Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T53952
(Former ID: TTDI03263)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
hHIPk2; Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HIPK2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Acts as a corepressor of several transcription factors, including SMAD1 and POU4F1/Brn3a and probably NK homeodomain transcription factors. Phosphorylates PDX1, ATF1, PML, p53/TP53, CREB1, CTBP1, CBX4, RUNX1, EP300, CTNNB1, HMGA1 and ZBTB4. Inhibits cell growth and promotes apoptosis through the activation of p53/TP53 both at the transcription level and at the protein level (by phosphorylation and indirect acetylation). The phosphorylation of p53/TP53 may be mediated by a p53/TP53-HIPK2-AXIN1 complex. Involved in the response to hypoxia by acting as a transcriptional co-suppressor of HIF1A. Mediates transcriptional activation of TP73. In response to TGFB, cooperates with DAXX to activate JNK. Negative regulator through phosphorylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation of CTNNB1 and the antiapoptotic factor CTBP1. In the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway acts as an intermediate kinase between MAP3K7/TAK1 and NLK to promote the proteasomal degradation of MYB. Phosphorylates CBX4 upon DNA damage and promotes its E3 SUMO-protein ligase activity. Activates CREB1 and ATF1 transcription factors by phosphorylation in response to genotoxic stress. In response to DNA damage, stabilizes PML by phosphorylation. PML, HIPK2 and FBXO3 may act synergically to activate p53/TP53-dependent transactivation. Promotes angiogenesis, and is involved in erythroid differentiation, especially during fetal liver erythropoiesis. Phosphorylation of RUNX1 and EP300 stimulates EP300 transcription regulation activity. Triggers ZBTB4 protein degradation in response to DNA damage. Modulates HMGA1 DNA-binding affinity. In response to high glucose, triggers phosphorylation-mediated subnuclear localization shifting of PDX1. Involved in the regulation of eye size, lens formation and retinal lamination during late embryogenesis. Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in transcription regulation, p53/TP53-mediated cellular apoptosis and regulation of the cell cycle.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAPVYEGMASHVQVFSPHTLQSSAFCSVKKLKIEPSSNWDMTGYGSHSKVYSQSKNIPLS
QPATTTVSTSLPVPNPSLPYEQTIVFPGSTGHIVVTSASSTSVTGQVLGGPHNLMRRSTV SLLDTYQKCGLKRKSEEIENTSSVQIIEEHPPMIQNNASGATVATATTSTATSKNSGSNS EGDYQLVQHEVLCSMTNTYEVLEFLGRGTFGQVVKCWKRGTNEIVAIKILKNHPSYARQG QIEVSILARLSTESADDYNFVRAYECFQHKNHTCLVFEMLEQNLYDFLKQNKFSPLPLKY IRPVLQQVATALMKLKSLGLIHADLKPENIMLVDPSRQPYRVKVIDFGSASHVSKAVCST YLQSRYYRAPEIILGLPFCEAIDMWSLGCVIAELFLGWPLYPGASEYDQIRYISQTQGLP AEYLLSAGTKTTRFFNRDTDSPYPLWRLKTPDDHEAETGIKSKEARKYIFNCLDDMAQVN MTTDLEGSDMLVEKADRREFIDLLKKMLTIDADKRITPIETLNHPFVTMTHLLDFPHSTH VKSCFQNMEICKRRVNMYDTVNQSKTPFITHVAPSTSTNLTMTFNNQLTTVHNQAPSSTS ATISLANPEVSILNYPSTLYQPSAASMAAVAQRSMPLQTGTAQICARPDPFQQALIVCPP GFQGLQASPSKHAGYSVRMENAVPIVTQAPGAQPLQIQPGLLAQQAWPSGTQQILLPPAW QQLTGVATHTSVQHATVIPETMAGTQQLADWRNTHAHGSHYNPIMQQPALLTGHVTLPAA QPLNVGVAHVMRQQPTSTTSSRKSKQHQSSVRNVSTCEVSSSQAISSPQRSKRVKENTPP RCAMVHSSPACSTSVTCGWGDVASSTTRERQRQTIVIPDTPSPTVSVITISSDTDEEEEQ KHAPTSTVSKQRKNVISCVTVHDSPYSDSSSNTSPYSVQQRAGHNNANAFDTKGSLENHC TGNPRTIIVPPLKTQASEVLVECDSLVPVNTSHHSSSYKSKSSSNVTSTSGHSSGSSSGA ITYRQQRPGPHFQQQQPLNLSQAQQHITTDRTGSHRRQQAYITPTMAQAPYSFPHNSPSH GTVHPHLAAAAAAAHLPTQPHLYTYTAPAALGSTGTVAHLVASQGSARHTVQHTAYPASI VHQVPVSMGPRVLPSPTIHPSQYPAQFAHQTYISASPASTVYTGYPLSPAKVNQYPYI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: CX-4945 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | HIPK2 kinase domain bound to CX-4945 | PDB:6P5S | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.19 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
QLVQHEVLCS
194 MTNTYEVLEF204 LGRGQVVKCW217 KRGTNEIVAI227 KILRQGQIEV244 SILARLSTES 254 ADDYNFVRAY264 ECFQHHTCLV276 FEMLEQNLYD286 FLKQNKFSPL296 PLKYIRPVLQ 306 QVATALMKLK316 SLGLIHADLK326 PENIMLVDPS336 RQPYRVKVID346 FGSASHVTLQ 363 SRYYRAPEII373 LGLPFCEAID383 MWSLGCVIAE393 LFLGWPLYPG403 ASEYDQIRYI 413 SQTQGLPAEY423 LLSAGTKTTR433 FFNRDTDPYP444 LWRLKTPDDH454 EAETGIKSKE 464 ARKYIFNCLD474 DMAQVNMTTD484 LEGSDMLVEK494 ADRREFIDLL504 KKMLTIDADK 514 RITPIETLNH524 PFVTMTHLLD534 F
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: L-serine-O-phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | HIPK2 kinase domain bound to CX-4945 | PDB:6P5S | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.19 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
QLVQHEVLCS
194 MTNTYEVLEF204 LGRGQVVKCW217 KRGTNEIVAI227 KILRQGQIEV244 SILARLSTES 254 ADDYNFVRAY264 ECFQHHTCLV276 FEMLEQNLYD286 FLKQNKFSPL296 PLKYIRPVLQ 306 QVATALMKLK316 SLGLIHADLK326 PENIMLVDPS336 RQPYRVKVID346 FGSASHVTLQ 363 SRYYRAPEII373 LGLPFCEAID383 MWSLGCVIAE393 LFLGWPLYPG403 ASEYDQIRYI 413 SQTQGLPAEY423 LLSAGTKTTR433 FFNRDTDPYP444 LWRLKTPDDH454 EAETGIKSKE 464 ARKYIFNCLD474 DMAQVNMTTD484 LEGSDMLVEK494 ADRREFIDLL504 KKMLTIDADK 514 RITPIETLNH524 PFVTMTHLLD534 F
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |
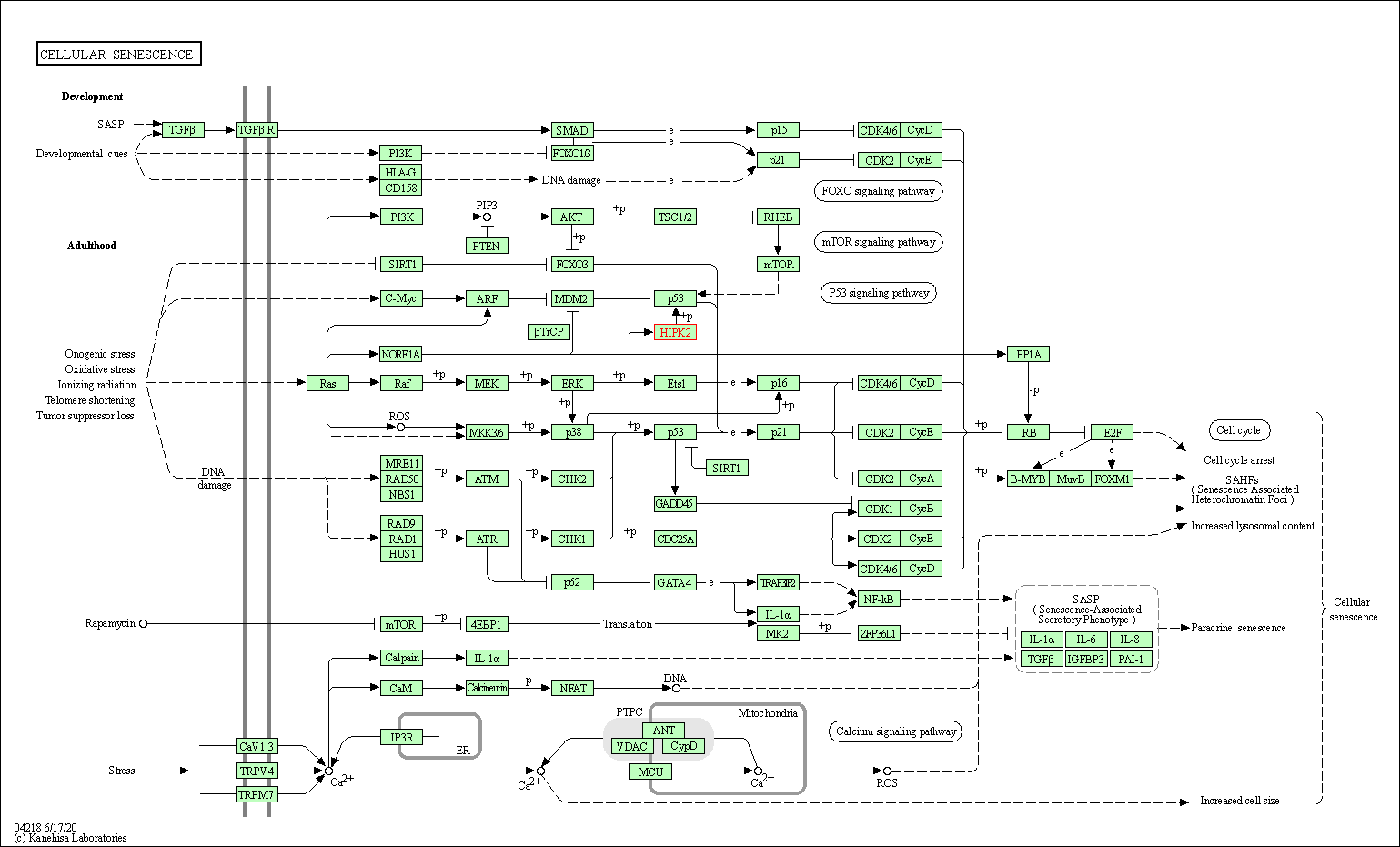
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 5.56E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.42E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.50E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.34E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.48E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Structure and Property Based Design of Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine Inhibitors of CK2 Kinase with Activity in Vivo. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jul 3;4(8):800-5. | |||||
| REF 2 | The crystal structure of the protein kinase HIPK2 reveals a unique architecture of its CMGC-insert region. J Biol Chem. 2019 Sep 13;294(37):13545-13559. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

