Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T00820
(Former ID: TTDR01270)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Inward rectifier potassium channel Kir6.2 (KCNJ11)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying, subfamily J, member 11; KCNJ11; KATP channel (Kir6.2/SUR2A); Inward rectifier K+ channel Kir6.2; IKATP
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KCNJ11
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
This receptor is controlled by G proteins. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by extracellular barium. Subunit of ATP-sensitive potassium channels (KATP). Can form cardiac and smooth muscle-type KATP channels with ABCC9. KCNJ11 forms the channel pore while ABCC9 is required for activation and regulation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Inward rectifier potassium channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MLSRKGIIPEEYVLTRLAEDPAEPRYRARQRRARFVSKKGNCNVAHKNIREQGRFLQDVF
TTLVDLKWPHTLLIFTMSFLCSWLLFAMAWWLIAFAHGDLAPSEGTAEPCVTSIHSFSSA FLFSIEVQVTIGFGGRMVTEECPLAILILIVQNIVGLMINAIMLGCIFMKTAQAHRRAET LIFSKHAVIALRHGRLCFMLRVGDLRKSMIISATIHMQVVRKTTSPEGEVVPLHQVDIPM ENGVGGNSIFLVAPLIIYHVIDANSPLYDLAPSDLHHHQDLEIIVILEGVVETTGITTQA RTSYLADEILWGQRFVPIVAEEDGRYSVDYSKFGNTIKVPTPLCTARQLDEDHSLLEALT LASARGPLRKRSVPMAKAKPKFSISPDSLS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T45B9P | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Cryo-EM structure of human KATP bound to ATP and ADP in quatrefoil form | PDB:6C3O | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.90 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
RARFVSKKGN
41 CNVAHKNIRE51 QGRFLQDVFT61 TLVDLKWPHT71 LLIFTMSFLC81 SWLLFAMAWW 91 LIAFAHGDLA101 PSEGTAEPCV111 TSIHSFSSAF121 LFSIEVQVTI131 GFGGRMVTEE 141 CPLAILILIV151 QNIVGLMINA161 IMLGCIFMKT171 AQAHRRAETL181 IFSKHAVIAL 191 RHGRLCFMLR201 VGDLRKSMII211 SATIHMQVVR221 KTTSPEGEVV231 PLHQVDIPME 241 NGVGGNSIFL251 VAPLIIYHVI261 DANSPLYDLA271 PSDLHHHQDL281 EIIVILEGVV 291 ETTGITTQAR301 TSYLADEILW311 GQRFVPIVAE321 EDGRYSVDYS331 KFGNTIKVPT 341 PLCTARQLDE351 DHSLLEAL
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |
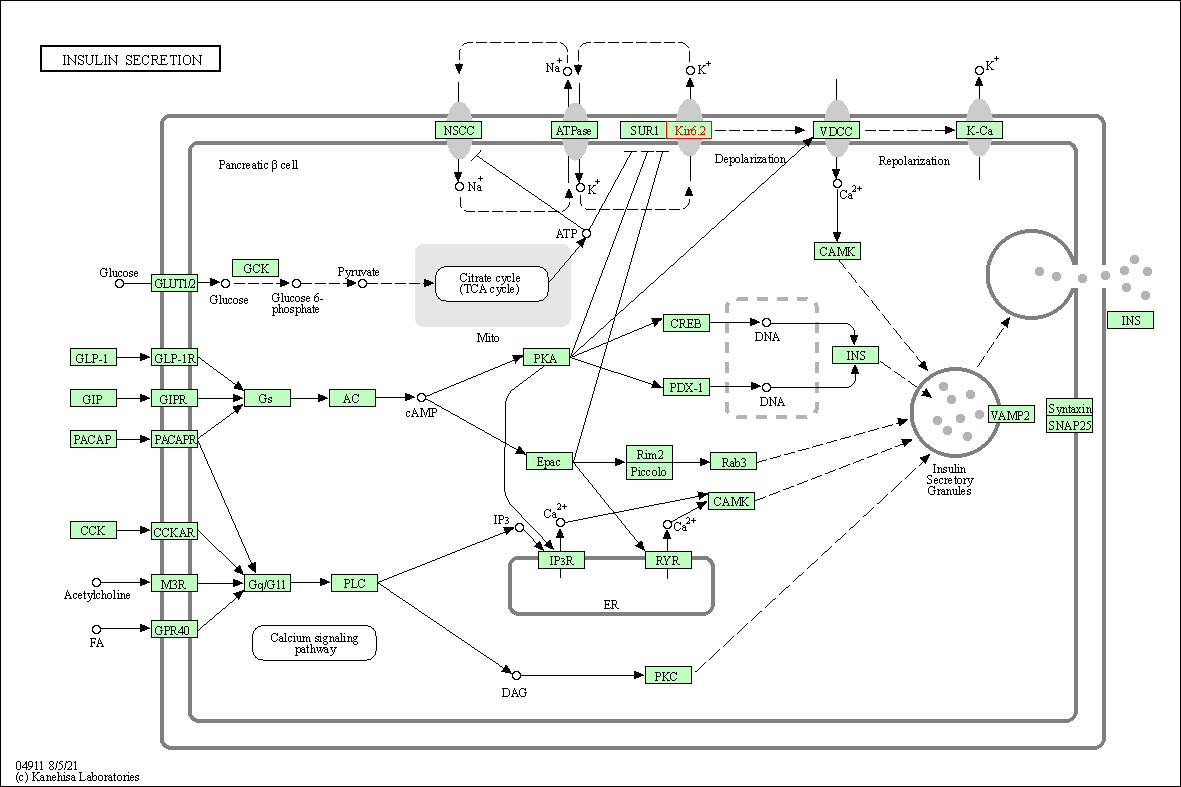
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |
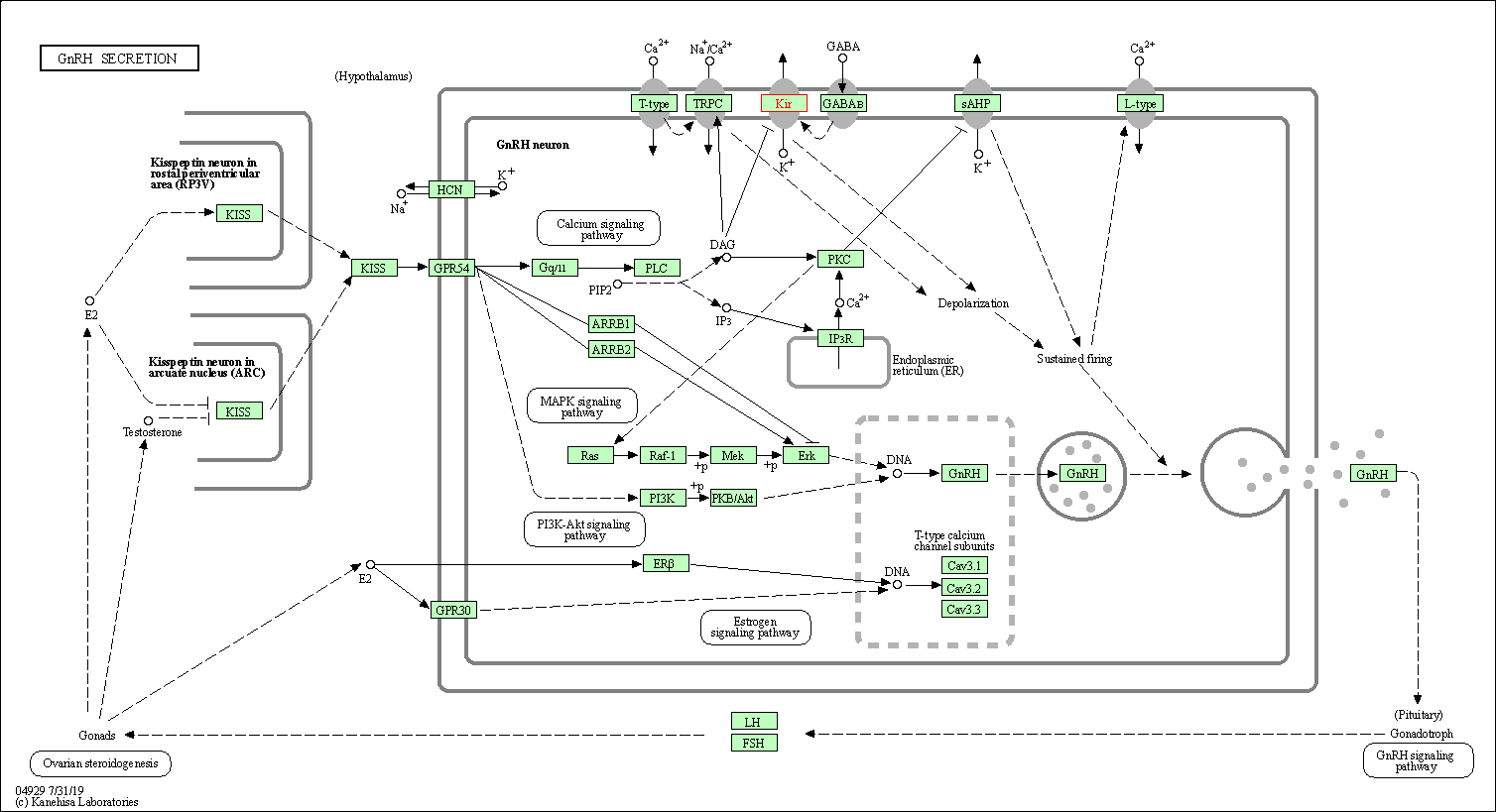
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 4 | Degree centrality | 4.30E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.21E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.82E-01 | Radiality | 1.30E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.25E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.60E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Insulin secretion | |||||
| 2 | Type II diabetes mellitus | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Muscle/Heart Contraction | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | FOXA2 and FOXA3 transcription factor networks | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ABC-family proteins mediated transport | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of insulin secretion | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Potassium Channels | |||||
| 2 | Integration of energy metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Type II diabetes mellitus | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Cardioselective K(ATP) channel blockers derived from a new series of m-anisamidoethylbenzenesulfonylthioureas. J Med Chem. 2001 Mar 29;44(7):1085-98. | |||||
| REF 2 | Molecular structure of human KATP in complex with ATP and ADP. Elife. 2017 Dec 29;6:e32481. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

