Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T87166
(Former ID: TTDC00141)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Glucokinase (GCK)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Hexokinase type IV; Hexokinase D; HK4; HK IV
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
GCK
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 4 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||||
| 2 | Diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A10] | |||||
| 3 | Acute diabete complication [ICD-11: 5A2Y] | |||||
| 4 | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B80-5B81] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the initial step in utilization of glucose by the beta-cell and liver at physiological glucose concentration. Glucokinase has a high Km for glucose, and so it is effective only when glucose is abundant. The role of GCK is to provide G6P for the synthesis of glycogen. Pancreatic glucokinase plays an important role in modulating insulin secretion. Hepatic glucokinase helps to facilitate the uptake and conversion of glucose by acting asan insulin-sensitive determinant of hepatic glucose usage.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.1.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MLDDRARMEAAKKEKVEQILAEFQLQEEDLKKVMRRMQKEMDRGLRLETHEEASVKMLPT
YVRSTPEGSEVGDFLSLDLGGTNFRVMLVKVGEGEEGQWSVKTKHQMYSIPEDAMTGTAE MLFDYISECISDFLDKHQMKHKKLPLGFTFSFPVRHEDIDKGILLNWTKGFKASGAEGNN VVGLLRDAIKRRGDFEMDVVAMVNDTVATMISCYYEDHQCEVGMIVGTGCNACYMEEMQN VELVEGDEGRMCVNTEWGAFGDSGELDEFLLEYDRLVDESSANPGQQLYEKLIGGKYMGE LVRLVLLRLVDENLLFHGEASEQLRTRGAFETRFVSQVESDTGDRKQIYNILSTLGLRPS TTDCDIVRRACESVSTRAAHMCSAGLAGVINRMRESRSEDVMRITVGVDGSVYKLHPSFK ERFHASVRRLTPSCEITFIESEEGSGRGAALVSAVACKKACMLGQ Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T82S6C | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 16 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AMG 151 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [2] | |
| 2 | AZD1656 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic complication | [3], [4] | |
| 3 | GK1-399 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic complication | [5] | |
| 4 | LY-2599506 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic complication | [6] | |
| 5 | LY-2608204 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [7] | |
| 6 | PF-04937319 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [8] | |
| 7 | PF-04991532 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic complication | [9] | |
| 8 | TTP399 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type 2 diabetes | [10] | |
| 9 | ADV-1002401 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [11] | |
| 10 | AZD5658 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [12] | |
| 11 | BMS-820132 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [13] | |
| 12 | DS-7309 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [14] | |
| 13 | HMS5552 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [15] | |
| 14 | TAK-329 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [16] | |
| 15 | TTP-547 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [17] | |
| 16 | ZYGK-1 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Diabetic complication | [18] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 3 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AZD6370 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [19] | |
| 2 | TTP-355 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Diabetic complication | [20] | |
| 3 | AZD-6714 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [21] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 4 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 8 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AMG 151 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 2 | GK1-399 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 3 | LY-2599506 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 4 | ADV-1002401 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 5 | BMS-820132 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 6 | DS-7309 | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 7 | TAK-329 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 8 | Beta-D-Glucose | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| Activator | [+] 14 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AZD1656 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | LY-2608204 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 3 | PF-04991532 | Drug Info | [26], [27] | |||
| 4 | TTP399 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 5 | AZD5658 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 6 | HMS5552 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 7 | TTP-547 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 8 | ZYGK-1 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 9 | AZD6370 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 10 | TTP-355 | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 11 | GKA-23 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 12 | GKA1 | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 13 | PSN-101 | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 14 | SKL-19014 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 2 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PF-04937319 | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 2 | Piragliatin | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| Stimulator | [+] 1 Stimulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | AZD-6714 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: PF-04937319 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Glucokinase in complex with activator and glucose | PDB:3S41 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.18 Å | Mutation | No | [40] |
| PDB Sequence |
ENLYFQGMKK
13 EKVEQILAEF23 QLQEEDLKKV33 MRRMQKEMDR43 GLRLETHEEA53 SVKMLPTYVR 63 STPEGSEVGD73 FLSLDLGGTN83 FRVMLVKVGS100 VKTKHQMYSI110 PEDAMTGTAE 120 MLFDYISECI130 SDFLDKHQMK140 HKKLPLGFTF150 SFPVRHEDID160 KGILLNWTKG 170 FKASGAEGNN180 VVGLLRDAIK190 RRGDFEMDVV200 AMVNDTVATM210 ISCYYEDHQC 220 EVGMIVGTGC230 NACYMEEMQN240 VELVEGDEGR250 MCVNTEWGAF260 GDSGELDEFL 270 LEYDRLVDES280 SANPGQQLYE290 KLIGGKYMGE300 LVRLVLLRLV310 DENLLFHGEA 320 SEQLRTRGAF330 ETRFVSQVES340 DTGDRKQIYN350 ILSTLGLRPS360 TTDCDIVRRA 370 CESVSTRAAH380 MCSAGLAGVI390 NRMRESRSED400 VMRITVGVDG410 SVYKLHPSFK 420 ERFHASVRRL430 TPSCEITFIE440 SEEGSGRGAA450 LVSAVACK
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: PF-04991532 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Glucokinase in complex with glucose and activator | PDB:3VF6 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.86 Å | Mutation | No | [41] |
| PDB Sequence |
HHENLYFQGM
11 KKEKVEQILA21 EFQLQEEDLK31 KVMRRMQKEM41 DRGLRLETHE51 EASVKMLPTY 61 VRSTPEGSEV71 GDFLSLDLGG81 TNFRVMLVKV91 GESVKTKHQM107 YSIPEDAMTG 117 TAEMLFDYIS127 ECISDFLDKH137 QMKHKKLPLG147 FTFSFPVRHE157 DIDKGILLNW 167 TKGFKASGAE177 GNNVVGLLRD187 AIKRRGDFEM197 DVVAMVNDTV207 ATMISCYYED 217 HQCEVGMIVG227 TGCNACYMEE237 MQNVELVEGD247 EGRMCVNTEW257 GAFGDSGELD 267 EFLLEYDRLV277 DESSANPGQQ287 LYEKLIGGKY297 MGELVRLVLL307 RLVDENLLFH 317 GEASEQLRTR327 GAFETRFVSQ337 VESDTGDRKQ347 IYNILSTLGL357 RPSTTDCDIV 367 RRACESVSTR377 AAHMCSAGLA387 GVINRMRESR397 SEDVMRITVG407 VDGSVYKLHP 417 SFKERFHASV427 RRLTPSCEIT437 FIESEEGSGR447 GAALVSAVAC457 K |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
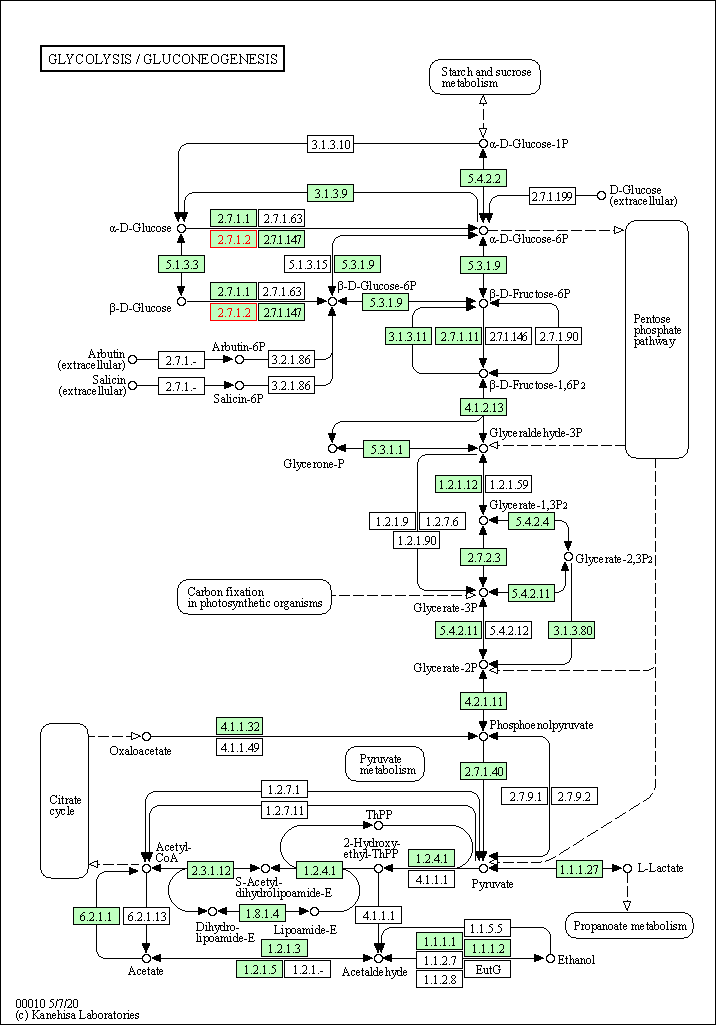
| Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis | hsa00010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
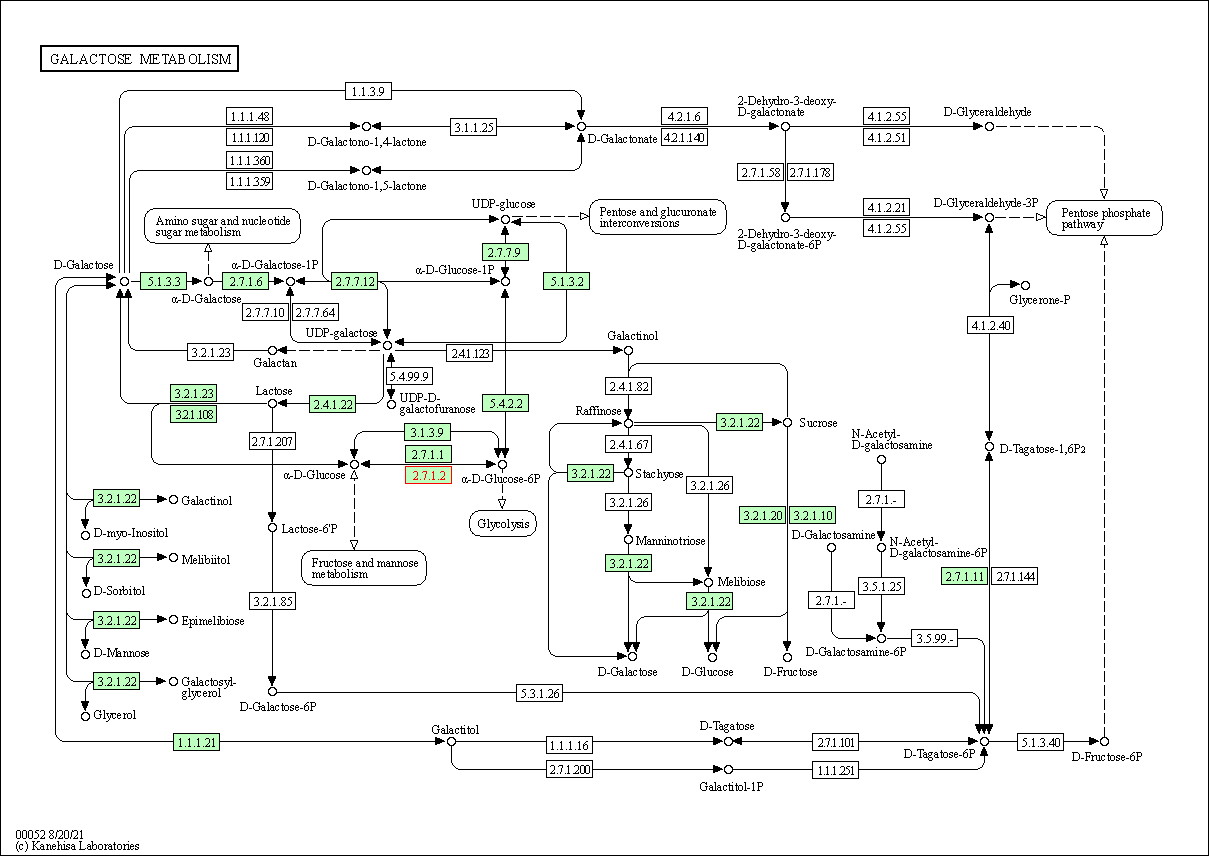
| Galactose metabolism | hsa00052 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
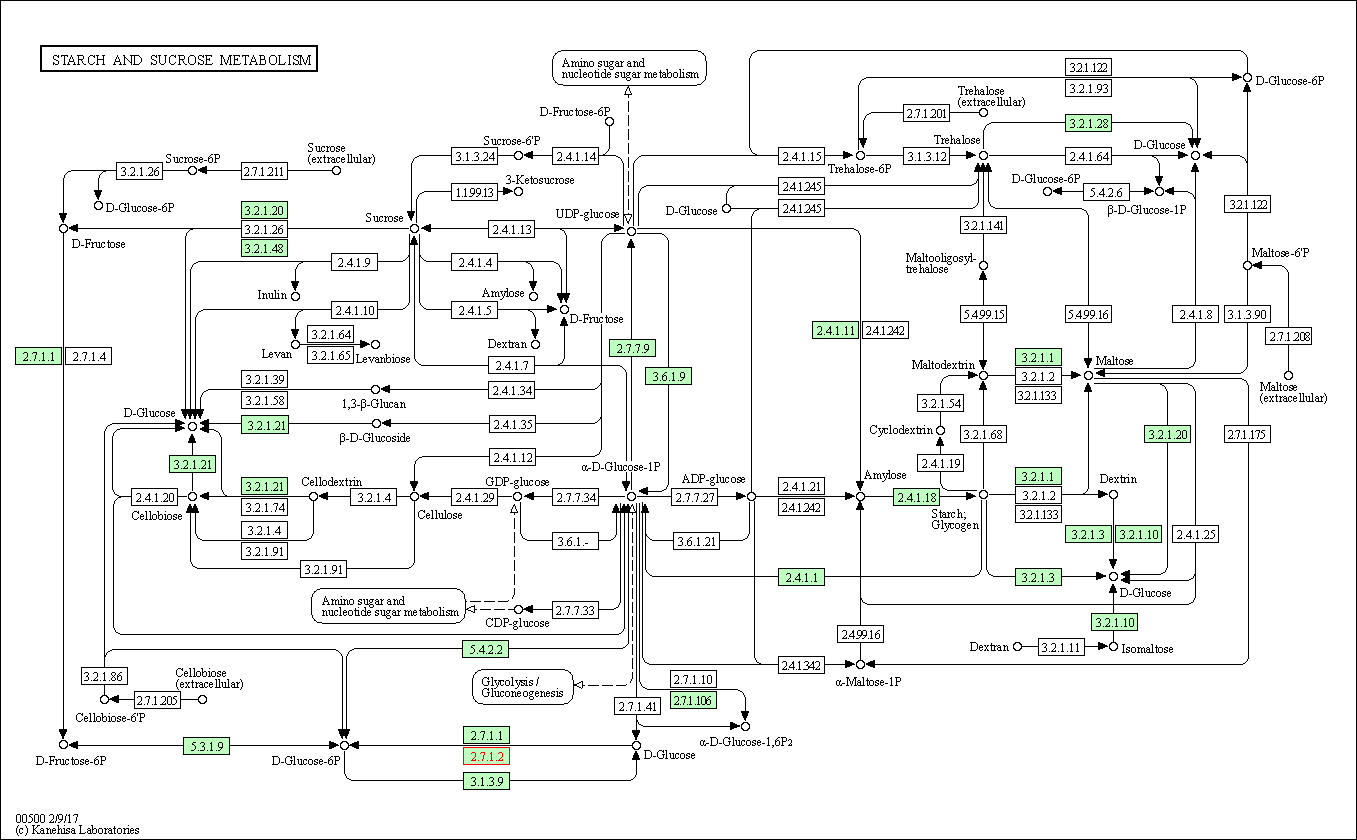
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | hsa00500 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
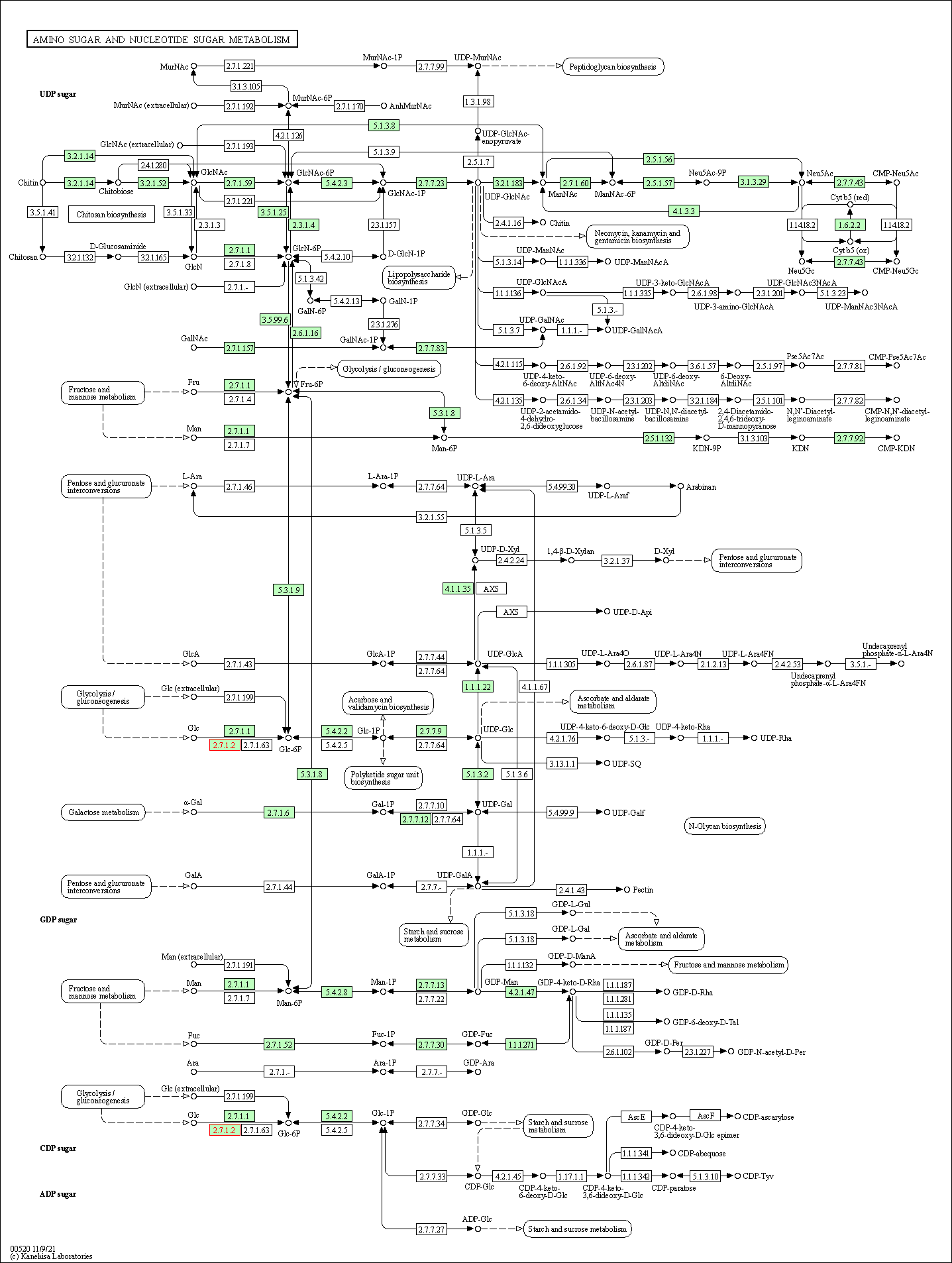
| Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | hsa00520 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neomycin, kanamycin and gentamicin biosynthesis | hsa00524 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin secretion | hsa04911 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 8 | Degree centrality | 8.59E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 6.57E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.11E-01 | Radiality | 1.37E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 7.14E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.39E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.33E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2009). | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01464437) AMG 151 Amgen Protocol Number 20100761. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7701). | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01152385) Japan Dose Regimen Study of AZD1656 in Japanese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02405260) Add Glucokinase Activator to Target A1c. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01024244) A Study of LY2599506 in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01408095) A Study in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01517373) Study To Understand Efficacy And Safety Of Investigational Agent (PF-04937319) Compared To Approved Agent (Glimepiride) In Patients With Diabetes On Metformin. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01338870) Study of Safety and Efficacy of PF-04991532 in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02405260) Add Glucokinase Activator to Target A1c (AGATA). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800031821) | |||||
| REF 12 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of AstraZeneca (2011). | |||||
| REF 13 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01290575) Multiple Ascending Dose Study of BMS-820132 in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 14 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01956305) Randomized, Placebo-controlled, 2 Period, Single-blind, Sequential, Multiple Ascending Dose Study. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 15 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 16 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01311076) TAK-329 Glucose Clamp Study. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 17 | New Therapeutic Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes: Small Molecule Approaches. Rob M. Jones, David E. Thurston, David Rotella, Salvatore Guccione, Ana Martinez. Page(92). | |||||
| REF 18 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01472809) A Clinical Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Oral ZYGK1 in Healthy Volunteers. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 19 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800022135) | |||||
| REF 20 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025266) | |||||
| REF 21 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00886366) Single Ascending Dose Study With Healthy Male Volunteers and Type II Diabetic Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 22 | This week in therapeutics Endocrine disease. SciBX 2(37); doi:10.1038/scibx.2009.1408. Sept. 24, 2009 | |||||
| REF 23 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of vTv Therapeutics, NCT02405260. | |||||
| REF 24 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Eli Lilly. | |||||
| REF 25 | Two dose-ranging studies with PF-04937319, a systemic partial activator of glucokinase, as add-on therapy to metformin in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Aug;17(8):751-9. | |||||
| REF 26 | The hepatoselective glucokinase activator PF-04991532 ameliorates hyperglycemia without causing hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2014 May 23;9(5):e97139. | |||||
| REF 27 | Comparison of the circulating metabolite profile of PF-04991532, a hepatoselective glucokinase activator, across preclinical species and humans: potential implications in metabolites in safety testing assessment. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Feb;43(2):190-8. | |||||
| REF 28 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of vTv Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 29 | The Hepatoselective Glucokinase Activator PF-04991532 Ameliorates Hyperglycemia without Causing Hepatic Steatosis in Diabetic Rats. PLoS One. 2014; 9(5): e97139. | |||||
| REF 30 | Utilization of the Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rat Model for Investigating Hypoglycemia-related Toxicities. Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Aug;43(6):825-37. | |||||
| REF 31 | Glucokinase alternative. SciBX 6(45); doi:10.1038/scibx.2013.1279. Nov. 21 2013 | |||||
| REF 32 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Takeda. | |||||
| REF 33 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 2798). | |||||
| REF 34 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025266) | |||||
| REF 35 | Glucokinase (GCK). SciBX 2(37); doi:10.1038/scibx.2009.1408. Sep. 24 2009 | |||||
| REF 36 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 37 | Stimulation of hepatocyte glucose metabolism by novel small molecule glucokinase activators. Diabetes. 2004 Mar;53(3):535-41. | |||||
| REF 38 | Piragliatin (RO4389620), a novel glucokinase activator, lowers plasma glucose both in the postabsorptive state and after a glucose challenge in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a mechanistic study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2010 Nov;95(11):5028-36. | |||||
| REF 39 | CenterWatch. Drugs in Clinical Trials Database. CenterWatch. 2008. | |||||
| REF 40 | Designing glucokinase activators with reduced hypoglycemia risk: discovery of N,N-dimethyl-5-(2-methyl-6-((5-methylpyrazin-2-yl)-carbamoyl)benzofuran-4-yloxy)pyrimidine-2-carboxamide as a clinical candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. doi:10.1039/C1MD00116G. | |||||
| REF 41 | Insights into mechanism of glucokinase activation: observation of multiple distinct protein conformations. J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 20;287(17):13598-610. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

