Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T10147
(Former ID: TTDS00360)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase sigma (R-PTP-sigma)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase sigma; Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase S; R-PTP-S
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PTPRS
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Bone paget disease [ICD-11: FB85] | |||||
| Function |
Binding to chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate proteoglycans has opposite effects on PTPRS oligomerization and regulation of neurite outgrowth. Contributes to the inhibition of neurite and axonal outgrowth by chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, also after nerve transection. Plays a role in stimulating neurite outgrowth in response to the heparan sulfate proteoglycan GPC2. Required for normal brain development, especially for normal development of the pituitary gland and the olfactory bulb. Functions as tyrosine phosphatase. Mediates dephosphorylation of NTRK1, NTRK2 and NTRK3. Plays a role in down-regulation of signaling cascades that lead to the activation of Akt and MAP kinases. Down-regulates TLR9-mediated activation of NF-kappa-B, as well as production of TNF, interferon alpha and interferon beta. Cell surface receptor that binds to glycosaminoglycans, including chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans and heparan sulfate proteoglycan.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Phosphoric monoester hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.1.3.48
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAPTWGPGMVSVVGPMGLLVVLLVGGCAAEEPPRFIKEPKDQIGVSGGVASFVCQATGDP
KPRVTWNKKGKKVNSQRFETIEFDESAGAVLRIQPLRTPRDENVYECVAQNSVGEITVHA KLTVLREDQLPSGFPNIDMGPQLKVVERTRTATMLCAASGNPDPEITWFKDFLPVDPSAS NGRIKQLRSETFESTPIRGALQIESSEETDQGKYECVATNSAGVRYSSPANLYVRELREV RRVAPRFSILPMSHEIMPGGNVNITCVAVGSPMPYVKWMQGAEDLTPEDDMPVGRNVLEL TDVKDSANYTCVAMSSLGVIEAVAQITVKSLPKAPGTPMVTENTATSITITWDSGNPDPV SYYVIEYKSKSQDGPYQIKEDITTTRYSIGGLSPNSEYEIWVSAVNSIGQGPPSESVVTR TGEQAPASAPRNVQARMLSATTMIVQWEEPVEPNGLIRGYRVYYTMEPEHPVGNWQKHNV DDSLLTTVGSLLEDETYTVRVLAFTSVGDGPLSDPIQVKTQQGVPGQPMNLRAEARSETS ITLSWSPPRQESIIKYELLFREGDHGREVGRTFDPTTSYVVEDLKPNTEYAFRLAARSPQ GLGAFTPVVRQRTLQSKPSAPPQDVKCVSVRSTAILVSWRPPPPETHNGALVGYSVRYRP LGSEDPEPKEVNGIPPTTTQILLEALEKWTQYRITTVAHTEVGPGPESSPVVVRTDEDVP SAPPRKVEAEALNATAIRVLWRSPAPGRQHGQIRGYQVHYVRMEGAEARGPPRIKDVMLA DAQWETDDTAEYEMVITNLQPETAYSITVAAYTMKGDGARSKPKVVVTKGAVLGRPTLSV QQTPEGSLLARWEPPAGTAEDQVLGYRLQFGREDSTPLATLEFPPSEDRYTASGVHKGAT YVFRLAARSRGGLGEEAAEVLSIPEDTPRGHPQILEAAGNASAGTVLLRWLPPVPAERNG AIVKYTVAVREAGALGPARETELPAAAEPGAENALTLQGLKPDTAYDLQVRAHTRRGPGP FSPPVRYRTFLRDQVSPKNFKVKMIMKTSVLLSWEFPDNYNSPTPYKIQYNGLTLDVDGR TTKKLITHLKPHTFYNFVLTNRGSSLGGLQQTVTAWTAFNLLNGKPSVAPKPDADGFIMV YLPDGQSPVPVQSYFIVMVPLRKSRGGQFLTPLGSPEDMDLEELIQDISRLQRRSLRHSR QLEVPRPYIAARFSVLPPTFHPGDQKQYGGFDNRGLEPGHRYVLFVLAVLQKSEPTFAAS PFSDPFQLDNPDPQPIVDGEEGLIWVIGPVLAVVFIICIVIAILLYKNKPDSKRKDSEPR TKCLLNNADLAPHHPKDPVEMRRINFQTPDSGLRSPLREPGFHFESMLSHPPIPIADMAE HTERLKANDSLKLSQEYESIDPGQQFTWEHSNLEVNKPKNRYANVIAYDHSRVILQPIEG IMGSDYINANYVDGYRCQNAYIATQGPLPETFGDFWRMVWEQRSATIVMMTRLEEKSRIK CDQYWPNRGTETYGFIQVTLLDTIELATFCVRTFSLHKNGSSEKREVRQFQFTAWPDHGV PEYPTPFLAFLRRVKTCNPPDAGPIVVHCSAGVGRTGCFIVIDAMLERIKPEKTVDVYGH VTLMRSQRNYMVQTEDQYSFIHEALLEAVGCGNTEVPARSLYAYIQKLAQVEPGEHVTGM ELEFKRLANSKAHTSRFISANLPCNKFKNRLVNIMPYESTRVCLQPIRGVEGSDYINASF IDGYRQQKAYIATQGPLAETTEDFWRMLWENNSTIVVMLTKLREMGREKCHQYWPAERSA RYQYFVVDPMAEYNMPQYILREFKVTDARDGQSRTVRQFQFTDWPEQGVPKSGEGFIDFI GQVHKTKEQFGQDGPISVHCSAGVGRTGVFITLSIVLERMRYEGVVDIFQTVKMLRTQRP AMVQTEDEYQFCYQAALEYLGSFDHYAT Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Etidronic acid | Drug Info | Approved | Paget's disease | [2], [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Etidronic acid | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Orthovanadate | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
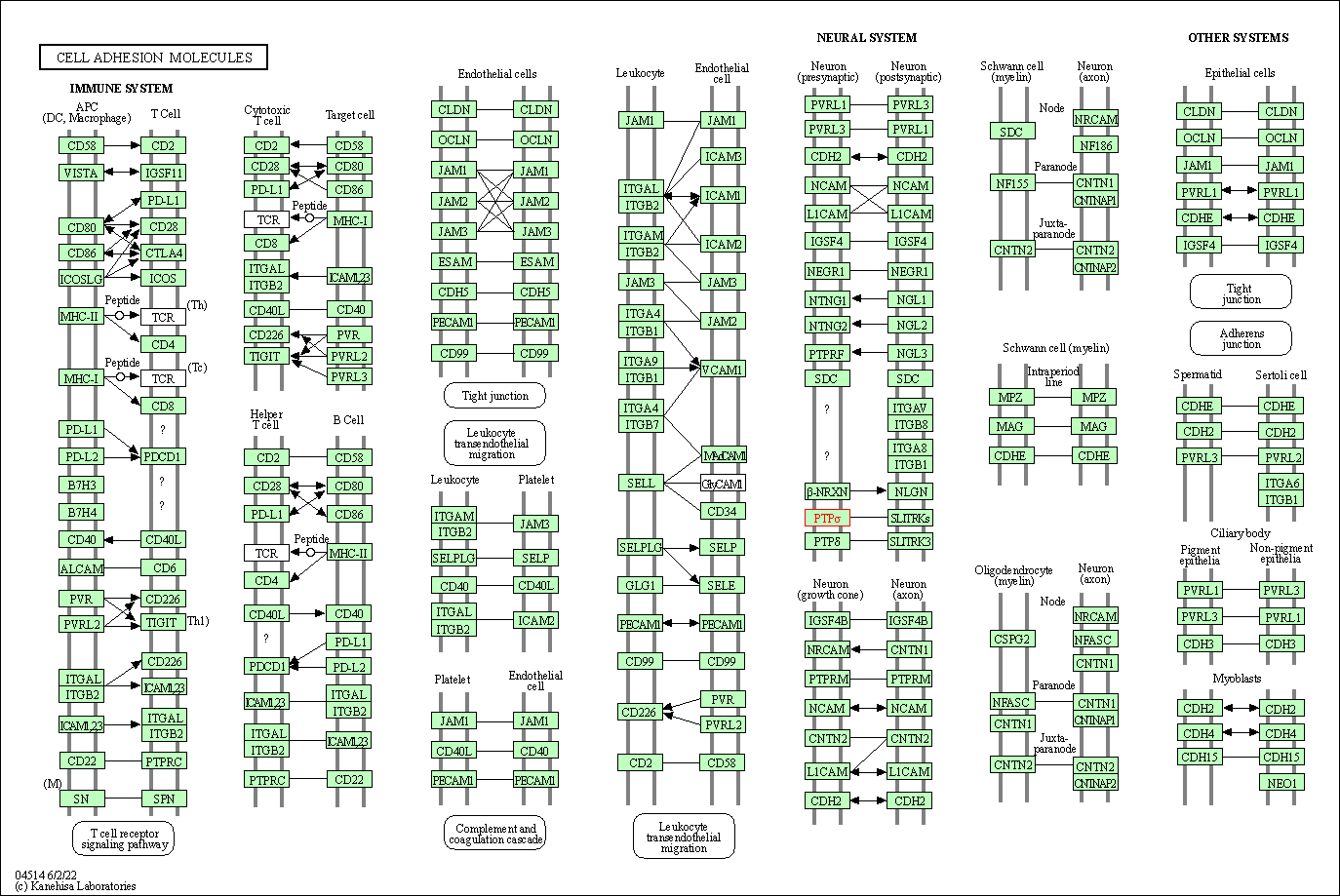
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 3.44E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.88E-01 | Radiality | 1.32E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.83E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.75E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ECM proteoglycans | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 1 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Extracellular matrix organization | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Human protein tyrosine phosphatase-sigma: alternative splicing and inhibition by bisphosphonates. J Bone Miner Res. 1996 Apr;11(4):535-43. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7184). | |||||
| REF 3 | Drug information of Didronel, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

