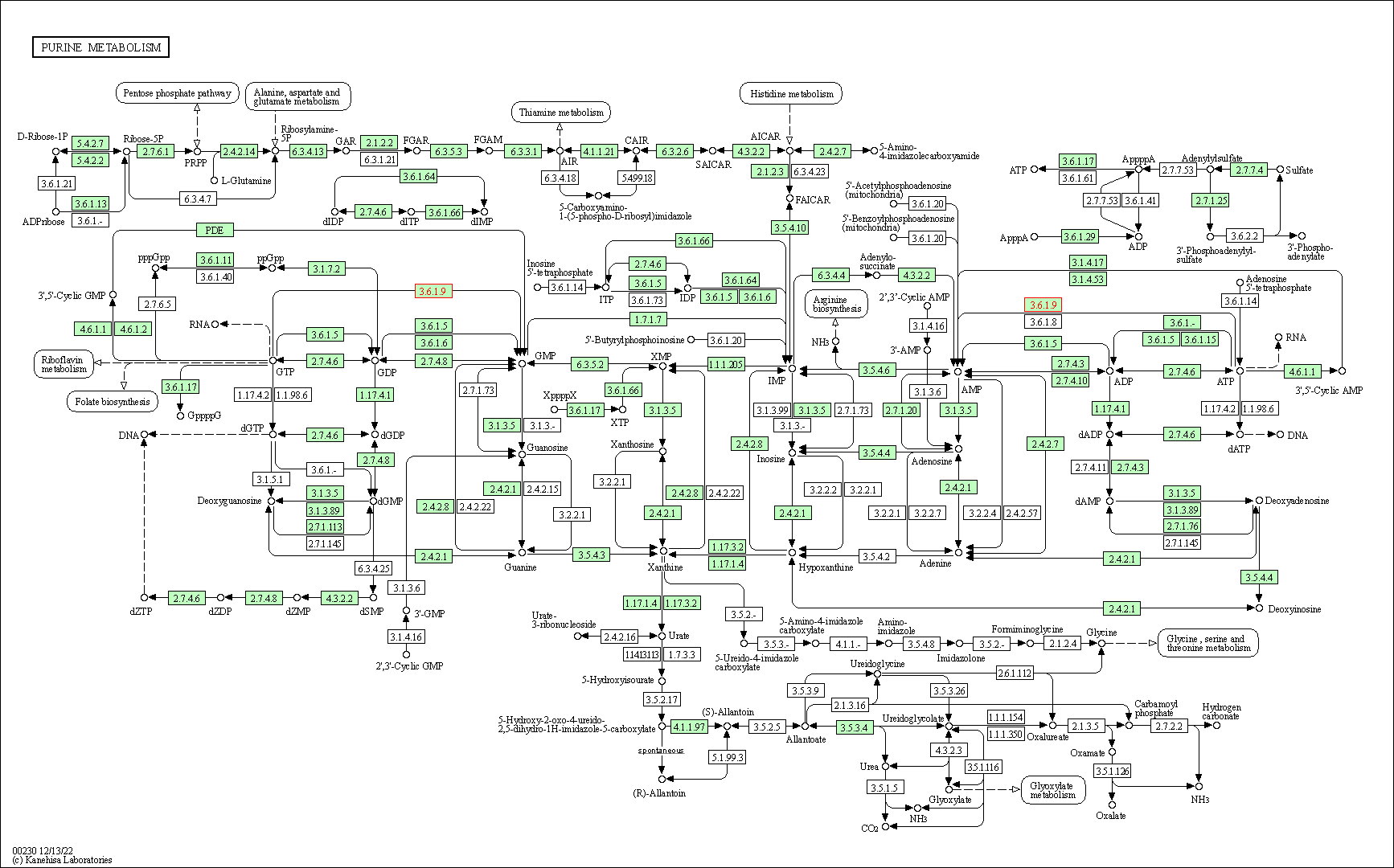
|
| Class: Metabolism => Nucleotide metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Pyrimidine metabolism | hsa00240 | Affiliated Target |
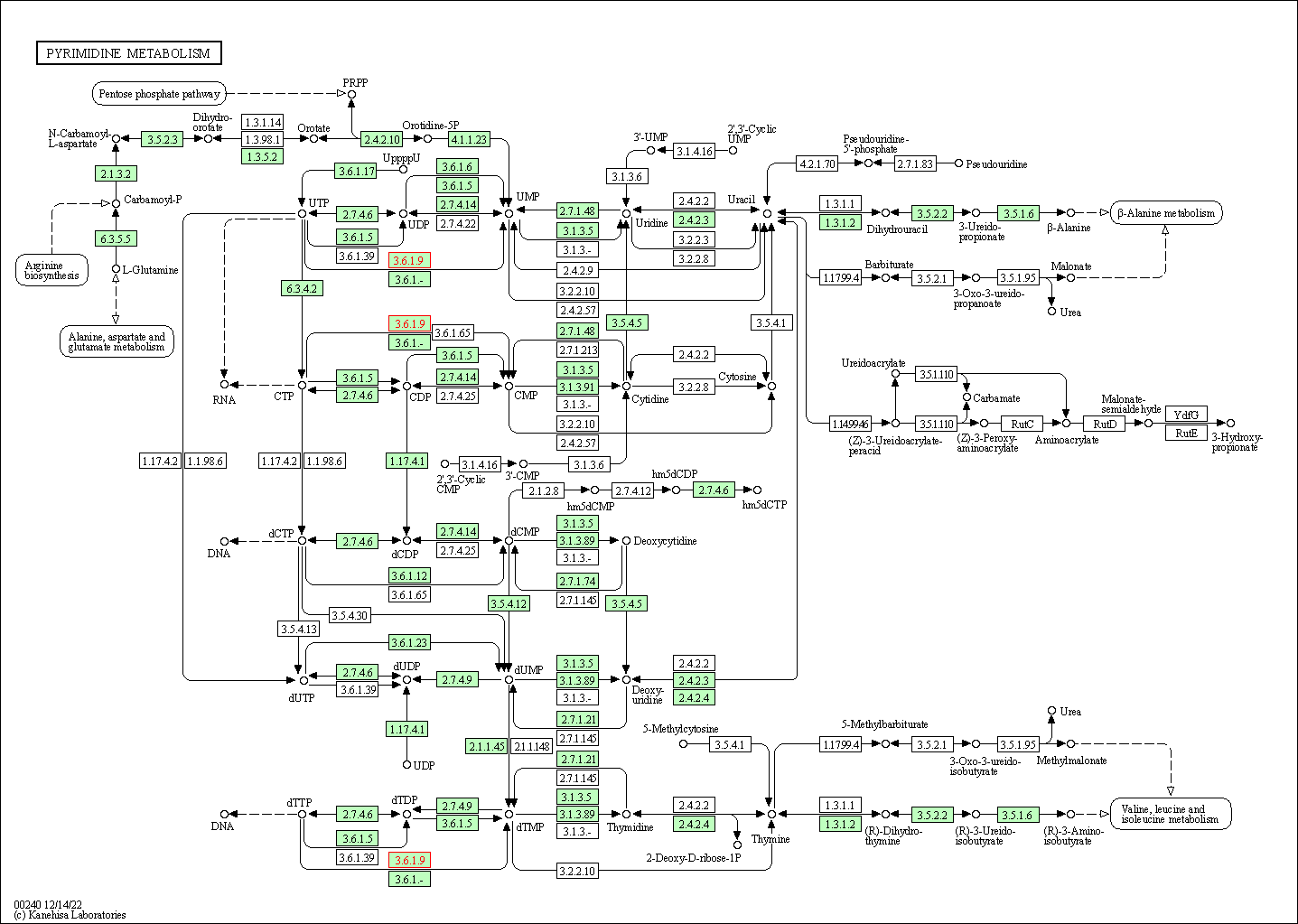
|
| Class: Metabolism => Nucleotide metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | hsa00500 | Affiliated Target |
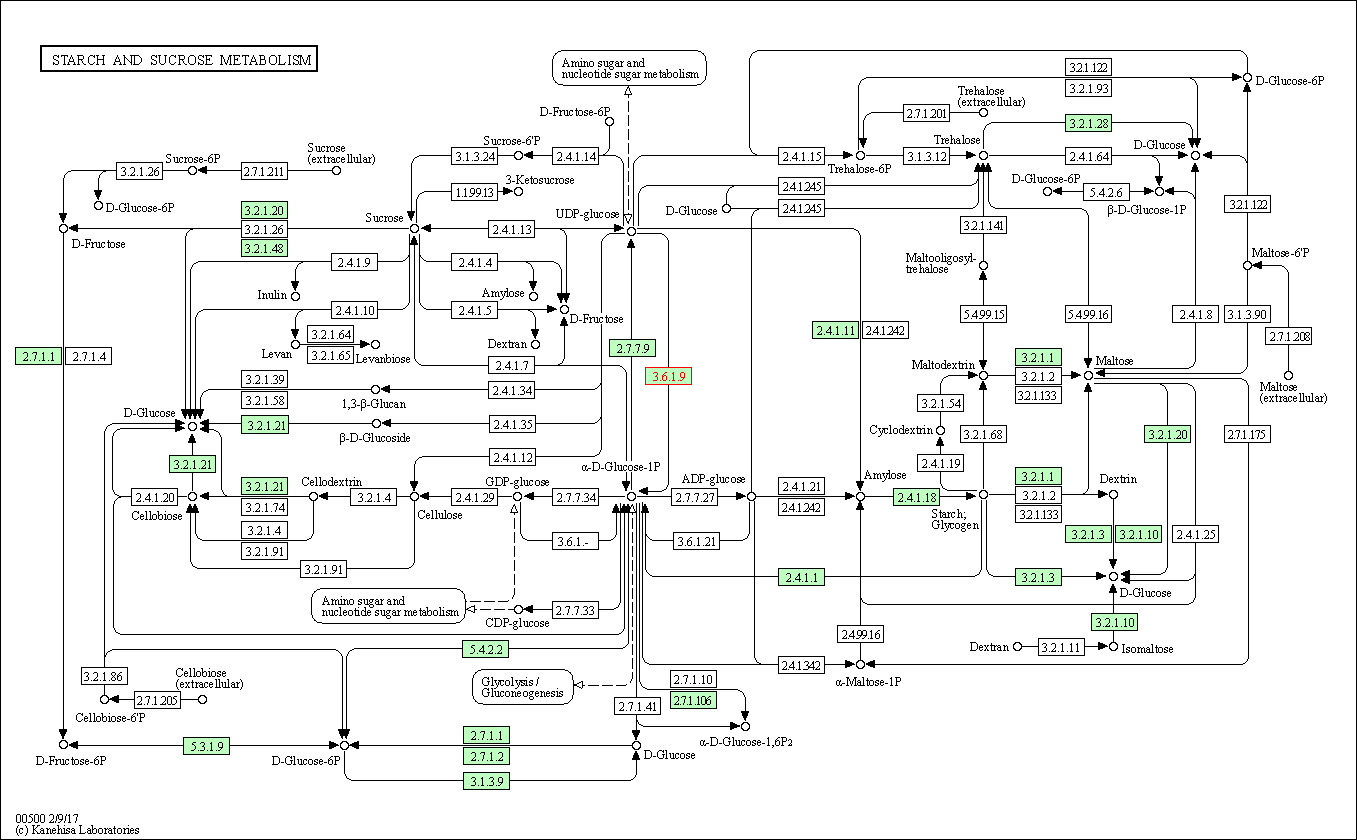
|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Riboflavin metabolism | hsa00740 | Affiliated Target |
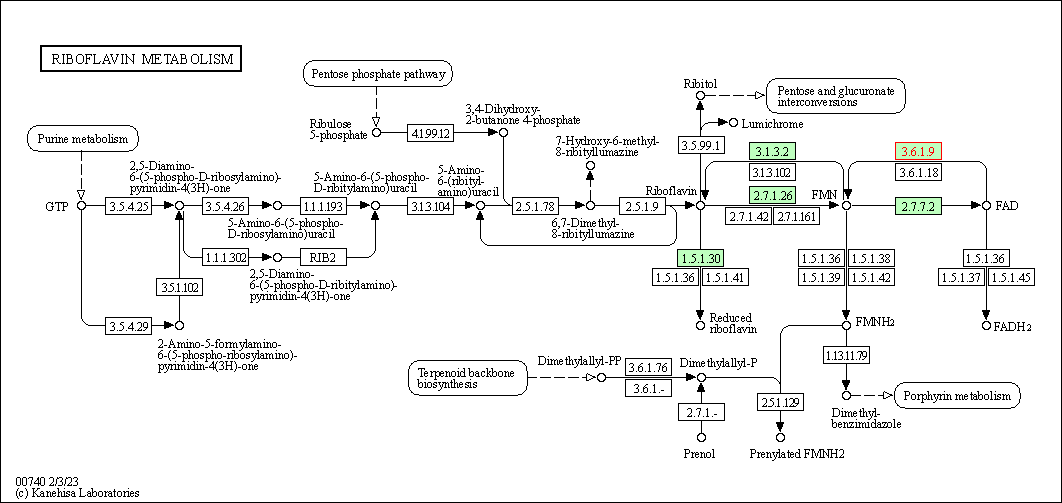
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | hsa00760 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | hsa00770 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 5 | Degree centrality | 5.37E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.41E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.45E-01 | Radiality | 1.18E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.20E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.91E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | Structural basis for nucleotide recognition by the ectoenzyme CD203c. FEBS J. 2018 Jul;285(13):2481-2494. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

