Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T97587
(Former ID: TTDS00445)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Integrin alpha-4 (ITGA4)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Very late antigen 4; VLA4 subunit alpha; VLA-4 subunit alpha; VLA-4; Integrin alphaIV; Integrin alpha4; Integrin alpha-IV; CD49d; CD49 antigenlike family member D; CD49 antigen-like family member D
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ITGA4
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Crohn disease [ICD-11: DD70] | |||||
| 2 | Multiple sclerosis [ICD-11: 8A40] | |||||
| 3 | Ulcerative colitis [ICD-11: DD71] | |||||
| Function |
Integrins alpha-4/beta-1 (VLA-4) and alpha-4/beta-7 are receptors for fibronectin. They recognize one or more domains within the alternatively spliced CS-1 and CS-5 regions of fibronectin. They are also receptors for VCAM1. Integrin alpha-4/beta-1 recognizes the sequence Q-I-D-S in VCAM1. Integrin alpha-4/beta-7 is also a receptor for MADCAM1. It recognizes the sequence L-D-T in MADCAM1. On activated endothelial cells integrin VLA-4 triggers homotypic aggregation for most VLA-4-positive leukocyte cell lines. It may also participate in cytolytic T-cell interactions with target cells. ITGA4:ITGB1 binds to fractalkine (CX3CL1) and may act as its coreceptor in CX3CR1-dependent fractalkine signaling. ITGA4:ITGB1 binds to PLA2G2A via a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and this induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Integrin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAWEARREPGPRRAAVRETVMLLLCLGVPTGRPYNVDTESALLYQGPHNTLFGYSVVLHS
HGANRWLLVGAPTANWLANASVINPGAIYRCRIGKNPGQTCEQLQLGSPNGEPCGKTCLE ERDNQWLGVTLSRQPGENGSIVTCGHRWKNIFYIKNENKLPTGGCYGVPPDLRTELSKRI APCYQDYVKKFGENFASCQAGISSFYTKDLIVMGAPGSSYWTGSLFVYNITTNKYKAFLD KQNQVKFGSYLGYSVGAGHFRSQHTTEVVGGAPQHEQIGKAYIFSIDEKELNILHEMKGK KLGSYFGASVCAVDLNADGFSDLLVGAPMQSTIREEGRVFVYINSGSGAVMNAMETNLVG SDKYAARFGESIVNLGDIDNDGFEDVAIGAPQEDDLQGAIYIYNGRADGISSTFSQRIEG LQISKSLSMFGQSISGQIDADNNGYVDVAVGAFRSDSAVLLRTRPVVIVDASLSHPESVN RTKFDCVENGWPSVCIDLTLCFSYKGKEVPGYIVLFYNMSLDVNRKAESPPRFYFSSNGT SDVITGSIQVSSREANCRTHQAFMRKDVRDILTPIQIEAAYHLGPHVISKRSTEEFPPLQ PILQQKKEKDIMKKTINFARFCAHENCSADLQVSAKIGFLKPHENKTYLAVGSMKTLMLN VSLFNAGDDAYETTLHVKLPVGLYFIKILELEEKQINCEVTDNSGVVQLDCSIGYIYVDH LSRIDISFLLDVSSLSRAEEDLSITVHATCENEEEMDNLKHSRVTVAIPLKYEVKLTVHG FVNPTSFVYGSNDENEPETCMVEKMNLTFHVINTGNSMAPNVSVEIMVPNSFSPQTDKLF NILDVQTTTGECHFENYQRVCALEQQKSAMQTLKGIVRFLSKTDKRLLYCIKADPHCLNF LCNFGKMESGKEASVHIQLEGRPSILEMDETSALKFEIRATGFPEPNPRVIELNKDENVA HVLLEGLHHQRPKRYFTIVIISSSLLLGLIVLLLISYVMWKAGFFKRQYKSILQEENRRD SWSYINSKSNDD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T06KGA | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 3 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Antegren | Drug Info | Approved | Multiple sclerosis | [2] | |
| 2 | Natalizumab | Drug Info | Approved | Crohn disease | [3] | |
| 3 | Vedolizmab | Drug Info | Approved | Crohn disease | [4] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 8 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PB006 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Crohn disease | [5] | |
| 2 | AMG-181 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Crohn disease | [6] | |
| 3 | BIO-1211 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Asthma | [7] | |
| 4 | GSK683699 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Inflammatory bowel disease | [8] | |
| 5 | Senktide | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Ischemic stroke | [9], [10] | |
| 6 | ELND-002 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Autoimmune diabetes | [11] | |
| 7 | ELND-004 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Autoimmune diabetes | [12] | |
| 8 | PTG-100 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Ulcerative colitis | [13] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 6 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Vedolizmab | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | BIO-1211 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 3 | ELND-002 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 4 | PTG-100 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 5 | ASP-2002 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 6 | CT301 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 3 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AMG-181 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 2 | Senktide | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 3 | ELND-004 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GSK683699 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: N-(2,6-Dichlorobenzoyl)-4-[1,6-Dimethyl-2-Oxo-4-(Trifluoromethyl)-1,2-Dihydropyridin-3-Yl]-L-Phenylalanine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | crystal structure of a4b7 headpiece complexed with Fab ACT-1 and RO0505376 | PDB:3V4V | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.10 Å | Mutation | Yes | [21] |
| PDB Sequence |
YNVDTESALL
10 YQGPHNTLFG20 YSVVLHSHGA30 NRWLLVGAPT40 ANWLANASVI50 NPGAIYRCRI 60 GKNPGQTCEQ70 LQLGSPNGEP80 CGKTCLEERD90 NQWLGVTLSR100 QPGENGSIVT 110 CGHRWKNIFY120 IKNENKLPTG130 GCYGVPPDLR140 TELSKRIAPC150 YQDYVKKFGE 160 NFASCQAGIS170 SFYTKDLIVM180 GAPGSSYWTG190 SLFVYNITTN200 KYKAFLDKQN 210 QVKFGSYLGY220 SVGAGHFRSQ230 HTTEVVGGAP240 QHEQIGKAYI250 FSIDEKELNI 260 LHEMKGKKLG270 SYFGASVCAV280 DLNADGFSDL290 LVGAPMQSTI300 REEGRVFVYI 310 NSGSGAVMNA320 METNLVGSDK330 YAARFGESIV340 NLGDIDNDGF350 EDVAIGAPQE 360 DDLQGAIYIY370 NGRADGISST380 FSQRIEGLQI390 SKSLSMFGQS400 ISGQIDADNN 410 GYVDVAVGAF420 RSDSAVLLRT430 RPVVIVDASL440 SHPESVNRTK450 FDCVENGWPS 460 VCIDLTLCFS470 YKGKEVPGYI480 VLFYNMSLDV490 NRKAESPPRF500 YFSSNGTSDV 510 ITGSIQVSSR520 EANCRTHQAF530 MRKDVRDILT540 PIQIEAAYHL550 GPHSTEEFPP 565 LQPILQQKKE575 KDIMKKTINF585 AR
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
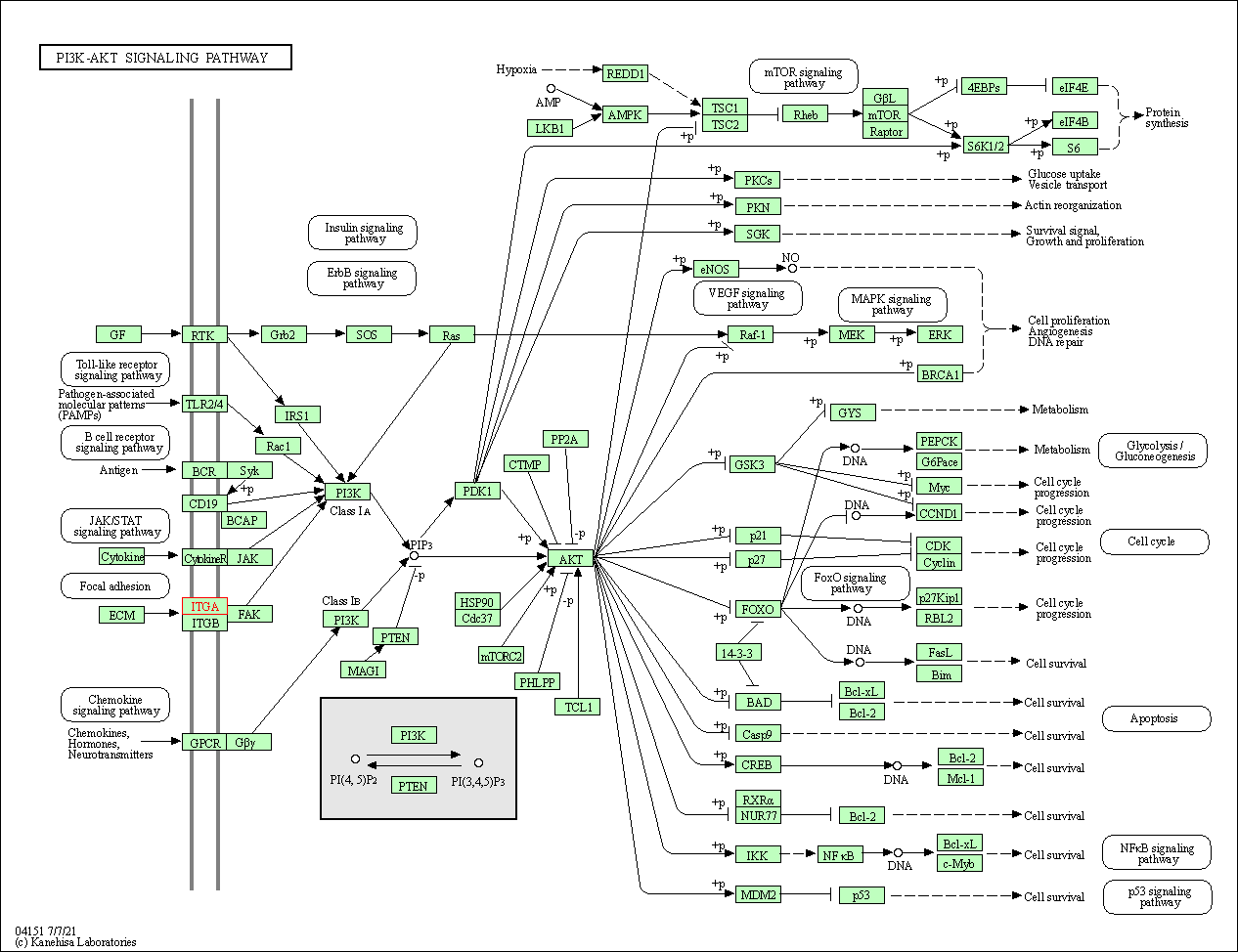
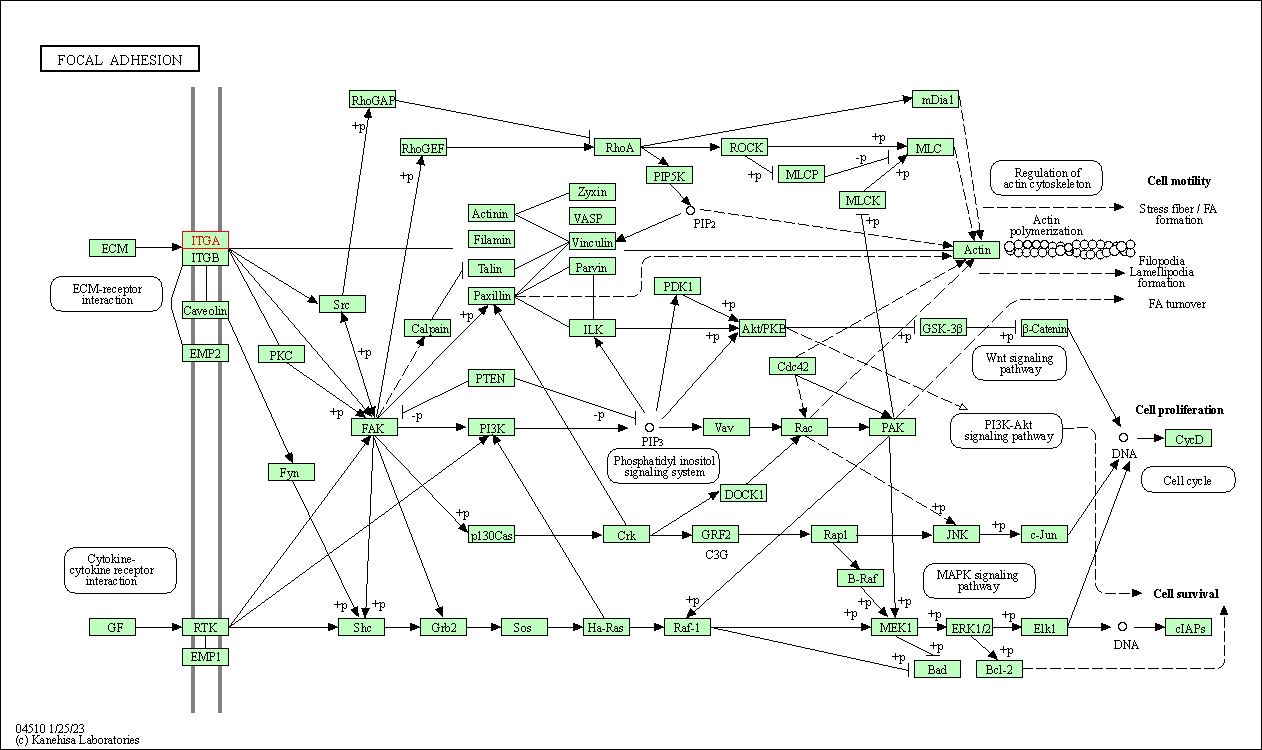
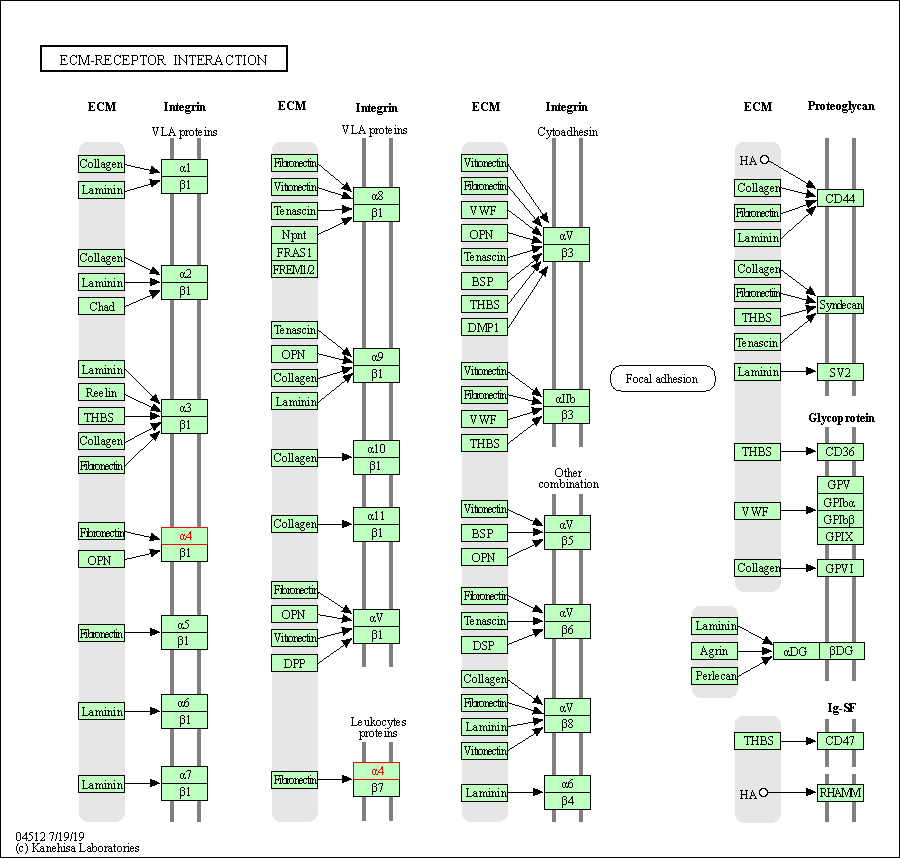
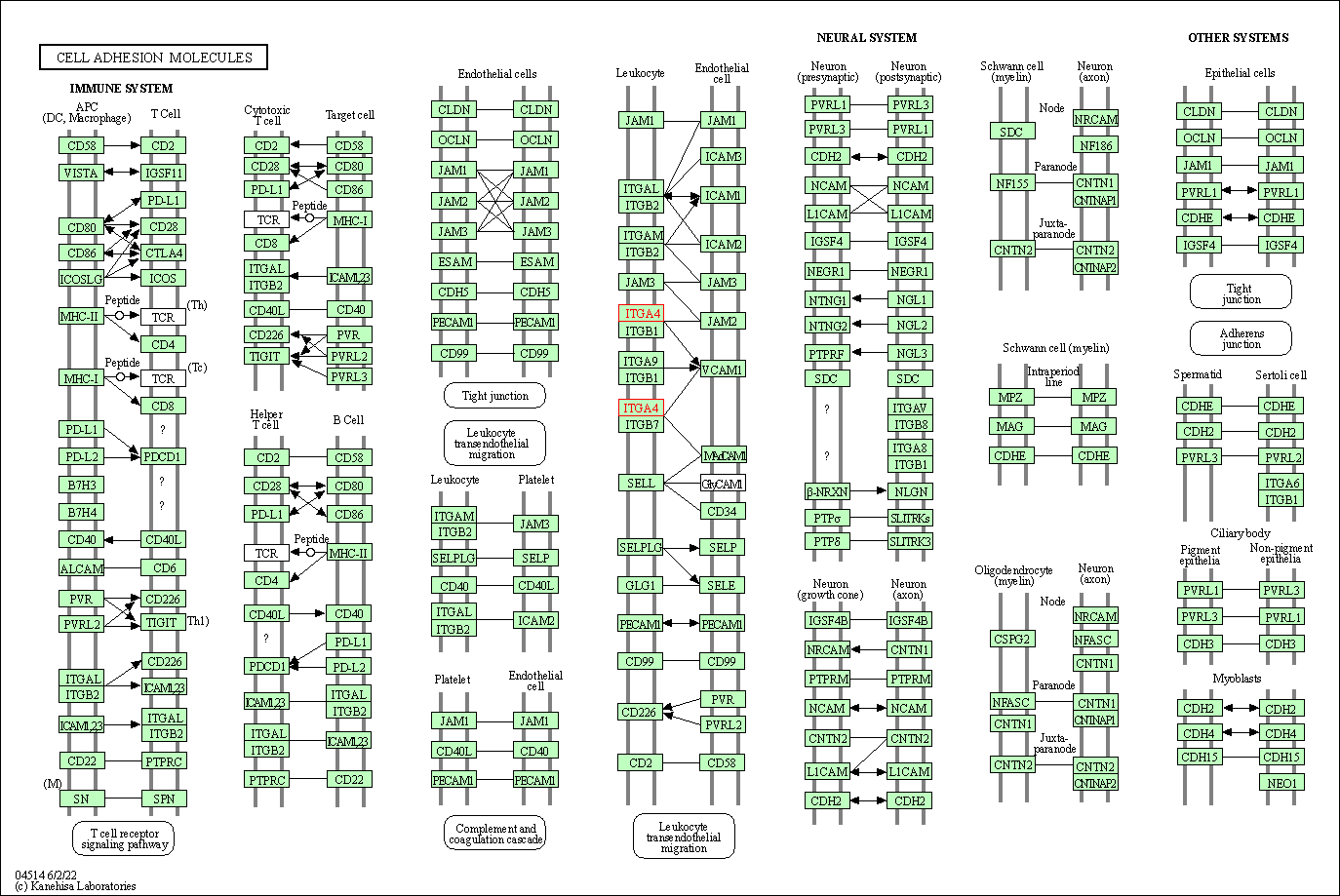
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ECM-receptor interaction | hsa04512 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cell adhesion molecules | hsa04514 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | hsa04640 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | hsa04670 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Intestinal immune network for IgA production | hsa04672 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | hsa04810 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell motility | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.10E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.25E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 9.94E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.66E+01 | Topological coefficient | 9.25E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Takeda (2009). | |||||
| REF 2 | 2004 approvals: the demise of the blockbuster. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005 Feb;4(2):93-4. | |||||
| REF 3 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. | |||||
| REF 4 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04115488) Efficacy and Safety of the Biosimilar Natalizumab PB006 in Comparison to Tysabri? in Patients With Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS). U.S.National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01696396) AMG 181 in Subjects With Moderate to Severe Crohn's Disease. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6589). | |||||
| REF 8 | Emerging drugs to treat Crohn's disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 Mar;12(1):49-59. | |||||
| REF 9 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 10 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 11 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01318421) A Study of ELND002 in Patients With Relapsing Forms of Multiple Sclerosis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800024932) | |||||
| REF 13 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 14 | Very late antigen 4 (VLA4) antagonists as anti-inflammatory agents. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998 Aug;2(4):453-7. | |||||
| REF 15 | Natalizumab in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment: From Biological Effects to Immune Monitoring. Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 24;11:549842. | |||||
| REF 16 | Efficacy and Safety of Proposed Biosimilar Natalizumab (PB006) in Patients With Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: The Antelope Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2023 Mar 1;80(3):298-307. | |||||
| REF 17 | A small-molecule, tight-binding inhibitor of the integrin alpha(4)beta(1) blocks antigen-induced airway responses and inflammation in experimental asthma in sheep. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Aug;162(2 Pt 1):603-11. | |||||
| REF 18 | Paxillin binding to the alpha 4 integrin subunit stimulates LFA-1 (integrin alpha L beta 2)-dependent T cell migration by augmenting the activation of focal adhesion kinase/proline-rich tyrosine kinase-2. J Immunol. 2003 Jun 15;170(12):5912-8. | |||||
| REF 19 | Asphelia to Present at C21 BioVentures Conference in Napa, CA. 10th Annual C21 BioVentures. May 15, 2008. | |||||
| REF 20 | Prolonged reversal of chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis using a small molecule inhibitor of alpha4 integrin. J Neuroimmunol. 2002 Oct;131(1-2):147-59. | |||||
| REF 21 | Structural specializations of Alpha(4)beta(7), an integrin that mediates rolling adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan 9;196(1):131-46. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

