Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T95371
(Former ID: TTDNC00373)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type I interferon receptor 1; IFNalpha/beta receptor 1; IFNR1; IFNAR; IFN-alpha/beta receptor 1; IFN-R-1; Cytokine receptor family 2 member 1; Cytokine receptor classII member 1; Cytokine receptor class-II member 1; CRF21; CRF2-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IFNAR1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Hepatitis virus infection [ICD-11: 1E50-1E51] | |||||
| 2 | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||||
| Function |
Functions in general as heterodimer with IFNAR2. Type I interferon binding activates the JAK-STAT signaling cascade, and triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of proteins including JAKs, TYK2, STAT proteins and the IFNR alpha- and beta-subunits themselves. Can form an active IFNB1 receptor by itself and activate a signaling cascade that does not involve activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Component of the receptor for type I interferons, including interferons alpha, IFNB1 and IFNW1.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MMVVLLGATTLVLVAVAPWVLSAAAGGKNLKSPQKVEVDIIDDNFILRWNRSDESVGNVT
FSFDYQKTGMDNWIKLSGCQNITSTKCNFSSLKLNVYEEIKLRIRAEKENTSSWYEVDSF TPFRKAQIGPPEVHLEAEDKAIVIHISPGTKDSVMWALDGLSFTYSLVIWKNSSGVEERI ENIYSRHKIYKLSPETTYCLKVKAALLTSWKIGVYSPVHCIKTTVENELPPPENIEVSVQ NQNYVLKWDYTYANMTFQVQWLHAFLKRNPGNHLYKWKQIPDCENVKTTQCVFPQNVFQK GIYLLRVQASDGNNTSFWSEEIKFDTEIQAFLLPPVFNIRSLSDSFHIYIGAPKQSGNTP VIQDYPLIYEIIFWENTSNAERKIIEKKTDVTVPNLKPLTVYCVKARAHTMDEKLNKSSV FSDAVCEKTKPGNTSKIWLIVGICIALFALPFVIYAAKVFLRCINYVFFPSLKPSSSIDE YFSEQPLKNLLLSTSEEQIEKCFIIENISTIATVEETNQTDEDHKKYSSQTSQDSGNYSN EDESESKTSEELQQDFV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 5 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | EMZ701 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hepatitis B virus infection | [2] | |
| 2 | MEDI-546 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Ovarian cancer | [3], [4] | |
| 3 | R-IFN-1a | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hepatitis C virus infection | [5] | |
| 4 | Zadaxin/lamivudine | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Hepatitis B virus infection | [6] | |
| 5 | Belerofon | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Hepatitis C virus infection | [7] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Omega interferon | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Hepatitis C virus infection | [8] | |
| 2 | BLX-883 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Hepatitis C virus infection | [9] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 8 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | EMZ701 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | MEDI-546 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | R-IFN-1a | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 4 | Zadaxin/lamivudine | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 5 | Belerofon | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 6 | Omega interferon | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 7 | BLX-883 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 8 | Ceplene/Peg-Intron/Rebetol | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |
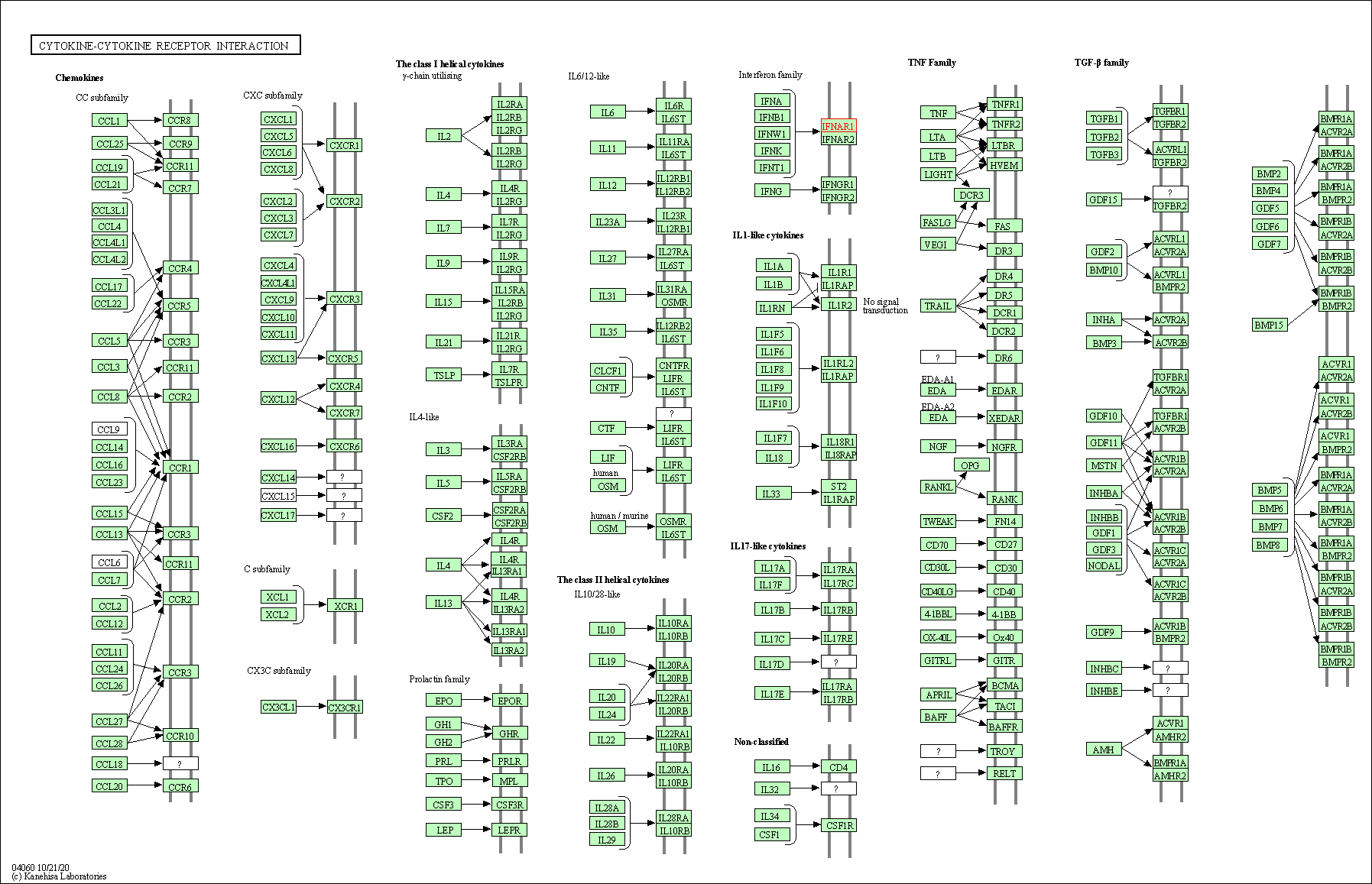
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
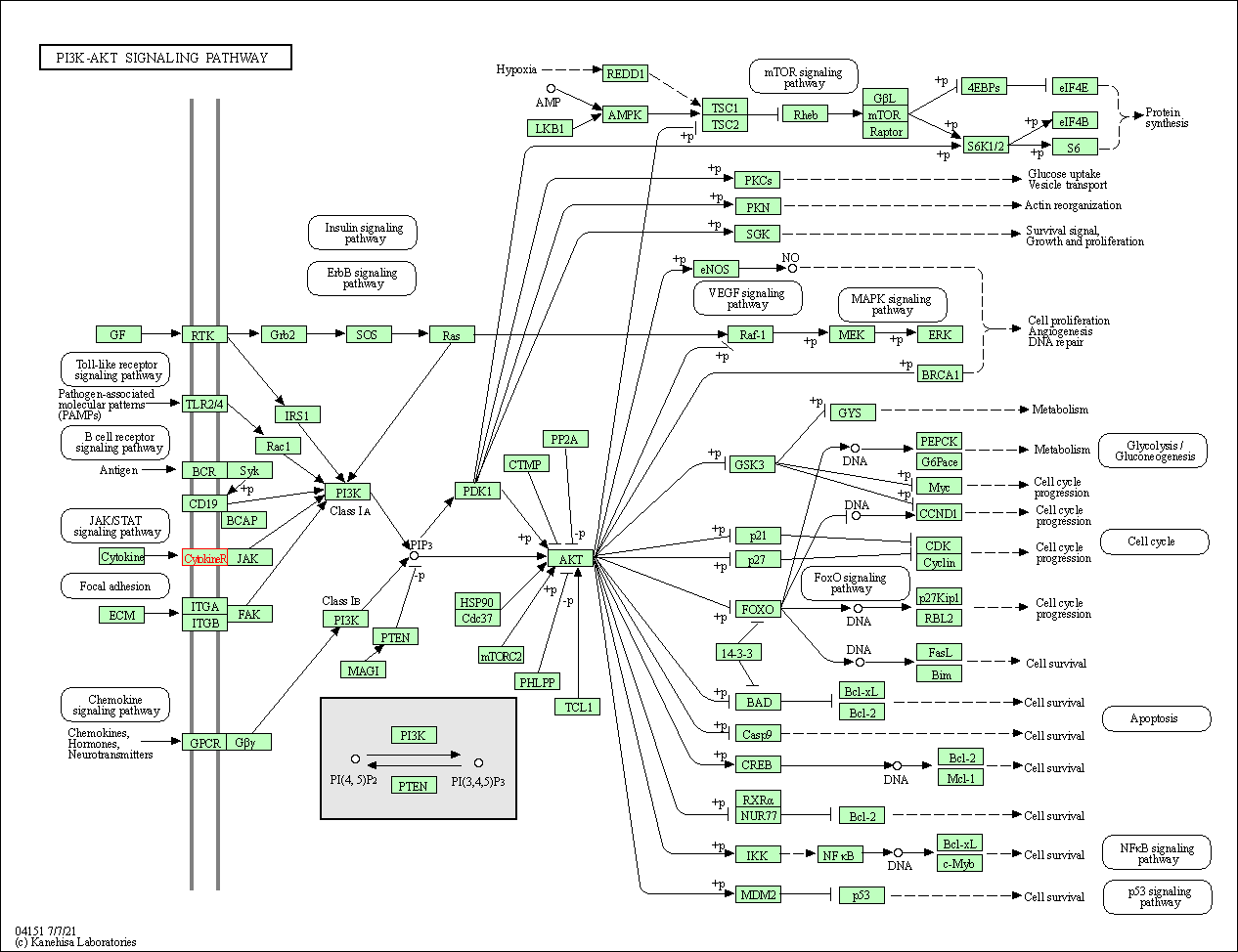
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |
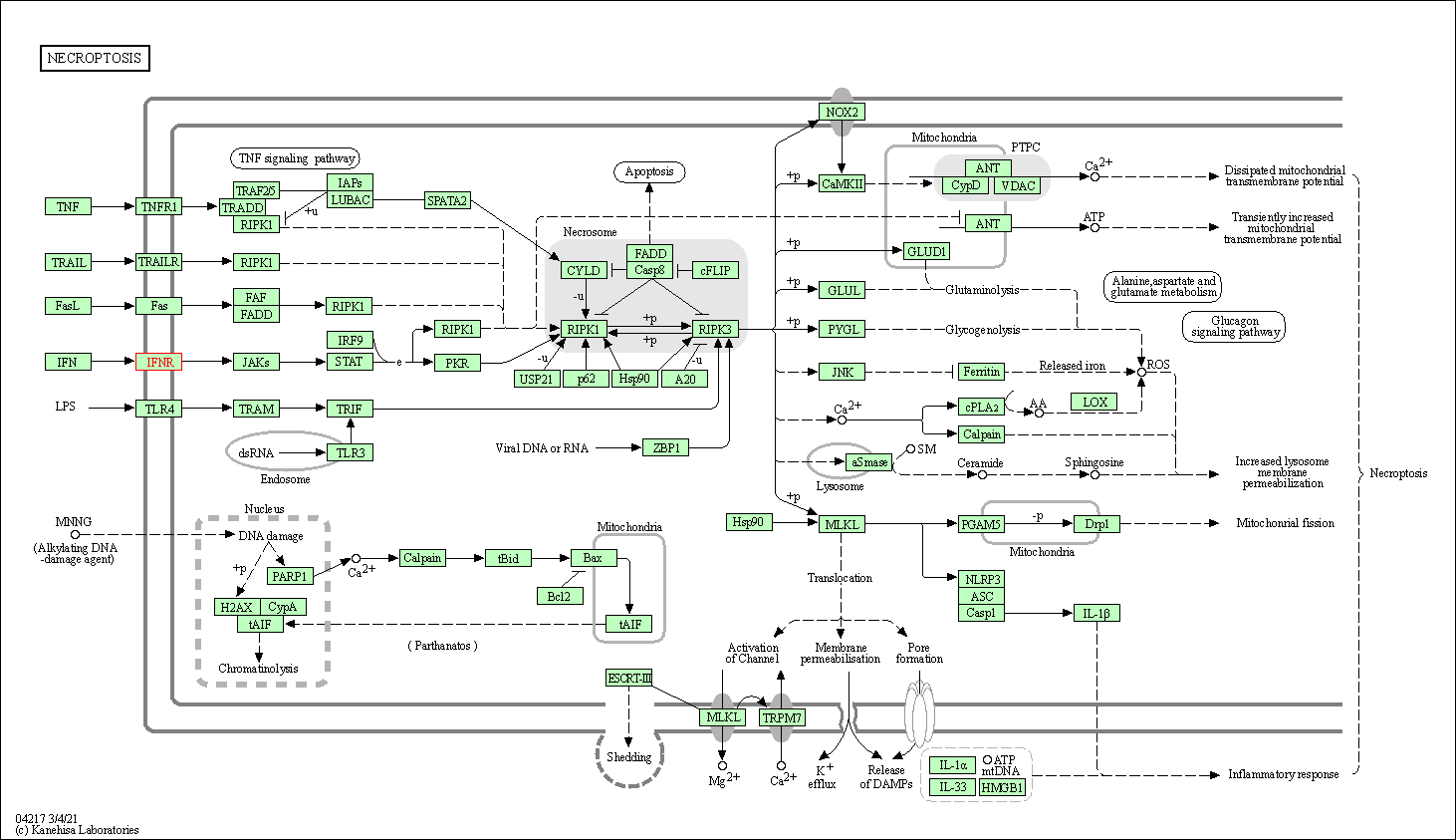
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |
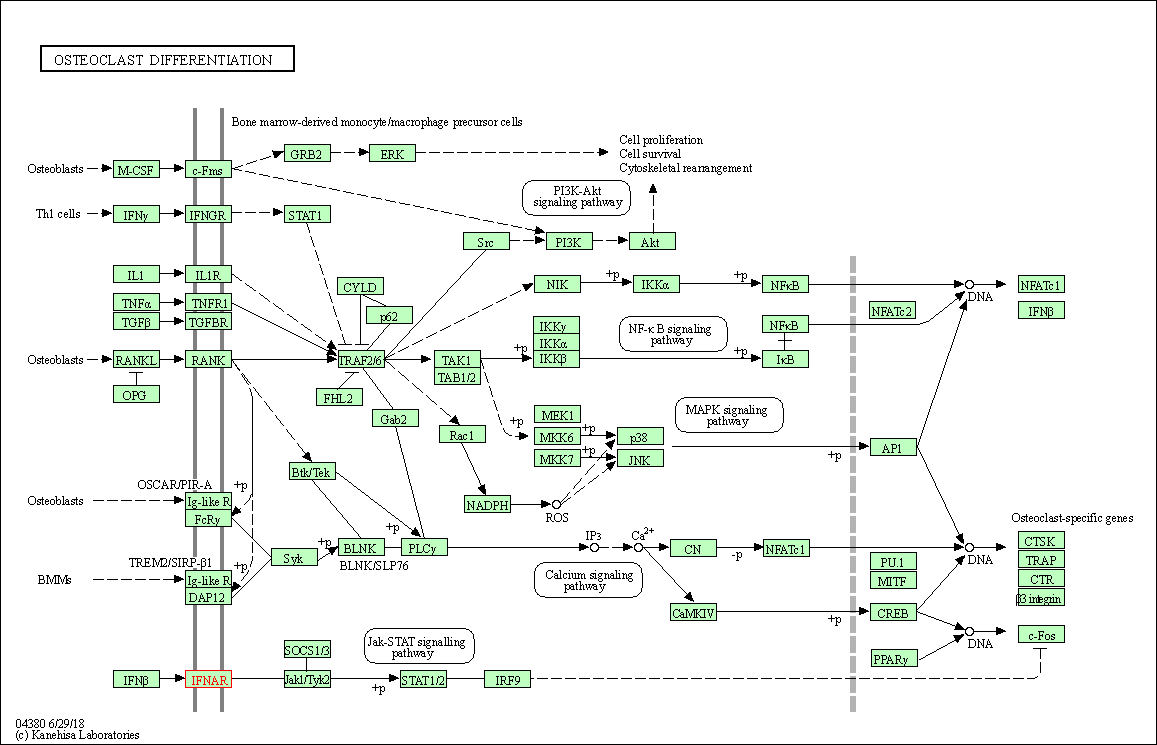
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
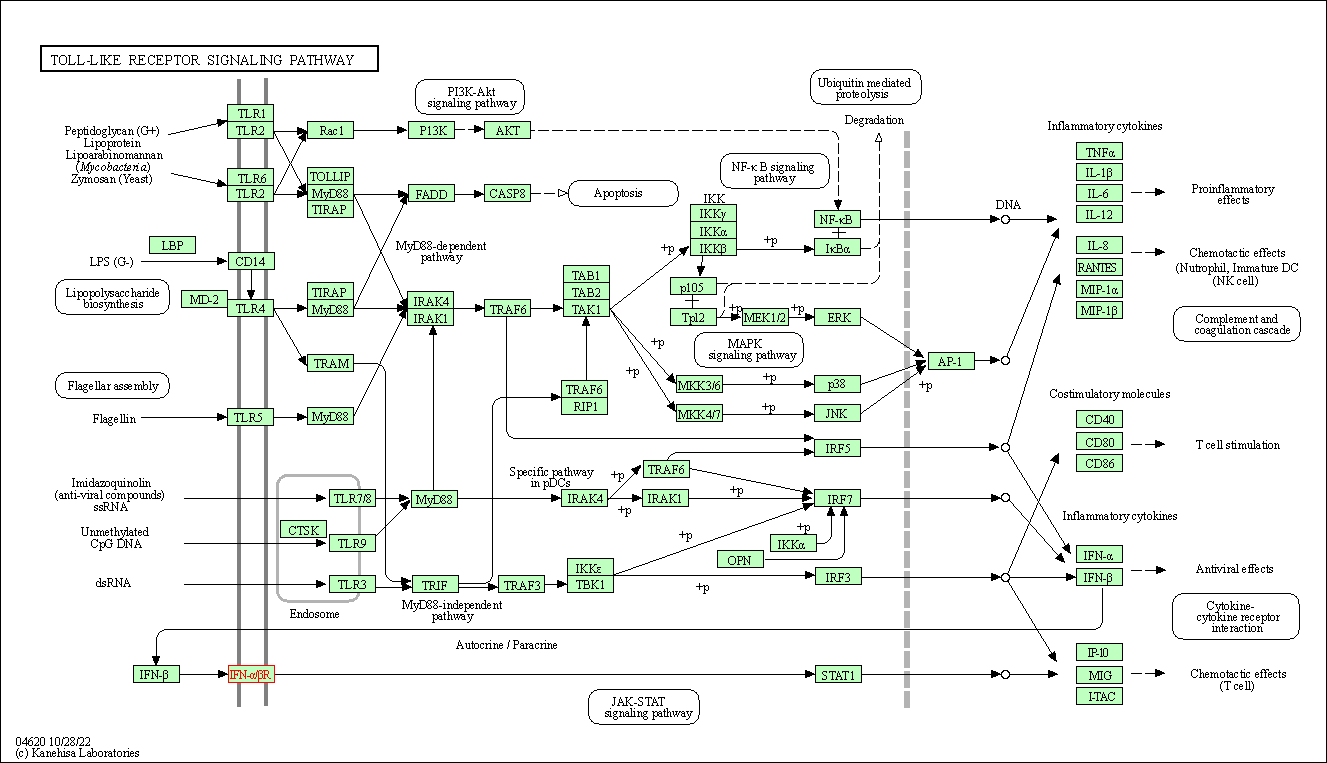
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
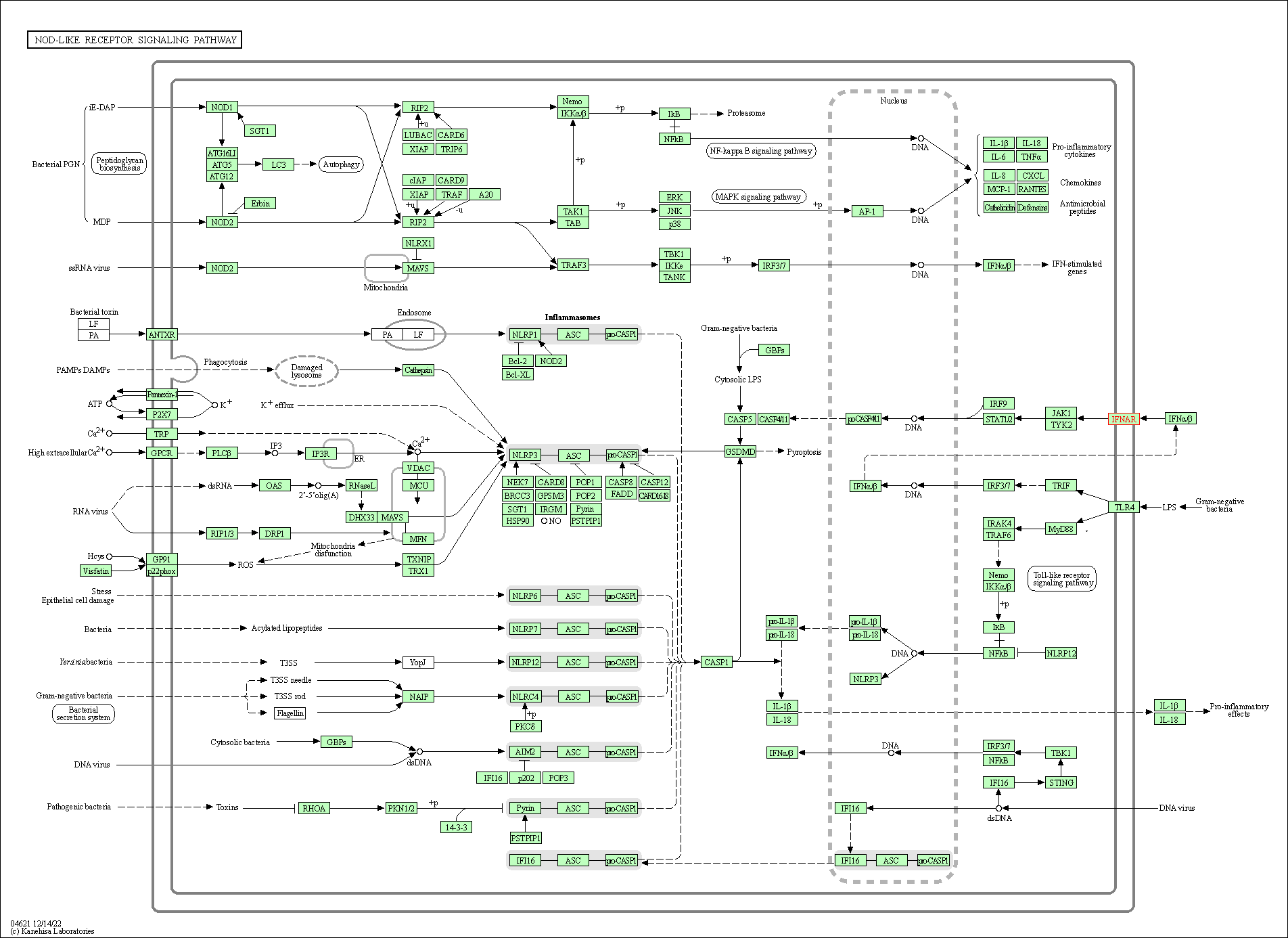
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |
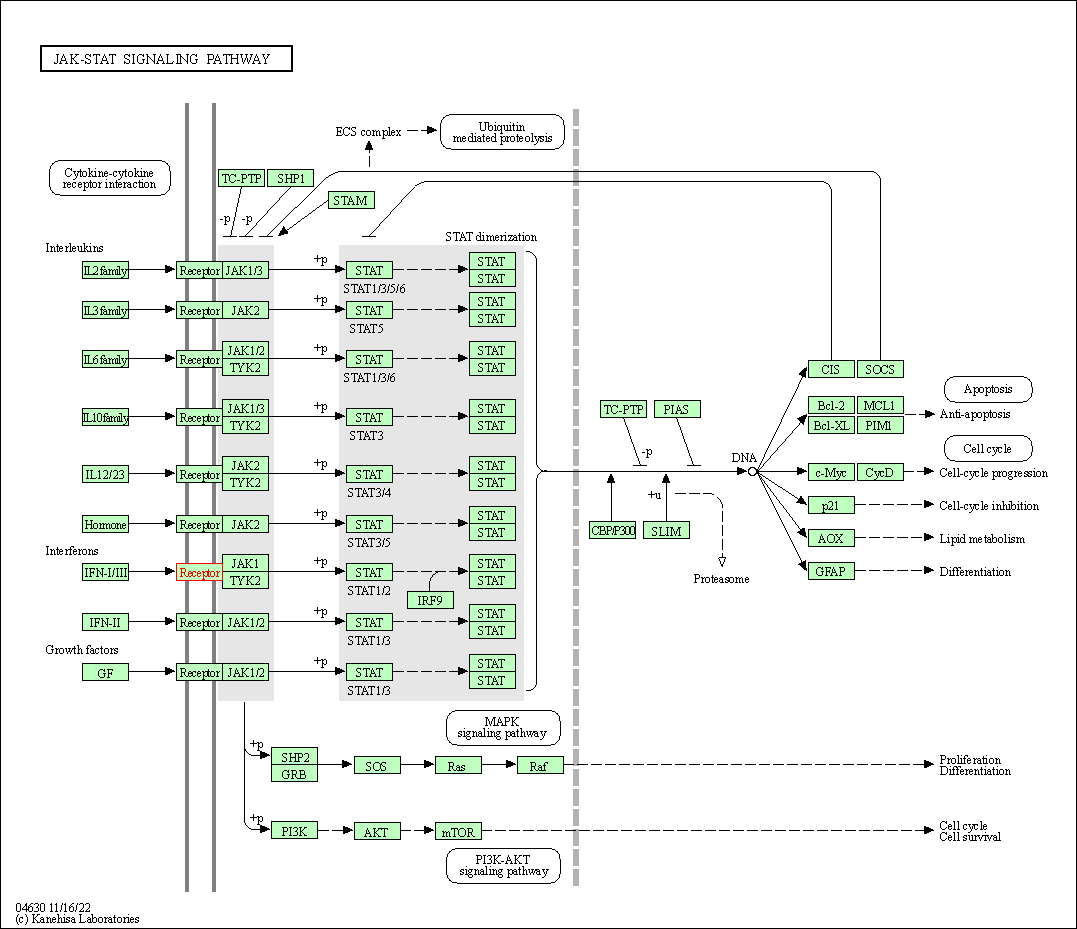
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | hsa04650 | Affiliated Target |
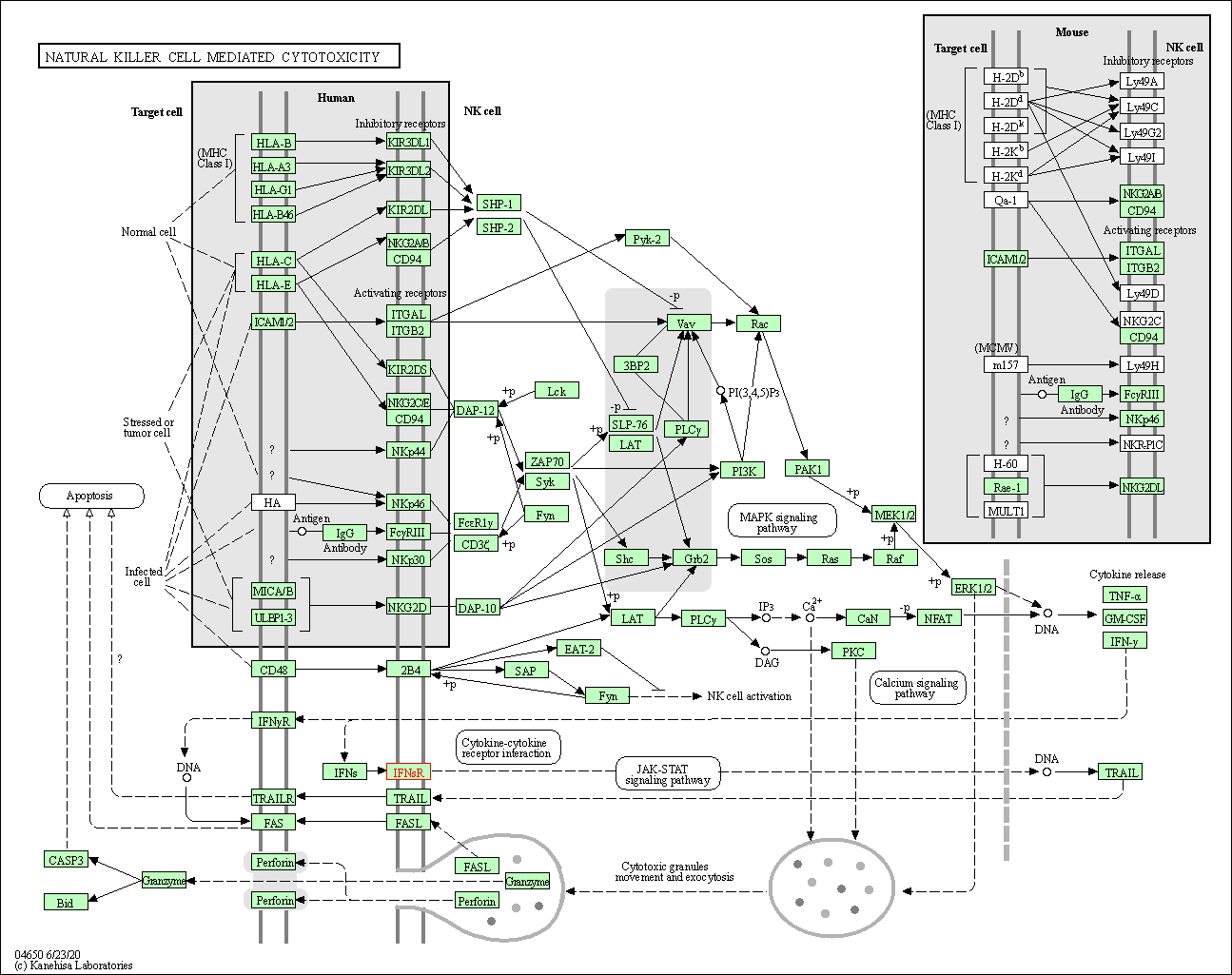
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 16 | Degree centrality | 1.72E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.53E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.21E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.75E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.78E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.04E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 11 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Osteoclast differentiation | |||||
| 4 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | |||||
| 6 | Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | |||||
| 7 | Hepatitis C | |||||
| 8 | Hepatitis B | |||||
| 9 | Measles | |||||
| 10 | Influenza A | |||||
| 11 | Herpes simplex infection | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 2 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Leptin Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 2 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Downstream signaling in naï | |||||
| 2 | ||||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Interferon alpha/beta signaling | |||||
| 2 | Regulation of IFNA signaling | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 5 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Interferon type I signaling pathways | |||||
| 3 | Interferon alpha/beta signaling | |||||
| 4 | Regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | Osteoclast Signaling | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Patent EP2766021 A1. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Transition Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8258). | |||||
| REF 4 | Molecular basis for antagonistic activity of anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-alpha receptor 1 antibody. MAbs. 2015;7(2):428-39. | |||||
| REF 5 | A phase II study of recombinant interferon-beta (r-hIFN-beta 1a) in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in the treatment of patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1997;75(3):423-6. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of SciClone. | |||||
| REF 7 | Nautilus Biotech Receives FDA Approval for Phase 1 Clinical Trial in the USA for Oral Belerofon(R), its Long-Lasting, Interferon-Alpha Drug. Nautilus Biotech. MAY 14, 2007. | |||||
| REF 8 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800005492) | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021901) | |||||
| REF 10 | Further study on the specificity and incidence of neutralizing antibodies to interferon (IFN) in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis patients treated with IFN beta-1a or IFN beta-1b. J Neurol Sci.1999 Oct 15;168(2):131-6. | |||||
| REF 11 | Zadaxin (thymosin alpha1) for the treatment of viral hepatitis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 1999 Mar;8(3):281-7. | |||||
| REF 12 | WO patent application no. 2009,0153,36, Controlled release interferon drug products and treatment of hcv infection using same. | |||||
| REF 13 | Human interferon omega--a review. Mult Scler. 1995;1 Suppl 1:S44-7. | |||||
| REF 14 | Patent CN103536906 A. | |||||
| REF 15 | Resistance to mericitabine, a nucleoside analogue inhibitor of HCV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Antivir Ther. 2012;17(3):411-23. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

