Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T00477
(Former ID: TTDR01324)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Serine Racemase (SRR)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
L-serine dehydratase; L-serine ammonia-lyase; D-serine dehydratase; D-serine ammonia-lyase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
SRR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Neurodegenerative disorder [ICD-11: 8A20-8A23] | |||||
| Function |
D-serine is a key coagonist with glutamate at NMDA receptors. Has dehydratase activity towards both L-serine and D-serine. Catalyzes the synthesis of D-serine from L-serine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Racemases and epimerase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 5.1.1.18
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MCAQYCISFADVEKAHINIRDSIHLTPVLTSSILNQLTGRNLFFKCELFQKTGSFKIRGA
LNAVRSLVPDALERKPKAVVTHSSGNHGQALTYAAKLEGIPAYIVVPQTAPDCKKLAIQA YGASIVYCEPSDESRENVAKRVTEETEGIMVHPNQEPAVIAGQGTIALEVLNQVPLVDAL VVPVGGGGMLAGIAITVKALKPSVKVYAAEPSNADDCYQSKLKGKLMPNLYPPETIADGV KSSIGLNTWPIIRDLVDDIFTVTEDEIKCATQLVWERMKLLIEPTAGVGVAAVLSQHFQT VSPEVKNICIVLSGGNVDLTSSITWVKQAERPASYQSVSV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T59LQ9 | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Pyridoxal phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure Description | X-ray crystal structure of human serine racemase in complex with malonate a potent inhibitor | PDB:3L6B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.50 Å | Mutation | Yes | [2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB Sequence |
AQYDISFADV
12 EKAHINIRDS22 IHLTPVLTSS32 ILNQLTGRNL42 FFKCELFQKT52 GSFKIRGALN 62 AVRSLVRKPK77 AVVTHSSGNH87 GQALTYAAKL97 EGIPAYIVVP107 QTAPDCKKLA 117 IQAYGASIVY127 CEPSDESREN137 VAKRVTEETE147 GIMVHPNQEP157 AVIAGQGTIA 167 LEVLNQVPLV177 DALVVPVGGG187 GMLAGIAITV197 KALKPSVKVY207 AAEPSNADDC 217 YQSKLKGKLM227 PNLYPPETIA237 DGVKSSIGLN247 TWPIIRDLVD257 DIFTVTEDEI 267 KCATQLVWER277 MKLLIEPTAG287 VGVAAVLSQH297 FQTVSPEVKN307 ICIVLSGGNV 317 DLTSSITWVK327 QA
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
☰3L6B Nodes: OProtein ▢Nucleotide ◇Chemical ▢Biopolymer Lines: Interactions at 4 Å Dynamically generated for selected residues. Nodes can be dragged or clicked. Label: Selection: Name:
Note: VAST+ finds other macromolecular structures that have a similar biological unit. To do this, VAST+ takes into consideration the complete set of 3D domains that VAST identified within a query structure, throughout all of its component protein molecules, and finds other macromolecular structures that have a similar set of proteins/3D domains. PDB ID: Note: VAST identifies 3D domains (substructures) within each protein structure in the Molecular Modeling Database (MMDB), and then finds other protein structures that have one or more similar 3D domains, using purely geometric criteria. You have two ways to do a VAST search. Option 1, search with your selection (all residues are selected by default) in the loaded structures: Option 2, search with PDB ID and chain name: PDB ID: Chain Name: Option 3, search with a PDB file: 1. your selection (all residues are selected by default) in the loaded structures to Foldseek web server. 2 (Optional). Once you see the structure neighbors, you can view the alignment in iCn3D by inputing a list of PDB chain IDs or AlphaFold UniProt IDs below. The PDB chain IDs are the same as the record names such as "1HHO_A". The UniProt ID is the text between "AF-" and "-F1". For example, the UniProt ID for the record name "AF-P69905-F1-model_v4" is "P69905". Chain ID List: BCIF/MMTF ID: PDB ID: Note: AlphaFold produces a per-residue confidence score (pLDDT) between 0 and 100: Very high (pLDDT > 90) Confident (90 > pLDDT > 70) Low (70 > pLDDT > 50) Very low (pLDDT < 50) AlphaFold Uniprot ID: PAE Map: NCBI Protein Accession: Note: Several PDB files could be concatenated into a single PDB file. Use the line "ENDMDL" to separate PDB files. PDB File: Multiple PDB Files: The custom JSON file on residue colors has the following format for proteins("ALA" and "ARG") and nucleotides("G" and "A"): {"ALA":"#C8C8C8", "ARG":"#145AFF", ..., "G":"#008000", "A":"#6080FF", ...} Residue Color File: The custom file for the structure has two columns separated by space or tab: residue number, and score in the range of 0-100. If you click "Apply Custom Color" button, the scores 0, 50 and 100 correspond to the three colors specified below. If you click "Apply Custom Tube", the selected residues will be displayed in a style similar to "B-factor Tube". Custom File: 1. Score to Color: 0: 50: 100: or 2. You can define your own reference numbers in a custom file using Excel, and then export it as a CSV file. An example file is shown below with cells separated by commas. refnum,11,12,,21,22,,10C,11C,20CThe first row defines the reference residue numbers, which could be any strings. The 1st cell could be anything. The rest cells are reference residue numbers (e.g., 11, 21, 10C, etc.) or empty cells. Each chain has a separate row. The first cell of the second row is the chain ID "1TUP_A". The rest cells are the corresponding real residue numbers for reference residue numbers in the first row. For example, the reference numbers for residues 100, 101, and 132 in the chain 1TUP_A are 11, 12, and 22, respectively. The fourth row shows another set of reference numners for the chain "1TUP_C". It could be a chain from a different structure. To select all residues corresponding to the reference numbers, you can simplay replace ":" with "%" in the Specification. For example, "%12" selects the residue 101 in 1TUP_A and the residue 111 in 1TUP_B. ".A%12" has the chain "A" filter and selects the residue 101 in 1TUP_A. Custom File: Enter the PDB IDs or MMDB IDs of the structures: ID1: ID2: VAST+ based on VAST: VAST+ based on TM-align: All chains will be aligned to the first chain in the comma-separated chain IDs. Each chain ID has the form of PDBID_chain (e.g., 1HHO_A, case sensitive) or UniprotID (e.g., P69905 for AlphaFold structures). Chain IDs: (Note: To align chains in custom PDB files, you could load them in "File > Open File > PDB Files (appendable)" and click "Analysis > Defined Sets". Finally select multiple chains in Defined Sets and click "File > Realign Selection".) All chains will be aligned to the first chain in the comma-separated chain IDs. Each chain ID has the form of PDBID_chain (e.g., 1HHO_A, case sensitive) or UniprotID (e.g., P69905 for AlphaFold structures). Chain IDs: The sequence alignment (followed by structure alignment) is based on residue numbers in the First/Master chain: (Note: To align chains in custom PDB files, you could load them in "File > Open File > PDB Files (appendable)" and click "Analysis > Defined Sets". Finally select multiple chains in Defined Sets and click "File > Realign Selection".) All chains will be aligned to the first chain in the comma-separated chain IDs. Each chain ID has the form of PDBID_chain (e.g., 1HHO_A, case sensitive) or UniprotID (e.g., P69905 for AlphaFold structures). Chain IDs: Each alignment is defined as " | "-separated residue lists in one line. "10-50" means a range of residues from 10 to 50. Option 1: Option 2: All chains will be aligned to the first chain in the comma-separated chain IDs. Each chain ID has the form of PDBID_chain (e.g., 1HHO_A, case sensitive) or UniprotID (e.g., P69905 for AlphaFold structures). Chain IDs: Each alignment is defined as " | "-separated residue lists in one line. "10-50" means a range of residues from 10 to 50. Please specify the mutations with a comma separated mutation list. Each mutation can be specified as "[uppercase PDB ID or AlphaFold UniProt ID]_[Chain Name]_[Residue Number]_[One Letter Mutant Residue]". E.g., the mutation of N501Y in the E chain of PDB 6M0J can be specified as "6M0J_E_501_Y". For AlphaFold structures, the "Chain ID" is "A". If you load a custom structure without PDB or UniProt ID, you can open "Seq. & Annotations" window and find the chain ID such as "stru_A". The part before the underscore is the structure ID, which can be used to specify the mutation such as "stru_A_...". Remember to choose "Show Mutation in: Current Page". Mutations: ID Type: PDB IDAlphaFold UniProt ID Show Mutation in: Current PageNew Page Mol2 File: SDF File: XYZ File: AlphaFold PAE File: File type: URL in the same host: Multiple mmCIF Files: mmCIF ID: MMDB or PDB ID: Note: The "biological unit" is the biochemically active form of a biomolecule, List of PDB, MMDB, or AlphaFold UniProt structures: or Note: The "biological unit" is the biochemically active form of a biomolecule, Enter a protein sequence ID (or FASTA sequence) and the aligned protein accession, which can be found using the BLAST search with the protein sequence ID or FASTA sequence as input. If the protein accession is not a PDB chain, the corresponding AlphaFold UniProt structure is used. Protein Sequence ID(NCBI protein accession of a sequence): or FASTA sequence: Aligned Protein Accession (or a chain of a PDB): The sequence to structure prediction is done via ESM Metagenomic Atlas. The sequence should be less than 400 characters. For any sequence longer than 400, please see the discussion here. FASTA sequence: Your note will be saved in the HTML file when you click "File > Save File > iCn3D PNG Image". Protein/Gene name: PubChem CID/Name/InchI: Chemical SMILES: Multiple iCn3D PNG images: State file: Since January 6, 2021, you can show the original view with the archived version of iCn3D by pasting your URL below and click "Show Originial View". Note the version in the parameter "v" was used to replace "full.html" with "full_[v].html" in the URL. Share Link URL: Selection file: Collection File: Structures: Note: Always load a PDB file before loading map files. If you don't specify the threshold below, a default one will be chosen. 2fofc contour at default threshold or at: σ fofc contour at default threshold or at: σ Note: Always load a PDB file before loading map files. If you don't specify the threshold below, a default one will be chosen. 2fofc contour at default threshold or at: σ URL in the same host: fofc contour at default threshold or at: σ URL in the same host: Click in the input box to use the color picker: Custom Color: Grid Size: Salt Concentration: M Potential contour at: kT/e(25.6mV at 298K) Note: Only the selected residues are used for DelPhi potential calculation by solving linear Poisson-Boltzmann equation. Grid Size: Salt Concentration: M Surface with max potential at: kT/e(25.6mV at 298K) Surface: Opacity: Wireframe: Note: Only the selected residues are used for DelPhi potential calculation by solving linear Poisson-Boltzmann equation. Potential contour at: kT/e(25.6mV at 298K) Note: Always load a PDB file before loading a PQR or DelPhi potential file. Potential contour at: kT/e(25.6mV at 298K) Grid Size: Salt Concentration: M PQR URL in the same host: Phi URL in the same host: Cube URL in the same host: Note: Always load a PDB file before loading a PQR or DelPhi potential file. Symmetry: Distance: Contact Type: 1. Choose interaction types and their thresholds:
4. Sort Interactions on: to show two lines of residue nodes to show map with atom details to show interactions with strength parameters in 0-200:
(Note: you can also adjust thresholds at #1 to add/remove interactions.) 5. and select new sets 1. Select sets below or use your current selection: 2. 1. Select sets below or use your current selection. 2. 1. Select sets below or use your current selection: 2. Overall maximum RMSD: Å 3. 1. Select sets below: 2. 1. Select sets below: 2. 1. Select sets below: 2. 1. Select sets below: 2. Hold Ctrl key to select multiple nodes/lines. Green: H-Bonds; Cyan: Salt Bridge/Ionic; Grey: Contacts Magenta: Halogen Bonds; Red: π-Cation; Blue: π-Stacking Scale: Hold Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Scale: Note: Nodes/Residues can be dragged. Both nodes and dashed lines/interactions can be clicked to select residues. Color legend for interactions (dashed lines): Green: H-Bonds; Cyan: Salt Bridge/Ionic; Grey: Contacts Magenta: Halogen Bonds; Red: π-Cation; Blue: π-Stacking Scale: Hold Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Scale: Hold Ctrl key to select multiple nodes. Scale:
Contour at: σ Contour at: σ Contour at: % of maximum EM values 1. Select the first set: 2. Sphere with a radius: Å 3. Select the second set to apply the sphere: 4. the sphere around the first set of atoms interacting/contacting residue pairs in a file Note: The membranes are parallel to the X-Y plane. The center of the membranes is at Z = 0. 1. Extracellular membrane Z-axis position: Å 2. intracellular membrane Z-axis position: Å 3. the adjusted membranes Note: The membranes are parallel to the X-Y plane. The center of the membranes is at Z = 0. 1. Z-axis position of the first X-Y plane: Å 2. Z-axis position of the second X-Y plane: Å 3. the region between the planes to Defined Sets 1. Text: 2. Size: 3. Color: 4. Pick TWO atoms while holding "Alt" key 5. 1. Text: 2. Size: 3. Color: 4. Color for all labels: 1. Pick TWO atoms while holding "Alt" key 2. Line Color: 3. 1. Pick TWO atoms while holding "Alt" key 2. Color: 3. 1. Select two sets
3. 1. Select two sets
2. Line style: 3. Line radius: 4. Color: 5. Opacity: 6. 1. Select a set: 2. Shape: 3. Radius: 4. Color: 5. Opacity: 6. 1. Select sets for pairwise distances
Note: Each set is represented by a vector, which is the X-axis of the principle axes. The angles between the vectors are then calculated. 1. Select sets for pairwise angles
1. Pick TWO atoms while holding "Alt" key 2. Line Radius: (for stabilizers, hydrogen bonds, distance lines, default 0.1) Coil Radius: (for coils, default 0.3) Stick Radius: (for sticks, default 0.4) Cross-Linkage Radius: (for cross-linkages, default 0.4) Trace Radius: (for C alpha trace, O3' trace, default 0.4) Ribbon Thickness: (for helix and sheet ribbons, nucleotide ribbons, default 0.2) Protein Ribbon Width: (for helix and sheet ribbons, default 1.3) Nucleotide Ribbon Width: (for nucleotide ribbons, default 0.8) Ball Scale: (for styles 'Ball and Stick' and 'Dot', default 0.3) Note: The following parameters will be saved in cache. You just need to set them once. 1. Shininess: (for the shininess of the 3D objects, default 40) 2. Three directional lights: Key Light: (for the light strength of the key light, default 0.8) Fill Light: (for the light strength of the fill light, default 0.4) Back Light: (for the light strength of the back light, default 0.2) 3. Thickness: Line Radius: (for stabilizers, hydrogen bonds, distance lines, default 0.1) Coil Radius: (for coils, default 0.3) Stick Radius: (for sticks, default 0.4) Cross-Linkage Radius: (for cross-linkages, default 0.4) Trace Radius: (for C alpha trace, O3' trace, default 0.4) Ribbon Thickness: (for helix and sheet ribbons, nucleotide ribbons, default 0.2) Protein Ribbon Width: (for helix and sheet ribbons, default 1.3) Nucleotide Ribbon Width: (for nucleotide ribbons, default 0.8) Ball Scale: (for styles 'Ball and Stick' and 'Dot', default 0.3) 4. Show Glycan Cartoon: (0: hide, 1: show, default 0) 5. Show Membrane: (0: hide, 1: show, default 1) 6. Enlarge Command Window: (0: Regular, 1: Large, default 0) Name: 1. URLs Used in Browsers Please copy one of the URLs below. They show the same result. (To add a title to share link, click "Windows > Your Note" and click "File > Share Link" again.) Original URL with commands: Lifelong Short URL:(To replace this URL, send a pull request to update share.html at iCn3D GitHub) Lifelong Short URL + Window Title:(To update the window title, click "Analysis > Your Note/Window Title".) 2. Commands Used in Jupyter Noteboook Please copy the following commands into a cell in Jupyter Notebook to show the same result. More details are at https://github.com/ncbi/icn3d/tree/master/jupyternotebook. Annotations:
Zoom: mouse wheel; Move: left button; Select Multiple Nodes: Ctrl Key and drag an Area Force on Nodes: Label Size: Internal Edges: Solvent Accessible Surface Area(SASA) calculated using the EDTSurf algorithm: (0-20% out is considered "in". 50-100% out is considered "out".) Toal: Å2 Color each residue based on the percentage of solvent accessilbe surface area. The color ranges from blue, to white, to red for a percentage of 0, 35(variable), and 100, respectively. Middle Percentage(White): % Select residue based on the percentage of solvent accessilbe surface area. The values are in the range of 0-100. Min Percentage: % Max Percentage: % Select residue based on B-factor/pLDDT. The values are in the range of 0-100. Min B-factor/pLDDT: % Max B-factor/pLDDT: % X: Y: Z: Vector 1, X: Y: Z: Vector 2, X: Y: Z: The angle is: degree. 0: 4: 8: 12: 1: 5: 9: 13: 2: 6: 10: 14: 3: 7: 11: 15: Choose an Ig template for selected residues: Choose an Ig template to align with selected residues: |
SER54
4.248
PHE55
3.415
LYS56
1.539
ASN86
2.913
PRO153
4.843
ASN154
4.046
PRO183
3.857
VAL184
3.783
GLY185
2.802
GLY186
3.013
GLY187
2.780
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
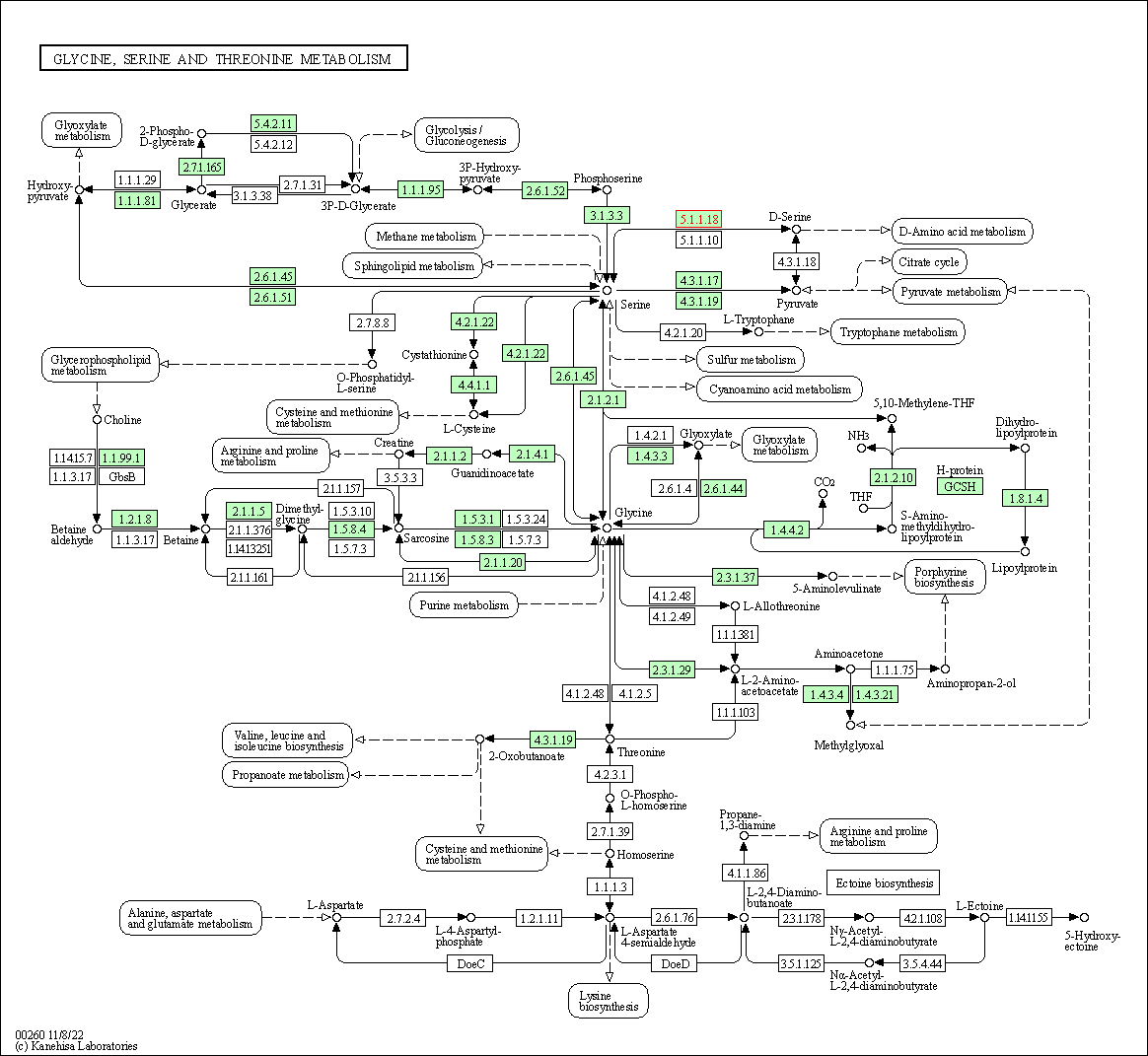
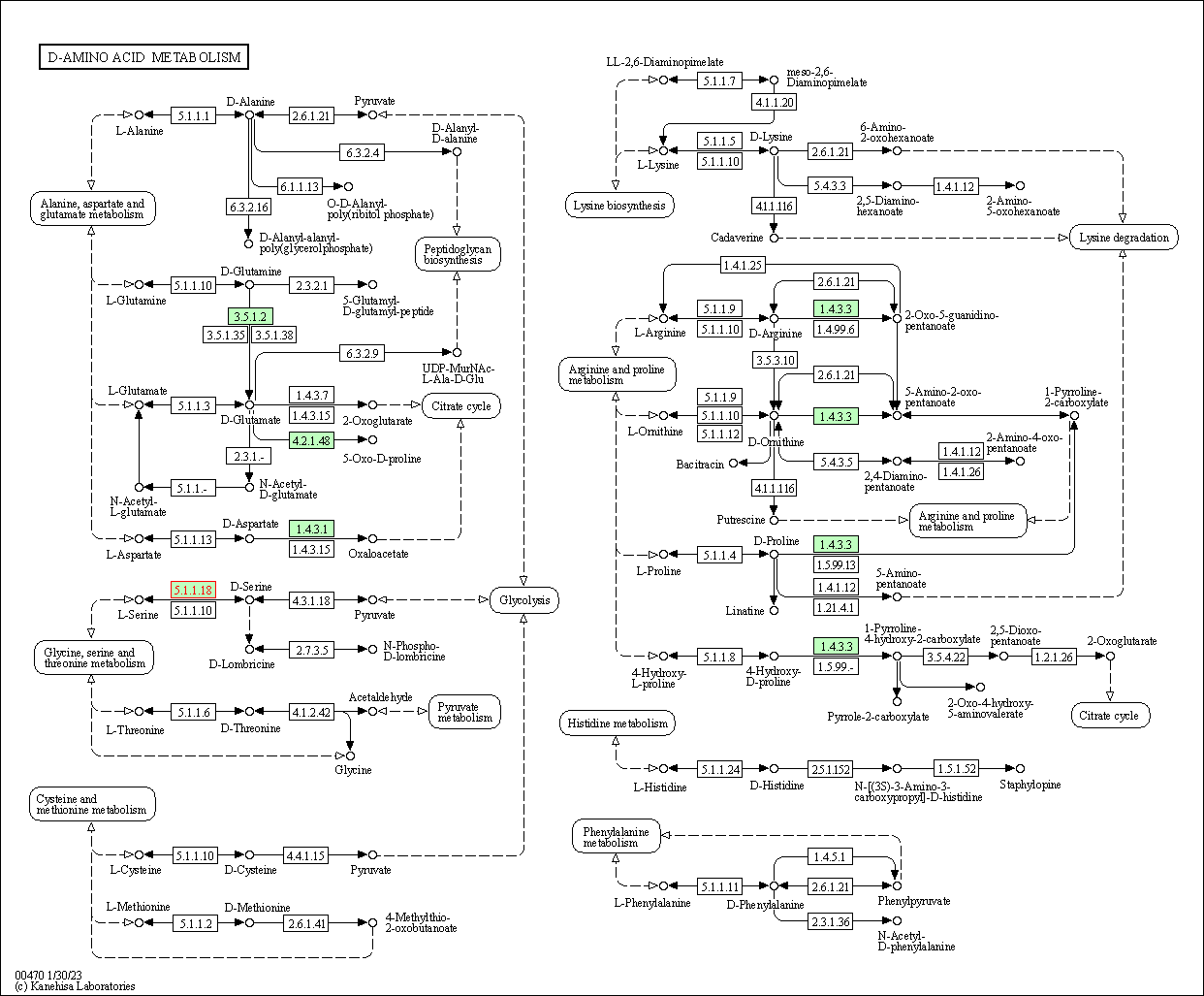
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | hsa00260 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| D-Amino acid metabolism | hsa00470 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of other amino acids | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Inhibition of human serine racemase, an emerging target for medicinal chemistry. Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Jun;12(7):1037-55. | |||||
| REF 2 | The structure of mammalian serine racemase: evidence for conformational changes upon inhibitor binding. J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12873-81. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

