Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T93266
(Former ID: TTDI03255)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Hyperpolarization cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 (HCN1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1; Brain cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1; BCNG1; BCNG-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HCN1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Contributes to the native pacemaker currents in heart (If) and in neurons (Ih). May mediate responses to sour stimuli. Hyperpolarization-activated ion channel exhibiting weak selectivity for potassium over sodium ions.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Voltage-gated ion channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MEGGGKPNSSSNSRDDGNSVFPAKASATGAGPAAAEKRLGTPPGGGGAGAKEHGNSVCFK
VDGGGGGGGGGGGGEEPAGGFEDAEGPRRQYGFMQRQFTSMLQPGVNKFSLRMFGSQKAV EKEQERVKTAGFWIIHPYSDFRFYWDLIMLIMMVGNLVIIPVGITFFTEQTTTPWIIFNV ASDTVFLLDLIMNFRTGTVNEDSSEIILDPKVIKMNYLKSWFVVDFISSIPVDYIFLIVE KGMDSEVYKTARALRIVRFTKILSLLRLLRLSRLIRYIHQWEEIFHMTYDLASAVVRIFN LIGMMLLLCHWDGCLQFLVPLLQDFPPDCWVSLNEMVNDSWGKQYSYALFKAMSHMLCIG YGAQAPVSMSDLWITMLSMIVGATCYAMFVGHATALIQSLDSSRRQYQEKYKQVEQYMSF HKLPADMRQKIHDYYEHRYQGKIFDEENILNELNDPLREEIVNFNCRKLVATMPLFANAD PNFVTAMLSKLRFEVFQPGDYIIREGAVGKKMYFIQHGVAGVITKSSKEMKLTDGSYFGE ICLLTKGRRTASVRADTYCRLYSLSVDNFNEVLEEYPMMRRAFETVAIDRLDRIGKKNSI LLQKFQKDLNTGVFNNQENEILKQIVKHDREMVQAIAPINYPQMTTLNSTSSTTTPTSRM RTQSPPVYTATSLSHSNLHSPSPSTQTPQPSAILSPCSYTTAVCSPPVQSPLAARTFHYA SPTASQLSLMQQQPQQQVQQSQPPQTQPQQPSPQPQTPGSSTPKNEVHKSTQALHNTNLT REVRPLSASQPSLPHEVSTLISRPHPTVGESLASIPQPVTAVPGTGLQAGGRSTVPQRVT LFRQMSSGAIPPNRGVPPAPPPPAAALPRESSSVLNTDPDAEKPRFASNL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: [3H]cAMP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human HCN1 channel in a hyperpolarized conformation | PDB:6UQF | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.04 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
MQRQFTSMLQ
103 PGVNKFSLRM113 FGSQKAVEKE123 QERVKTAGFW133 IIHPYSDFRF143 YWDLIMLIMM 153 VGNLVIIPVG163 ITFFTEQTTT173 PWIIFNVASD183 TVCLLDLIMN193 FRTGTVNEDS 203 SEIILDPKVI213 KMNYLKSWFV223 VDFISSIPVD233 YIFLIVERAL254 RIVRFTKILC 264 LLRLLRLSRL274 IRYIHQWEEI284 FHMTYDLASA294 VVRIFNLIGM304 MLLLCHWDGC 314 LQFLVPLLQD324 FPPDCWVSLN334 EMVNDSWGKQ344 YSYALFKAMS354 HMLCIGYGAQ 364 APVSMSDLWI374 TMLSMIVGAT384 CYAMFVGHAT394 ALIQSLDSSR404 RQYQEKYKQV 414 EQYMSFHKLP424 ADMRQKIHDY434 YEHRYQGKIF444 DEENILNELN454 DPLREEIVNF 464 NCRKLVATMP474 LFANADPNFV484 TAMLSKLRFE494 VFQPGDYIIR504 EGAVGKKMYF 514 IQHGVAGVIT524 KSSKEMKLTD534 GSYFGEICLL544 TKGRRTASVR554 ADTYCRLYSL 564 SVDNFNEVLE574 EYPMMRRAFE584 TVAIDRLDRI594 GKKNSILLQK604 FQKDLNTGVF 614 NNQENEILKQ624 IVKHDREMVQ634 A
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |
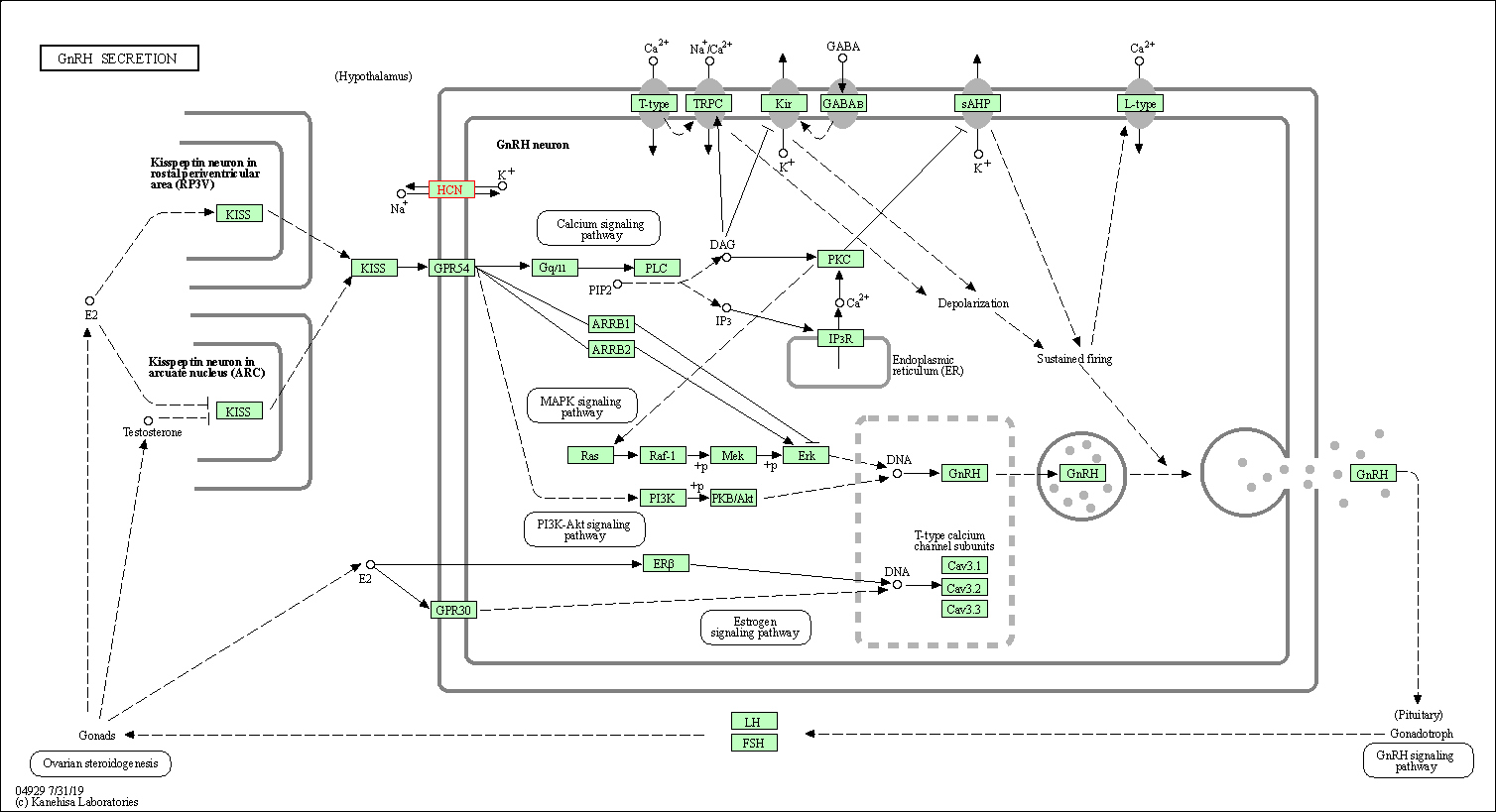
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Novel blockers of hyperpolarization-activated current with isoform selectivity in recombinant cells and native tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(2):602-16. | |||||
| REF 2 | Voltage Sensor Movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell. 2019 Dec 12;179(7):1582-1589.e7. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

