Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T78692
(Former ID: TTDS00150)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Inward rectifier potassium channel Kir3.4 (KCNJ5)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying, subfamily J, member 5; KCNJ5; KATP-1; KATP channel; Inward rectifier K+ channel Kir3.4; Heart KATP channel; GIRK4; Cardiac inward rectifier; CIR
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
KCNJ5
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Acute myeloid leukaemia [ICD-11: 2A60] | |||||
| 2 | Hodgkin lymphoma [ICD-11: 2B30] | |||||
| Function |
This potassium channel is controlled by G proteins. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by external barium.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Inward rectifier potassium channel
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAGDSRNAMNQDMEIGVTPWDPKKIPKQARDYVPIATDRTRLLAEGKKPRQRYMEKSGKC
NVHHGNVQETYRYLSDLFTTLVDLKWRFNLLVFTMVYTVTWLFFGFIWWLIAYIRGDLDH VGDQEWIPCVENLSGFVSAFLFSIETETTIGYGFRVITEKCPEGIILLLVQAILGSIVNA FMVGCMFVKISQPKKRAETLMFSNNAVISMRDEKLCLMFRVGDLRNSHIVEASIRAKLIK SRQTKEGEFIPLNQTDINVGFDTGDDRLFLVSPLIISHEINQKSPFWEMSQAQLHQEEFE VVVILEGMVEATGMTCQARSSYMDTEVLWGHRFTPVLTLEKGFYEVDYNTFHDTYETNTP SCCAKELAEMKREGRLLQYLPSPPLLGGCAEAGLDAEAEQNEEDEPKGLGGSREARGSV Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Acute myeloid leukaemia | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor (gating inhibitor) | [+] 1 Inhibitor (gating inhibitor) drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Activator | [+] 1 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PIP2 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
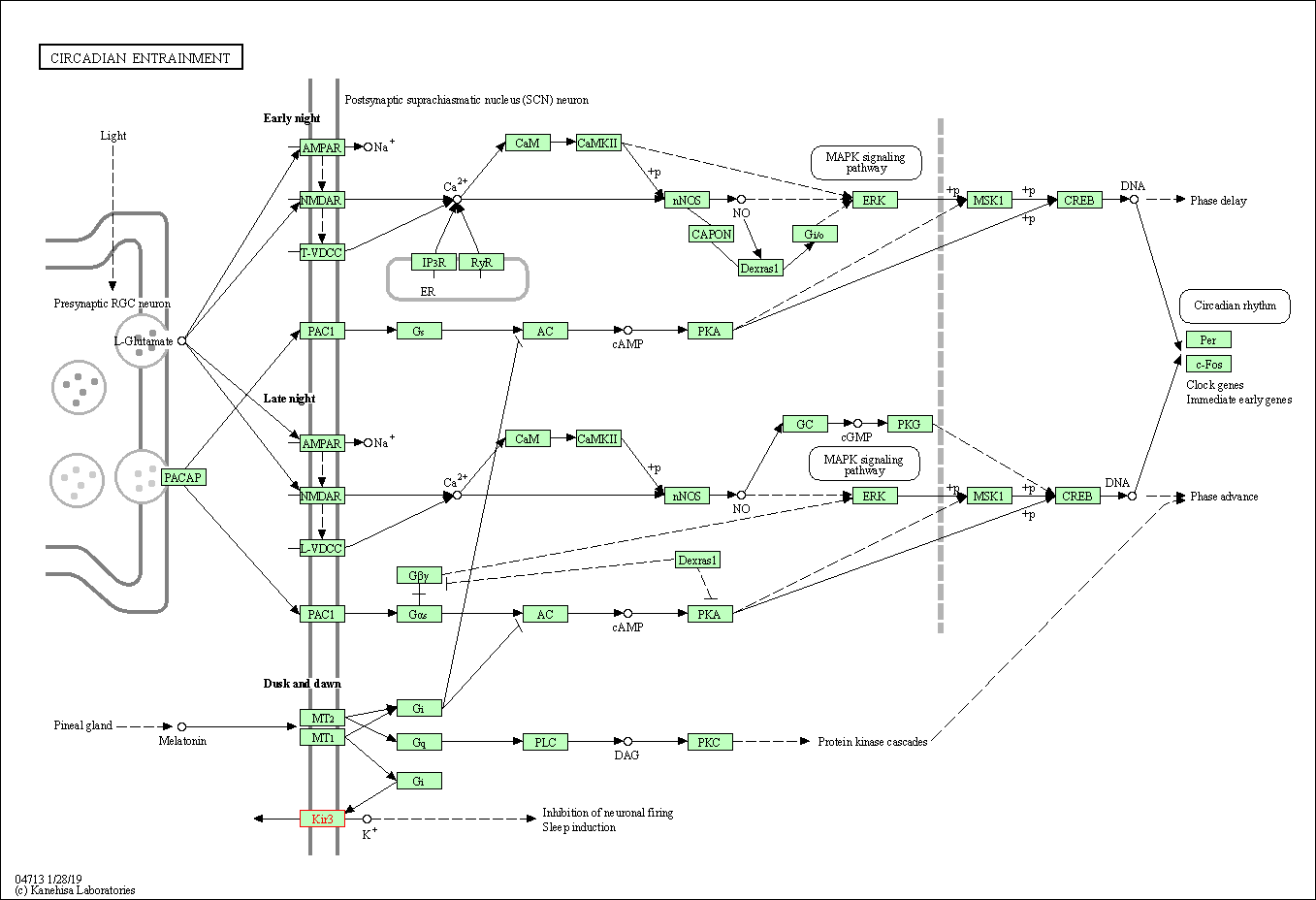
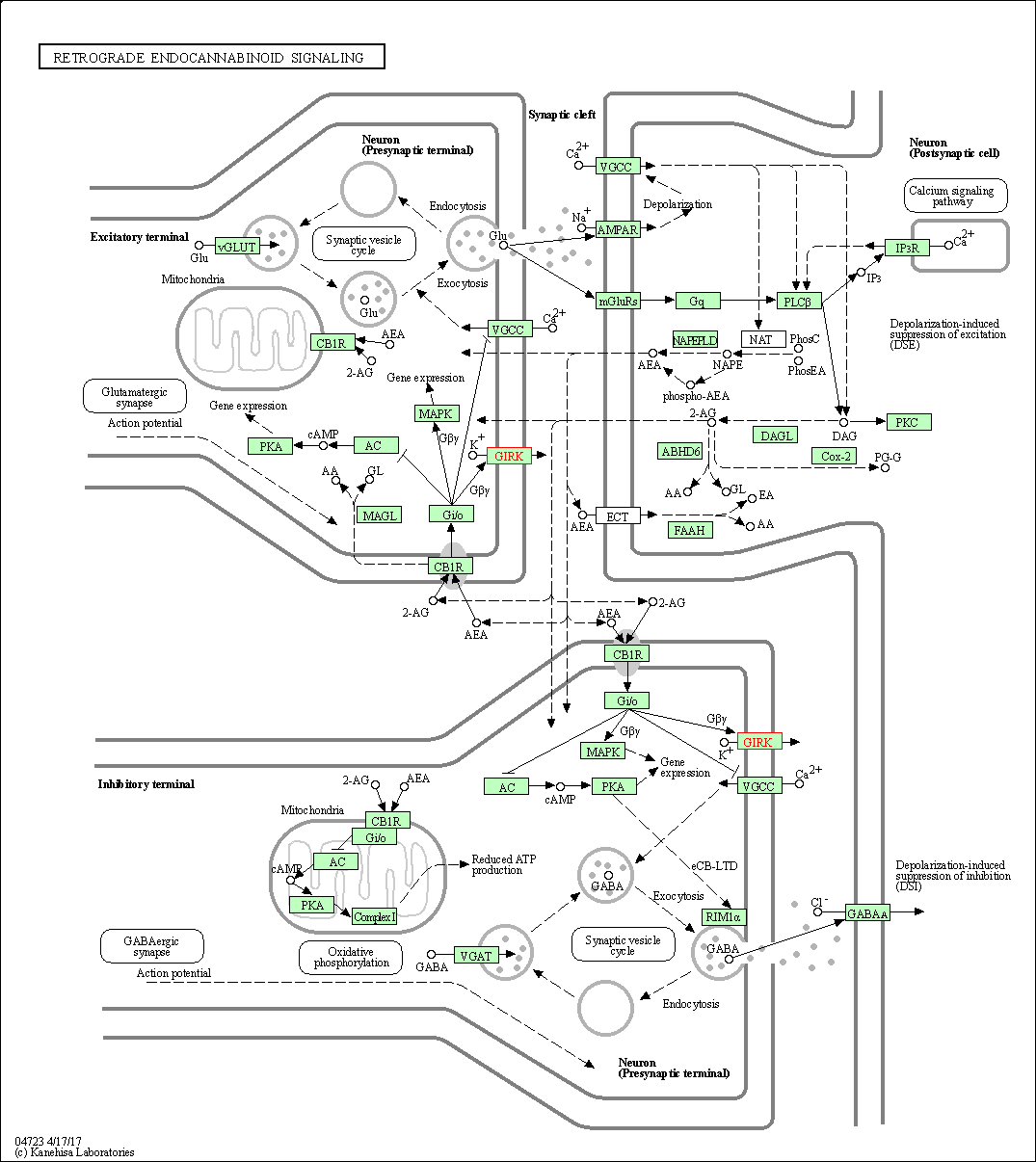
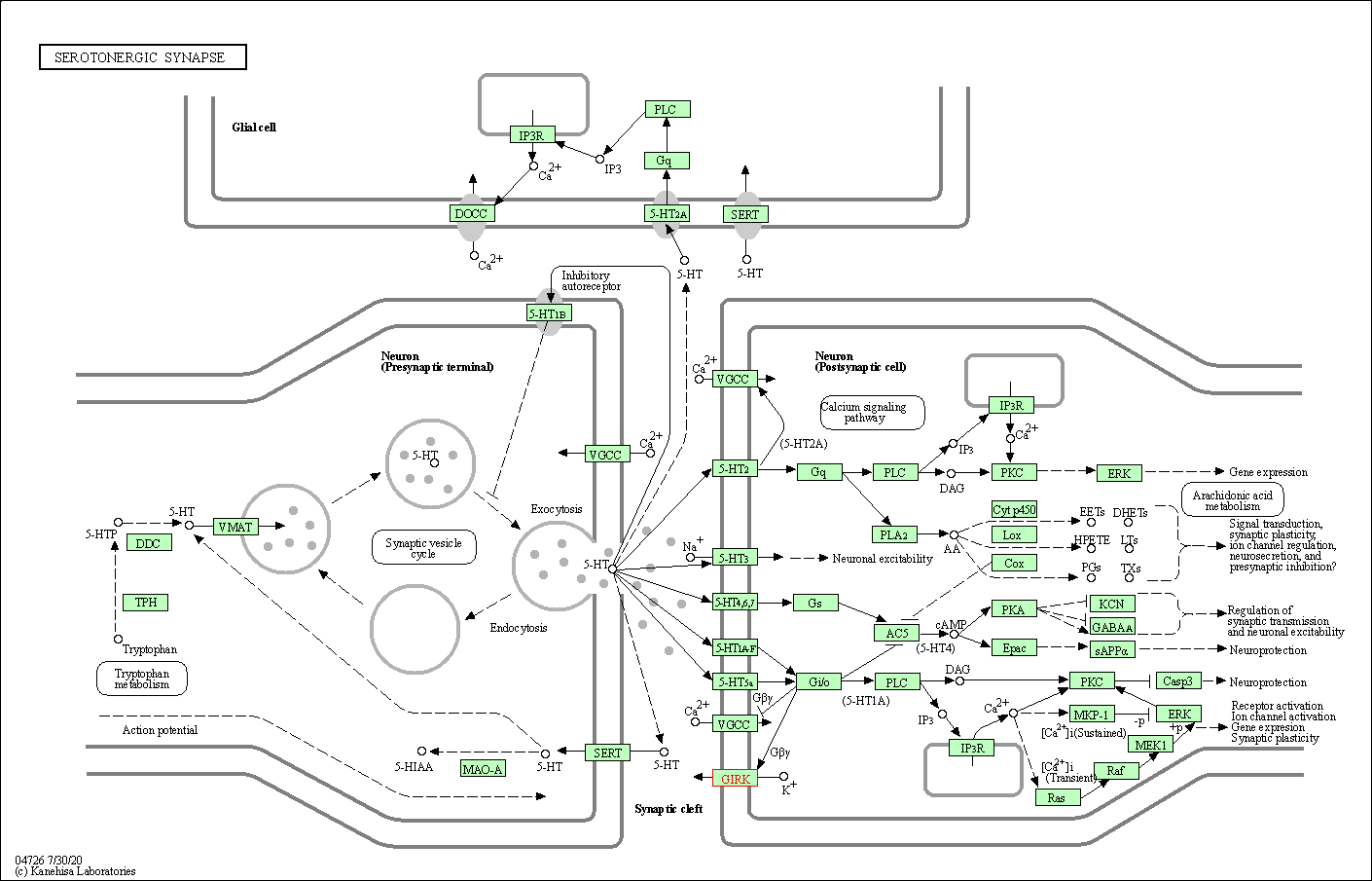
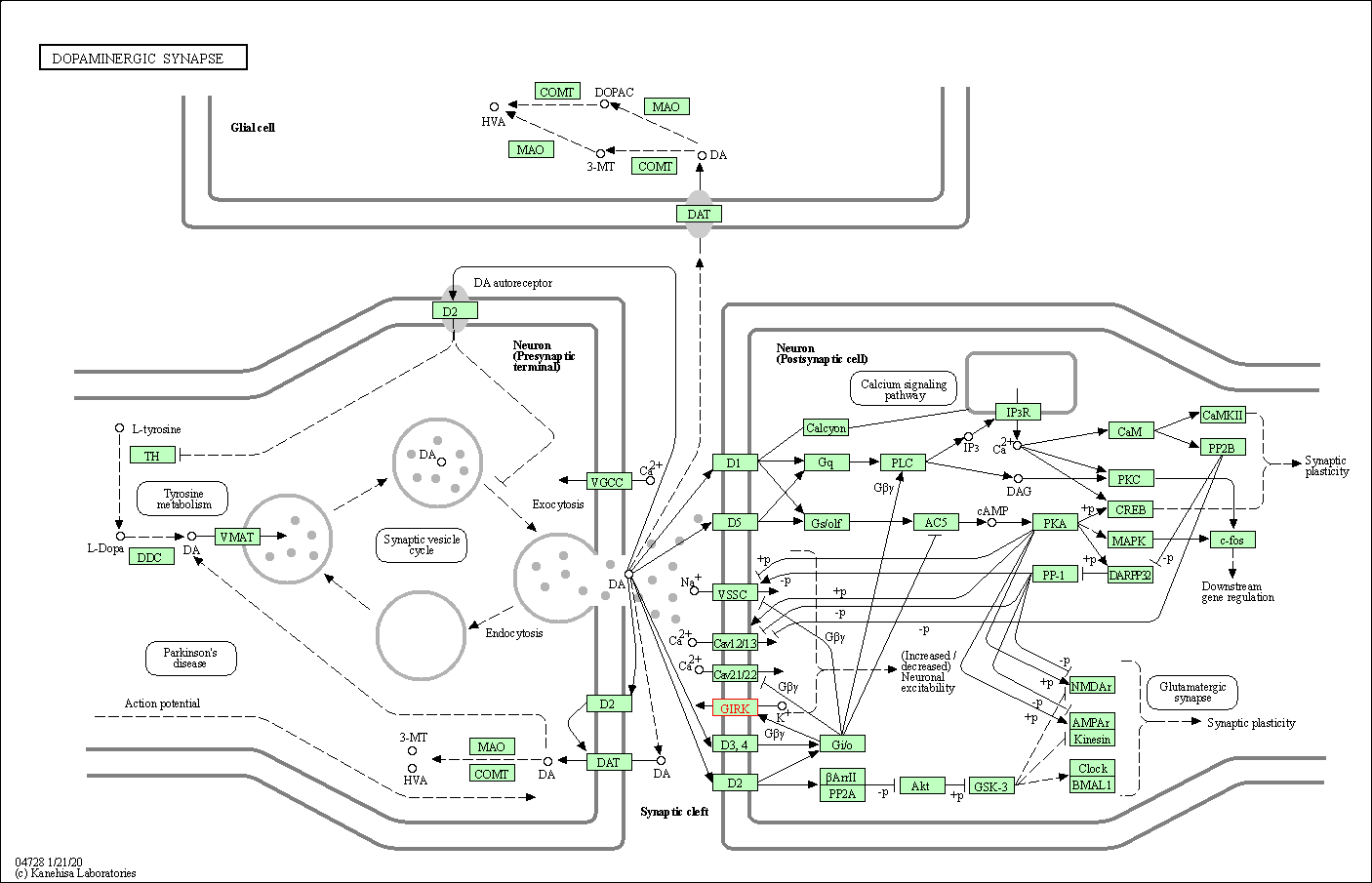
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Serotonergic synapse | hsa04726 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
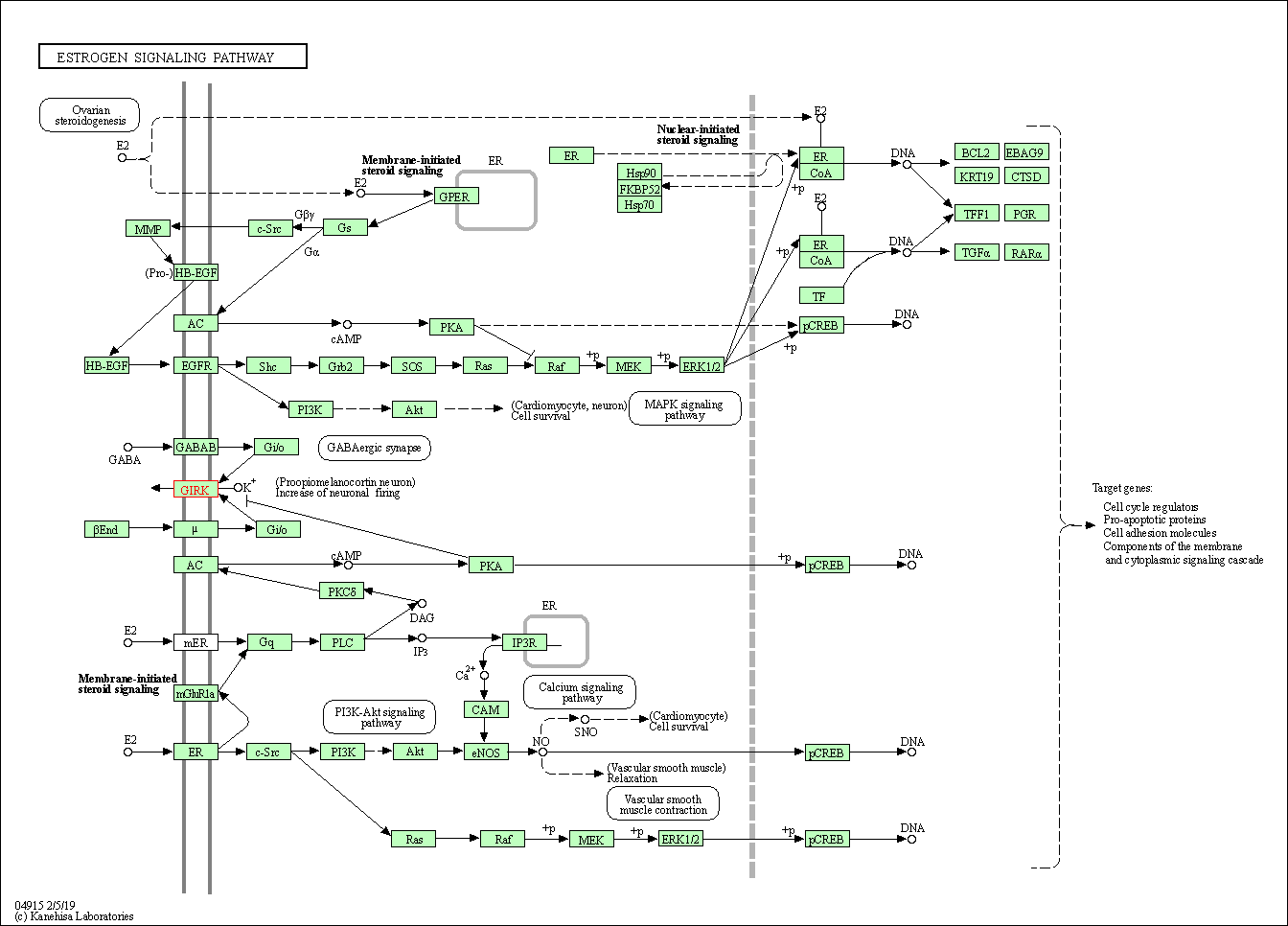
| Estrogen signaling pathway | hsa04915 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
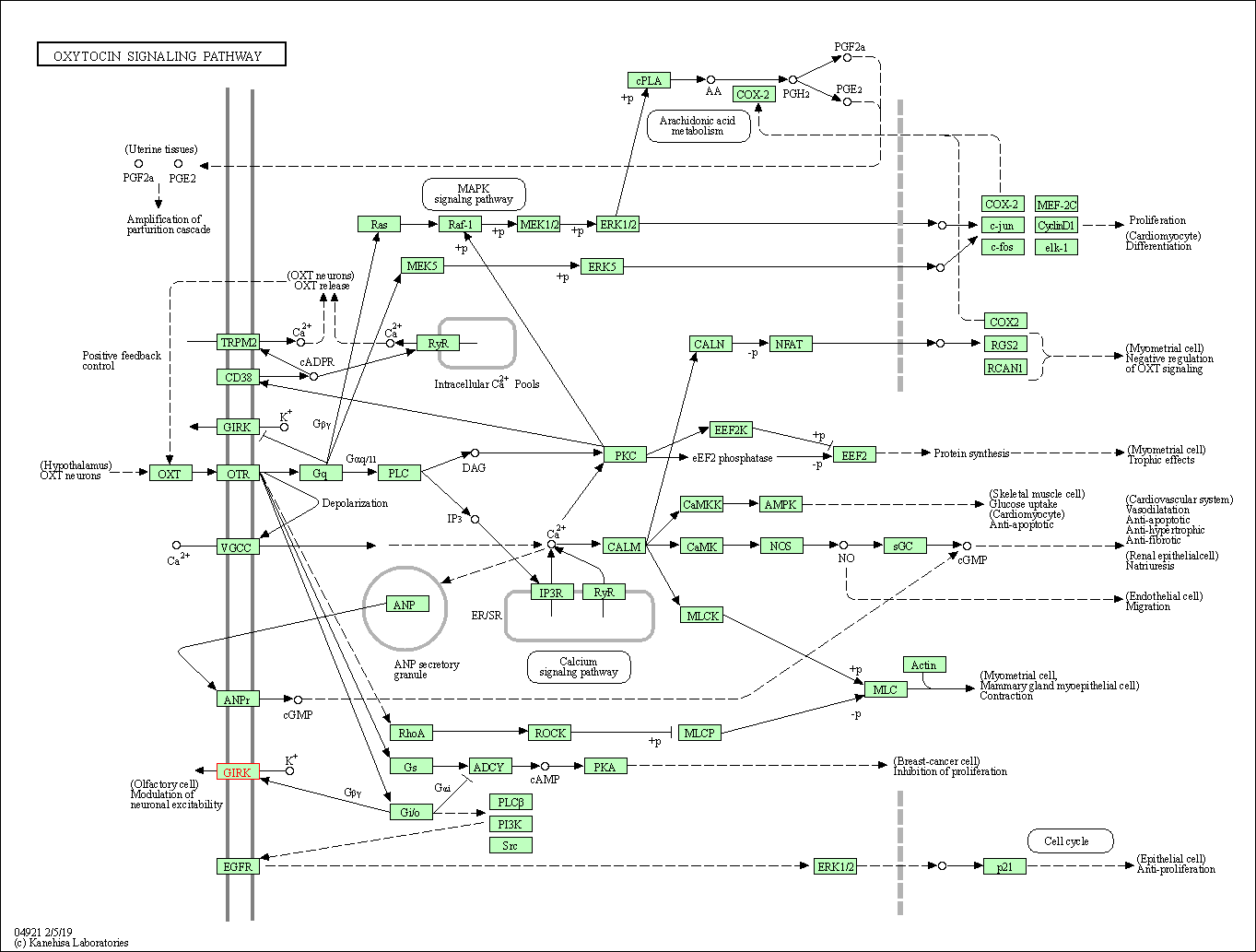
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | hsa04921 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
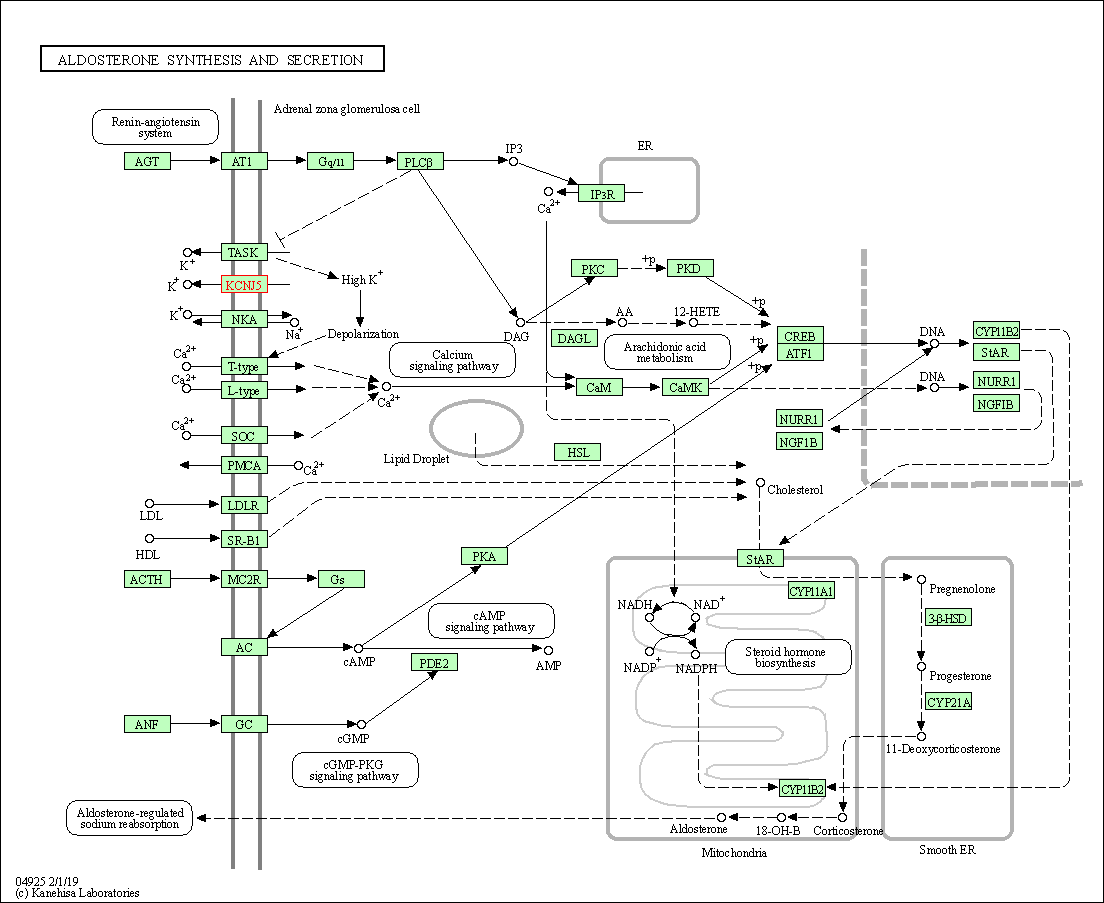
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
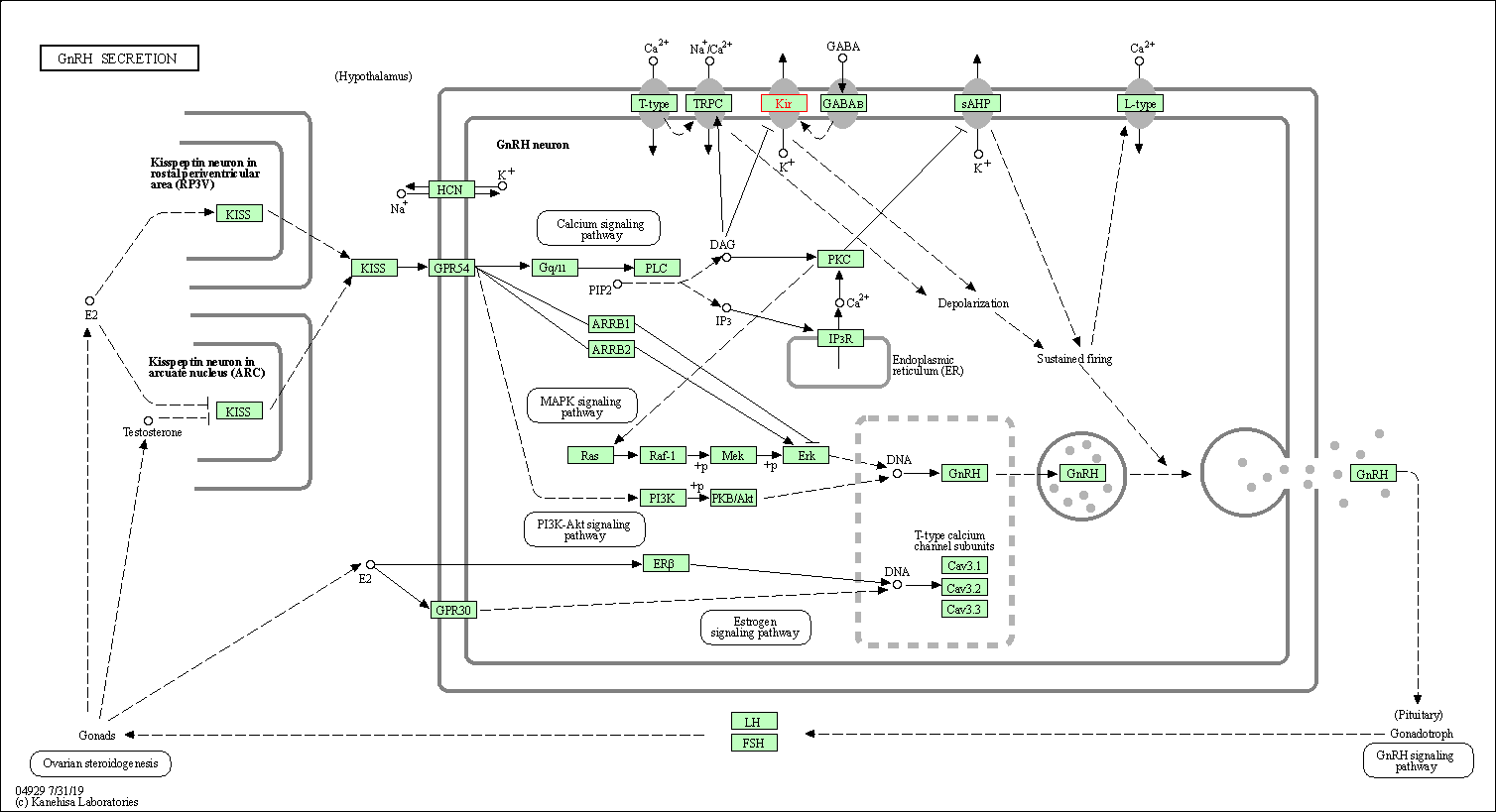
| GnRH secretion | hsa04929 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 1 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 0.00E+00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.35E-01 | Radiality | 1.13E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.00E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.00E+00 | Eccentricity | 14 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 7 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Circadian entrainment | |||||
| 2 | Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | |||||
| 3 | Serotonergic synapse | |||||
| 4 | Dopaminergic synapse | |||||
| 5 | Estrogen signaling pathway | |||||
| 6 | Oxytocin signaling pathway | |||||
| 7 | Morphine addiction | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 2 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| 2 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 2 and 4 signaling pathway | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Muscle/Heart Contraction | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels | |||||
| 2 | Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell | |||||
| 2 | Neurotransmitter Receptor Binding And Downstream Transmission In The Postsynaptic Cell | |||||
| 3 | Notch Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 4 | Potassium Channels | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| Target QSAR Model | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Molecular basis for the inhibition of G protein-coupled inward rectifier K(+) channels by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 27;101(4):1087-92. | |||||
| REF 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 3 | PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science. 1998 Nov 6;282(5391):1141-4. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

