Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T53159
(Former ID: TTDR00147)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
ERK activator kinase 7 (MAP2K7)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Stress-activated protein kinase kinase 4; SKK4; SAPKK4; SAPKK-4; SAPK kinase 4; PRKMK7; Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7; MKK7; MEK7; MEK 7; MAPKK 7; MAPK/ERK kinase7; MAPK/ERK kinase 7; MAP kinase kinase 7; JNKK2; JNKK 2; JNK-activating kinase 2; JNK kinase 2; JNK activating kinase 2; Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7; C-Jun N-terminal kinase kinase 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAP2K7
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Essential component of the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAP/JNK) signaling pathway. With MAP2K4/MKK4, is the one of the only known kinase to directly activate the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinases MAPK8/JNK1, MAPK9/JNK2 and MAPK10/JNK3. MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 both activate the JNKs by phosphorylation, but they differ in their preference for the phosphorylation site in the Thr-Pro-Tyr motif. MAP2K4/MKK4 shows preference for phosphorylation of the Tyr residue and MAP2K7/MKK7 for the Thr residue. The monophosphorylation of JNKs on the Thr residue is sufficient to increase JNK activity indicating that MAP2K7/MKK7 is important to trigger JNK activity, while the additional phosphorylation of the Tyr residue by MAP2K4/MKK4 ensures optimal JNK activation. Has a specific role in JNK signal transduction pathway activated by proinflammatory cytokines. The MKK/JNK signaling pathway is also involved in mitochondrial death signaling pathway, including the release cytochrome c, leading to apoptosis. Part of a non-canonical MAPK signaling pathway, composed of the upstream MAP3K12 kinase and downstream MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1, that enhances the AP-1-mediated transcription of APP in response to APOE. Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.12.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAASSLEQKLSRLEAKLKQENREARRRIDLNLDISPQRPRPTLQLPLANDGGSRSPSSES
SPQHPTPPARPRHMLGLPSTLFTPRSMESIEIDQKLQEIMKQTGYLTIGGQRYQAEINDL ENLGEMGSGTCGQVWKMRFRKTGHVIAVKQMRRSGNKEENKRILMDLDVVLKSHDCPYIV QCFGTFITNTDVFIAMELMGTCAEKLKKRMQGPIPERILGKMTVAIVKALYYLKEKHGVI HRDVKPSNILLDERGQIKLCDFGISGRLVDSKAKTRSAGCAAYMAPERIDPPDPTKPDYD IRADVWSLGISLVELATGQFPYKNCKTDFEVLTKVLQEEPPLLPGHMGFSGDFQSFVKDC LTKDHRKRPKYNKLLEHSFIKRYETLEVDVASWFKDVMAKTESPRTSGVLSQPHLPFFR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T74V1Z | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Ibrutinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of MKK7 (MAP2K7) with ibrutinib bound at allosteric site | PDB:6YZ4 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.70 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
KQTGYLTIGG
126 QRYQAEINDL136 ENLGEMGGQV150 WKMRFRKTGH160 VIAVKQMRRS170 GNKEENKRIL 180 MDLDVVLKSH190 DCPYIVQCFG200 TFITNTDVFI210 AMELMGTCAE220 KLKKRMQGPI 230 PERILGKMTV240 AIVKALYYLK250 EKHGVIHRDV260 KPSNILLDER270 GQIKLCDFGI 280 SGRLGCAAYM300 APERIDPPDP310 TKPDYDIRAD320 VWSLGISLVE330 LATGQFPYKN 340 CKTDFEVLTK350 VLQEEPPLLP360 GHMGFSGDFQ370 SFVKDCLTKD380 HRKRPKYNKL 390 LEHSFIKRYE400 TLEVDVASWF410 KDVMAKTESP420
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: 3-Sulfinoalanine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of MKK7 (MAP2K7) in complex with K00007 | PDB:6YG4 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
TGYLTIGGQR
128 YQAEINDLEN138 LGEMGQVWKM153 RFRKTGHVIA163 VKQMRRSGNK173 EENKRILMDL 183 DVVLKSHDCP193 YIVQCFGTFI203 TNTDVFIAME213 LMGTAEKLKK224 RMQGPIPERI 234 LGKMTVAIVK244 ALYYLKEKHG254 VIHRDVKPSN264 ILLDERGQIK274 LDFGISGIRA 319 DVWSLGISLV329 ELATGQFPYK339 NCKTDFEVLT349 KVLQEEPPLL359 PGHMGFSGDF 369 QSFVKDCLTK379 DHRKRPKYNK389 LLEHSFIKRY399 ETLEVDVASW409 FKDVMAKT |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |
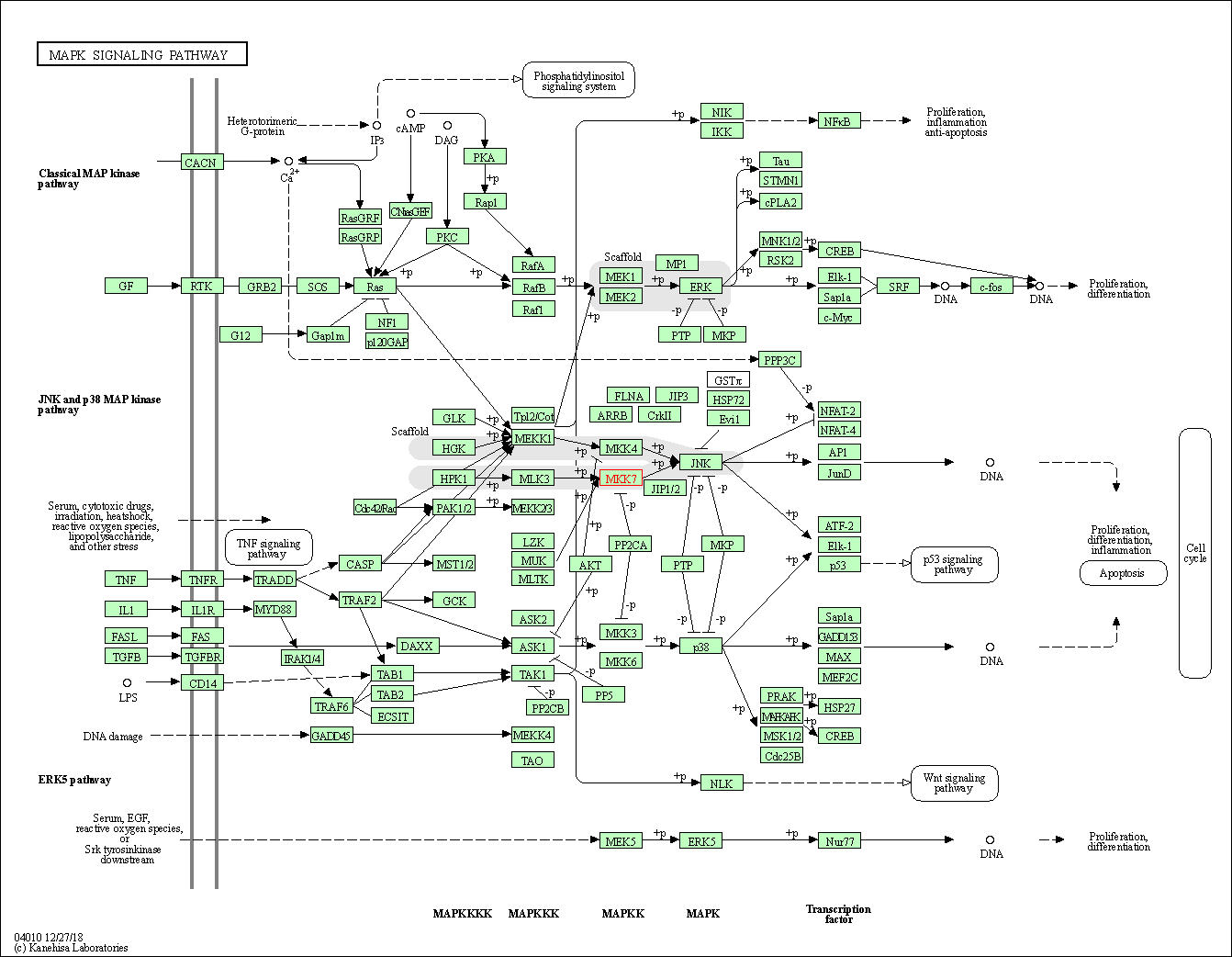
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |
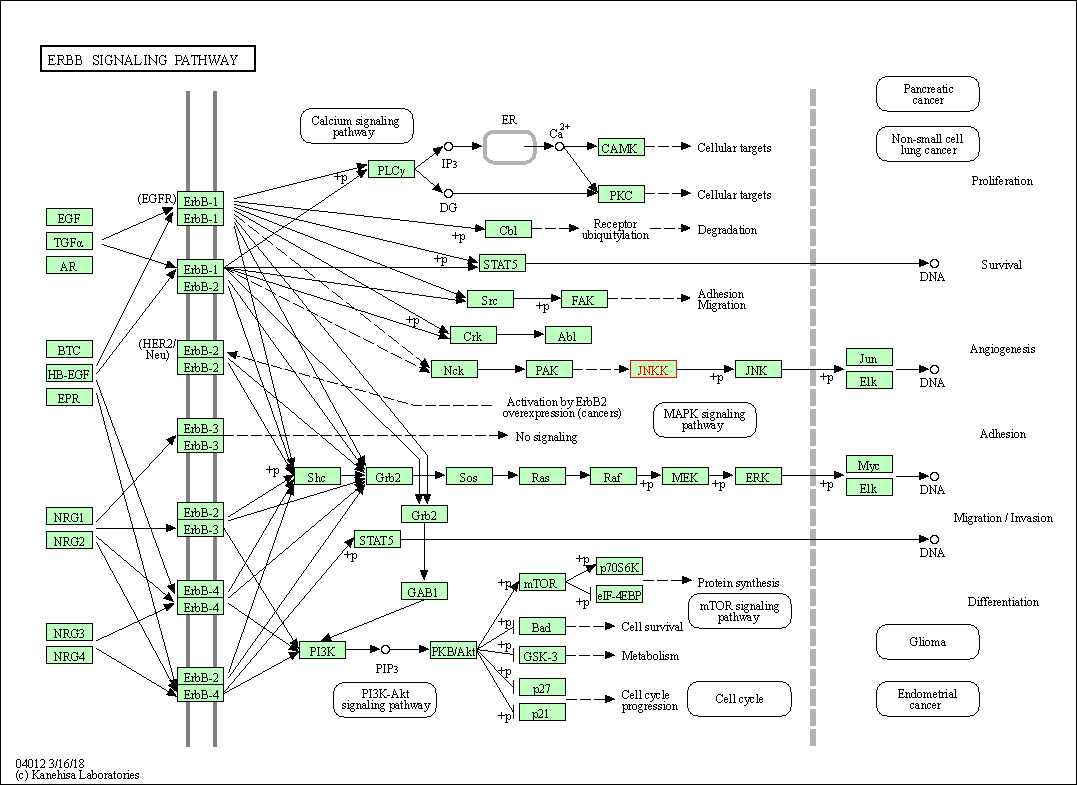
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |
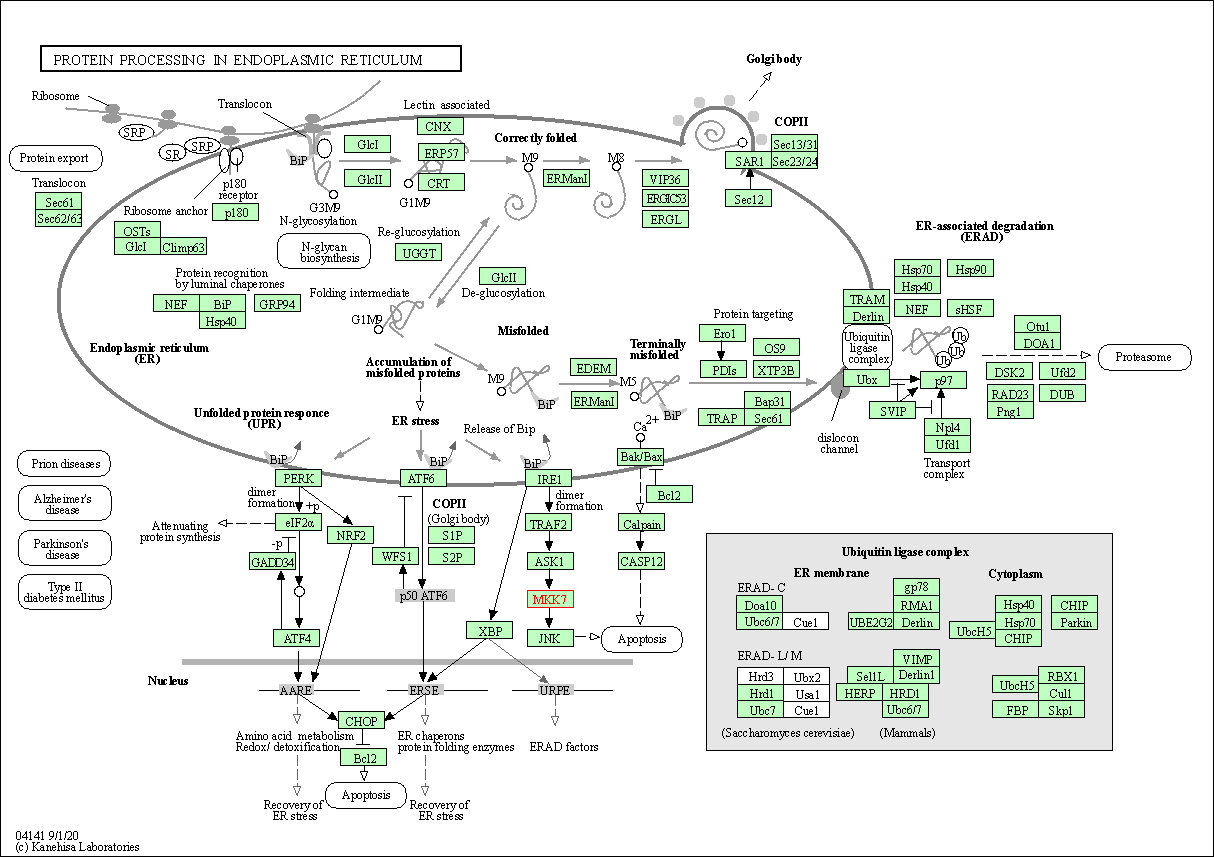
|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |
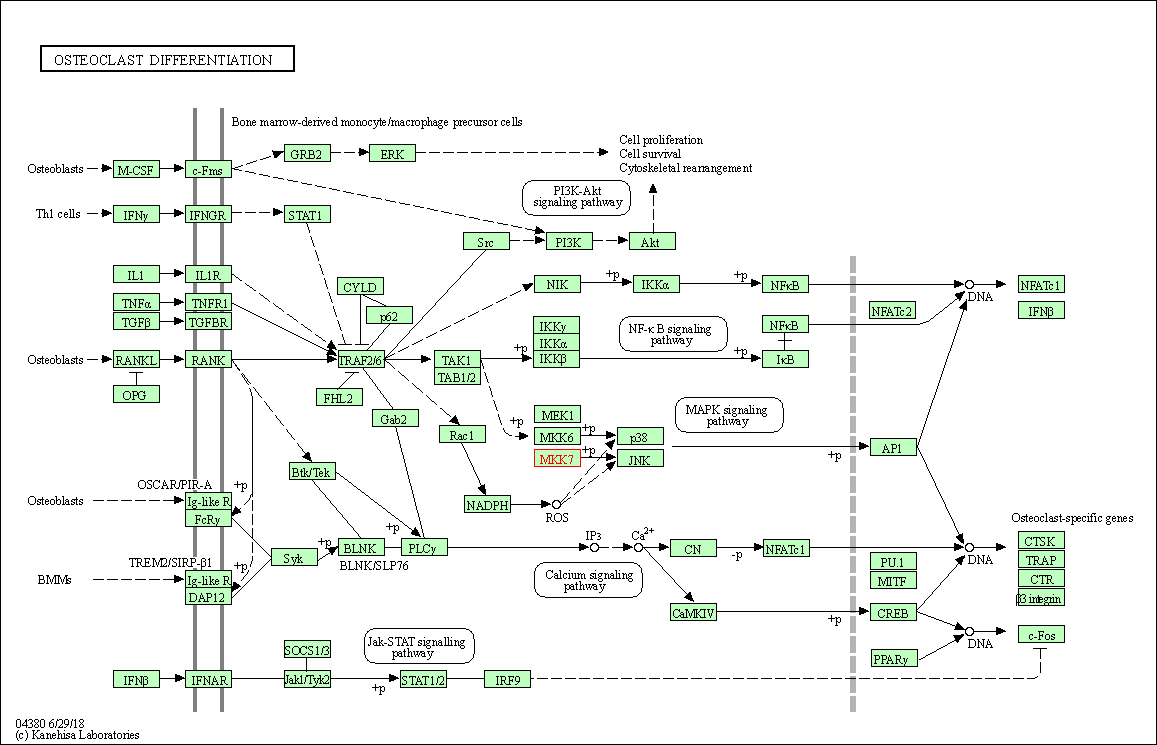
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Tight junction | hsa04530 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 15 | Degree centrality | 1.61E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.88E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.27E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.29E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.43E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.13E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | miR-125b inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition of triple-negative breast cancer by targeting MAP2K7. Onco Targets Ther. 2016 May 4;9:2639-48. | |||||
| REF 2 | Catalytic Domain Plasticity of MKK7 Reveals Structural Mechanisms of Allosteric Activation and Diverse Targeting Opportunities. Cell Chem Biol. 2020 Oct 15;27(10):1285-1295.e4. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

