Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T46628
(Former ID: TTDC00123)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit; MTP
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MTTP
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hyper-lipoproteinaemia [ICD-11: 5C80] | |||||
| Function |
Required for the secretion of plasma lipoproteins that contain apolipoprotein B. Catalyzes the transport of triglyceride, cholesteryl ester, and phospholipid between phospholipid surfaces.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MILLAVLFLCFISSYSASVKGHTTGLSLNNDRLYKLTYSTEVLLDRGKGKLQDSVGYRIS
SNVDVALLWRNPDGDDDQLIQITMKDVNVENVNQQRGEKSIFKGKSPSKIMGKENLEALQ RPTLLHLIHGKVKEFYSYQNEAVAIENIKRGLASLFQTQLSSGTTNEVDISGNCKVTYQA HQDKVIKIKALDSCKIARSGFTTPNQVLGVSSKATSVTTYKIEDSFVIAVLAEETHNFGL NFLQTIKGKIVSKQKLELKTTEAGPRLMSGKQAAAIIKAVDSKYTAIPIVGQVFQSHCKG CPSLSELWRSTRKYLQPDNLSKAEAVRNFLAFIQHLRTAKKEEILQILKMENKEVLPQLV DAVTSAQTSDSLEAILDFLDFKSDSSIILQERFLYACGFASHPNEELLRALISKFKGSIG SSDIRETVMIITGTLVRKLCQNEGCKLKAVVEAKKLILGGLEKAEKKEDTRMYLLALKNA LLPEGIPSLLKYAEAGEGPISHLATTALQRYDLPFITDEVKKTLNRIYHQNRKVHEKTVR TAAAAIILNNNPSYMDVKNILLSIGELPQEMNKYMLAIVQDILRFEMPASKIVRRVLKEM VAHNYDRFSRSGSSSAYTGYIERSPRSASTYSLDILYSGSGILRRSNLNIFQYIGKAGLH GSQVVIEAQGLEALIAATPDEGEENLDSYAGMSAILFDVQLRPVTFFNGYSDLMSKMLSA SGDPISVVKGLILLIDHSQELQLQSGLKANIEVQGGLAIDISGAMEFSLWYRESKTRVKN RVTVVITTDITVDSSFVKAGLETSTETEAGLEFISTVQFSQYPFLVCMQMDKDEAPFRQF EKKYERLSTGRGYVSQKRKESVLAGCEFPLHQENSEMCKVVFAPQPDSTSSGWF Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T35FQV | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BMS-201038 | Drug Info | Approved | Familial hypercholesterolemia | [2], [3] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 5 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Granotapide | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [4] | |
| 2 | Implitapide | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [5] | |
| 3 | JNJ-16269110 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [6] | |
| 4 | SLx-4090 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hyperlipidaemia | [7] | |
| 5 | KD020 | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Kidney disease | [8] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GR-328713 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Arteriosclerosis | [9] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 5 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BMS-201038 | Drug Info | [1], [10] | |||
| 2 | Granotapide | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 3 | Implitapide | Drug Info | [12], [13], [14] | |||
| 4 | JNJ-16269110 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 5 | DIRLOTAPIDE | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 3 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SLx-4090 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 2 | KD020 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | GR-328713 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat digestion and absorption | hsa04975 | Affiliated Target |
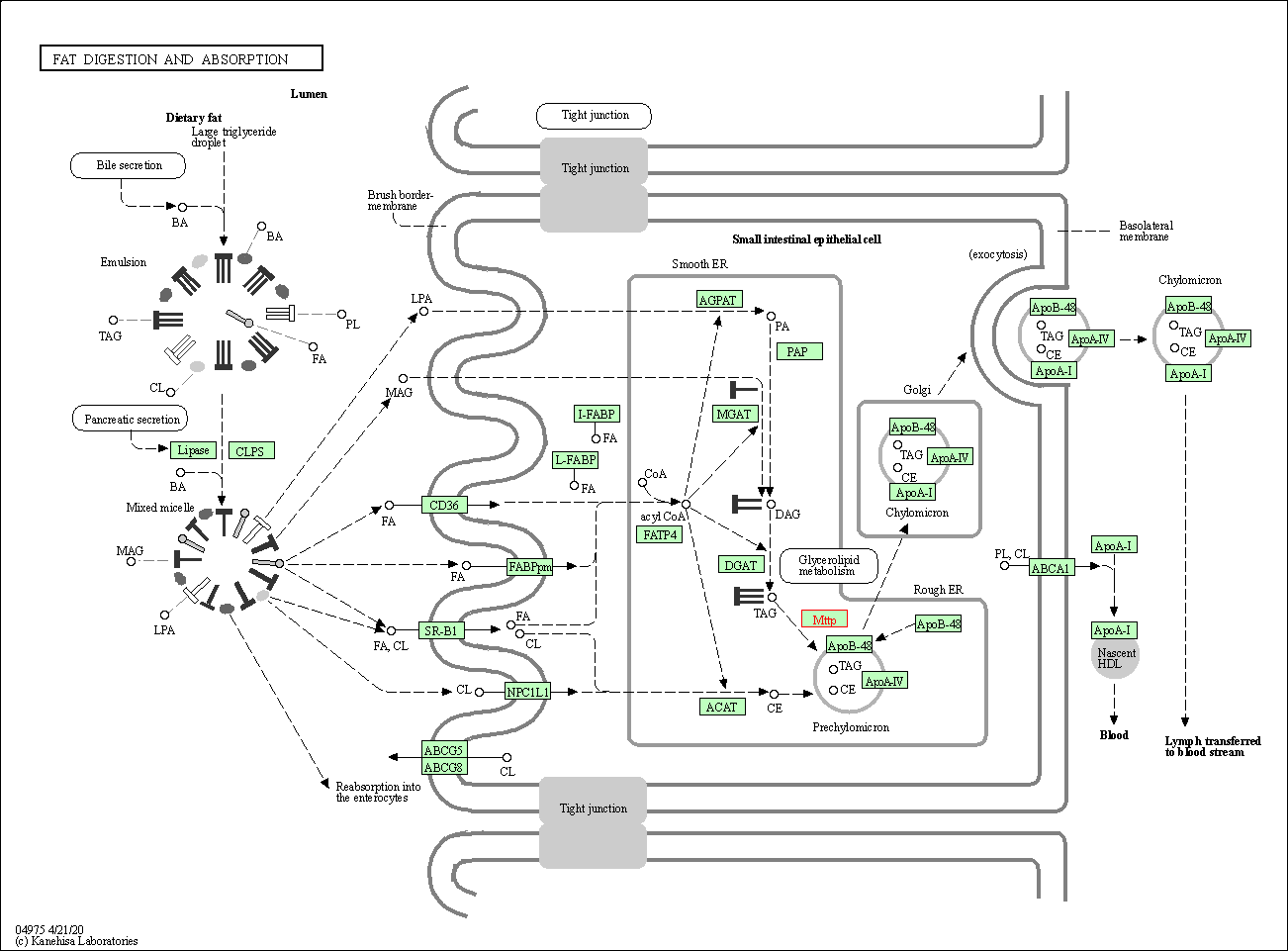
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 4 | Degree centrality | 4.30E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.32E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.87E-01 | Radiality | 1.32E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 5.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.10E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.39E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 1 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Fat digestion and absorption | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Chylomicron-mediated lipid transport | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Statin Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Lipid digestion, mobilization, and transport | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Dyslipidemia and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009 Apr;20(2):157-8. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7439). | |||||
| REF 3 | Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Feb;12(2):87-90. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00929539) Safety and Efficacy Study of JTT-130 in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00080132) Implitapide in Patients With Hypertriglyceridemia (HTG) on Maximal, Concurrent Triglyceride-Lowering Therapy. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00672386) A Study of the Safety and Effectiveness of a R256918 in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01675154) Phase 2 Study of Orlistat and SLx-4090 for the Treatment of Type 1 Hyperlipoproteinemia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800020855) | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800008868) | |||||
| REF 10 | Gateways to clinical trials. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Apr;29(3):231-45. | |||||
| REF 11 | JTT-130, a novel intestine-specific inhibitor of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein, suppresses food intake and gastric emptying with the elevation of plasma peptide YY and glucagon-like peptide-1 in a dietary fat-dependent manner. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Mar;336(3):850-6. | |||||
| REF 12 | Novel nonstatin strategies to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2009 Jan;11(1):67-70. | |||||
| REF 13 | Lipid-lowering drugs. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 May;63(10):1165-78. | |||||
| REF 14 | Implitapide, a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein inhibitor, reduces progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice fed a Western-type diet: involvement of the inhibition of postprandial triglyceride elevation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005 Feb;28(2):247-52. | |||||
| REF 15 | A small-molecule inhibitor of enterocytic microsomal triglyceride transfer protein, SLx-4090: biochemical, pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic, and safety profile. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Jun;337(3):775-85. | |||||
| REF 16 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Kadmon Pharmaceuticals. | |||||
| REF 17 | Patent CN101237870 B. | |||||
| REF 18 | In vitro and in vivo profile of 5-[(4'-trifluoromethyl-biphenyl-2-carbonyl)-amino]-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid benzylmethyl carbamoylamide (dirlota... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Apr 1;17(7):1996-9. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

