Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T14065
(Former ID: TTDC00031)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Integrin beta-7 (ITGB7)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Gut homing receptor beta subunit
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ITGB7
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Crohn disease [ICD-11: DD70] | |||||
| 2 | Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71] | |||||
| Function |
Integrin alpha-4/beta-7 interacts with the cell surface adhesion molecules MADCAM1 which is normally expressed by the vascular endothelium of the gastrointestinal tract. Interacts also with VCAM1 and fibronectin, an extracellular matrix component. It recognizes one or more domains within the alternatively spliced CS-1 region of fibronectin. Interactions involves the tripeptide L-D-T in MADCAM1, and L-D-V in fibronectin. Binds to HIV-1 gp120, thereby allowing the virus to enter GALT, which is thought to be the major trigger of AIDS disease. Interaction would involve a tripeptide L-D-I in HIV-1 gp120. Integrin alpha-E/beta-7 (HML-1) is a receptor for E-cadherin. Integrin alpha-4/beta-7 (Peyer patches-specific homing receptor LPAM-1) is an adhesion molecule that mediates lymphocyte migration and homing to gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT).
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Integrin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MVALPMVLVLLLVLSRGESELDAKIPSTGDATEWRNPHLSMLGSCQPAPSCQKCILSHPS
CAWCKQLNFTASGEAEARRCARREELLARGCPLEELEEPRGQQEVLQDQPLSQGARGEGA TQLAPQRVRVTLRPGEPQQLQVRFLRAEGYPVDLYYLMDLSYSMKDDLERVRQLGHALLV RLQEVTHSVRIGFGSFVDKTVLPFVSTVPSKLRHPCPTRLERCQSPFSFHHVLSLTGDAQ AFEREVGRQSVSGNLDSPEGGFDAILQAALCQEQIGWRNVSRLLVFTSDDTFHTAGDGKL GGIFMPSDGHCHLDSNGLYSRSTEFDYPSVGQVAQALSAANIQPIFAVTSAALPVYQELS KLIPKSAVGELSEDSSNVVQLIMDAYNSLSSTVTLEHSSLPPGVHISYESQCEGPEKREG KAEDRGQCNHVRINQTVTFWVSLQATHCLPEPHLLRLRALGFSEELIVELHTLCDCNCSD TQPQAPHCSDGQGHLQCGVCSCAPGRLGRLCECSVAELSSPDLESGCRAPNGTGPLCSGK GHCQCGRCSCSGQSSGHLCECDDASCERHEGILCGGFGRCQCGVCHCHANRTGRACECSG DMDSCISPEGGLCSGHGRCKCNRCQCLDGYYGALCDQCPGCKTPCERHRDCAECGAFRTG PLATNCSTACAHTNVTLALAPILDDGWCKERTLDNQLFFFLVEDDARGTVVLRVRPQEKG ADHTQAIVLGCVGGIVAVGLGLVLAYRLSVEIYDRREYSRFEKEQQQLNWKQDSNPLYKS AITTTINPRFQEADSPTL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Vedolizmab | Drug Info | Approved | Crohn disease | [2] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Rhumab Beta7 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Ulcerative colitis | [3] | |
| 2 | AMG-181 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Crohn disease | [4] | |
| 3 | PTG-100 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Ulcerative colitis | [5] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 2 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Vedolizmab | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | PTG-100 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Glutathione | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of the filamin A repeat 21 complexed with the integrin beta7 cytoplasmic tail peptide | PDB:2BRQ | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.10 Å | Mutation | No | [9] |
| PDB Sequence |
PLYKSAITTT
785 INPR
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: N-(2,6-Dichlorobenzoyl)-4-[1,6-Dimethyl-2-Oxo-4-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2-Dihydropyridin-3-Yl]-L-Phenylalanine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | crystal structure of a4b7 headpiece complexed with Fab ACT-1 and RO0505376 | PDB:3V4V | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | Yes | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
RGQQEVLQDQ
90 PLSQGARGEG100 ATQLAPQRVR110 VTLRPGEPQQ120 LQVRFLRAEG130 YPVDLYYLMD 140 LSYSMKDDLE150 RVRQLGHALL160 VRLQEVTHSV170 RIGFGSFVDK180 TVLPFVSTVP 190 SKLRHPCPTR200 LERCQSPFSF210 HHVLSLTGDA220 QAFEREVGRQ230 SVSGNLDSPE 240 GGFDAILQAA250 LCQEQIGWRN260 VSRLLVFTSD270 DTFHTAGDGK280 LGGIFMPSDG 290 HCHLDSNGLY300 SRSTEFDYPS310 VGQVAQALSA320 ANIQPIFAVT330 SAALPVYQEL 340 SKLIPKSAVG350 ELSEDSSNVV360 QLIMDAYNSL370 SSTVTLEHSS380 LPPGVHISYE 390 SQCEGPEKRE400 GKAEDRGQCN410 HVRINQTVTF420 WVSLQATHCL430 PEPHLLRLRA 440 LGFSEELIVE450 LHTLC
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
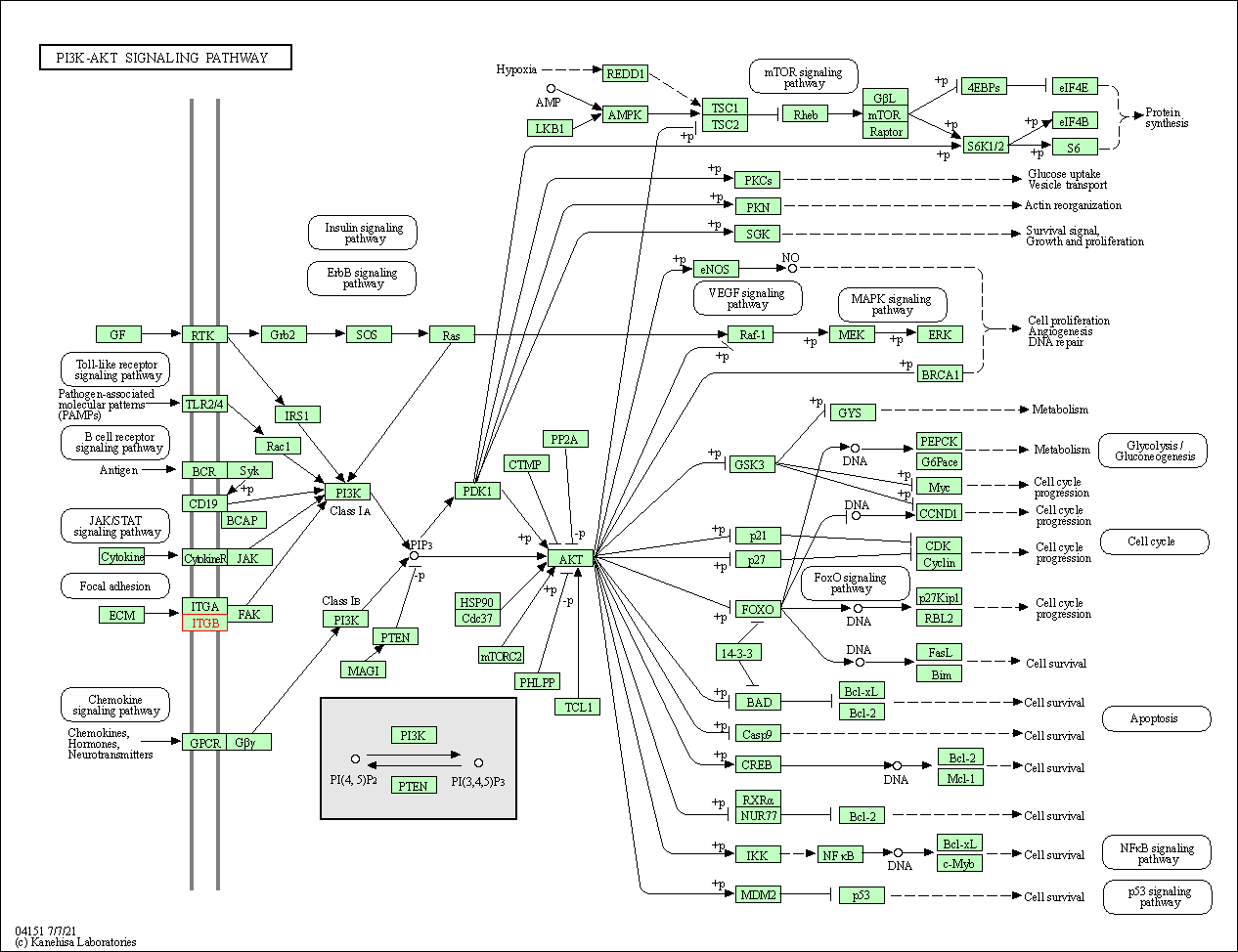
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |
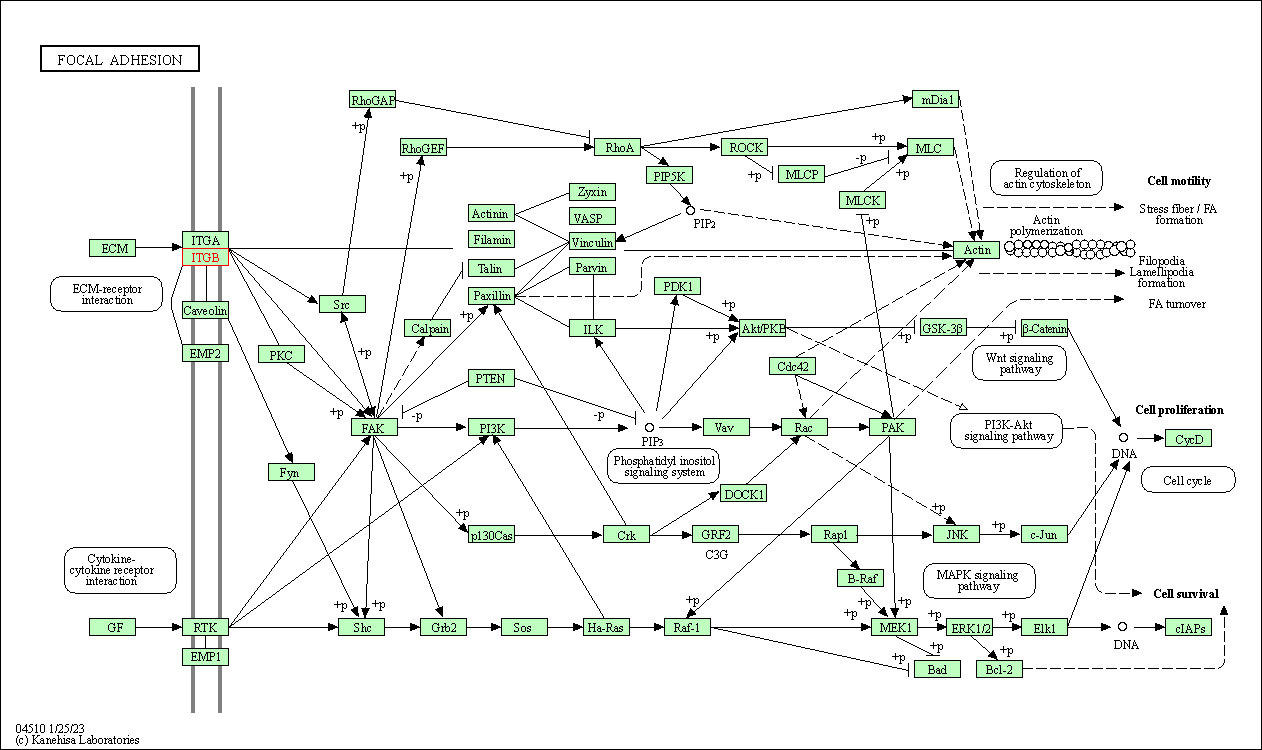
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ECM-receptor interaction | hsa04512 | Affiliated Target |
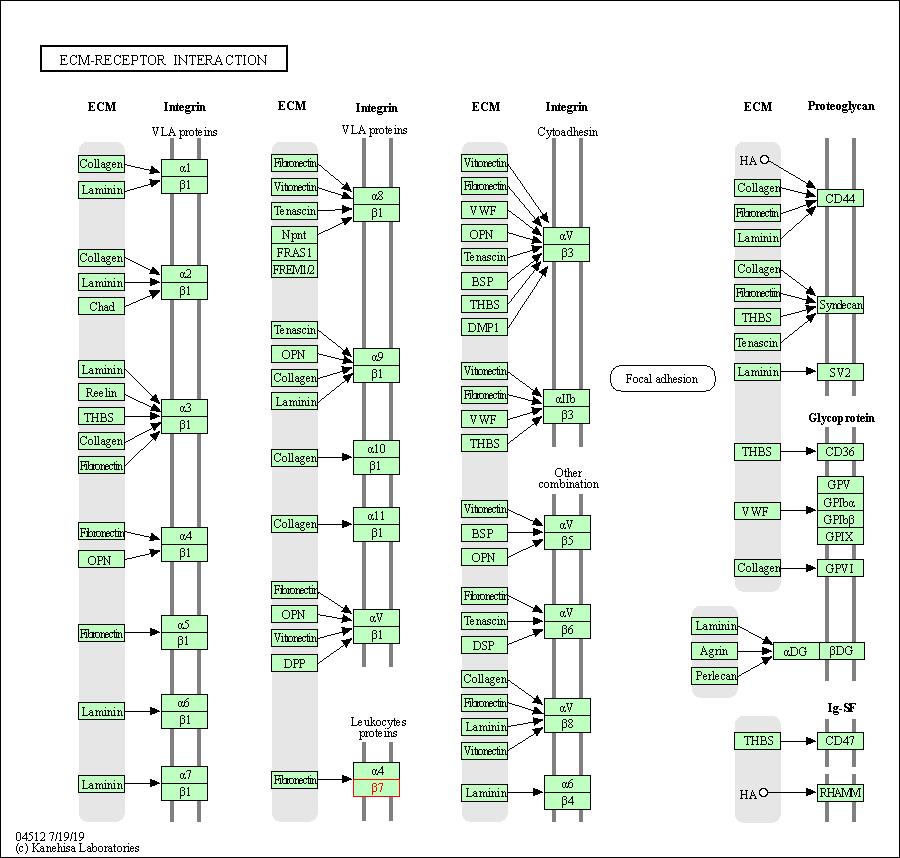
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | Affiliated Target |
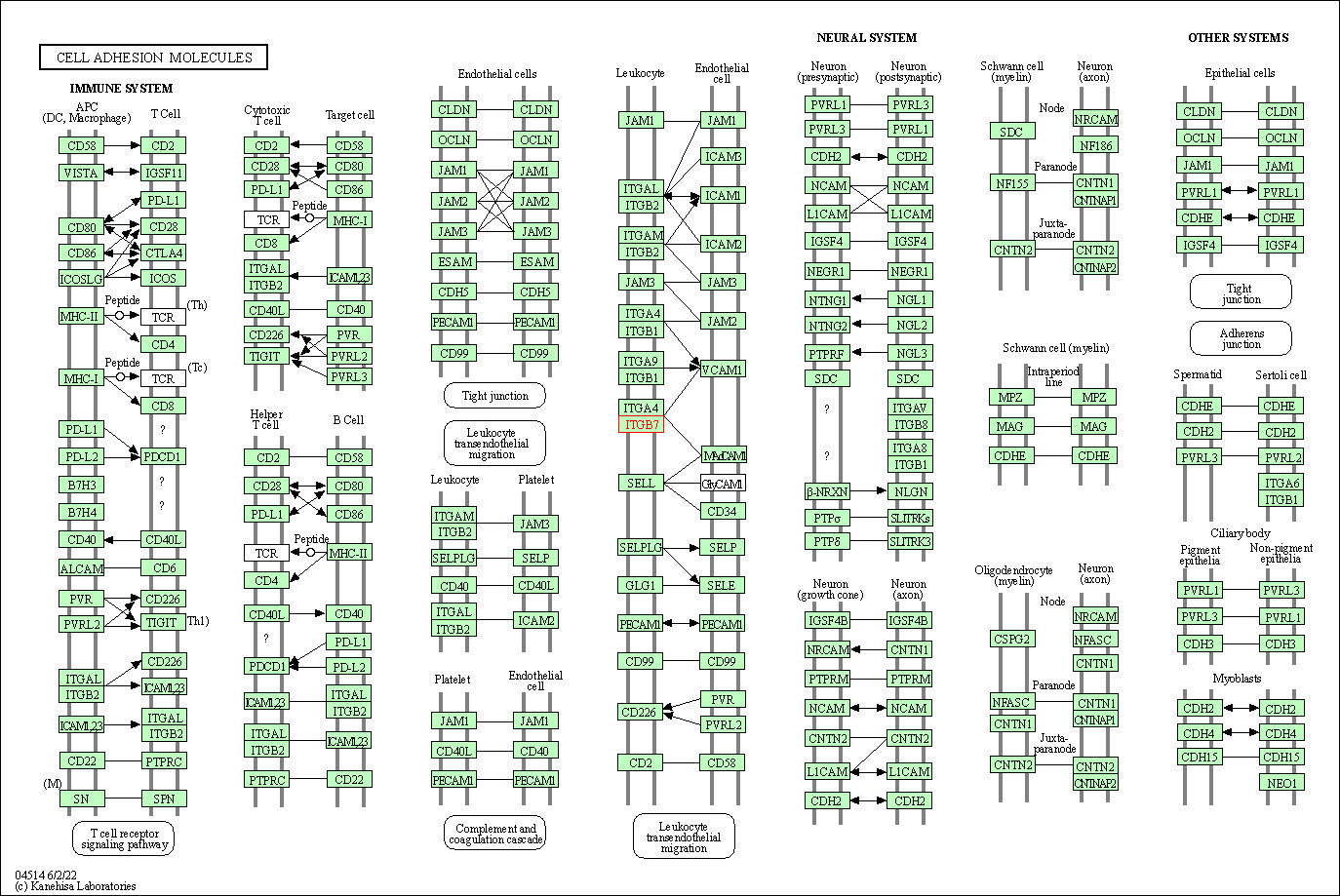
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Intestinal immune network for IgA production | hsa04672 | Affiliated Target |
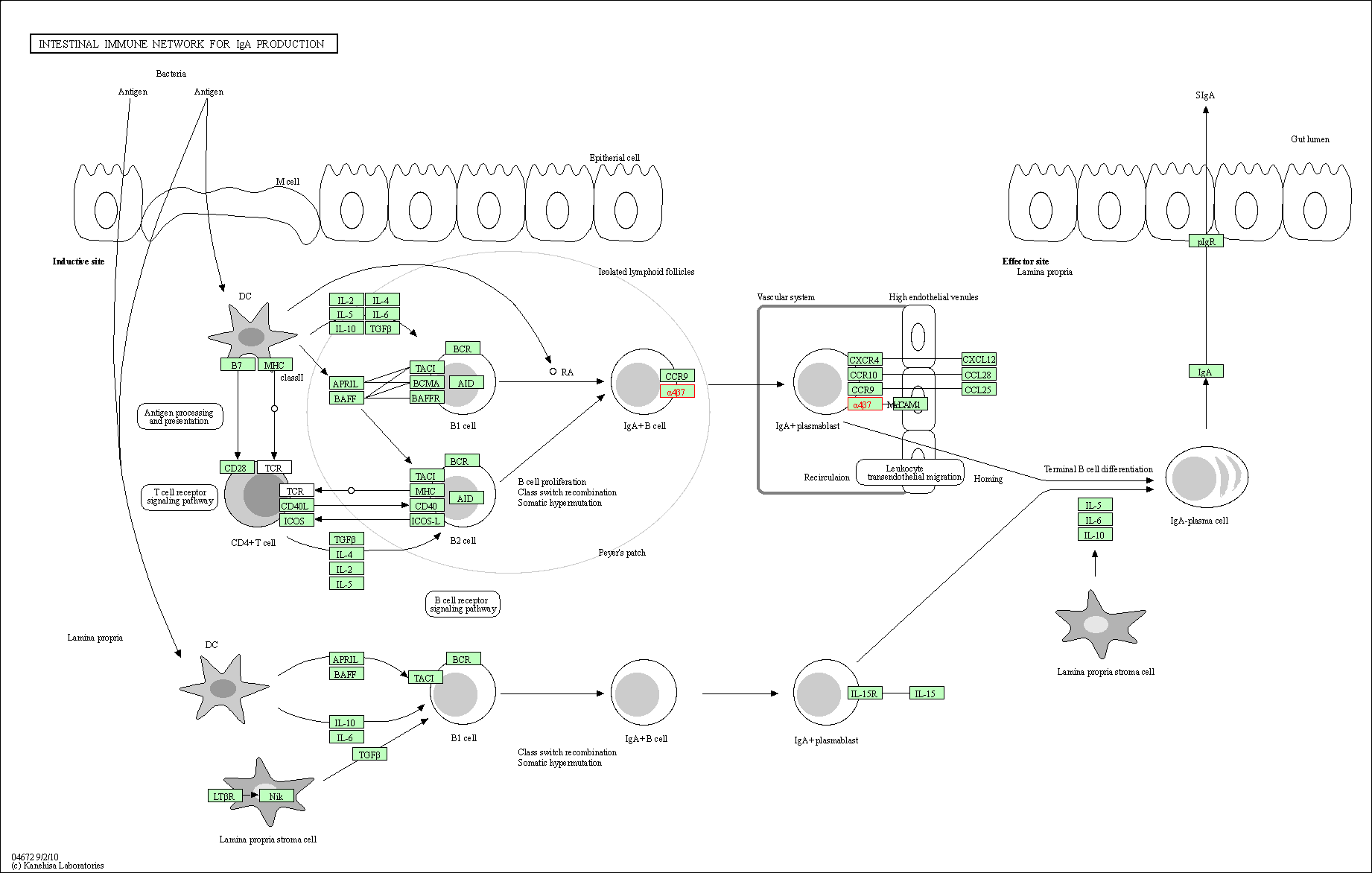
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |
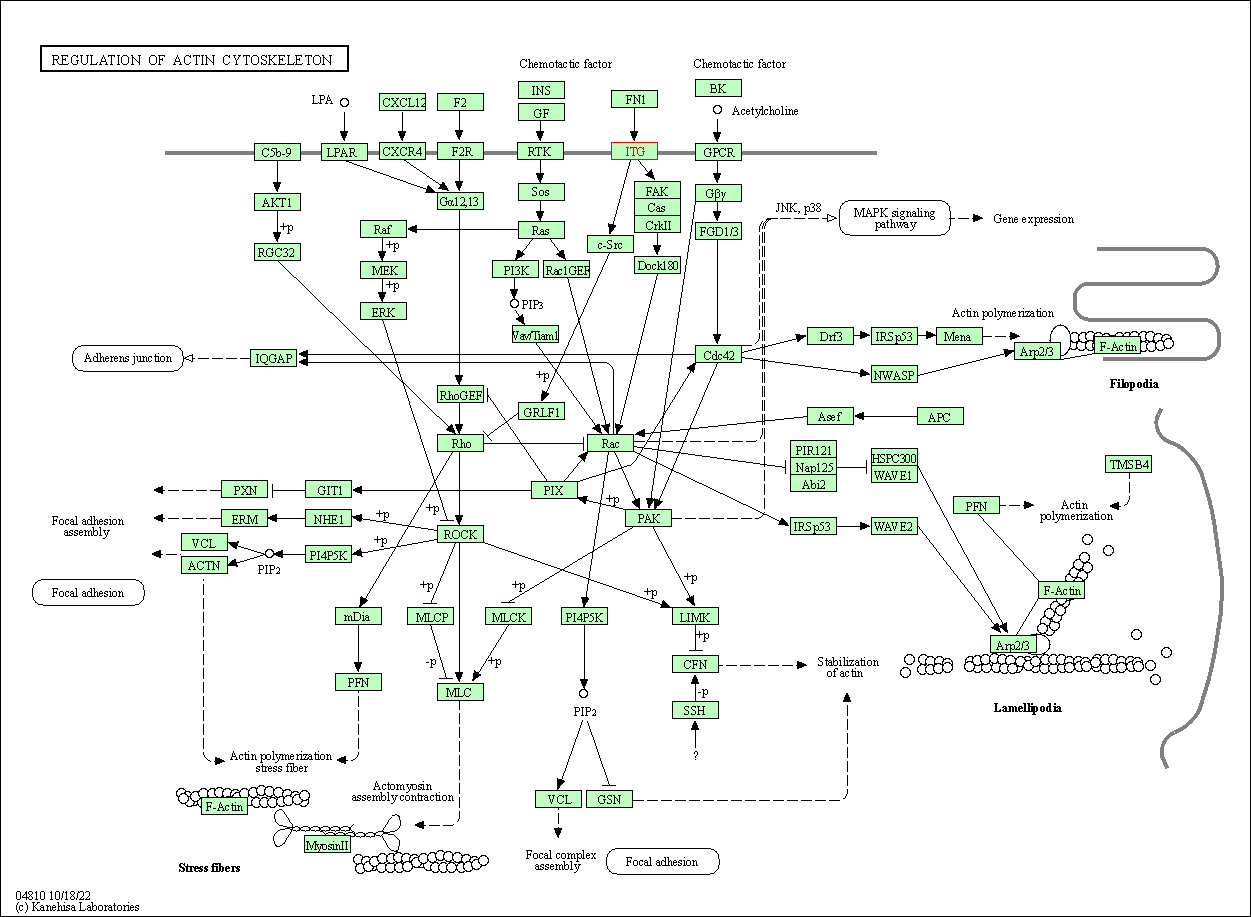
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 16 | Degree centrality | 1.72E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.33E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.20E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.92E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.05E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Takeda (2009). | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026082) | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01696396) AMG 181 in Subjects With Moderate to Severe Crohn's Disease. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 6 | A randomised phase I study of etrolizumab (rhuMAb beta7) in moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2013 Aug;62(8):1122-30. | |||||
| REF 7 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Genentech (2009). | |||||
| REF 8 | Pharmacology of AMG 181, a human anti-alpha4 beta7 antibody that specifically alters trafficking of gut-homing T cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2013 May;169(1):51-68. | |||||
| REF 9 | The molecular basis of filamin binding to integrins and competition with talin. Mol Cell. 2006 Feb 3;21(3):337-47. | |||||
| REF 10 | Structural specializations of Alpha(4)beta(7), an integrin that mediates rolling adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan 9;196(1):131-46. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

