Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T25362
(Former ID: TTDI03361)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Lysine-specific demethylase 3A (KDM3A)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
TSGA; KIAA0742; Jumonji domain-containing protein 1A; JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2A; JMJD1A; JMJD1; JHDM2A
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KDM3A
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Preferentially demethylates mono- and dimethylated H3 'Lys-9' residue, with a preference for dimethylated residue, while it has weak or no activity on trimethylated H3 'Lys-9'. Demethylation of Lys residue generates formaldehyde and succinate. Involved in hormone-dependent transcriptional activation, by participating in recruitment to androgen-receptor target genes, resulting in H3 'Lys-9' demethylation and transcriptional activation. Involved in spermatogenesis by regulating expression of target genes such as PRM1 and TNP1 which are required for packaging and condensation of sperm chromatin. Involved in obesity resistance through regulation of metabolic genes such as PPARA and UCP1. Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.14.11.-
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MVLTLGESWPVLVGRRFLSLSAADGSDGSHDSWDVERVAEWPWLSGTIRAVSHTDVTKKD
LKVCVEFDGESWRKRRWIEVYSLLRRAFLVEHNLVLAERKSPEISERIVQWPAITYKPLL DKAGLGSITSVRFLGDQQRVFLSKDLLKPIQDVNSLRLSLTDNQIVSKEFQALIVKHLDE SHLLKGDKNLVGSEVKIYSLDPSTQWFSATVINGNPASKTLQVNCEEIPALKIVDPSLIH VEVVHDNLVTCGNSARIGAVKRKSSENNGTLVSKQAKSCSEASPSMCPVQSVPTTVFKEI LLGCTAATPPSKDPRQQSTPQAANSPPNLGAKIPQGCHKQSLPEEISSCLNTKSEALRTK PDVCKAGLLSKSSQIGTGDLKILTEPKGSCTQPKTNTDQENRLESVPQALTGLPKECLPT KASSKAELEIANPPELQKHLEHAPSPSDVSNAPEVKAGVNSDSPNNCSGKKVEPSALACR SQNLKESSVKVDNESCCSRSNNKIQNAPSRKSVLTDPAKLKKLQQSGEAFVQDDSCVNIV AQLPKCRECRLDSLRKDKEQQKDSPVFCRFFHFRRLQFNKHGVLRVEGFLTPNKYDNEAI GLWLPLTKNVVGIDLDTAKYILANIGDHFCQMVISEKEAMSTIEPHRQVAWKRAVKGVRE MCDVCDTTIFNLHWVCPRCGFGVCVDCYRMKRKNCQQGAAYKTFSWLKCVKSQIHEPENL MPTQIIPGKALYDVGDIVHSVRAKWGIKANCPCSNRQFKLFSKPASKEDLKQTSLAGEKP TLGAVLQQNPSVLEPAAVGGEAASKPAGSMKPACPASTSPLNWLADLTSGNVNKENKEKQ PTMPILKNEIKCLPPLPPLSKSSTVLHTFNSTILTPVSNNNSGFLRNLLNSSTGKTENGL KNTPKILDDIFASLVQNKTTSDLSKRPQGLTIKPSILGFDTPHYWLCDNRLLCLQDPNNK SNWNVFRECWKQGQPVMVSGVHHKLNSELWKPESFRKEFGEQEVDLVNCRTNEIITGATV GDFWDGFEDVPNRLKNEKEPMVLKLKDWPPGEDFRDMMPSRFDDLMANIPLPEYTRRDGK LNLASRLPNYFVRPDLGPKMYNAYGLITPEDRKYGTTNLHLDVSDAANVMVYVGIPKGQC EQEEEVLKTIQDGDSDELTIKRFIEGKEKPGALWHIYAAKDTEKIREFLKKVSEEQGQEN PADHDPIHDQSWYLDRSLRKRLHQEYGVQGWAIVQFLGDVVFIPAGAPHQVHNLYSCIKV AEDFVSPEHVKHCFWLTQEFRYLSQTHTNHEDKLQVKNVIYHAVKDAVAMLKASESSFGK P Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T59EAH | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |
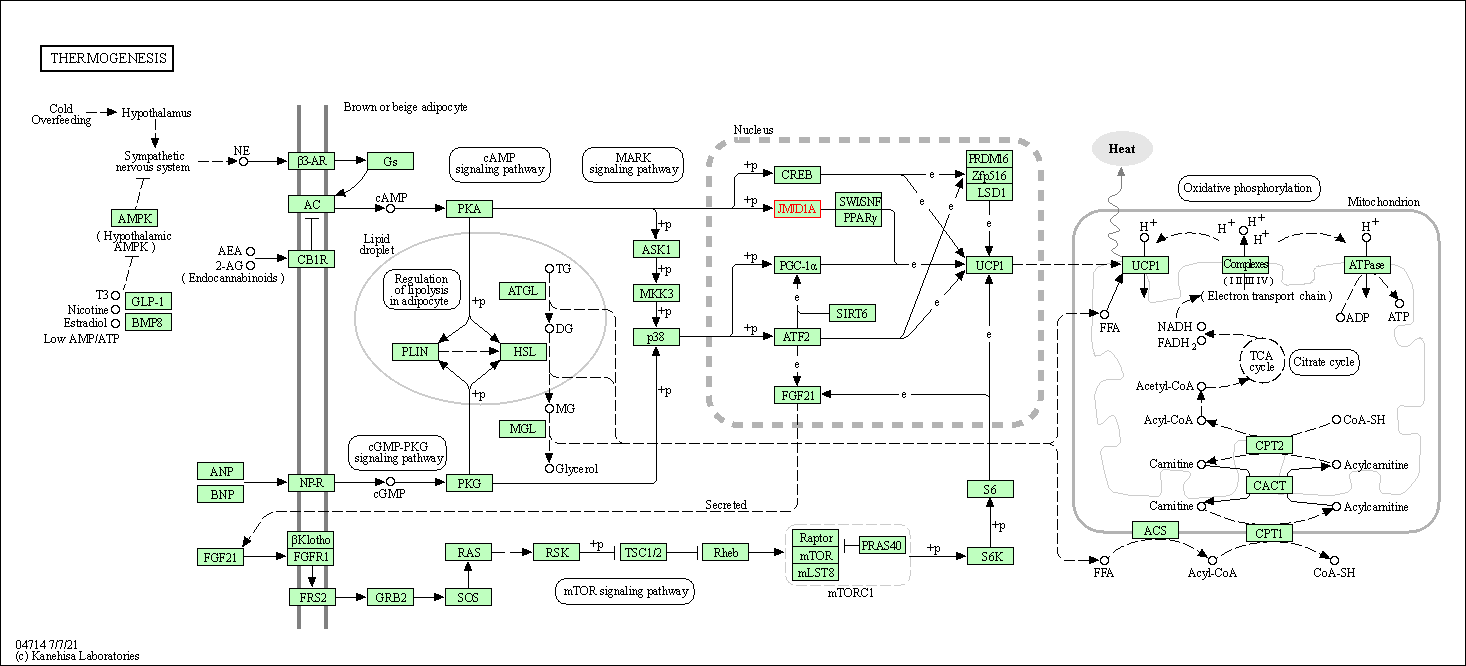
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 1 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 0.00E+00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.03E-01 | Radiality | 1.35E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.20E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.00E+00 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | A cell-permeable ester derivative of the JmjC histone demethylase inhibitor IOX1. ChemMedChem. 2014 Mar;9(3):566-71. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

