Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T80526
(Former ID: TTDI03086)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Casein kinase II alpha prime (CSNK2A2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Casein kinase II subunit alpha'; CK2A2; CK II alpha'
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CSNK2A2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Regulates numerous cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcription, as well as viral infection. May act as a regulatory node which integrates and coordinates numerous signals leading to an appropriate cellular response. During mitosis, functions as a component of the p53/TP53-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) that maintains cyclin-B-CDK1 activity and G2 arrest in response to spindle damage. Also required for p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis, phosphorylating 'Ser-392' of p53/TP53 following UV irradiation. Can also negatively regulate apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspases CASP9 and CASP2 and the apoptotic regulator NOL3. Phosphorylation protects CASP9 from cleavage and activation by CASP8, and inhibits the dimerization of CASP2 and activation of CASP8. Regulates transcription by direct phosphorylation of RNA polymerases I, II, III and IV. Also phosphorylates and regulates numerous transcription factors including NF-kappa-B, STAT1, CREB1, IRF1, IRF2, ATF1, SRF, MAX, JUN, FOS, MYC and MYB. Phosphorylates Hsp90 and its co-chaperones FKBP4 and CDC37, which is essential for chaperone function. Regulates Wnt signaling by phosphorylating CTNNB1 and the transcription factor LEF1. Acts as an ectokinase that phosphorylates several extracellular proteins. During viral infection, phosphorylates various proteins involved in the viral life cycles of EBV, HSV, HBV, HCV, HIV, CMV and HPV. Catalytic subunit of a constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase complex that phosphorylates a large number of substrates containing acidic residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated serine or threonine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MPGPAAGSRARVYAEVNSLRSREYWDYEAHVPSWGNQDDYQLVRKLGRGKYSEVFEAINI
TNNERVVVKILKPVKKKKIKREVKILENLRGGTNIIKLIDTVKDPVSKTPALVFEYINNT DFKQLYQILTDFDIRFYMYELLKALDYCHSKGIMHRDVKPHNVMIDHQQKKLRLIDWGLA EFYHPAQEYNVRVASRYFKGPELLVDYQMYDYSLDMWSLGCMLASMIFRREPFFHGQDNY DQLVRIAKVLGTEELYGYLKKYHIDLDPHFNDILGQHSRKRWENFIHSENRHLVSPEALD LLDKLLRYDHQQRLTAKEAMEHPYFYPVVKEQSQPCADNAVLSSGLTAAR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T12RJE | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Vitamin B3 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of CK2a2 form-2 | PDB:5YF9 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.89 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
AGSRARVYAE
15 VNSLRSREYW25 DYEAHVPSWG35 NQDDYQLVRK45 LGEVFEAINI60 TNNERVVVKI 70 LKPVKKKKIK80 REVKILENLR90 GGTNIIKLID100 TVKDPVSKTP110 ALVFEYINNT 120 DFKQLYQILT130 DFDIRFYMYE140 LLKALDYCHS150 KGIMHRDVKP160 HNVMIDHQQK 170 KLRLIDWGLA180 EFYHPAQEYN190 VRVASRYFKG200 PELLVDYQMY210 DYSLDMWSLG 220 CMLASMIFRR230 EPFFHGQDNY240 DQLVRIAKVL250 GTEELYGYLK260 KYHIDLDPHF 270 NDILGQHSRK280 RWENFIHSEN290 RHLVSPEALD300 LLDKLLRYDH310 QQRLTAKEAM 320 EHPYFYPVV
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: CX-4945 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | STRUCTURE OF PROTEIN KINASE CK2 CATALYTIC SUBUNIT (ISOFORM CK2ALPHA'; CSNK2A2 Gene product) IN COMPLEX WITH the inhibitor CX-4945 (Silmitasertib) | PDB:6HMB | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.04 Å | Mutation | Yes | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
GSRARVYAEV
16 NSLRSREYWD26 YEAHVPSWGN36 QDDYQLVRKL46 GRGKYSEVFE56 AINITNNERV 66 VVKILKPVKK76 KKIKREVKIL86 ENLRGGTNII96 KLIDTVKDPV106 SKTPALVFEY 116 INNTDFKQLY126 QILTDFDIRF136 YMYELLKALD146 YCHSKGIMHR156 DVKPHNVMID 166 HQQKKLRLID176 WGLAEFYHPA186 QEYNVRVASR196 YFKGPELLVD206 YQMYDYSLDM 216 WSLGCMLASM226 IFRREPFFHG236 QDNYDQLVRI246 AKVLGTEELY256 GYLKKYHIDL 266 DPHFNDILGQ276 HSRKRWENFI286 HSENRHLVSP296 EALDLLDKLL306 RYDHQQRLTA 316 KEAMEHPYFY326 PVVKEQSQ
|
|||||
|
|
LEU46
2.402
GLY47
2.473
ARG48
3.579
GLY49
4.886
GLU53
4.985
VAL54
2.693
VAL67
2.817
LYS69
1.896
GLU82
4.641
ILE96
2.388
PHE114
3.116
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
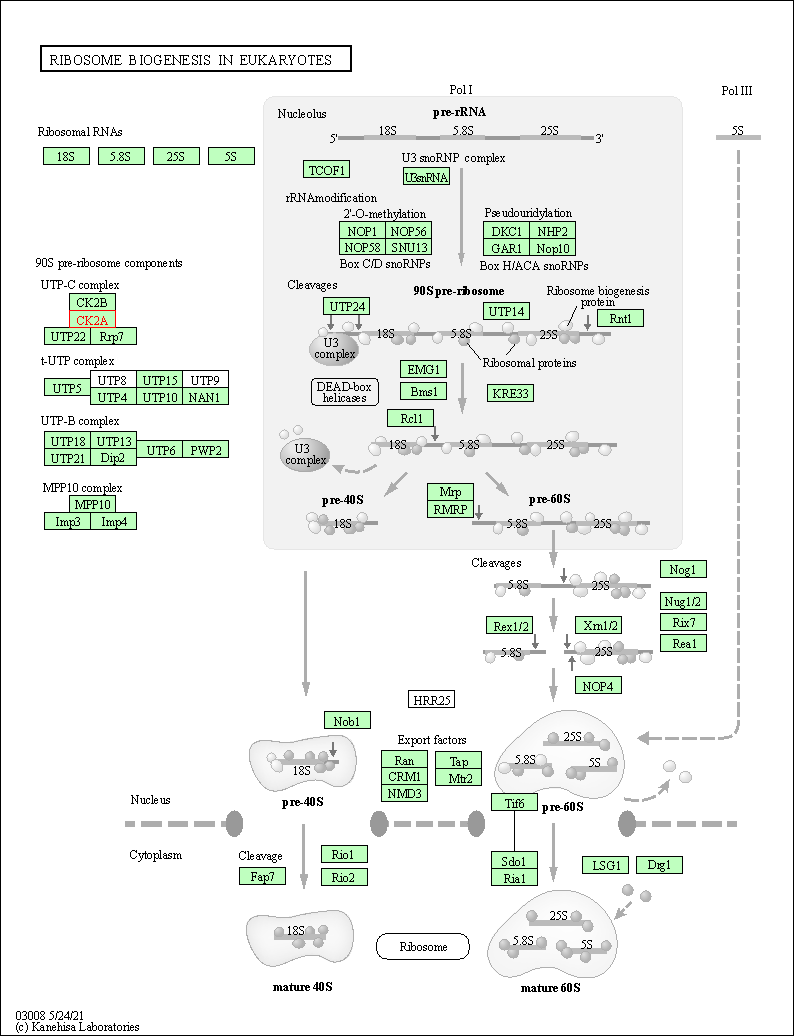
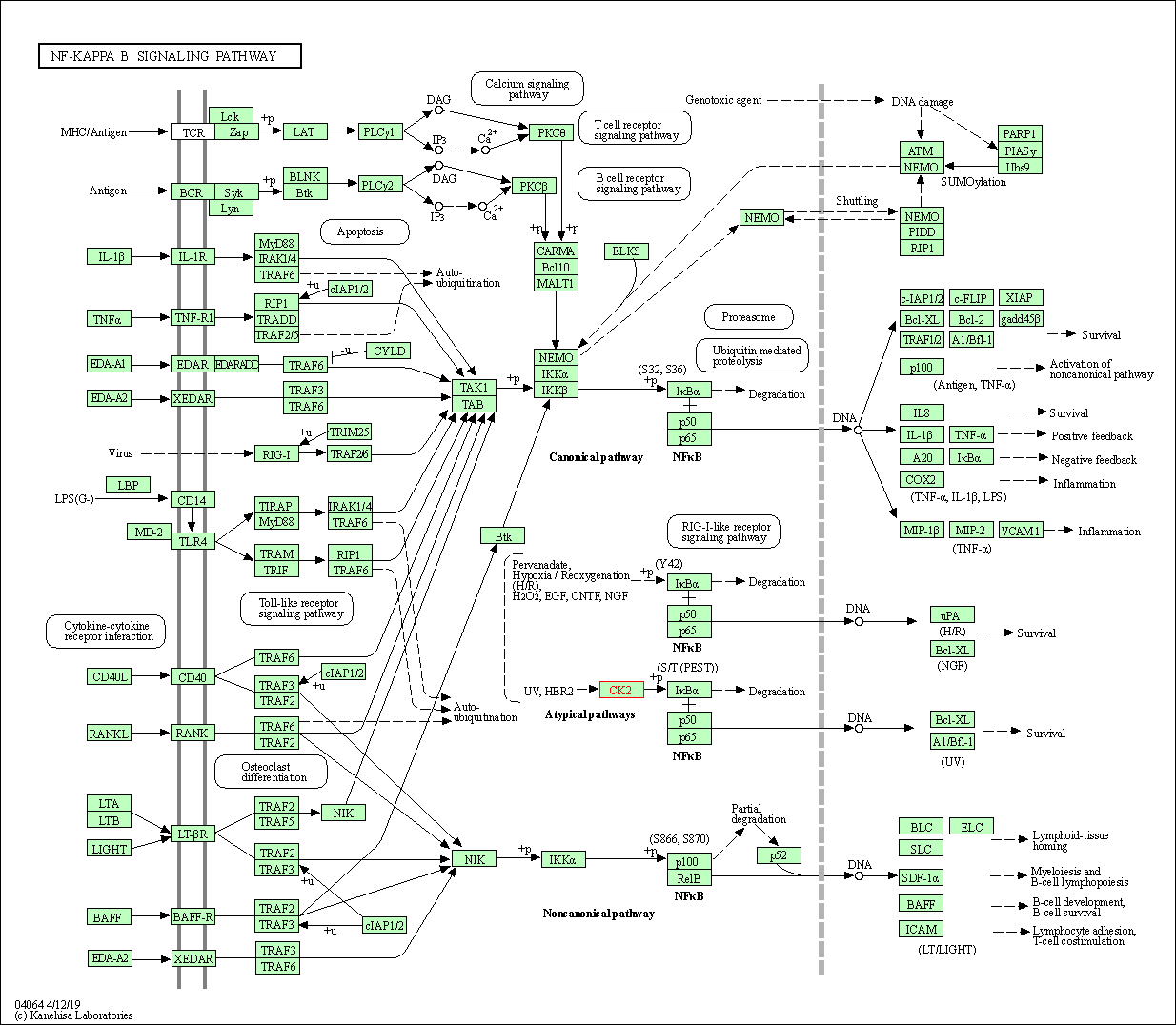
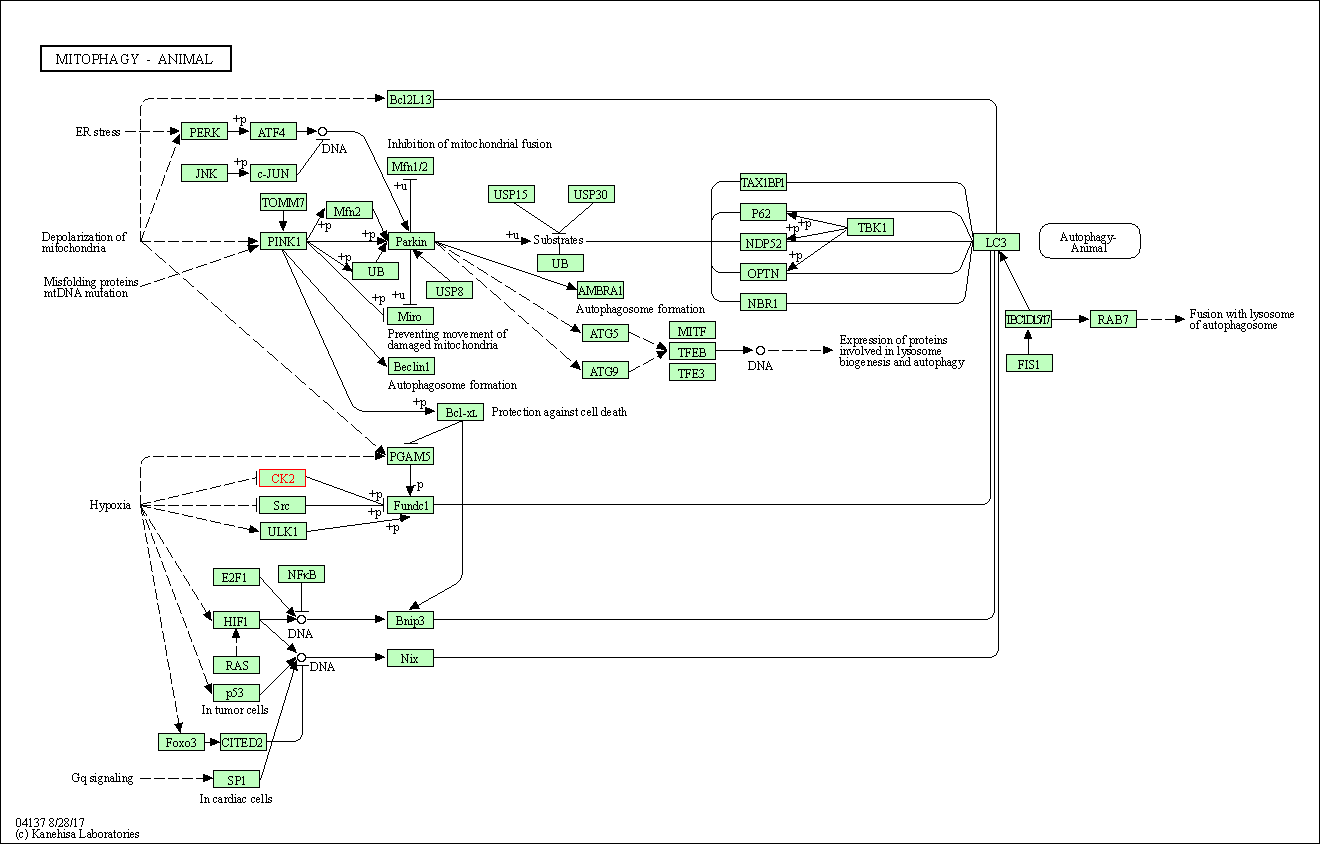
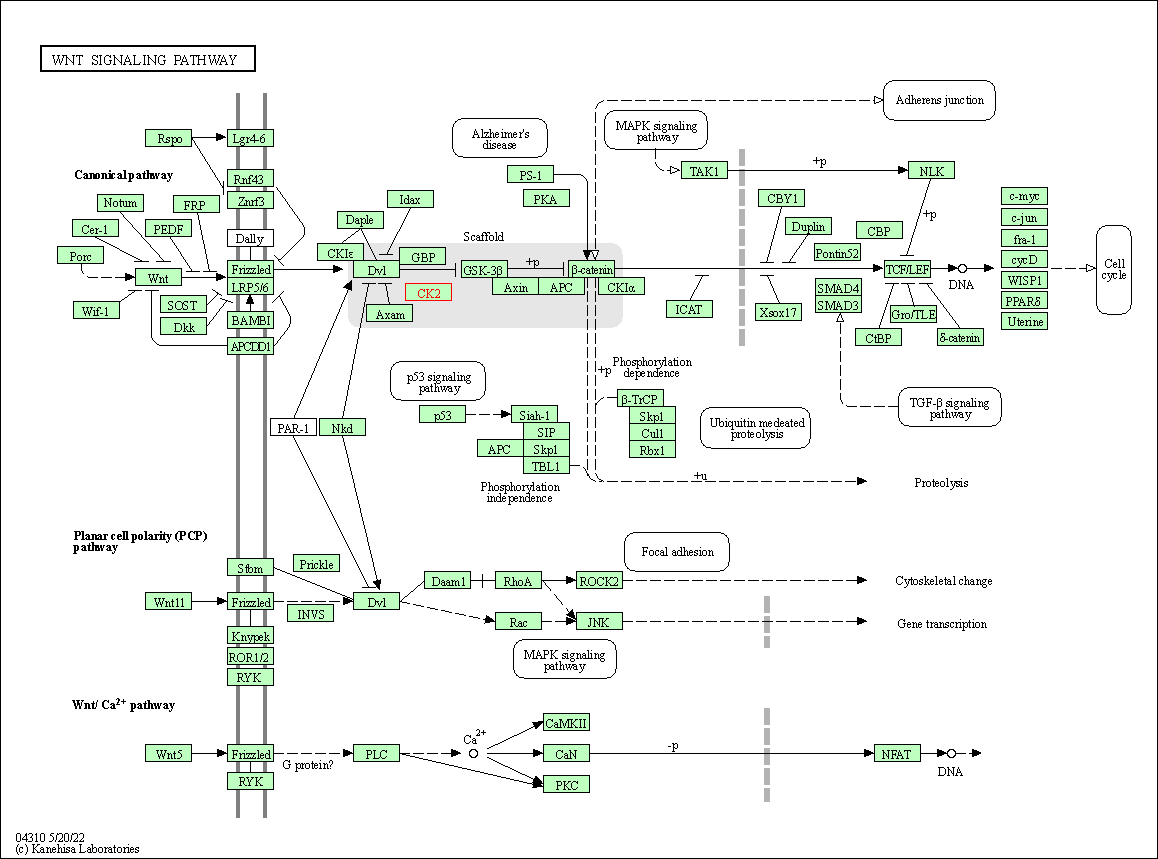
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | hsa03008 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Translation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Mitophagy - animal | hsa04137 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adherens junction | hsa04520 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 9 | Degree centrality | 9.67E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 5.96E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.35E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.50E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.41E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.23E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | CK2alpha and CK2alpha' subunits differ in their sensitivity to 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo- and 4,5,6,7-tetraiodo-1H-benzimidazole derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2012 Jan;47(1):345-50. | |||||
| REF 2 | Substituted pyrrolotriazines as protein kinase inhibitors. US8791257. | |||||
| REF 3 | Imidazotriazinecarbonitriles useful as kinase inhibitors. US8940736. | |||||
| REF 4 | Crystal structures of human CK2Alpha2 in new crystal forms arising from a subtle difference in salt concentration. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2018 May 1;74(Pt 5):288-293. | |||||
| REF 5 | Diacritic Binding of an Indenoindole Inhibitor by CK2Alpha Paralogs Explored by a Reliable Path to Atomic Resolution CK2Alpha' Structures. ACS Omega. 2019 Mar 19;4(3):5471-5478. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

