Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D02ZSU
|
||||
| Former ID |
DIB016750
|
||||
| Drug Name |
NS-49
|
||||
| Synonyms |
Garomefrine hydrochloride; ABT-232; PNO-49B
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Urinary incontinence [ICD9: 788.3; ICD10:N39.3, N39.4, R32] | Discontinued in Phase 2 | [1], [2] | ||
| Company |
Nippon Shinyaku Co Ltd
|
||||
| Structure |
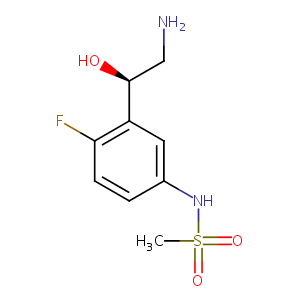
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C9H13FN2O3S
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C9H13FN2O3S/c1-16(14,15)12-6-2-3-8(10)7(4-6)9(13)5-11/h2-4,9,12-13H,5,11H2,1H3/t9-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XYLJNMCMDOOJRW-VIFPVBQESA-N
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID | |||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | Alpha-1D adrenergic receptor | Target Info | Modulator | [3] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Calcium signaling pathway | ||||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | |||||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | |||||
| Salivary secretion | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | IL2 Signaling Pathway | ||||
| Reactome | Adrenoceptors | ||||
| G alpha (q) signalling events | |||||
| G alpha (12/13) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | Monoamine GPCRs | ||||
| Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell | |||||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK | |||||
| GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| GPCRs, Other | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | (http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/) Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 481). | ||||
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800005693) | ||||
| REF 3 | Pharmacokinetics of NS-49, a phenethylamine class alpha 1A-adrenoceptor agonist. 3rd communication: metabolism in rats, rabbits, dogs and monkeys, and effects on hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme activities in rats after repeated administration. Arzneimittelforschung. 1999 Jul;49(7):612-7. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

