Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T15068
(Former ID: TTDR00669)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Focal adhesion kinase 1 (FAK)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
pp125FAK; p125FAK; Protein-tyrosine kinase 2; Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 71; PPP1R71; Focal adhesion kinase-related nonkinase; FRNK; FAK1; FADK 1; FADK
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PTK2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 6 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||||
| 2 | Peritoneal cancer [ICD-11: 2C51] | |||||
| 3 | Metastatic tumour [ICD-11: 2D50-2E2Z] | |||||
| 4 | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||||
| 5 | Pulmonary hypertension [ICD-11: BB01] | |||||
| 6 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Required for early embryonic development and placenta development. Required for embryonic angiogenesis, normal cardiomyocyte migration and proliferation, and normal heart development. Regulates axon growth and neuronal cell migration, axon branching and synapse formation; required for normal development of the nervous system. Plays a role in osteogenesis and differentiation of osteoblasts. Functions in integrin signal transduction, but also in signaling downstream of numerous growth factor receptors, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR), EPHA2, netrin receptors and LDL receptors. Forms multisubunit signaling complexes with SRC and SRC family members upon activation; this leads to the phosphorylation of additional tyrosine residues, creating binding sites for scaffold proteins, effectors and substrates. Regulates numerous signaling pathways. Promotes activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the AKT1 signaling cascade. Promotes activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling cascade. Promotes localized and transient activation of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), and thereby modulates the activity of Rho family GTPases. Signaling via CAS family members mediates activation of RAC1. Recruits the ubiquitin ligase MDM2 to P53/TP53 in the nucleus, and thereby regulates P53/TP53 activity, P53/TP53 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylates SRC; this increases SRC kinase activity. Phosphorylates ACTN1, ARHGEF7, GRB7, RET and WASL. Promotes phosphorylation of PXN and STAT1; most likely PXN and STAT1 are phosphorylated by a SRC family kinase that is recruited to autophosphorylated PTK2/FAK1, rather than by PTK2/FAK1 itself. Promotes phosphorylation of BCAR1; GIT2 and SHC1; this requires both SRC and PTK2/FAK1. Promotes phosphorylation of BMX and PIK3R1. Isoform 6 (FRNK) does not contain a kinase domain and inhibits PTK2/FAK1 phosphorylation and signaling. Its enhanced expression can attenuate the nuclear accumulation of LPXN and limit its ability to enhance serum response factor (SRF)-dependent gene transcription. Non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulating cell migration, adhesion, spreading, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, formation and disassembly of focal adhesions and cell protrusions, cell cycle progression, cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAAAYLDPNLNHTPNSSTKTHLGTGMERSPGAMERVLKVFHYFESNSEPTTWASIIRHGD
ATDVRGIIQKIVDSHKVKHVACYGFRLSHLRSEEVHWLHVDMGVSSVREKYELAHPPEEW KYELRIRYLPKGFLNQFTEDKPTLNFFYQQVKSDYMLEIADQVDQEIALKLGCLEIRRSY WEMRGNALEKKSNYEVLEKDVGLKRFFPKSLLDSVKAKTLRKLIQQTFRQFANLNREESI LKFFEILSPVYRFDKECFKCALGSSWIISVELAIGPEEGISYLTDKGCNPTHLADFTQVQ TIQYSNSEDKDRKGMLQLKIAGAPEPLTVTAPSLTIAENMADLIDGYCRLVNGTSQSFII RPQKEGERALPSIPKLANSEKQGMRTHAVSVSETDDYAEIIDEEDTYTMPSTRDYEIQRE RIELGRCIGEGQFGDVHQGIYMSPENPALAVAIKTCKNCTSDSVREKFLQEALTMRQFDH PHIVKLIGVITENPVWIIMELCTLGELRSFLQVRKYSLDLASLILYAYQLSTALAYLESK RFVHRDIAARNVLVSSNDCVKLGDFGLSRYMEDSTYYKASKGKLPIKWMAPESINFRRFT SASDVWMFGVCMWEILMHGVKPFQGVKNNDVIGRIENGERLPMPPNCPPTLYSLMTKCWA YDPSRRPRFTELKAQLSTILEEEKAQQEERMRMESRRQATVSWDSGGSDEAPPKPSRPGY PSPRSSEGFYPSPQHMVQTNHYQVSGYPGSHGITAMAGSIYPGQASLLDQTDSWNHRPQE IAMWQPNVEDSTVLDLRGIGQVLPTHLMEERLIRQQQEMEEDQRWLEKEERFLKPDVRLS RGSIDREDGSLQGPIGNQHIYQPVGKPDPAAPPKKPPRPGAPGHLGSLASLSSPADSYNE GVKLQPQEISPPPTANLDRSNDKVYENVTGLVKAVIEMSSKIQPAPPEEYVPMVKEVGLA LRTLLATVDETIPLLPASTHREIEMAQKLLNSDLGELINKMKLAQQYVMTSLQQEYKKQM LTAAHALAVDAKNLLDVIDQARLKMLGQTRPH Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05675 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T98RXH | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 7 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | VS-6063 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Ovarian cancer | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | BI-853520 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [4] | |
| 3 | CEP-37440 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [5] | |
| 4 | GSK-2256098 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [6], [7] | |
| 5 | IN10018 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Metastatic melanoma | [8] | |
| 6 | PF-562271 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [9] | |
| 7 | VS-4718 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [10] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 9 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | VS-6063 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | GSK-2256098 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 3 | IN10018 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 4 | PF-562271 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 5 | VS-4718 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 6 | 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5a]pyridine derivative 1 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 7 | BMS-536924 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 8 | PF-228 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 9 | PMID23414845C30 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 2 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BI-853520 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 2 | CEP-37440 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Focal Adhesion Kinase Domain with 2 molecules in the Asymmetric Unit Complexed with ADP and ATP | PDB:2IJM | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.19 Å | Mutation | No | [20] |
| PDB Sequence |
DYEIQRERIE
423 LGRCIGEGQF433 GDVHQGIYMS443 PENPALAVAI453 KTCKNCTSDS463 VREKFLQEAL 473 TMRQFDHPHI483 VKLIGVITEN493 PVWIIMELCT503 LGELRSFLQV513 RKYSLDLASL 523 ILYAYQLSTA533 LAYLESKRFV543 HRDIAARNVL553 VSSNDCVKLG563 DFGLSLPIKW 588 MAPESINFRR598 FTSASDVWMF608 GVCMWEILMH618 GVKPFQGVKN628 NDVIGRIENG 638 ERLPMPPNCP648 PTLYSLMTKC658 WAYDPSRRPR668 FTELKAQLST678 ILEEEKAQQE 688
|
|||||
|
|
ILE428
3.512
GLY429
3.604
GLU430
3.569
GLY431
3.060
GLN432
2.557
PHE433
4.815
VAL436
3.461
ALA452
3.538
LYS454
2.932
GLU471
2.872
VAL484
4.507
MET499
3.340
GLU500
2.758
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: PF-562271 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure Analysis of Focal Adhesion Kinase with a Methanesulfonamide Diaminopyrimidine Inhibitor | PDB:3BZ3 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.20 Å | Mutation | No | [21] |
| PDB Sequence |
DYEIQRERIE
423 LGRCIGEGQF433 GDVHQGIYMS443 PLAVAIKTCK457 NCTSDSVREK467 FLQEALTMRQ 477 FDHPHIVKLI487 GVITENPVWI497 IMELCTLGEL507 RSFLQVRKYS517 LDLASLILYA 527 YQLSTALAYL537 ESKRFVHRDI547 AARNVLVSSN557 DCVKLGDFGL567 SRYLPIKWMA 590 PESINFRRFT600 SASDVWMFGV610 CMWEILMHGV620 KPFQGVKNND630 VIGRIENGER 640 LPMPPNCPPT650 LYSLMTKCWA660 YDPSRRPRFT670 ELKAQLSTIL680 EEEKAQQEE |
|||||
|
|
ARG426
2.633
ILE428
3.607
GLY429
3.935
GLU430
3.757
GLY431
4.329
VAL436
3.519
GLN438
3.631
ALA452
3.687
LYS454
4.500
VAL484
3.924
MET499
3.397
GLU500
3.164
LEU501
3.523
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|






| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
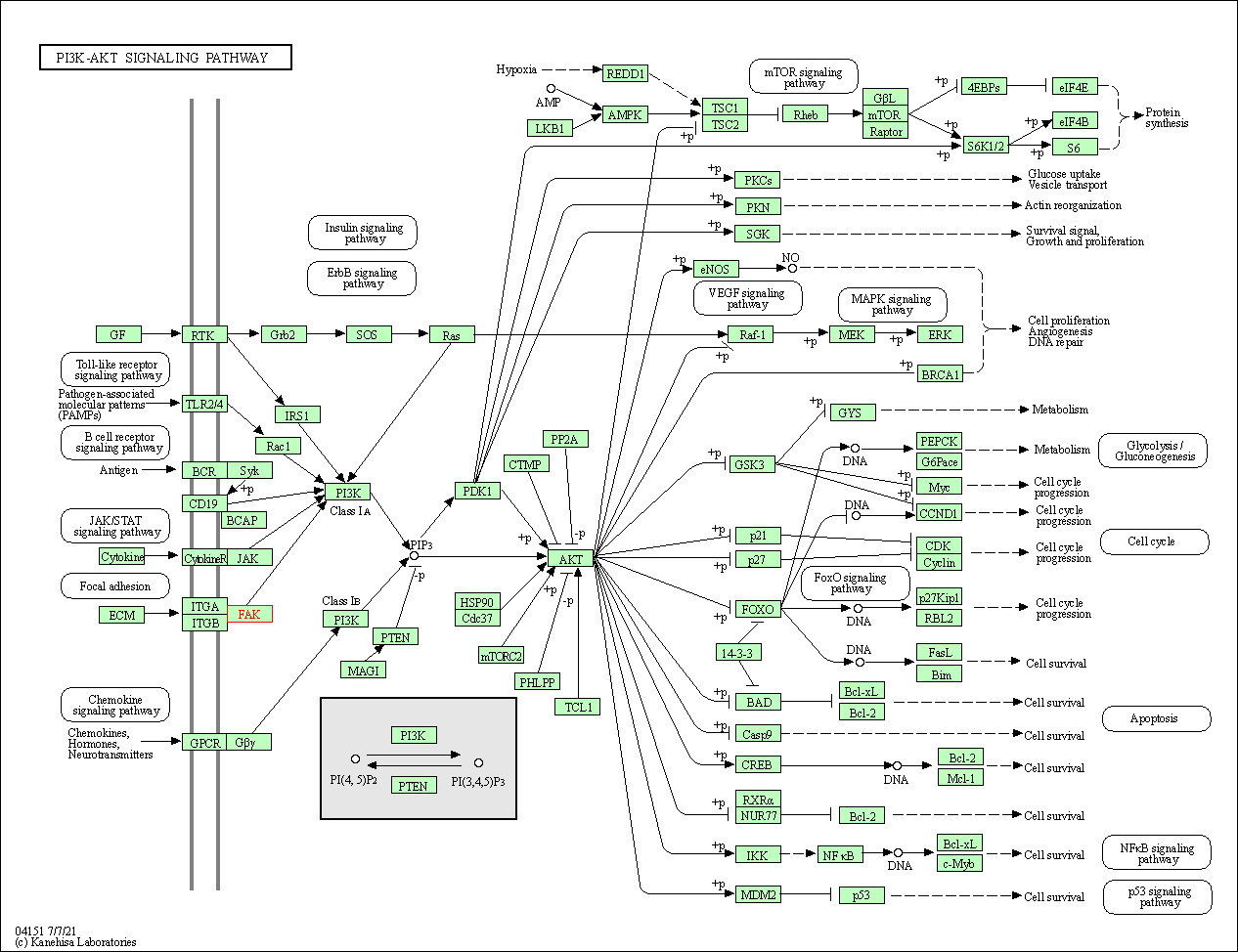
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
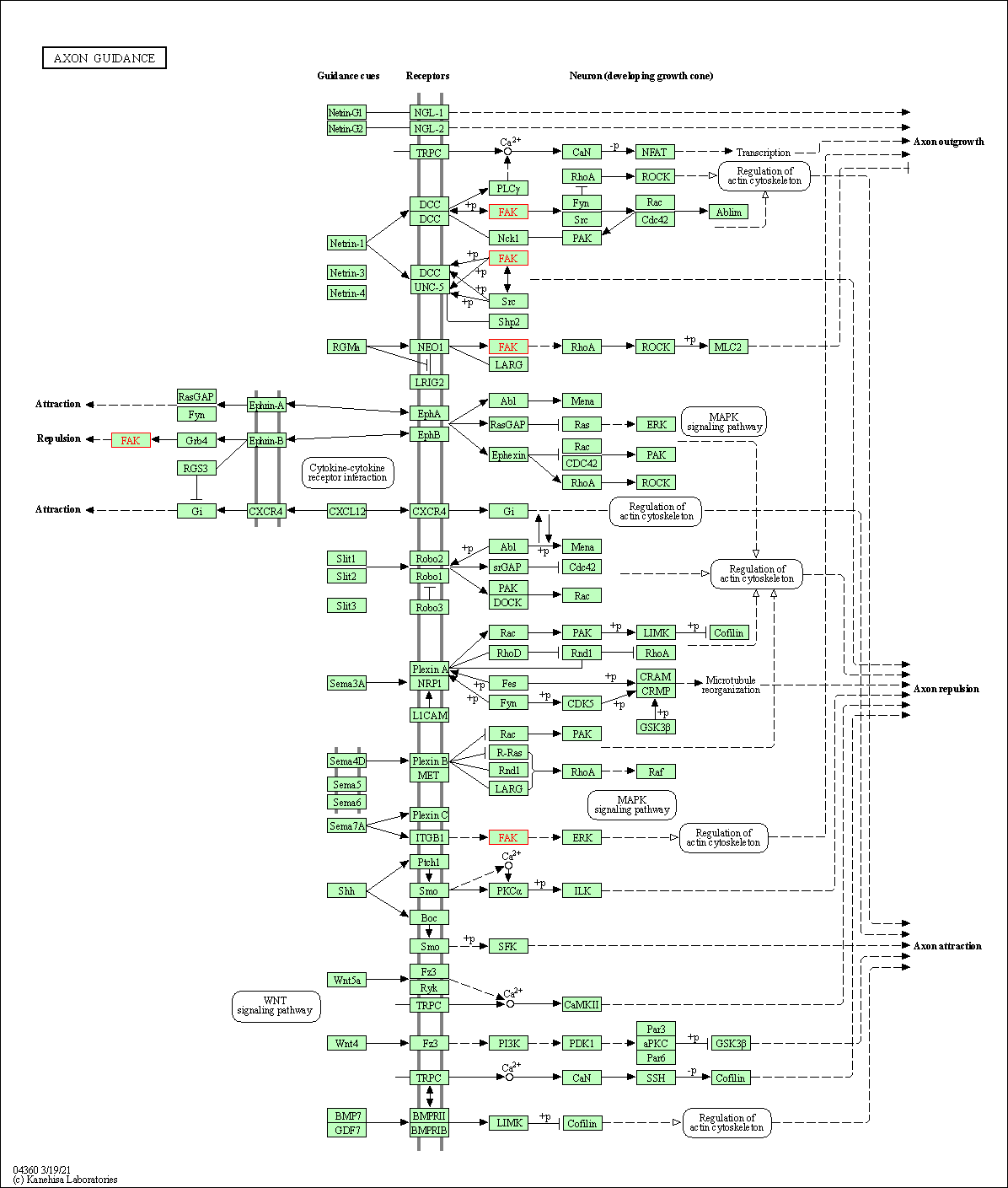
| Axon guidance | hsa04360 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
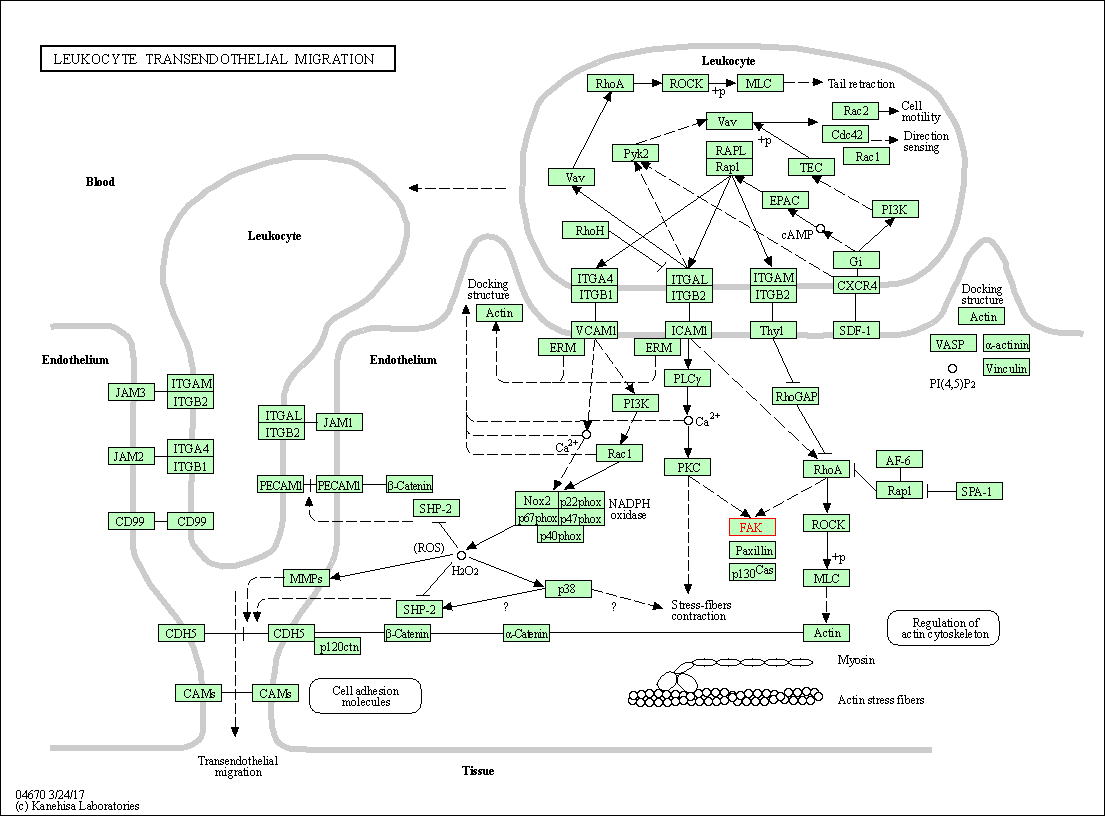
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | hsa04670 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 66 | Degree centrality | 7.09E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 7.54E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.71E-01 | Radiality | 1.46E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.57E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.98E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.90E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Role of focal adhesion kinase in regulating YB-1-mediated paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Oct 2;105(19):1485-95. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01905111) A Study of BI 853520 in Japanese and Taiwanese Patients With Various Types of Advanced or Metastatic Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01922752) To Determine the Maximum Tolerated Dose of Oral CEP-37440 in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7939). | |||||
| REF 7 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800031307) | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04109456) IN10018 Monotherapy and Combination Therapy for Metastatic Melanoma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00666926) Study Of PF-00562271, Including Patients With Pancreatic, Head And Neck, Prostatic Neoplasms. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01849744) Phase I Dose Escalation Study of VS-4718 in Subjects With Metastatic Non-Hematologic Malignancies. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 12 | A small molecule FAK kinase inhibitor, GSK2256098, inhibits growth and survival of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Cycle. 2014;13(19):3143-9. | |||||
| REF 13 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of InxMed. | |||||
| REF 14 | Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2135-45. | |||||
| REF 15 | FAK Inhibition disrupts a beta5 integrin signaling axis controlling anchorage-independent ovarian carcinoma growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Aug;13(8):2050-61. | |||||
| REF 16 | Inhibitors of JAK-family kinases: an update on the patent literature 2013-2015, part 1.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Feb;27(2):127-143. | |||||
| REF 17 | Discovery of a (1H-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyridin-2-one (BMS-536924) inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor I receptor kinase with in vivo antitum... J Med Chem. 2005 Sep 8;48(18):5639-43. | |||||
| REF 18 | Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2007 May 18;282(20):14845-52. | |||||
| REF 19 | Structure-based discovery of cellular-active allosteric inhibitors of FAK. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Mar 15;23(6):1779-85. | |||||
| REF 20 | Crystal Structure of Focal Adhesion Kinase Catalytic Domain Complexed with ATP and Novel 7H-Pyrrolo [2,3-d] pyrimidine Inhibitor Scaffolds | |||||
| REF 21 | Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, PF-562,271. Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 15;68(6):1935-44. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

