Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T64682
(Former ID: TTDR01250)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Sgk1 (SGK1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1; SGK1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
SGK1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||||
| Function |
Plays an important role in cellular stress response. Contributes to regulation of renal Na(+) retention, renal K(+) elimination, salt appetite, gastric acid secretion, intestinal Na(+)/H(+) exchange and nutrient transport, insulin-dependent salt sensitivity of blood pressure, salt sensitivity of peripheral glucose uptake, cardiac repolarization and memory consolidation. Up-regulates Na(+) channels: SCNN1A/ENAC, SCN5A and ASIC1/ACCN2, K(+) channels: KCNJ1/ROMK1, KCNA1-5, KCNQ1-5 and KCNE1, epithelial Ca(2+) channels: TRPV5 and TRPV6, chloride channels: BSND, CLCN2 and CFTR, glutamate transporters: SLC1A3/EAAT1, SLC1A2 /EAAT2, SLC1A1/EAAT3, SLC1A6/EAAT4 and SLC1A7/EAAT5, amino acid transporters: SLC1A5/ASCT2, SLC38A1/SN1 and SLC6A19, creatine transporter: SLC6A8, Na(+)/dicarboxylate cotransporter: SLC13A2/NADC1, Na(+)-dependent phosphate cotransporter: SLC34A2/NAPI-2B, glutamate receptor: GRIK2/GLUR6. Up-regulates carriers: SLC9A3/NHE3, SLC12A1/NKCC2, SLC12A3/NCC, SLC5A3/SMIT, SLC2A1/GLUT1, SLC5A1/SGLT1 and SLC15A2/PEPT2. Regulates enzymes: GSK3A/B, PMM2 and Na(+)/K(+) ATPase, and transcription factors: CTNNB1 and nuclear factor NF-kappa-B. Stimulates sodium transport into epithelial cells by enhancing the stability and expression of SCNN1A/ENAC. This is achieved by phosphorylating the NEDD4L ubiquitin E3 ligase, promoting its interaction with 14-3-3 proteins, thereby preventing it from binding to SCNN1A/ENAC and targeting it for degradation. Regulates store-operated Ca(+2) entry (SOCE) by stimulating ORAI1 and STIM1. Regulates KCNJ1/ROMK1 directly via its phosphorylation or indirectly via increased interaction with SLC9A3R2/NHERF2. Phosphorylates MDM2 and activates MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of p53/TP53. Phosphorylates MAPT/TAU and mediates microtubule depolymerization and neurite formation in hippocampal neurons. Phosphorylates SLC2A4/GLUT4 and up-regulates its activity. Phosphorylates APBB1/FE65 and promotes its localization to the nucleus. Phosphorylates MAPK1/ERK2 and activates it by enhancing its interaction with MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Phosphorylates FBXW7 and plays an inhibitory role in the NOTCH1 signaling. Phosphorylates FOXO1 resulting in its relocalization from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Phosphorylates FOXO3, promoting its exit from the nucleus and interference with FOXO3-dependent transcription. Phosphorylates BRAF and MAP3K3/MEKK3 and inhibits their activity. Phosphorylates SLC9A3/NHE3 in response to dexamethasone, resulting in its activation and increased localization at the cell membrane. Phosphorylates CREB1. Necessary for vascular remodeling during angiogenesis. Sustained high levels and activity may contribute to conditions such as hypertension and diabetic nephropathy. Isoform 2 exhibited a greater effect on cell plasma membrane expression of SCNN1A/ENAC and Na(+) transport than isoform 1. Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is involved in the regulation of a wide variety of ion channels, membrane transporters, cellular enzymes, transcription factors, neuronal excitability, cell growth, proliferation, survival, migration and apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MTVKTEAAKGTLTYSRMRGMVAILIAFMKQRRMGLNDFIQKIANNSYACKHPEVQSILKI
SQPQEPELMNANPSPPPSPSQQINLGPSSNPHAKPSDFHFLKVIGKGSFGKVLLARHKAE EVFYAVKVLQKKAILKKKEEKHIMSERNVLLKNVKHPFLVGLHFSFQTADKLYFVLDYIN GGELFYHLQRERCFLEPRARFYAAEIASALGYLHSLNIVYRDLKPENILLDSQGHIVLTD FGLCKENIEHNSTTSTFCGTPEYLAPEVLHKQPYDRTVDWWCLGAVLYEMLYGLPPFYSR NTAEMYDNILNKPLQLKPNITNSARHLLEGLLQKDRTKRLGAKDDFMEIKSHVFFSLINW DDLINKKITPPFNPNVSGPNDLRHFDPEFTEEPVPNSIGKSPDSVLVTASVKEAAEAFLG FSYAPPTDSFL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T47YVM | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: AMP-PNP | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Inactive Serum and Glucocorticoid- Regulated Kinase 1 in Complex with AMP-PNP | PDB:2R5T | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | Yes | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
QINLGPSSNP
91 HAKPSDFHFL101 KVIGKGSFGK111 VLLARHKAEE121 VFYAVKVLQK131 KAILVLLKNV 154 KHPFLVGLHF164 SFQTADKLYF174 VLDYINGGEL184 FYHLQRERCF194 LEPRARFYAA 204 EIASALGYLH214 SLNIVYRDLK224 PENILLDSQG234 HIVLTDFGLC244 KENIEHNSTT 254 STFCGTPEYL264 APEVLHKQPY274 DRTVDWWCLG284 AVLYEMLYGL294 PPFYSRNTAE 304 MYDNILNKPL314 QLKPNITNSA324 RHLLEGLLQK334 DRTKRLGAKD344 DFMEIKSHVF 354 FSLINWDDLI364 NKKITPPFNP374 NVSG
|
|||||
|
|
ILE104
3.349
GLY105
3.999
LYS106
4.054
GLY107
3.119
SER108
2.719
PHE109
2.853
GLY110
3.789
VAL112
3.886
ALA125
3.484
LYS127
2.544
VAL160
3.587
LEU176
4.032
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Sgk1-IN-3 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in complex with pyrazolopyridine inhibitor 3a | PDB:7PUE | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.51 Å | Mutation | Yes | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
QINLGPSSNP
91 HAKPSDFHFL101 KVIGKGGKVL113 LARHKAEEVF123 YAVKVLQKKA133 IVLLKNVKHP 157 FLVGLHFSFQ167 TADKLYFVLD177 YINGGELFYH187 LQREACFLEP197 RARFYAAEIA 207 SALGYLHSLN217 IVYRDLKPEN227 ILLDSQGHIV237 LTDFGLCKTS255 TFCGTPEYLA 265 PEVLHKQPYD275 RTVDWWCLGA285 VLYEMLYGLP295 PFYSRNTAEM305 YDNILNKPLQ 315 LKPNITNSAR325 HLLEGLLQKD335 RTKRLGAKDD345 FMEIKSHVFF355 SLINWDDLIN 365 KKITPPFNPN375 V
|
|||||
|
|
ILE104
3.316
GLY105
3.707
VAL112
3.903
ALA125
3.386
LYS127
3.174
LYS152
4.133
VAL160
3.719
LEU162
3.739
PHE174
3.456
LEU176
3.535
ASP177
2.610
TYR178
3.435
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
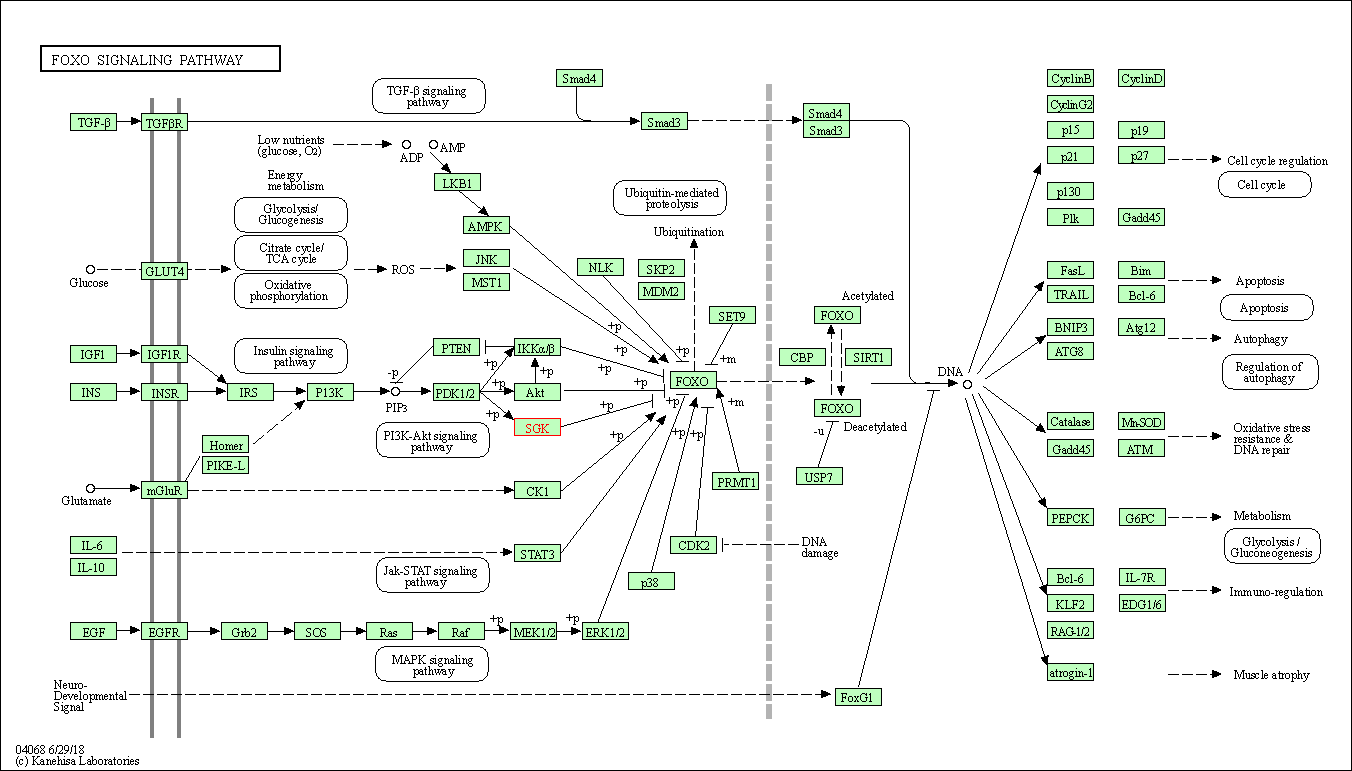
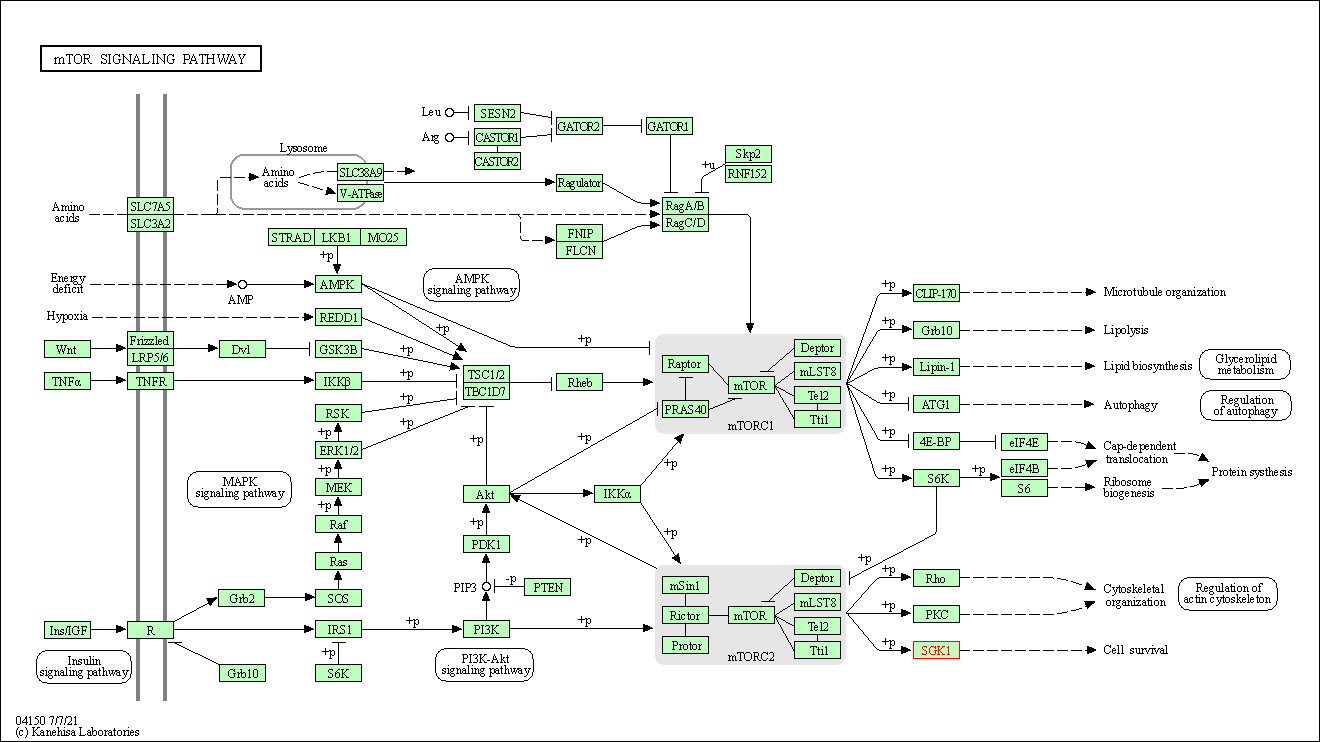
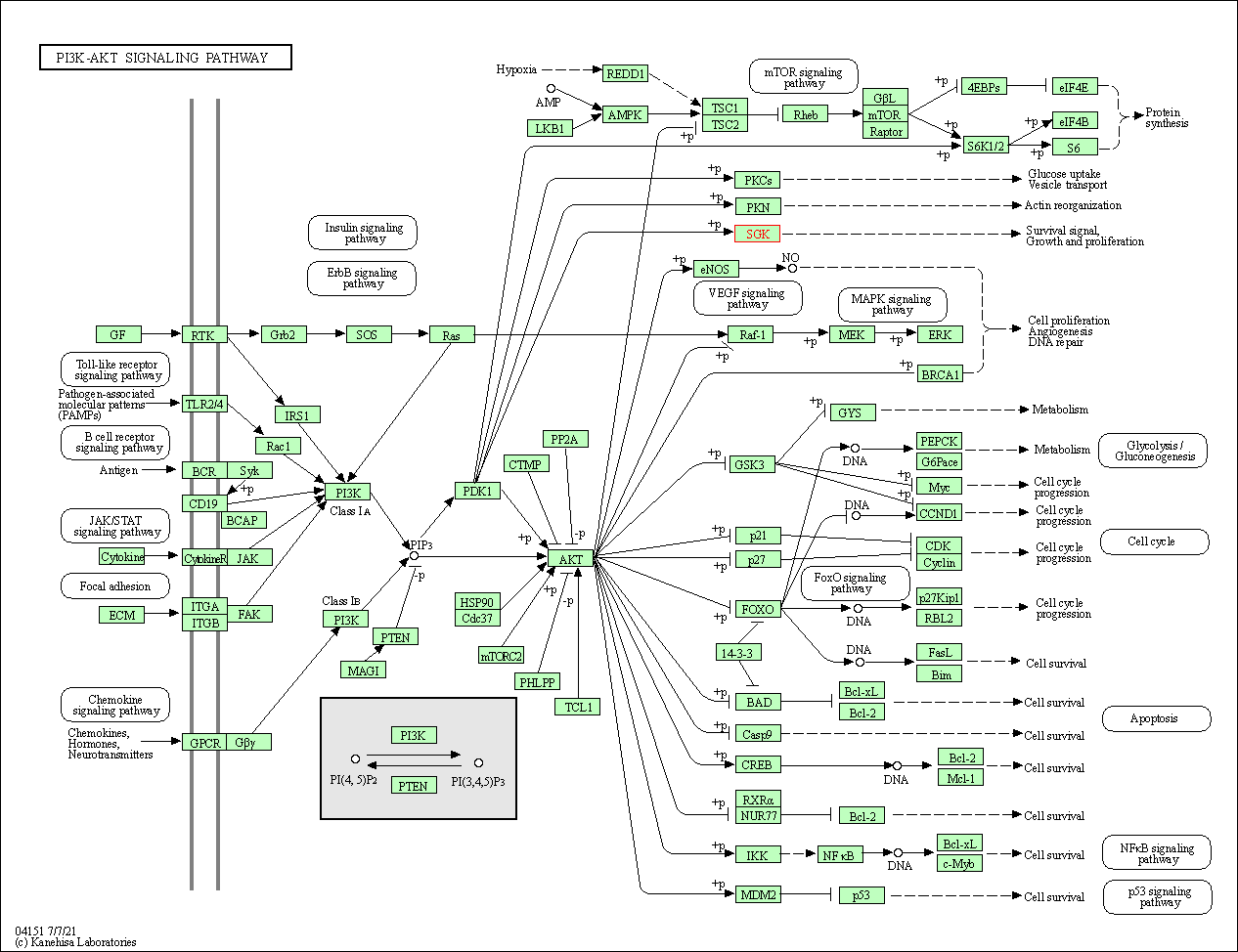

| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | hsa04960 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Excretory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 13 | Degree centrality | 1.40E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.24E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.28E-01 | Radiality | 1.40E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.31E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.24E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.26E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 3 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | FoxO signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 3 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL5 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | FSH Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 3 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 5 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Insulin Pathway | |||||
| 2 | Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network | |||||
| 3 | mTOR signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | FoxO family signaling | |||||
| 5 | Class I PI3K signaling events | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 1 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Stimuli-sensing channels | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 3 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Insulin Signaling | |||||
| 2 | Iron uptake and transport | |||||
| 3 | FSH signaling pathway | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105. | |||||
| REF 2 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 3 | The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J. 2007 Dec 15;408(3):297-315. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 8040). | |||||
| REF 5 | Crystal structure of the kinase domain of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in complex with AMP PNP. Protein Sci. 2007 Dec;16(12):2761-9. | |||||
| REF 6 | Rational Design of Highly Potent, Selective, and Bioavailable SGK1 Protein Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J Med Chem. 2022 Jan 27;65(2):1567-1584. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

