Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T97719
|
|||||
| Target Name |
HUMAN bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Bruton's tyrosine kinase; Bruton tyrosine kinase; BPK; B-cell progenitor kinase; B cell progenitor kinase; Agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase; Agammaglobulinaemia tyrosine kinase; AGMX1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
BTK
|
|||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60-2B33] | |||||
| Function |
Binding of antigen to the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) triggers signaling that ultimately leads to B-cell activation. After BCR engagement and activation at the plasma membrane, phosphorylates PLCG2 at several sites, igniting the downstream signaling pathway through calcium mobilization, followed by activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) family members. PLCG2 phosphorylation is performed in close cooperation with the adapter protein B-cell linker protein BLNK. BTK acts as a platform to bring together a diverse array of signaling proteins and is implicated in cytokine receptor signaling pathways. Plays an important role in the function of immune cells of innate as well as adaptive immunity, as a component of the Toll-like receptors (TLR) pathway. The TLR pathway acts as a primary surveillance system for the detection of pathogens and are crucial to the activation of host defense. Especially, is a critical molecule in regulating TLR9 activation in splenic B-cells. Within the TLR pathway, induces tyrosine phosphorylation of TIRAP which leads to TIRAP degradation. BTK plays also a critical role in transcription regulation. Induces the activity of NF-kappa-B, which is involved in regulating the expression of hundreds of genes. BTK is involved on the signaling pathway linking TLR8 and TLR9 to NF-kappa-B. Transiently phosphorylates transcription factor GTF2I on tyrosine residues in response to BCR. GTF2I then translocates to the nucleus to bind regulatory enhancer elements to modulate gene expression. ARID3A and NFAT are other transcriptional target of BTK. BTK is required for the formation of functional ARID3A DNA-binding complexes. There is however no evidence that BTK itself binds directly to DNA. BTK has a dual role in the regulation of apoptosis. Non-receptor tyrosine kinase indispensable for B lymphocyte development, differentiation and signaling.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAAVILESIFLKRSQQKKKTSPLNFKKRLFLLTVHKLSYYEYDFERGRRGSKKGSIDVEK
ITCVETVVPEKNPPPERQIPRRGEESSEMEQISIIERFPYPFQVVYDEGPLYVFSPTEEL RKRWIHQLKNVIRYNSDLVQKYHPCFWIDGQYLCCSQTAKNAMGCQILENRNGSLKPGSS HRKTKKPLPPTPEEDQILKKPLPPEPAAAPVSTSELKKVVALYDYMPMNANDLQLRKGDE YFILEESNLPWWRARDKNGQEGYIPSNYVTEAEDSIEMYEWYSKHMTRSQAEQLLKQEGK EGGFIVRDSSKAGKYTVSVFAKSTGDPQGVIRHYVVCSTPQSQYYLAEKHLFSTIPELIN YHQHNSAGLISRLKYPVSQQNKNAPSTAGLGYGSWEIDPKDLTFLKELGTGQFGVVKYGK WRGQYDVAIKMIKEGSMSEDEFIEEAKVMMNLSHEKLVQLYGVCTKQRPIFIITEYMANG CLLNYLREMRHRFQTQQLLEMCKDVCEAMEYLESKQFLHRDLAARNCLVNDQGVVKVSDF GLSRYVLDDEYTSSVGSKFPVRWSPPEVLMYSKFSSKSDIWAFGVLMWEIYSLGKMPYER FTNSETAEHIAQGLRLYRPHLASEKVYTIMYSCWHEKADERPTFKILLSNILDVMDEES Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs in Phase 2 Trial | [+] 1 | + | ||||
| 1 | Acalabrutinib | Drug Info | Approved | leukaemia | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Acalabrutinib | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Dasatinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structures of human Bruton's tyrosine kinase in active and inactive conformations suggests a mechanism of activation for TEC family kinases. | PDB:3K54 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.94 Å | Mutation | Yes | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
YGSWEIDPKD
401 LTFLKELGTG411 QFGVVKYGKW421 RGQYDVAIKM431 IKEFIEEAKV448 MMNLSHEKLV 458 QLYGVCTKQR468 PIFIITEYMA478 NGCLLNYLRE488 MRHRFQTQQL498 LEMCKDVCEA 508 MEYLESKQFL518 HRDLAARNCL528 VNDQGVVKVS538 DFGFPVRWSP565 PEVLMYSKFS 575 SKSDIWAFGV585 LMWEIYSLGK595 MPYERFTNSE605 TAEHIAQGLR615 LYRPHLASEK 625 VYTIMYSCWH635 EKADERPTFK645 ILLSNILDVM655 DEE
|
|||||
|
|
LEU408
3.772
GLY409
4.796
PHE413
4.135
VAL416
4.088
ALA428
3.367
ILE429
4.025
LYS430
3.495
GLU445
3.320
MET449
3.940
VAL458
3.717
ILE472
3.599
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Ibrutinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | BTK1 SOAKED WITH IBRUTINIB-Rev | PDB:5P9I | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.11 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
GLGYGSWEID
398 PKDLTFLKEL408 GTGQFGVVKY418 GKWRGQYDVA428 IKMIKEGSMS438 EDEFIEEAKV 448 MMNLSHEKLV458 QLYGVCTKQR468 PIFIITEYMA478 NGCLLNYLRE488 MRHRFQTQQL 498 LEMCKDVCEA508 MEYLESKQFL518 HRDLAARNCL528 VNDQGVVKVS538 DFGLSRYVLD 548 DEYTSSVGSK558 FPVRWSPPEV568 LMYSKFSSKS578 DIWAFGVLMW588 EIYSLGKMPY 598 ERFTNSETAE608 HIAQGLRLYR618 PHLASEKVYT628 IMYSCWHEKA638 DERPTFKILL 648 SNILDVMDEE658 S
|
|||||
|
|
LEU408
3.579
GLY409
4.000
THR410
3.926
GLY411
3.851
VAL416
3.729
ALA428
3.263
LYS430
3.249
MET449
3.466
VAL458
4.075
ILE472
3.959
THR474
3.342
GLU475
2.858
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |
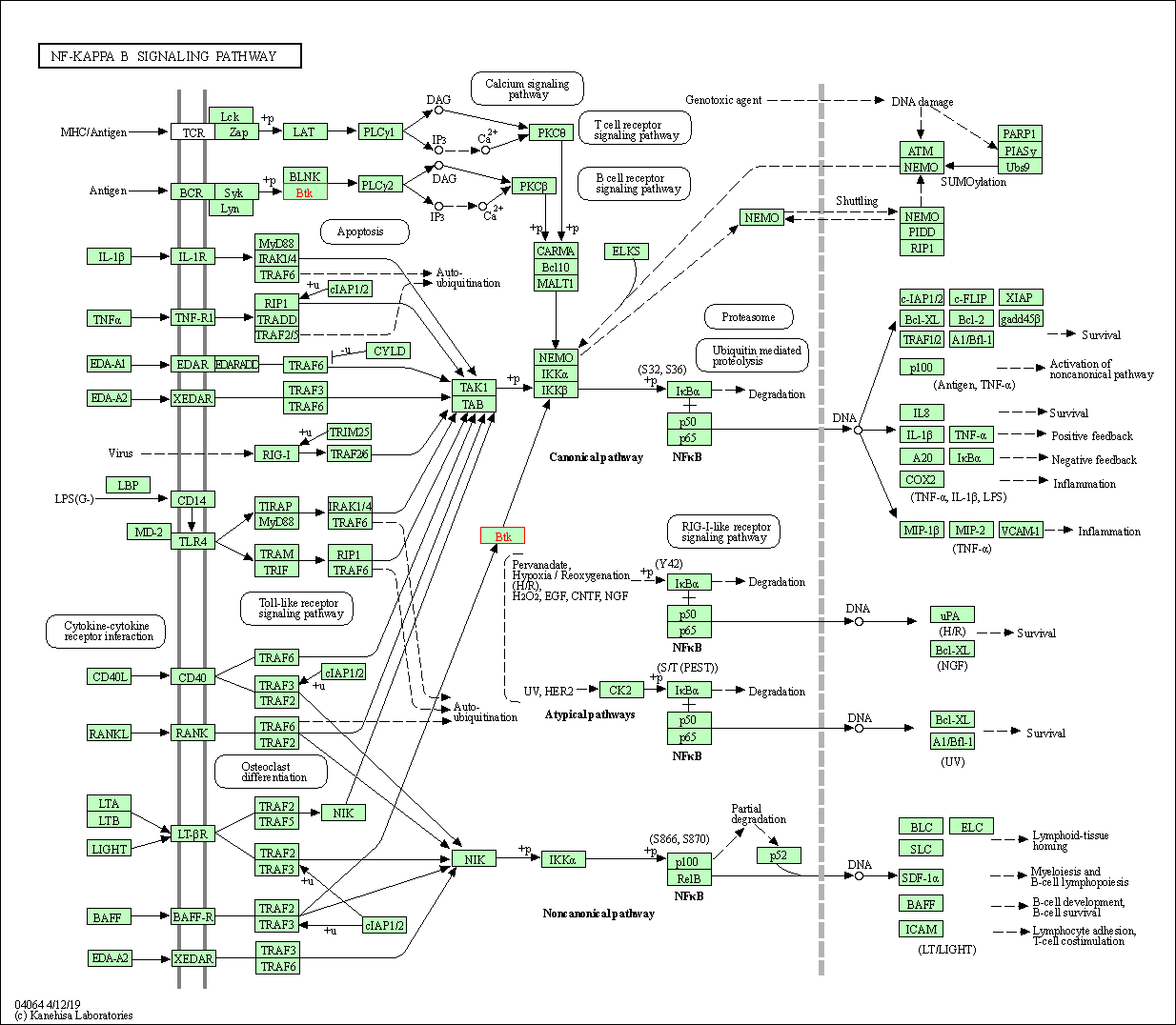
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |
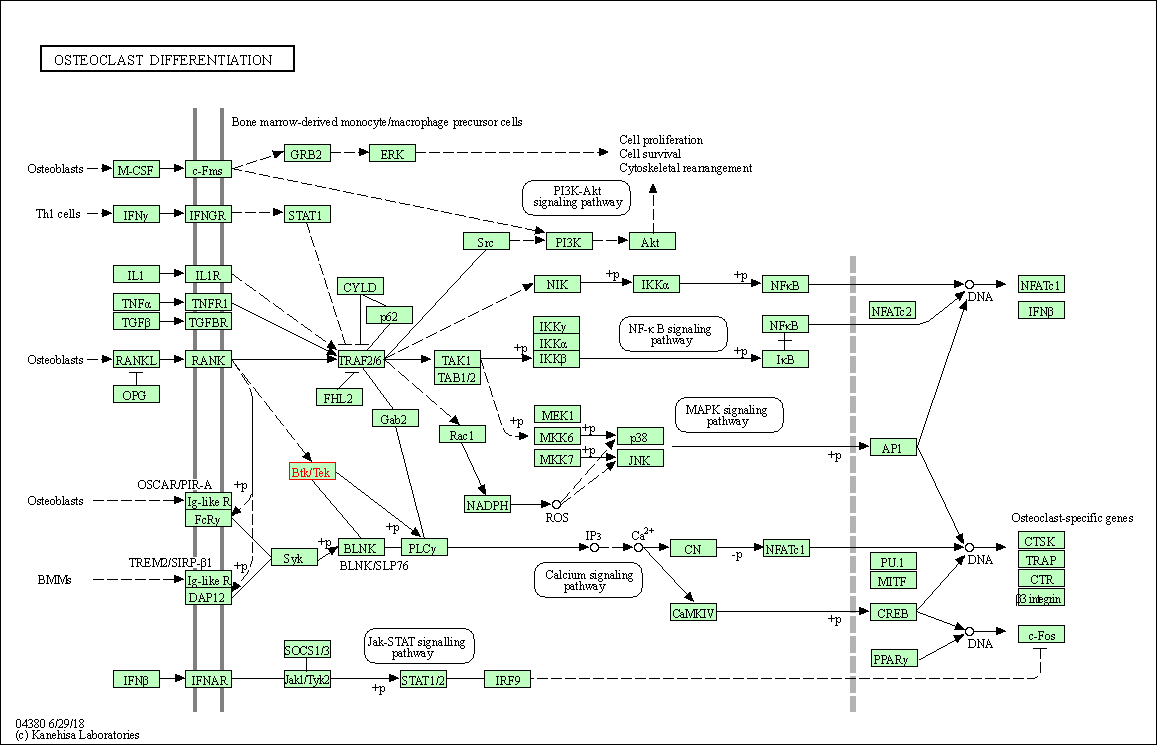
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |
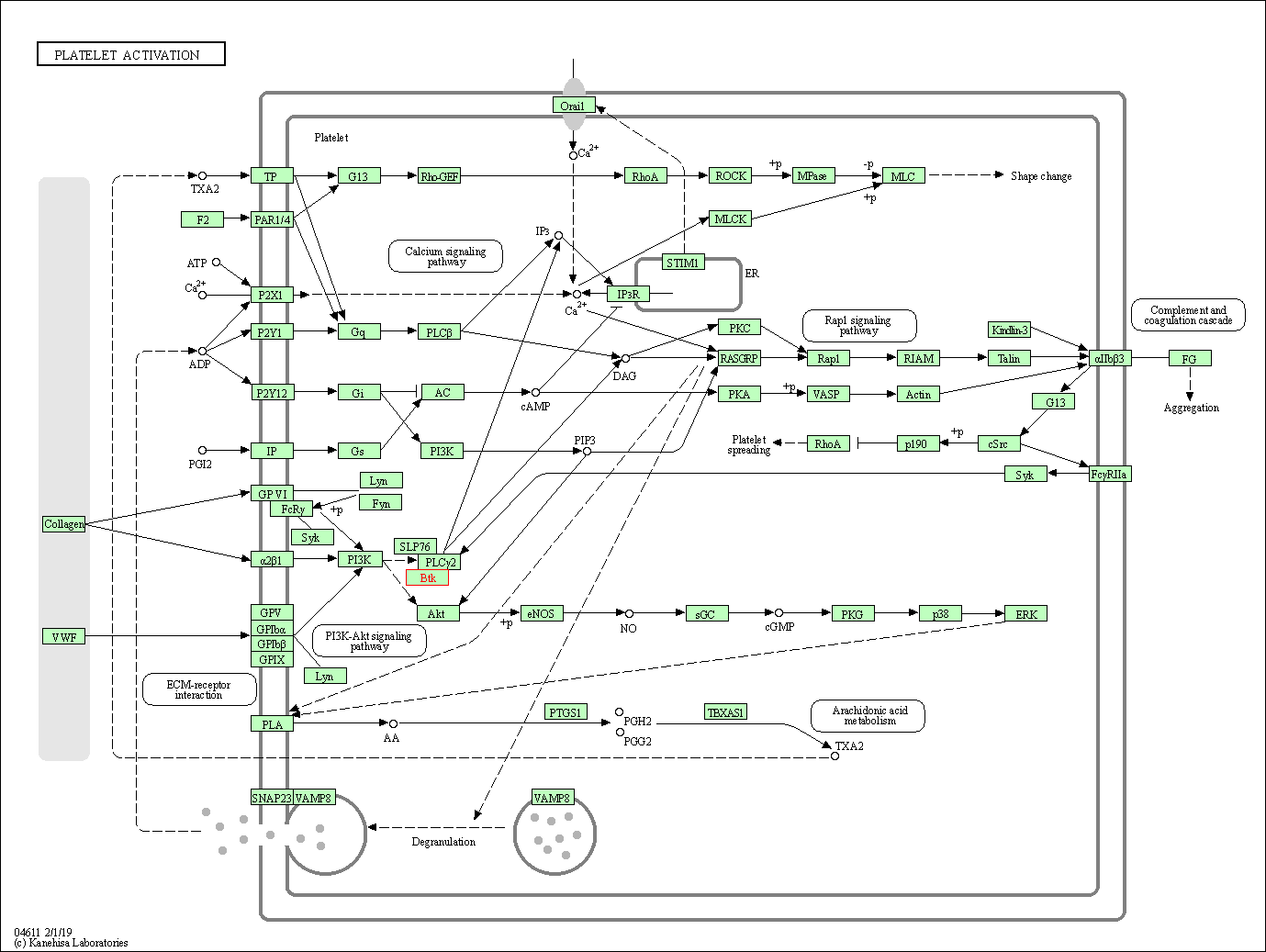
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |
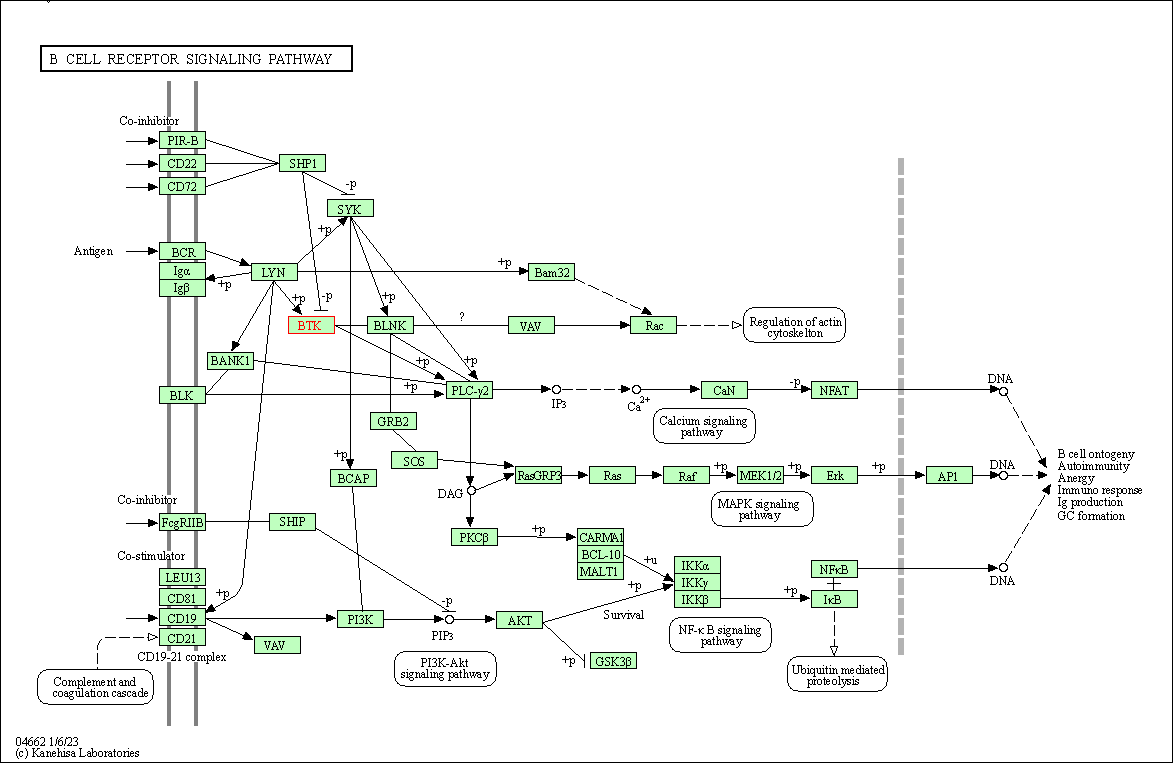
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 7.89E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.25E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.22E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.07E+01 | Topological coefficient | 9.41E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | AstraZeneca initiates CALAVI clinical trial with Calquence against COVID-19 | |||||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2019. Application Number: (NDA) 210259 | |||||
| REF 3 | Structures of human Bruton's tyrosine kinase in active and inactive conformations suggest a mechanism of activation for TEC family kinases. Protein Sci. 2010 Mar;19(3):429-39. | |||||
| REF 4 | Ability of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Sequester Y551 and Prevent Phosphorylation Determines Potency for Inhibition of Fc Receptor but not B-Cell Receptor Signaling. Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;91(3):208-219. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

