Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T18390
(Former ID: TTDI00083)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Large tumor suppressor homolog 2 (LATS2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Warts-like kinase; Serine/threonine-protein kinase kpm; Serine/threonine-protein kinase LATS2; Kinase phosphorylated during mitosis protein; KPM
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
LATS2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration. Acts as a tumor suppressor which plays a critical role in centrosome duplication, maintenance of mitotic fidelity and genomic stability. Negatively regulates G1/S transition by down-regulating cyclin E/CDK2 kinase activity. Negative regulator of the androgen receptor. Phosphorylates SNAI1 in the nucleus leading to its nuclear retention and stabilization, which enhances its epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor cell invasion/migration activities. This tumor-promoting activity is independent of its effects upon YAP1 or WWTR1/TAZ. Negative regulator of YAP1 in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MRPKTFPATTYSGNSRQRLQEIREGLKQPSKSSVQGLPAGPNSDTSLDAKVLGSKDATRQ
QQQMRATPKFGPYQKALREIRYSLLPFANESGTSAAAEVNRQMLQELVNAGCDQEMAGRA LKQTGSRSIEAALEYISKMGYLDPRNEQIVRVIKQTSPGKGLMPTPVTRRPSFEGTGDSF ASYHQLSGTPYEGPSFGADGPTALEEMPRPYVDYLFPGVGPHGPGHQHQHPPKGYGASVE AAGAHFPLQGAHYGRPHLLVPGEPLGYGVQRSPSFQSKTPPETGGYASLPTKGQGGPPGA GLAFPPPAAGLYVPHPHHKQAGPAAHQLHVLGSRSQVFASDSPPQSLLTPSRNSLNVDLY ELGSTSVQQWPAATLARRDSLQKPGLEAPPRAHVAFRPDCPVPSRTNSFNSHQPRPGPPG KAEPSLPAPNTVTAVTAAHILHPVKSVRVLRPEPQTAVGPSHPAWVPAPAPAPAPAPAPA AEGLDAKEEHALALGGAGAFPLDVEYGGPDRRCPPPPYPKHLLLRSKSEQYDLDSLCAGM EQSLRAGPNEPEGGDKSRKSAKGDKGGKDKKQIQTSPVPVRKNSRDEEKRESRIKSYSPY AFKFFMEQHVENVIKTYQQKVNRRLQLEQEMAKAGLCEAEQEQMRKILYQKESNYNRLKR AKMDKSMFVKIKTLGIGAFGEVCLACKVDTHALYAMKTLRKKDVLNRNQVAHVKAERDIL AEADNEWVVKLYYSFQDKDSLYFVMDYIPGGDMMSLLIRMEVFPEHLARFYIAELTLAIE SVHKMGFIHRDIKPDNILIDLDGHIKLTDFGLCTGFRWTHNSKYYQKGSHVRQDSMEPSD LWDDVSNCRCGDRLKTLEQRARKQHQRCLAHSLVGTPNYIAPEVLLRKGYTQLCDWWSVG VILFEMLVGQPPFLAPTPTETQLKVINWENTLHIPAQVKLSPEARDLITKLCCSADHRLG RNGADDLKAHPFFSAIDFSSDIRKQPAPYVPTISHPMDTSNFDPVDEESPWNDASEGSTK AWDTLTSPNNKHPEHAFYEFTFRRFFDDNGYPFRCPKPSGAEASQAESSDLESSDLVDQT EGCQPVYV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | Affiliated Target |
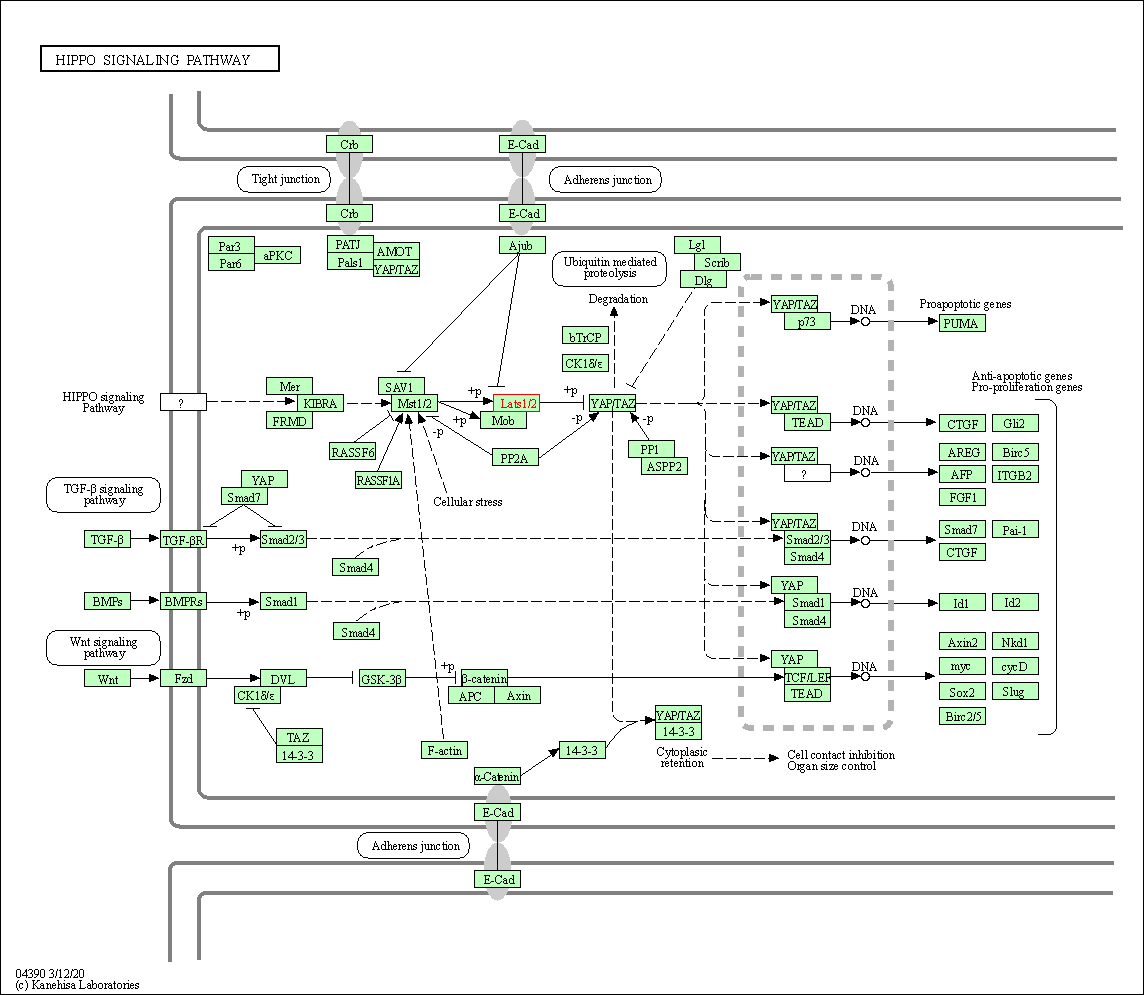
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species | hsa04392 | Affiliated Target |
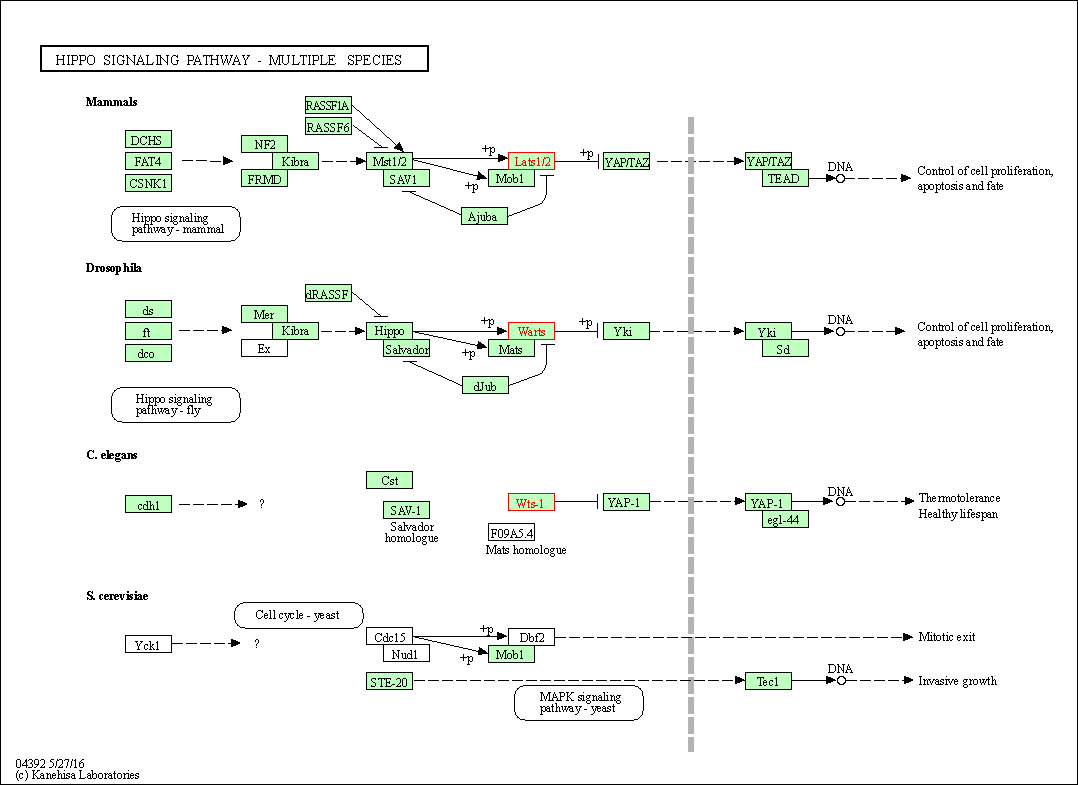
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 15 | Degree centrality | 1.61E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 9.24E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.21E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.10E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.43E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.07E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Coregulation of Androgen receptor activity | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Signaling by Hippo | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives as highly selective and potent Rho kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 12;53(15):5727-37. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

