Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T97008
|
|||||
| Target Name |
S-adenosylmethionine synthase type-2 (MAT2A)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Methionine adenosyltransferase II; Methionine adenosyltransferase 2; MAT-II; MAT 2; AdoMet synthase 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAT2A
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A80-2A86] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the formation of S-adenosylmethionine from methionine and ATP. The reaction comprises two steps that are both catalyzed by the same enzyme: formation of S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) and triphosphate, and subsequent hydrolysis of the triphosphate.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
AdoMet synthase family
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.5.1.6
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MNGQLNGFHEAFIEEGTFLFTSESVGEGHPDKICDQISDAVLDAHLQQDPDAKVACETVA
KTGMILLAGEITSRAAVDYQKVVREAVKHIGYDDSSKGFDYKTCNVLVALEQQSPDIAQG VHLDRNEEDIGAGDQGLMFGYATDETEECMPLTIVLAHKLNAKLAELRRNGTLPWLRPDS KTQVTVQYMQDRGAVLPIRVHTIVISVQHDEEVCLDEMRDALKEKVIKAVVPAKYLDEDT IYHLQPSGRFVIGGPQGDAGLTGRKIIVDTYGGWGAHGGGAFSGKDYTKVDRSAAYAARW VAKSLVKGGLCRRVLVQVSYAIGVSHPLSISIFHYGTSQKSERELLEIVKKNFDLRPGVI VRDLDLKKPIYQRTAAYGHFGRDSFPWEVPKKLKY Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T49PKX | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AG-270 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lymphoma | [1] | |
| 2 | AG-270 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Lymphoma | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 2 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AG-270 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | AG-270 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | The structure of Human MAT2A in complex with SAM, Adenosine, Methionine and PPNP. | PDB:5A1I | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.09 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
EGTFLFTSES
24 VGEGHPDKIC34 DQISDAVLDA44 HLQQDPDAKV54 ACETVAKTGM64 ILLAGEITSR 74 AAVDYQKVVR84 EAVKHIGYDD94 SSKGFDYKTC104 NVLVALEQQS114 PDIAQGVHLD 124 RNEEDIGAGD134 QGLMFGYATD144 ETEECMPLTI154 VLAHKLNAKL164 AELRRNGTLP 174 WLRPDSKTQV184 TVQYMQDRGA194 VLPIRVHTIV204 ISVQHDEEVC214 LDEMRDALKE 224 KVIKAVVPAK234 YLDEDTIYHL244 QPSGRFVIGG254 PQGDAGLTGR264 KIIVDTYGGW 274 GAHGGGAFSG284 KDYTKVDRSA294 AYAARWVAKS304 LVKGGLCRRV314 LVQVSYAIGV 324 SHPLSISIFH334 YGTSQKSERE344 LLEIVKKNFD354 LRPGVIVRDL364 DLKKPIYQRT 374 AAYGHFGRDS384 FPWEVPKKLK394 Y
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Ademetionine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of human methionine adenosyltransferase 2A (MAT2A) in complex with SAM and allosteric inhibitor AGI-43192 | PDB:7RWG | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 0.97 Å | Mutation | No | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
FIEEGTFLFT
21 SESVGEGHPD31 KICDQISDAV41 LDAHLQQDPD51 AKVACETVAK61 TGMILLAGEI 71 TSRAAVDYQK81 VVREAVKHIG91 YDDSSKGFDY101 KTCNVLVALE111 QQSPDIAQGV 121 HLDRNEEDIG131 AGDQGLMFGY141 ATDETEECMP151 LTIVLAHKLN161 AKLAELRRNG 171 TLPWLRPDSK181 TQVTVQYMQD191 RGAVLPIRVH201 TIVISVQHDE211 EVCLDEMRDA 221 LKEKVIKAVV231 PAKYLDEDTI241 YHLQPSGRFV251 IGGPQGDAGL261 TGRKIIVDTY 271 GGWGAHGGGA281 FSGKDYTKVD291 RSAAYAARWV301 AKSLVKGGLC311 RRVLVQVSYA 321 IGVSHPLSIS331 IFHYGTSQKS341 ERELLEIVKK351 NFDLRPGVIV361 RDLDLKKPIY 371 QRTAAYGHFG381 RDSFPWEVPK391 KLKY
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | hsa00270 | Affiliated Target |
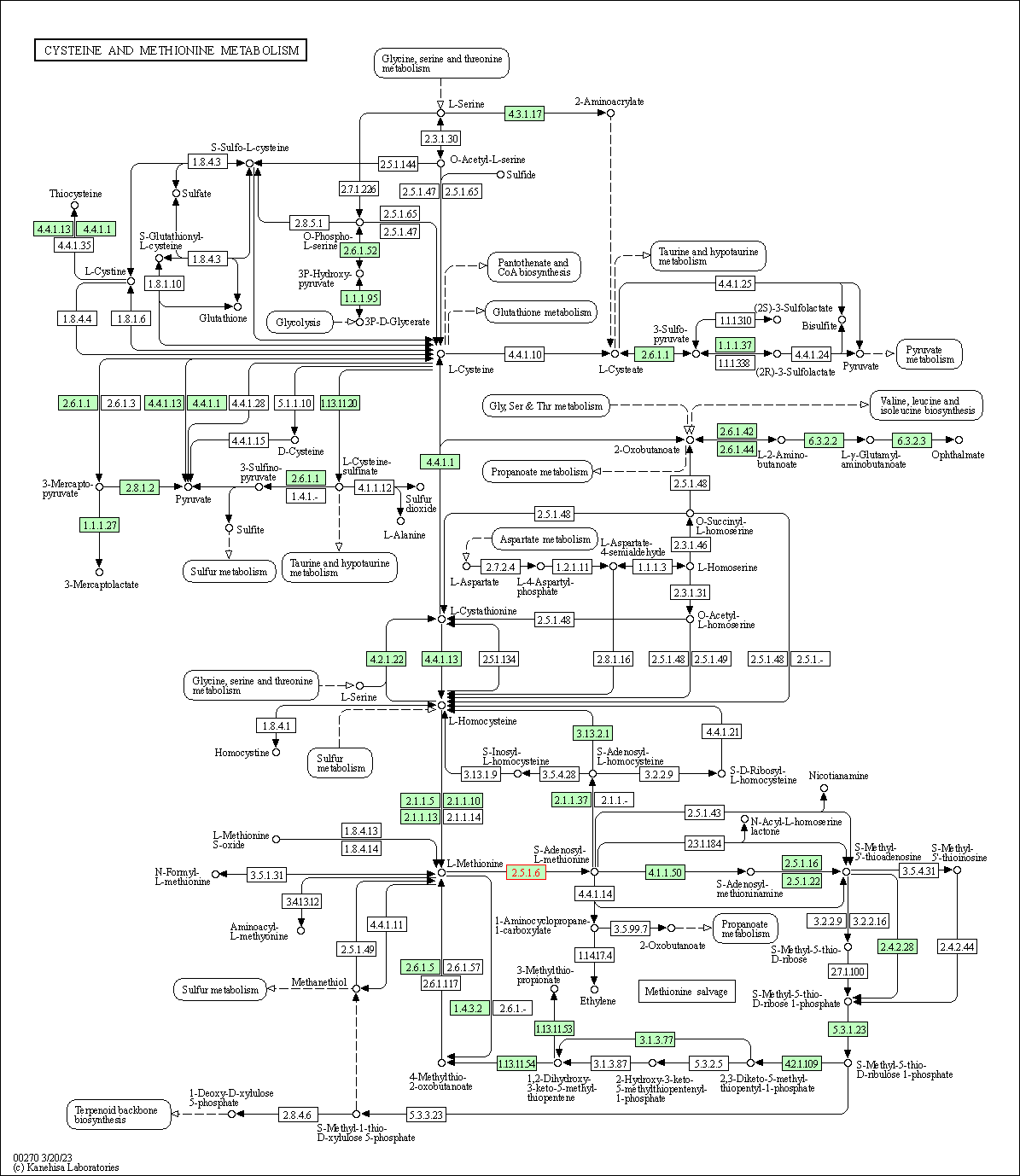
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 5.11E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.54E-01 | Radiality | 1.21E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 5.33E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.67E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.95E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03435250) Study of AG-270 in Participants With Advanced Solid Tumors or Lymphoma With MTAP Loss. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Discovery of AG-270, a First-in-Class Oral MAT2A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Tumors with Homozygous MTAP Deletion. J Med Chem. 2021 Apr 22;64(8):4430-4449. | |||||
| REF 4 | Crystallography captures catalytic steps in human methionine adenosyltransferase enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 23;113(8):2104-9. | |||||
| REF 5 | Leveraging Structure-Based Drug Design to Identify Next-Generation MAT2A Inhibitors, Including Brain-Penetrant and Peripherally Efficacious Leads. J Med Chem. 2022 Mar 24;65(6):4600-4615. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

