Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T37735
(Former ID: TTDI02082)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Glutamate decarboxylase (GLUL)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Glutamateammonia ligase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
GLUL
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Discontinued target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Parkinsonism [ICD-11: 8A00] | |||||
| Function |
Its role depends on tissue localization: in the brain, it regulates the levels of toxic ammonia and converts neurotoxic glutamate to harmless glutamine, whereas in the liver, it is one of the enzymes responsible for the removal of ammonia. Essential for proliferation of fetal skin fibroblasts. Independently of its glutamine synthetase activity, required for endothelial cell migration during vascular development: acts by regulating membrane localization and activation of the GTPase RHOJ, possibly by promoting RHOJ palmitoylation. May act as a palmitoyltransferase for RHOJ: able to autopalmitoylate and then transfer the palmitoyl group to RHOJ. Plays a role in ribosomal 40S subunit biogenesis. Glutamine synthetase that catalyzes the ATP-dependent conversion of glutamate and ammonia to glutamine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Carbon-nitrogen ligase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 6.3.1.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MTTSASSHLNKGIKQVYMSLPQGEKVQAMYIWIDGTGEGLRCKTRTLDSEPKCVEELPEW
NFDGSSTLQSEGSNSDMYLVPAAMFRDPFRKDPNKLVLCEVFKYNRRPAETNLRHTCKRI MDMVSNQHPWFGMEQEYTLMGTDGHPFGWPSNGFPGPQGPYYCGVGADRAYGRDIVEAHY RACLYAGVKIAGTNAEVMPAQWEFQIGPCEGISMGDHLWVARFILHRVCEDFGVIATFDP KPIPGNWNGAGCHTNFSTKAMREENGLKYIEEAIEKLSKRHQYHIRAYDPKGGLDNARRL TGFHETSNINDFSAGVANRSASIRIPRTVGQEKKGYFEDRRPSANCDPFSVTEALIRTCL LNETGDEPFQYKN Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T40JMU | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NLX-P101 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Parkinson disease | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NLX-P101 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: adenosine diphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human glutamine synthetase in complex with ADP and phosphate | PDB:2OJW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.05 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
YFQSMASSHL
9 NKGIKQVYMS19 LPQGEKVQAM29 YIWIDGTGEG39 LRCKTRTLDS49 EPKCVEELPE 59 WNFDGSSTLQ69 SEGSNSDMYL79 VPAAMFRDPF89 RKDPNKLVLC99 EVFKYNRRPA 109 ETNLRHTCKR119 IMDMVSNQHP129 WFGMEQEYTL139 MGDGHPFGWP150 SNGFPGPQGP 160 YYCGVGADRA170 YGRDIVEAHY180 RACLYAGVKI190 AGTNAEVMPA200 QWEFQIGPCE 210 GISMGDHLWV220 ARFILHRVCE230 DFGVIATFDP240 KPIPGNWNGA250 GCHTNFSTKA 260 MREENGLKYI270 EEAIEKLSKR280 HQYHIRAYDP290 KGGLDNARRL300 TSNINDFSAG 315 VANRSASIRI325 PRTVGQEKKG335 YFEDRRPSAN345 CDPFSVTEAL355 IRTCLLNETG 365
|
|||||
|
|
TRP130
3.461
PHE131
3.950
GLY132
3.547
MET133
4.180
GLU134
3.049
ALA191
3.738
ASN194
4.806
GLU203
3.105
GLN205
3.209
ILE206
3.709
GLY207
3.446
PRO208
3.371
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: L-Methionine-S-sulfoximine phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human glutamine synthetase in complex with ADP and methionine sulfoximine phosphate | PDB:2QC8 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
NKGIKQVYMS
19 LPQGEKVQAM29 YIWIDGTGEG39 LRCKTRTLDS49 EPKCVEELPE59 WNFDGSSTLQ 69 SEGSNSDMYL79 VPAAMFRDPF89 RKDPNKLVLC99 EVFKYNRRPA109 ETNLRHTCKR 119 IMDMVSNQHP129 WFGMEQEYTL139 MGTDGHPFGW149 PSNGFPGPQG159 PYYCGVGADR 169 AYGRDIVEAH179 YRACLYAGVK189 IAGTNAEVMP199 AQWEFQIGPC209 EGISMGDHLW 219 VARFILHRVC229 EDFGVIATFD239 PKPIPGNWNG249 AGCHTNFSTK259 AMREENGLKY 269 IEEAIEKLSK279 RHQYHIRAYD289 PKGGLDNARR299 LTGFHETSNI309 NDFSAGVANR 319 SASIRIPRTV329 GQEKKGYFED339 RRPSANCDPF349 SVTEALIRTC359 LLNETG |
|||||
|
|
GLU134
2.829
GLU136
2.707
TYR162
3.848
ASN194
4.932
GLU196
2.997
VAL197
3.975
GLN201
4.394
GLU203
3.105
ASN248
3.887
GLY249
2.664
ALA250
4.035
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arginine biosynthesis | hsa00220 | Affiliated Target |
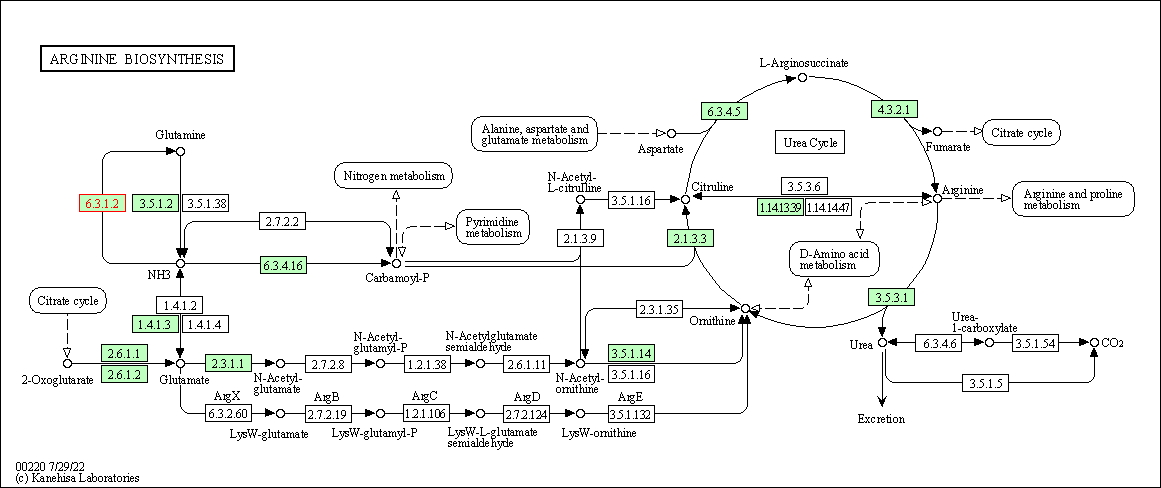
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | hsa00250 | Affiliated Target |
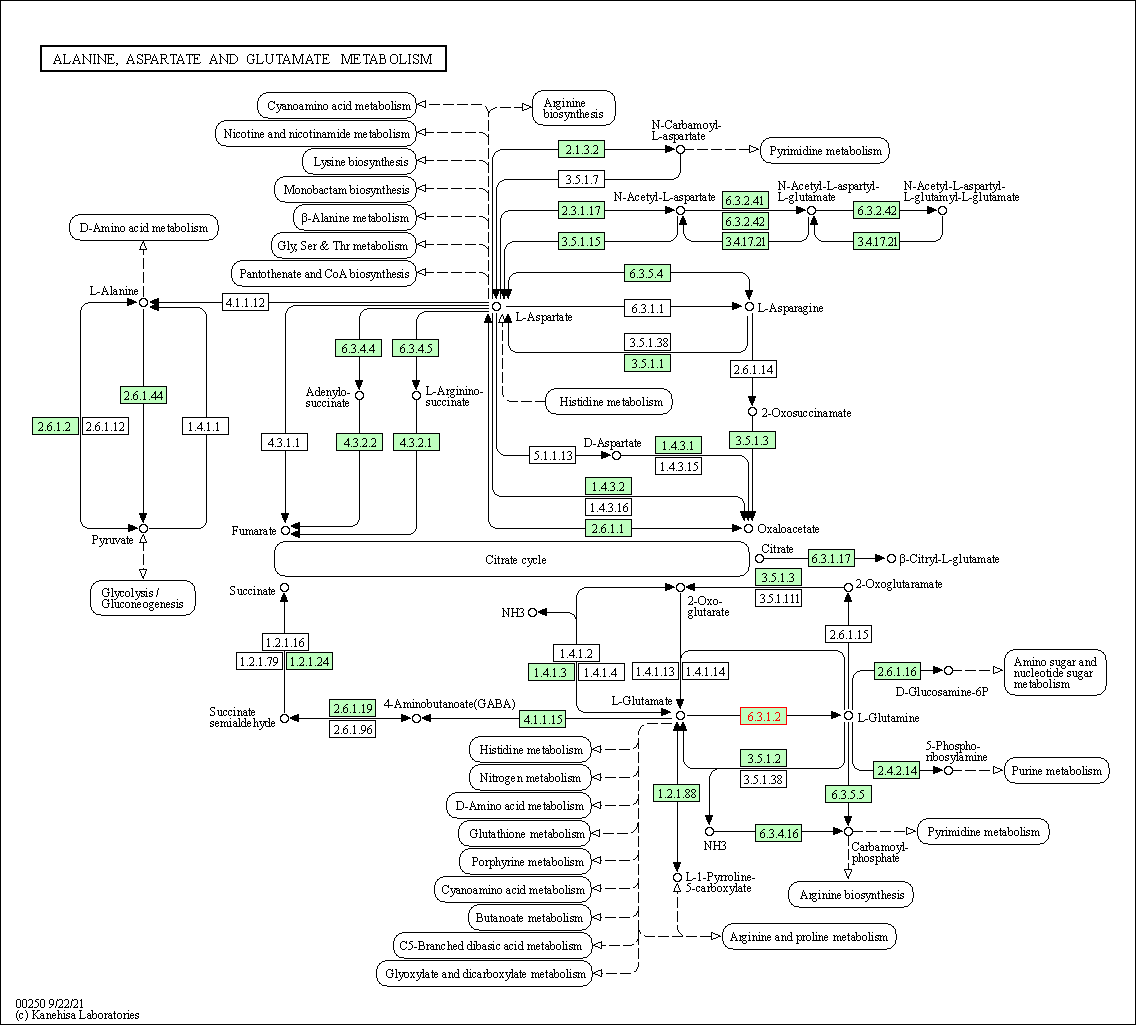
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | hsa00630 | Affiliated Target |
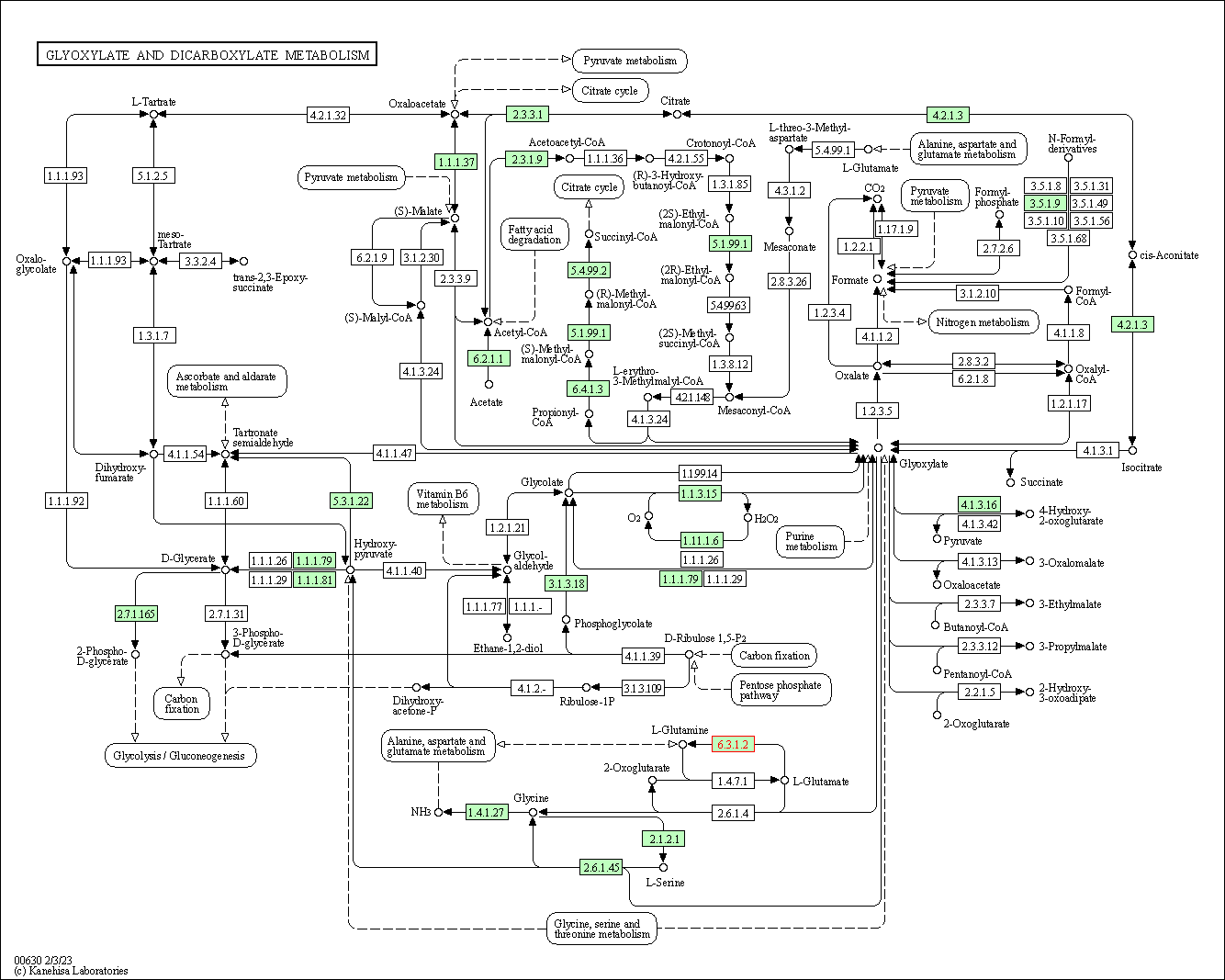
|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Nitrogen metabolism | hsa00910 | Affiliated Target |
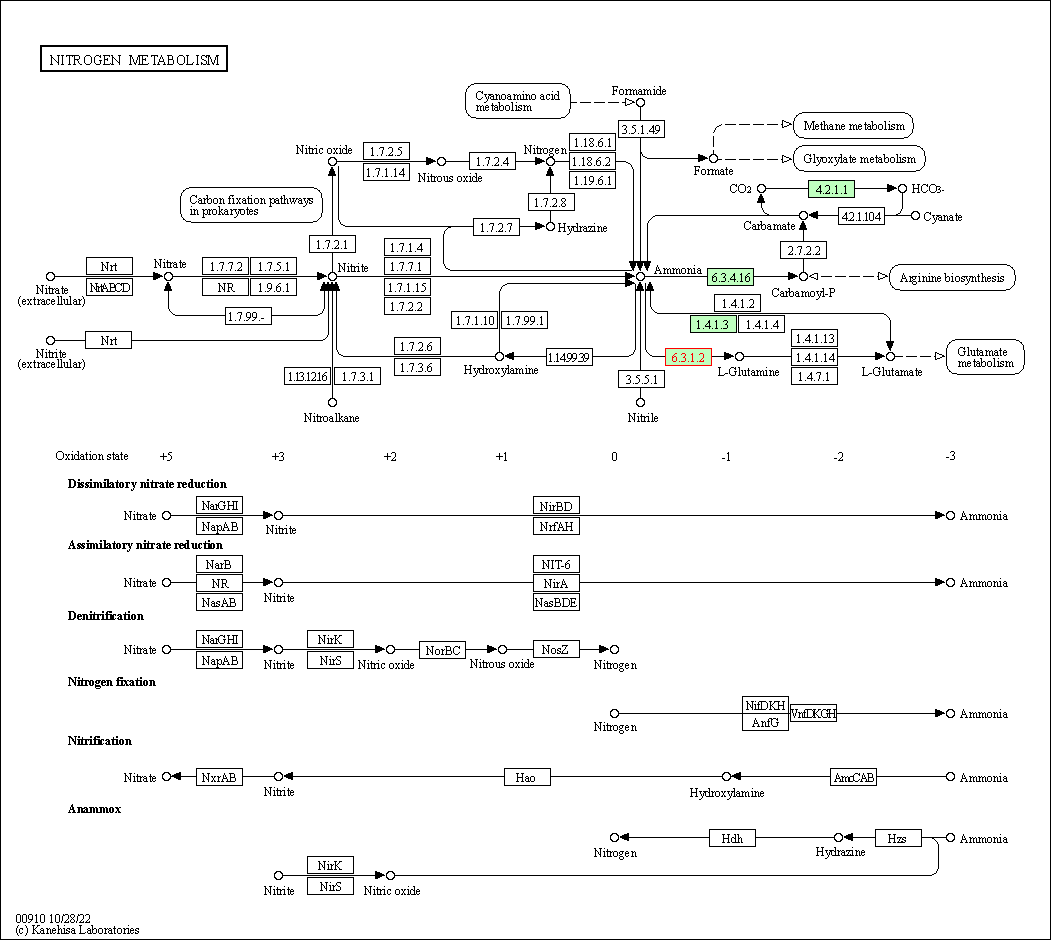
|
| Class: Metabolism => Energy metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glutamatergic synapse | hsa04724 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GABAergic synapse | hsa04727 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 5.51E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.89E-01 | Radiality | 1.32E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.50E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.22E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.00E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 3 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glutamate dependent acid resistance | |||||
| 2 | GABA shunt | |||||
| 3 | Glutamine biosynthesis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 8 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Arginine and proline metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Nitrogen metabolism | |||||
| 5 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 6 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | |||||
| 7 | Glutamatergic synapse | |||||
| 8 | GABAergic synapse | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glutamine glutamate conversion | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Amino acid synthesis and interconversion (transamination) | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Metabolism of amino acids and derivatives | |||||
| 2 | TNF alpha Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 3 | Neurotransmitter uptake and Metabolism In Glial Cells | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | NLX-P101, an adeno-associated virus gene therapy encoding glutamic acid decarboxylase, for the potential treatment of Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Jul;11(7):813-22. | |||||
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800017938) | |||||
| REF 3 | Crystal structures of mammalian glutamine synthetases illustrate substrate-induced conformational changes and provide opportunities for drug and herbicide design. J Mol Biol. 2008 Jan 4;375(1):217-28. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

