Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T43718
(Former ID: TTDI02191)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-like protein 3; TIL3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TLR5
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 3 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91] | |||||
| 2 | Radiation effect [ICD-11: NF00] | |||||
| 3 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Recognizes small molecular motifs named pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMPs) expressed by pathogens and microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) usually expressed by resident microbiota. Upon ligand binding such as bacterial flagellins, recruits intracellular adapter proteins MYD88 and TRIF leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and induction of the inflammatory response. Plays thereby an important role in the relationship between the intestinal epithelium and enteric microbes and contributes to the gut microbiota composition throughout life. Pattern recognition receptor (PRR) located on the cell surface that participates in the activation of innate immunity and inflammatory response.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Toll-like receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGDHLDLLLGVVLMAGPVFGIPSCSFDGRIAFYRFCNLTQVPQVLNTTERLLLSFNYIRT
VTASSFPFLEQLQLLELGSQYTPLTIDKEAFRNLPNLRILDLGSSKIYFLHPDAFQGLFH LFELRLYFCGLSDAVLKDGYFRNLKALTRLDLSKNQIRSLYLHPSFGKLNSLKSIDFSSN QIFLVCEHELEPLQGKTLSFFSLAANSLYSRVSVDWGKCMNPFRNMVLEILDVSGNGWTV DITGNFSNAISKSQAFSLILAHHIMGAGFGFHNIKDPDQNTFAGLARSSVRHLDLSHGFV FSLNSRVFETLKDLKVLNLAYNKINKIADEAFYGLDNLQVLNLSYNLLGELYSSNFYGLP KVAYIDLQKNHIAIIQDQTFKFLEKLQTLDLRDNALTTIHFIPSIPDIFLSGNKLVTLPK INLTANLIHLSENRLENLDILYFLLRVPHLQILILNQNRFSSCSGDQTPSENPSLEQLFL GENMLQLAWETELCWDVFEGLSHLQVLYLNHNYLNSLPPGVFSHLTALRGLSLNSNRLTV LSHNDLPANLEILDISRNQLLAPNPDVFVSLSVLDITHNKFICECELSTFINWLNHTNVT IAGPPADIYCVYPDSFSGVSLFSLSTEGCDEEEVLKSLKFSLFIVCTVTLTLFLMTILTV TKFRGFCFICYKTAQRLVFKDHPQGTEPDMYKYDAYLCFSSKDFTWVQNALLKHLDTQYS DQNRFNLCFEERDFVPGENRIANIQDAIWNSRKIVCLVSRHFLRDGWCLEAFSYAQGRCL SDLNSALIMVVVGSLSQYQLMKHQSIRGFVQKQQYLRWPEDFQDVGWFLHKLSQQILKKE KEKKKDNNIPLQTVATIS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T87TVN | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CBLB-502 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Acute radiation syndrome | [1], [2] | |
| 2 | Entolimod | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [3] | |
| 3 | STAT-600 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acute radiation syndrome | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Agonist | [+] 3 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CBLB-502 | Drug Info | [1], [2] | |||
| 2 | Entolimod | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 3 | STAT-600 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |
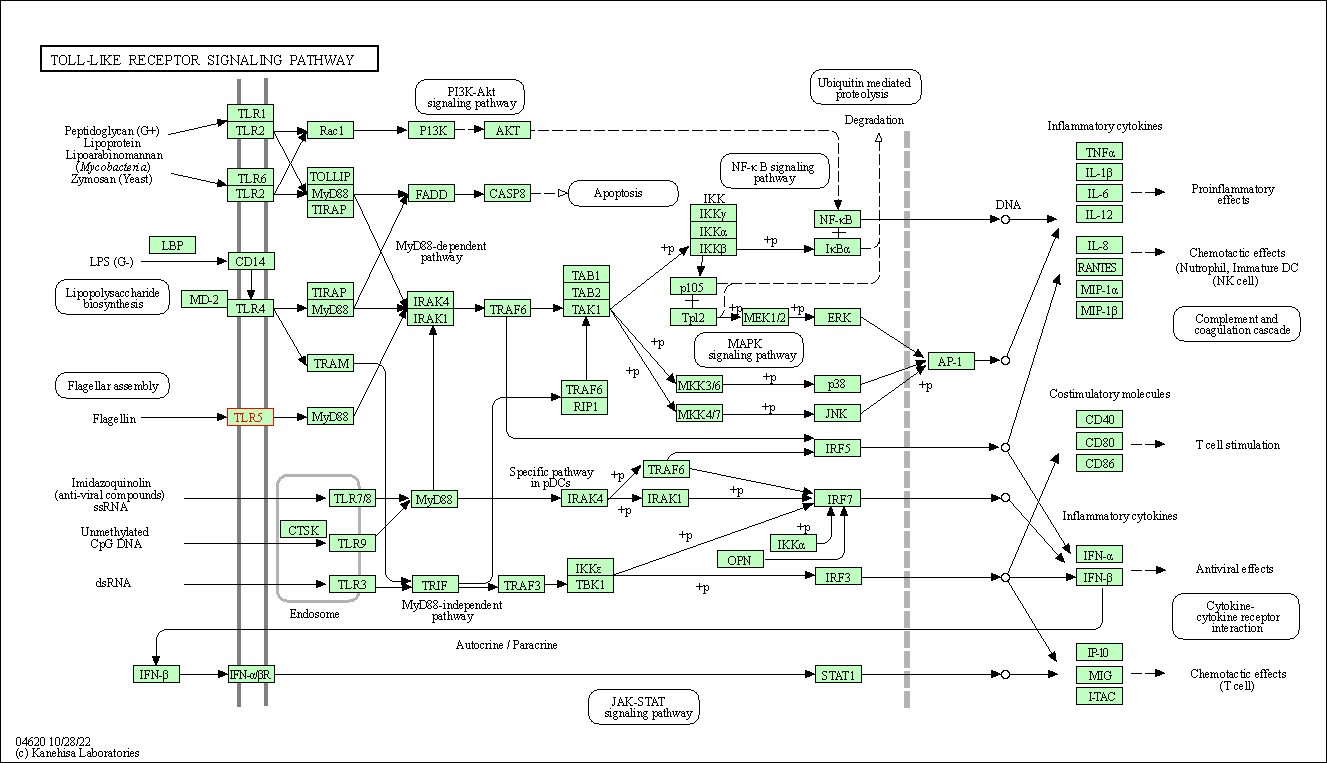
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 1 | Degree centrality | 1.07E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 0.00E+00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.92E-01 | Radiality | 1.33E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 4.60E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.00E+00 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | |||||
| 3 | Salmonella infection | |||||
| 4 | Legionellosis | |||||
| 5 | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | MyD88 deficiency (TLR5) | |||||
| 2 | IRAK4 deficiency (TLR5) | |||||
| 3 | MyD88 cascade initiated on plasma membrane | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 5 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | MyD88 cascade initiated on plasma membrane | |||||
| 3 | Toll-Like Receptors Cascades | |||||
| 4 | Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection | |||||
| 5 | Regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Recombinant TLR5 agonist CBLB502 promotes NK cell-mediated anti-CMV immunity in mice. PLoS One. 2014 May 30;9(5):e96165. | |||||
| REF 2 | A flagellin-derived toll-like receptor 5 agonist stimulates cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated tumor immunity. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 14;9(1):e85587. | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 4 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Statera Biopharma | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

