Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T64830
(Former ID: TTDC00253)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Somatostatin receptor type 5 (SSTR5)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Somatostatin receptor 5; SSTR5; SS5R
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
SSTR5
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Cushing syndrome [ICD-11: 5A70] | |||||
| Function |
Receptor for somatostatin 28 and to a lesser extent for somatostatin-14. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Increases cell growth inhibition activity of SSTR2 following heterodimerization.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MEPLFPASTPSWNASSPGAASGGGDNRTLVGPAPSAGARAVLVPVLYLLVCAAGLGGNTL
VIYVVLRFAKMKTVTNIYILNLAVADVLYMLGLPFLATQNAASFWPFGPVLCRLVMTLDG VNQFTSVFCLTVMSVDRYLAVVHPLSSARWRRPRVAKLASAAAWVLSLCMSLPLLVFADV QEGGTCNASWPEPVGLWGAVFIIYTAVLGFFAPLLVICLCYLLIVVKVRAAGVRVGCVRR RSERKVTRMVLVVVLVFAGCWLPFFTVNIVNLAVALPQEPASAGLYFFVVILSYANSCAN PVLYGFLSDNFRQSFQKVLCLRKGSGAKDADATEPRPDRIRQQQEATPPAHRAAANGLMQ TSKL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T54G5E | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pasireotide | Drug Info | Approved | Cushing disease | [2], [3] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | FR-121196 | Drug Info | Terminated | Alzheimer disease | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 17 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pasireotide | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | ODT-8 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 3 | Cytotoxin Peptide Conjugate | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | D-Phe-c[Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys]-Asp-NH2 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 5 | Des-AA1,2,4,12,13-[D-Trp8]SRIF | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 6 | Des-AA1,2,4,13-[D-Trp8]SRIF | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 7 | Des-AA1,2,4,5,13-[D-Trp8]-SRIF | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 8 | Des-AA1,2,4,5-[D-Trp8]SRIF | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 9 | Des-AA1,2,5,12,13-[D-Trp8]SRIF | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 10 | Des-AA1,2,5-[D-Trp8,Tyr11]SRIF | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 11 | Des-AA5-[D-Trp8]SRIF | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 12 | H-D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys-Thr-NH2 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 13 | H-D-Phe-c[Cys-Ala-D-Trp-Lys-Thr-Cys]-Thr-NH2 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 14 | H-DPhe-c[Cys-Phe-DTrp-Lys-Thr-Cys]-Thr-NH2 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 15 | PTR-3046 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 16 | SOMATOSTATIN | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 17 | SRIF-28 | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 2 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | FR-121196 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | 99mTc-MIP-1407 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 3 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CGP 23996 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 2 | L-817,818 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 3 | SRIF-14 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
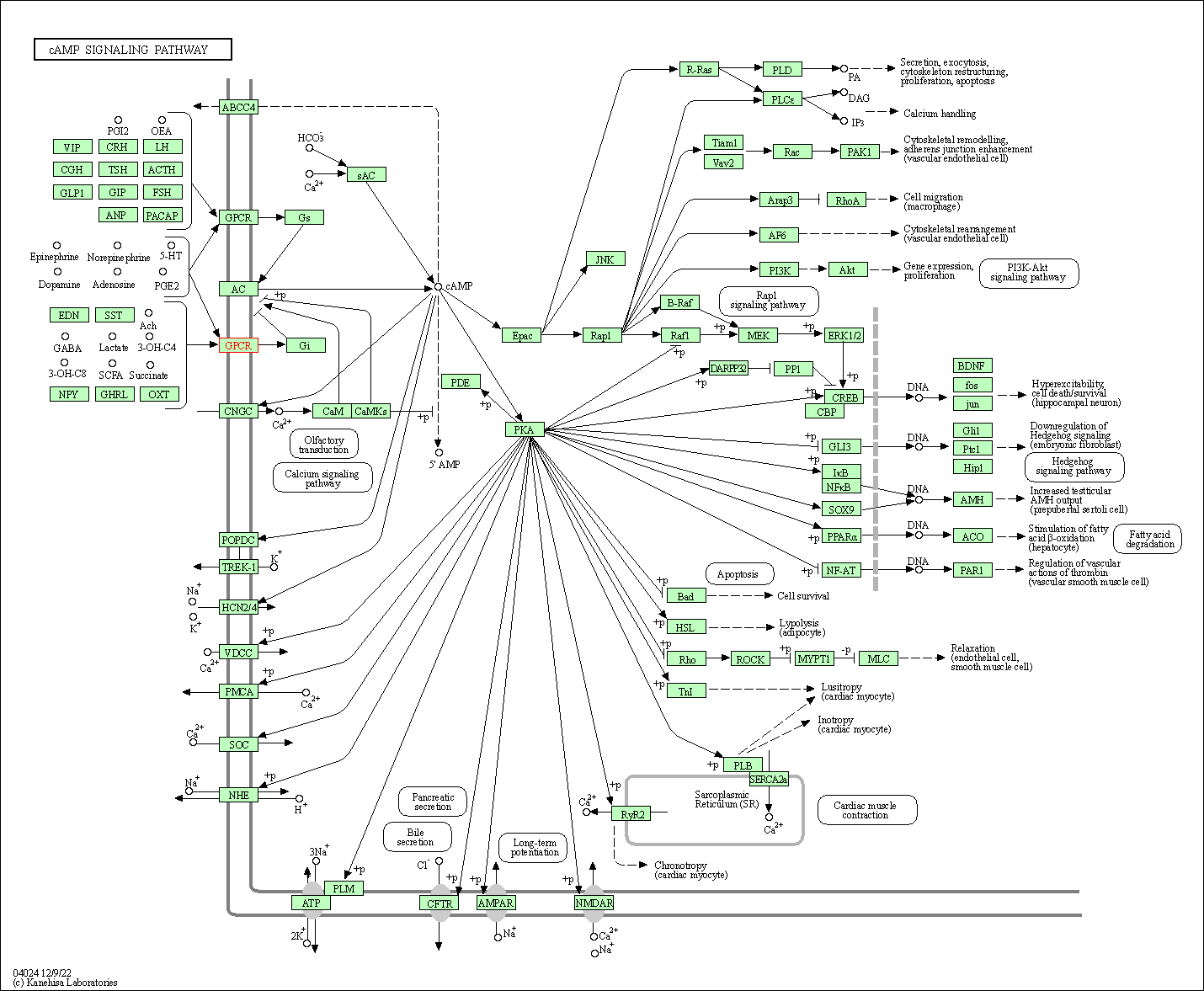

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
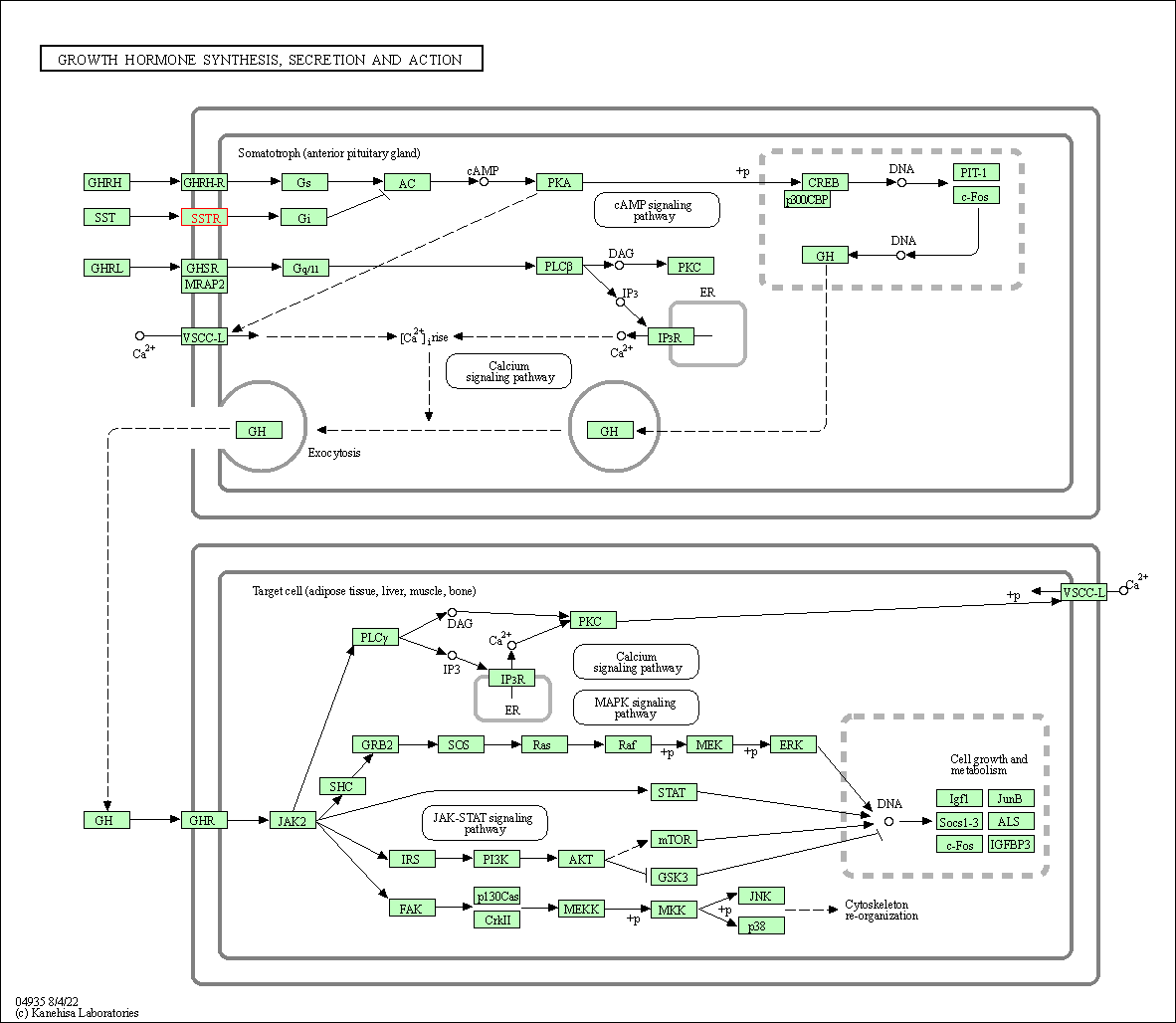
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 1 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 0.00E+00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.49E-01 | Radiality | 1.19E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 8.00E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.00E+00 | Eccentricity | 14 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 2 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | cAMP signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 2 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| 2 | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gq alpha and Go alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Peptide ligand-binding receptors | |||||
| 2 | G alpha (i) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 4 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| 2 | Peptide GPCRs | |||||
| 3 | GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| 4 | GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 359). | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02527993) Treatment of Hypoglycemia Following Gastric Bypass Surgery. | |||||
| REF 4 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800001380) | |||||
| REF 5 | Somatostatin receptor 1 selective analogues: 3. Dicyclic peptides. J Med Chem. 2005 Jan 27;48(2):515-22. | |||||
| REF 6 | Role of somatostatin in the augmentation of hippocampal long-term potentiation by FR121196, a putative cognitive enhancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep 7;241(1):27-34. | |||||
| REF 7 | [125I][Tyr3]octreotide labels human somatostatin sst2 and sst5 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 May 8;348(2-3):311-20. | |||||
| REF 8 | An adjustable release rate linking strategy for cytotoxin-peptide conjugates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Mar 10;13(5):799-803. | |||||
| REF 9 | Discovery of iodinated somatostatin analogues selective for hsst2 and hsst5 with excellent inhibition of growth hormone and prolactin release from ... J Med Chem. 2005 Oct 20;48(21):6643-52. | |||||
| REF 10 | Somatostatin receptor 1 selective analogues: 2. N(alpha)-Methylated scan. J Med Chem. 2005 Jan 27;48(2):507-14. | |||||
| REF 11 | Novel sst2-selective somatostatin agonists. Three-dimensional consensus structure by NMR. J Med Chem. 2006 Jul 27;49(15):4487-96. | |||||
| REF 12 | Rapid identification of subtype-selective agonists of the somatostatin receptor through combinatorial chemistry. Science. 1998 Oct 23;282(5389):737-40. | |||||
| REF 13 | Highly potent 4-amino-indolo[2,3-c]azepin-3-one-containing somatostatin mimetics with a range of sst receptor selectivities. J Med Chem. 2009 Jan 8;52(1):95-104. | |||||
| REF 14 | Novel octreotide dicarba-analogues with high affinity and different selectivity for somatostatin receptors. J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 26;53(16):6188-97. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

