Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T94197
(Former ID: TTDI03494)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Protein kinase N2 (PKN2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2; Protein-kinase C-related kinase 2; Protein kinase C-like 2; PRKCL2; PRK2; PKN gamma
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PKN2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Plays a role in the regulation of cell cycle progression, actin cytoskeleton assembly, cell migration, cell adhesion, tumor cell invasion and transcription activation signaling processes. Phosphorylates CTTN in hyaluronan-induced astrocytes and hence decreases CTTN ability to associate with filamentous actin. Phosphorylates HDAC5, therefore lead to impair HDAC5 import. Direct RhoA target required for the regulation of the maturation of primordial junctions into apical junction formation in bronchial epithelial cells. Required for G2/M phases of the cell cycle progression and abscission during cytokinesis in a ECT2-dependent manner. Stimulates FYN kinase activity that is required for establishment of skin cell-cell adhesion during keratinocytes differentiation. Regulates epithelial bladder cells speed and direction of movement during cell migration and tumor cell invasion. Inhibits Akt pro-survival-induced kinase activity. Mediates Rho protein-induced transcriptional activation via the c-fos serum response factor (SRF). Involved in the negative regulation of ciliogenesis. PKC-related serine/threonine-protein kinase and Rho/Rac effector protein that participates in specific signal transduction responses in the cell.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.13
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MASNPERGEILLTELQGDSRSLPFSENVSAVQKLDFSDTMVQQKLDDIKDRIKREIRKEL
KIKEGAENLRKVTTDKKSLAYVDNILKKSNKKLEELHHKLQELNAHIVVSDPEDITDCPR TPDTPNNDPRCSTSNNRLKALQKQLDIELKVKQGAENMIQMYSNGSSKDRKLHGTAQQLL QDSKTKIEVIRMQILQAVQTNELAFDNAKPVISPLELRMEELRHHFRIEFAVAEGAKNVM KLLGSGKVTDRKALSEAQARFNESSQKLDLLKYSLEQRLNEVPKNHPKSRIIIEELSLVA ASPTLSPRQSMISTQNQYSTLSKPAALTGTLEVRLMGCQDILENVPGRSKATSVALPGWS PSETRSSFMSRTSKSKSGSSRNLLKTDDLSNDVCAVLKLDNTVVGQTSWKPISNQSWDQK FTLELDRSRELEISVYWRDWRSLCAVKFLRLEDFLDNQRHGMCLYLEPQGTLFAEVTFFN PVIERRPKLQRQKKIFSKQQGKTFLRAPQMNINIATWGRLVRRAIPTVNHSGTFSPQAPV PTTVPVVDVRIPQLAPPASDSTVTKLDFDLEPEPPPAPPRASSLGEIDESSELRVLDIPG QDSETVFDIQNDRNSILPKSQSEYKPDTPQSGLEYSGIQELEDRRSQQRFQFNLQDFRCC AVLGRGHFGKVLLAEYKNTNEMFAIKALKKGDIVARDEVDSLMCEKRIFETVNSVRHPFL VNLFACFQTKEHVCFVMEYAAGGDLMMHIHTDVFSEPRAVFYAACVVLGLQYLHEHKIVY RDLKLDNLLLDTEGFVKIADFGLCKEGMGYGDRTSTFCGTPEFLAPEVLTETSYTRAVDW WGLGVLIYEMLVGESPFPGDDEEEVFDSIVNDEVRYPRFLSTEAISIMRRLLRRNPERRL GASEKDAEDVKKHPFFRLIDWSALMDKKVKPPFIPTIRGREDVSNFDDEFTSEAPILTPP REPRILSEEEQEMFRDFDYIADWC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Phosphonothreonine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of Akt1 in complex with a selective inhibitor | PDB:6CCY | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.18 Å | Mutation | Yes | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
GSLRVTMNEF
150 EYLKLLGKGT160 FGKVILVKEK170 ATGRYYAMKI180 LKKEVIVAKD190 EVAHTLTESR 200 VLQNSRHPFL210 TALKYSFQTH220 DRLCFVMEYA230 NGGELFFHLS240 RERVFSEDRA 250 RFYGAEIVSA260 LDYLHSEKNV270 VYRDLKLENL280 MLDKDGHIKI290 TDFGLCKEGI 300 KDGATMKFCG311 TPEYLAPEVL321 EDNDYGRAVD331 WWGLGVVMYE341 MMCGRLPFYN 351 QDHEKLFELI361 LMEEIRFPRT371 LGPEAKSLLS381 GLLKKDPKQR391 LGGGPSDAKE 401 IMQHRFFAGI411 VWQHVYEKKL421 SPPFKPQVTS431 EVDTRYFDEE441 FTAQMITITE 468 QEMFRDFDYI478 ADWEG
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: L-serine-O-phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human Protein Kinase N2 (PKN2, PRKCL2) in complex with ATPgammaS | PDB:4CRS | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.75 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
SMSQQRFQFN
653 LQDFRCCAVL663 LRGHFGKVLL673 AEYKNTNEMF683 AIKALKKGDI693 VARDEVDSLM 703 CEKRIFETVN713 SVRHPFLVNL723 FACFQTKEHV733 CFVMEYAAGG743 DLMMHIHTDV 753 FEPRAVFYAA764 CVVLGLQYLH774 EHKIVYRDLK784 LDNLLLDTEG794 FVKIADFGLC 804 KEGMGYGDRT814 SFCGTPEFLA825 PEVLTETSYT835 RAVDWWGLGV845 LIYEMLVGES 855 PFPGDDEEEV865 FDSIVNDEVR875 YPRFLSTEAI885 SIMRRLLRRN895 PERRLGASEK 905 DAEDVKKHPF915 FRLIDWSALM925 DKKVKPPFIP935 TIRGREDVSN945 FDDEFTSEAP 955 ILPPREPREM973 FRDFDYIADW983 C
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |
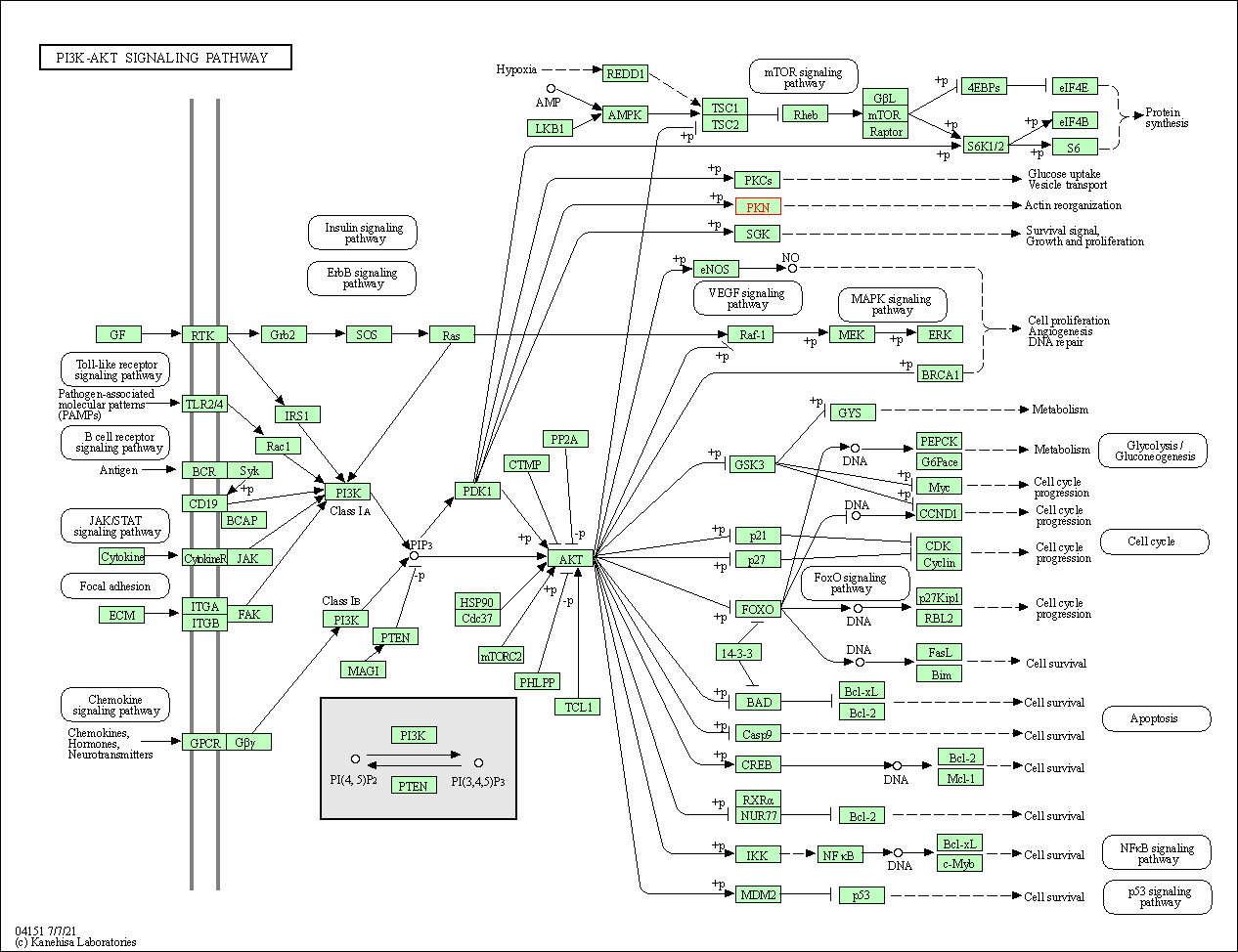
|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |
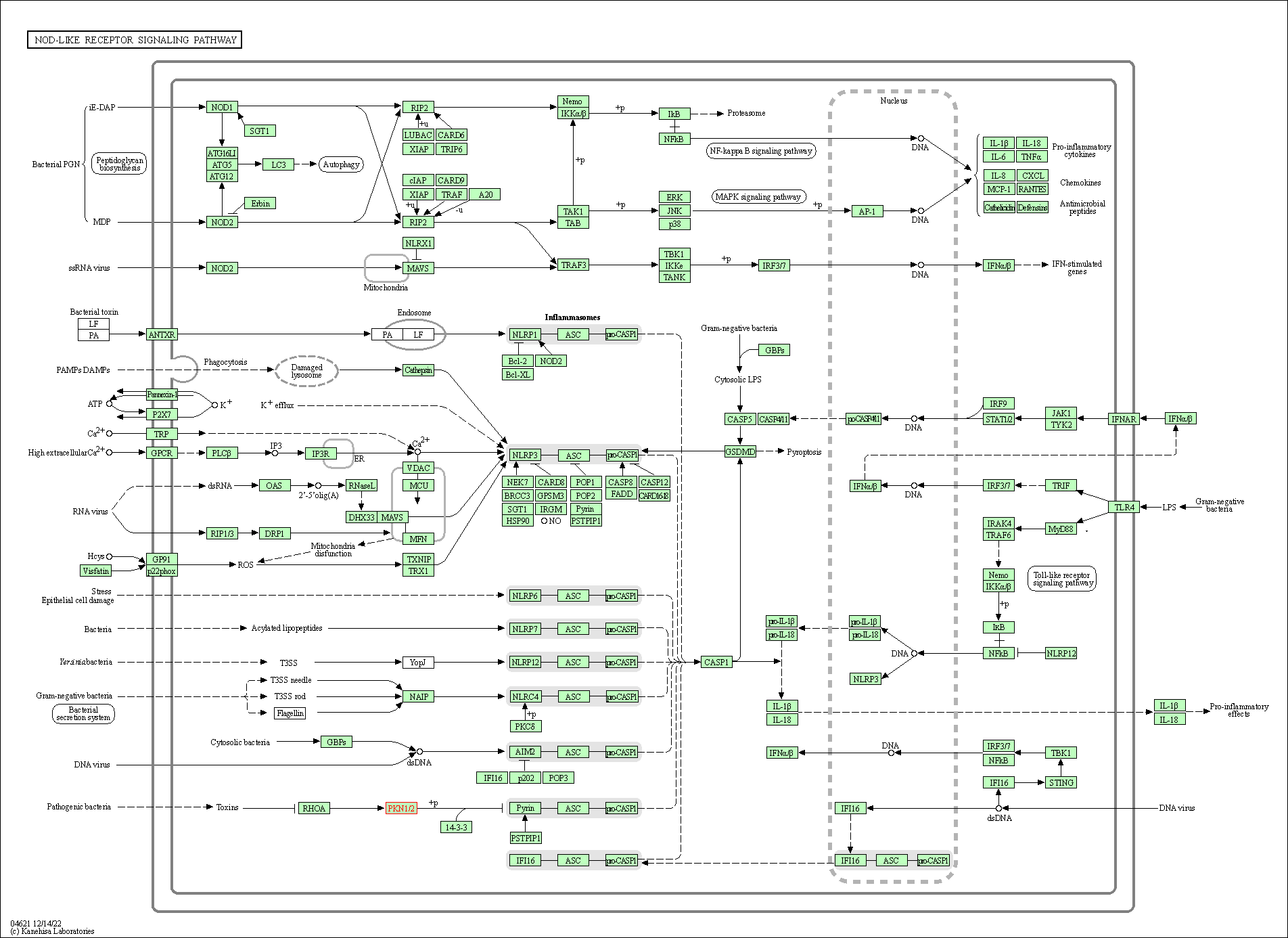
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 2 | Degree centrality | 2.15E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.44E-06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.13E-01 | Radiality | 1.37E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.55E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.07E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Substituted 2H-isoquinolin-1-ones as potent Rho-kinase inhibitors: part 3, aryl substituted pyrrolidines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jun 15;20(12):3746-9. | |||||
| REF 2 | Discovery of chiral dihydropyridopyrimidinones as potent, selective and orally bioavailable inhibitors of AKT. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Jun 1;28(10):1887-1891. | |||||
| REF 3 | Structure of Pkn2 | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

