| Drug General Information |
| Drug ID |
D05IML
|
| Former ID |
DNC003951
|
| Drug Name |
NIGULDIPINE
|
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
| Indication |
Discovery agent
|
Terminated |
[1],
[2]
|
|---|
| Structure |
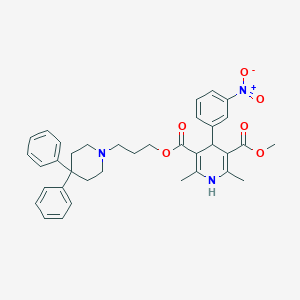
|
Download
2D MOL
3D MOL
|
| Formula |
C36H39N3O6
|
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C36H39N3O6/c1-25-31(34(40)44-3)33(27-12-10-17-30(24-27)39(42)43)32(26(2)37-25)35(41)45-23-11-20-38-21-18-36(19-22-38,28-13-6-4-7-14-28)29-15-8-5-9-16-29/h4-10,12-17,24,33,37H,11,18-23H2,1-3H3/t33-/m0/s1
|
| InChIKey |
SVJMLYUFVDMUHP-XIFFEERXSA-N
|
| PubChem Compound ID |
|
| PubChem Substance ID |
8186958, 11113931, 11113932, 14911982, 43117981, 80372166, 85789015, 103567485, 103942848, 104321194, 117381126, 134341334, 135018553, 135650717, 139282946, 179149614, 184547327, 198971262, 225146125, 225146175, 226595902
|
| Target and Pathway |
| Target(s) |
Alpha-1B adrenergic receptor |
Target Info |
Inhibitor |
[3]
|
|---|
| Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C |
Target Info |
Inhibitor |
[3]
|
| Alpha-1D adrenergic receptor |
Target Info |
Inhibitor |
[3]
|
| Alpha-1A adrenergic receptor |
Target Info |
Inhibitor |
[3]
|
|
KEGG Pathway
|
Calcium signaling pathway
|
|
cGMP-PKG signaling pathway
|
|
Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction
|
|
Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes
|
|
Vascular smooth muscle contraction
|
|
Salivary secretionhsa04010:MAPK signaling pathway
|
|
cAMP signaling pathway
|
|
Cardiac muscle contraction
|
|
Circadian entrainment
|
|
Long-term potentiation
|
|
Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling
|
|
Glutamatergic synapse
|
|
Cholinergic synapse
|
|
Serotonergic synapse
|
|
GABAergic synapse
|
|
Dopaminergic synapse
|
|
Insulin secretion
|
|
GnRH signaling pathway
|
|
Oxytocin signaling pathway
|
|
Type II diabetes mellitus
|
|
Alzheimer's disease
|
|
Amphetamine addiction
|
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
|
|
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
|
|
Dilated cardiomyopathyhsa04020:Calcium signaling pathway
|
|
Salivary secretionhsa04020:Calcium signaling pathway
|
|
AMPK signaling pathway
|
|
Salivary secretion
|
|
NetPath Pathway
|
IL2 Signaling PathwayNetPath_14:IL2 Signaling PathwayNetPath_14:IL2 Signaling Pathway
|
|
PANTHER Pathway
|
Alpha adrenergic receptor signaling pathwayP00003:Alzheimer disease-amyloid secretase pathway
|
|
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway
|
|
5HT2 type receptor mediated signaling pathway
|
|
Beta1 adrenergic receptor signaling pathway
|
|
Beta2 adrenergic receptor signaling pathway
|
|
Oxytocin receptor mediated signaling pathway
|
|
Nicotine pharmacodynamics pathwayP00002:Alpha adrenergic receptor signaling pathway
|
|
Pathway Interaction Database
|
LPA receptor mediated events
|
|
PathWhiz Pathway
|
Muscle/Heart Contraction
|
|
Reactome
|
Adrenoceptors
|
|
G alpha (q) signalling events
|
|
G alpha (12/13) signalling eventsR-HSA-400042:Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion
|
|
NCAM1 interactions
|
|
Regulation of insulin secretionR-HSA-390696:Adrenoceptors
|
|
G alpha (12/13) signalling eventsR-HSA-390696:Adrenoceptors
|
|
G alpha (12/13) signalling events
|
|
WikiPathways
|
Monoamine GPCRs
|
|
Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell
|
|
GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like
|
|
Vitamin D Receptor Pathway
|
|
Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK
|
|
GPCR ligand binding
|
|
GPCR downstream signaling
|
|
AMPK SignalingWP536:Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell
|
|
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
|
|
Alzheimers Disease
|
|
NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth
|
|
Integration of energy metabolism
|
|
Nicotine Activity on Chromaffin CellsWP58:Monoamine GPCRs
|
|
GPCRs, OtherWP58:Monoamine GPCRs
|
|
Endothelin Pathways
|
|
AMPK Signaling
|
| References |
| REF 1 | (http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/) Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 487). |
|---|
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002398) |
|---|
| REF 3 | J Med Chem. 1995 Sep 15;38(19):3681-716.Alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors: from the gene to the clinic. 2. Structure-activity relationships and therapeutic applications. |
|---|