Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T42976
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Glutathione S-transferase A3 (GSTA3)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Glutathione S-transferase A3-3; GST class-alpha member 3
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
GSTA3
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles. Catalyzes isomerization reactions that contribute to the biosynthesis of steroid hormones. Efficiently catalyze obligatory double-bond isomerizations of delta(5)-androstene-3,17-dione and delta(5)-pregnene-3,20-dione, precursors to testosterone and progesterone, respectively.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.5.1.18
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAGKPKLHYFNGRGRMEPIRWLLAAAGVEFEEKFIGSAEDLGKLRNDGSLMFQQVPMVEI
DGMKLVQTRAILNYIASKYNLYGKDIKERALIDMYTEGMADLNEMILLLPLCRPEEKDAK IALIKEKTKSRYFPAFEKVLQSHGQDYLVGNKLSRADISLVELLYYVEELDSSLISNFPL LKALKTRISNLPTVKKFLQPGSPRKPPADAKALEEARKIFRF Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Glutathione | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Glutathione transferase A3-3 in complex with glutathione and delta-4- androstene-3-17-dione | PDB:2VCV | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.80 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
KPKLHYFNGR
13 GRMEPIRWLL23 AAAGVEFEEK33 FIGSAEDLGK43 LRNDGSLMFQ53 QVPMVEIDGM 63 KLVQTRAILN73 YIASKYNLYG83 KDIKERALID93 MYTEGMADLN103 EMILLLPLCR 113 PEEKDAKIAL123 IKEKTKSRYF133 PAFEKVLQSH143 GQDYLVGNKL153 SRADISLVEL 163 LYYVEELDSS173 LISNFPLLKA183 LKTRISNLPT193 VKKFLQPGSP203 RKPPADAKAL 213 EEARKIFRF
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: 4-ANDROSTENE-3-17-DIONE | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Glutathione transferase A3-3 in complex with glutathione and delta-4- androstene-3-17-dione | PDB:2VCV | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.80 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
KPKLHYFNGR
13 GRMEPIRWLL23 AAAGVEFEEK33 FIGSAEDLGK43 LRNDGSLMFQ53 QVPMVEIDGM 63 KLVQTRAILN73 YIASKYNLYG83 KDIKERALID93 MYTEGMADLN103 EMILLLPLCR 113 PEEKDAKIAL123 IKEKTKSRYF133 PAFEKVLQSH143 GQDYLVGNKL153 SRADISLVEL 163 LYYVEELDSS173 LISNFPLLKA183 LKTRISNLPT193 VKKFLQPGSP203 RKPPADAKAL 213 EEARKIFRF
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
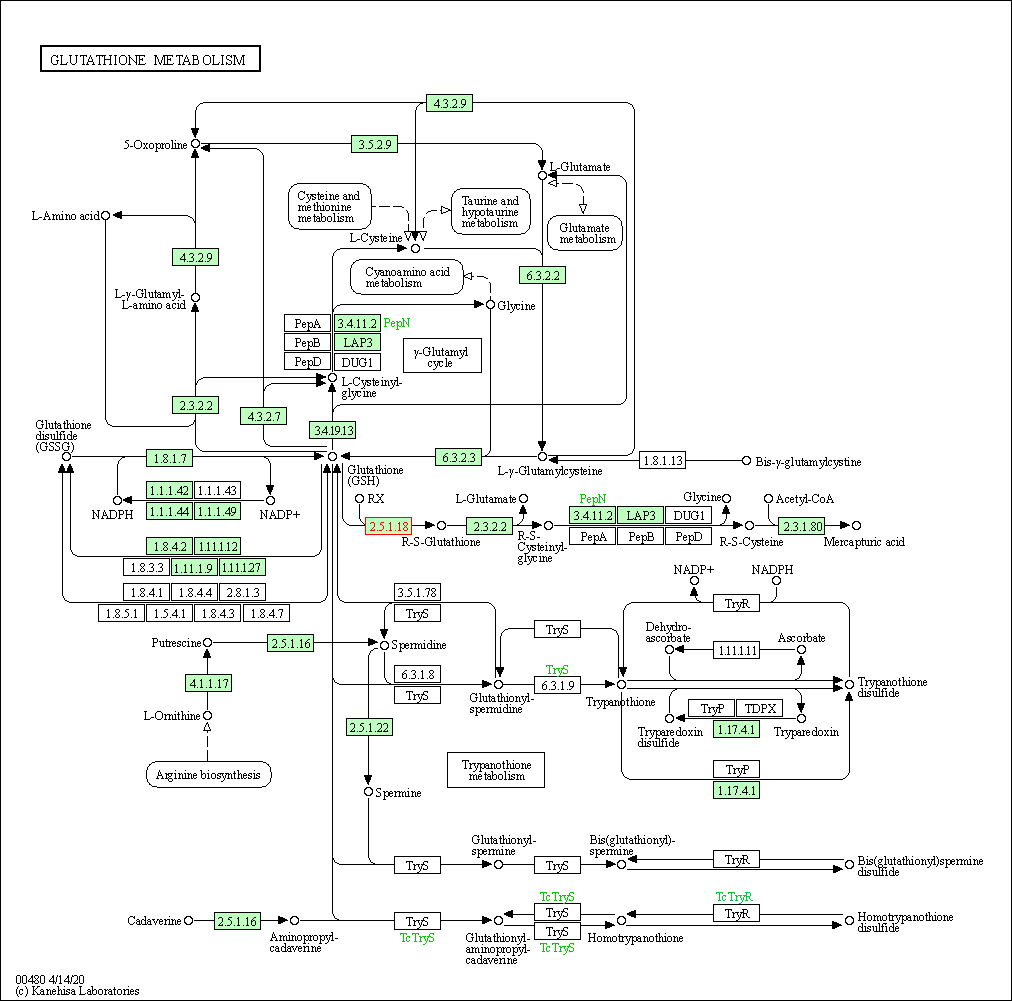
| Glutathione metabolism | hsa00480 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of other amino acids | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
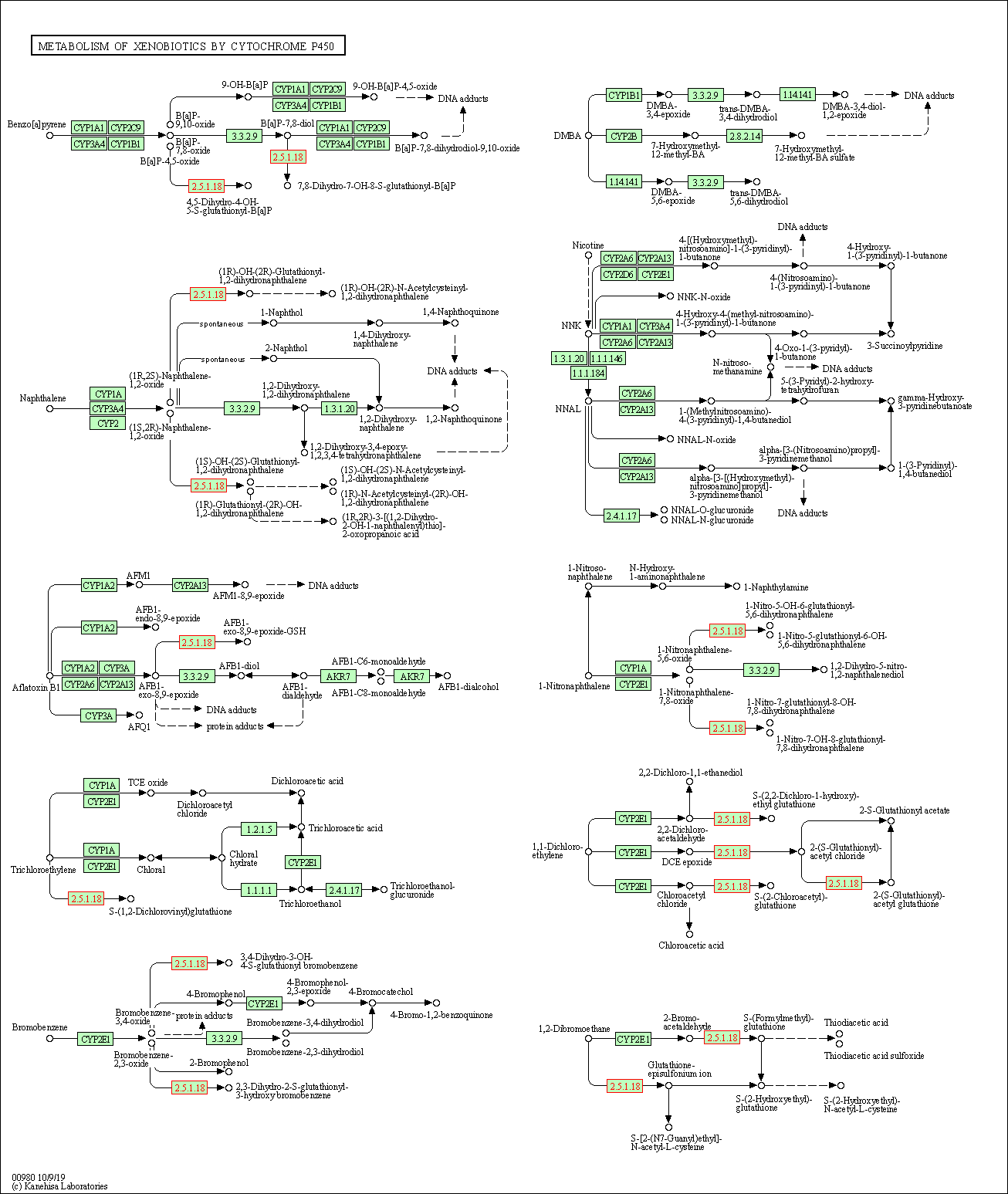
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | hsa00980 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
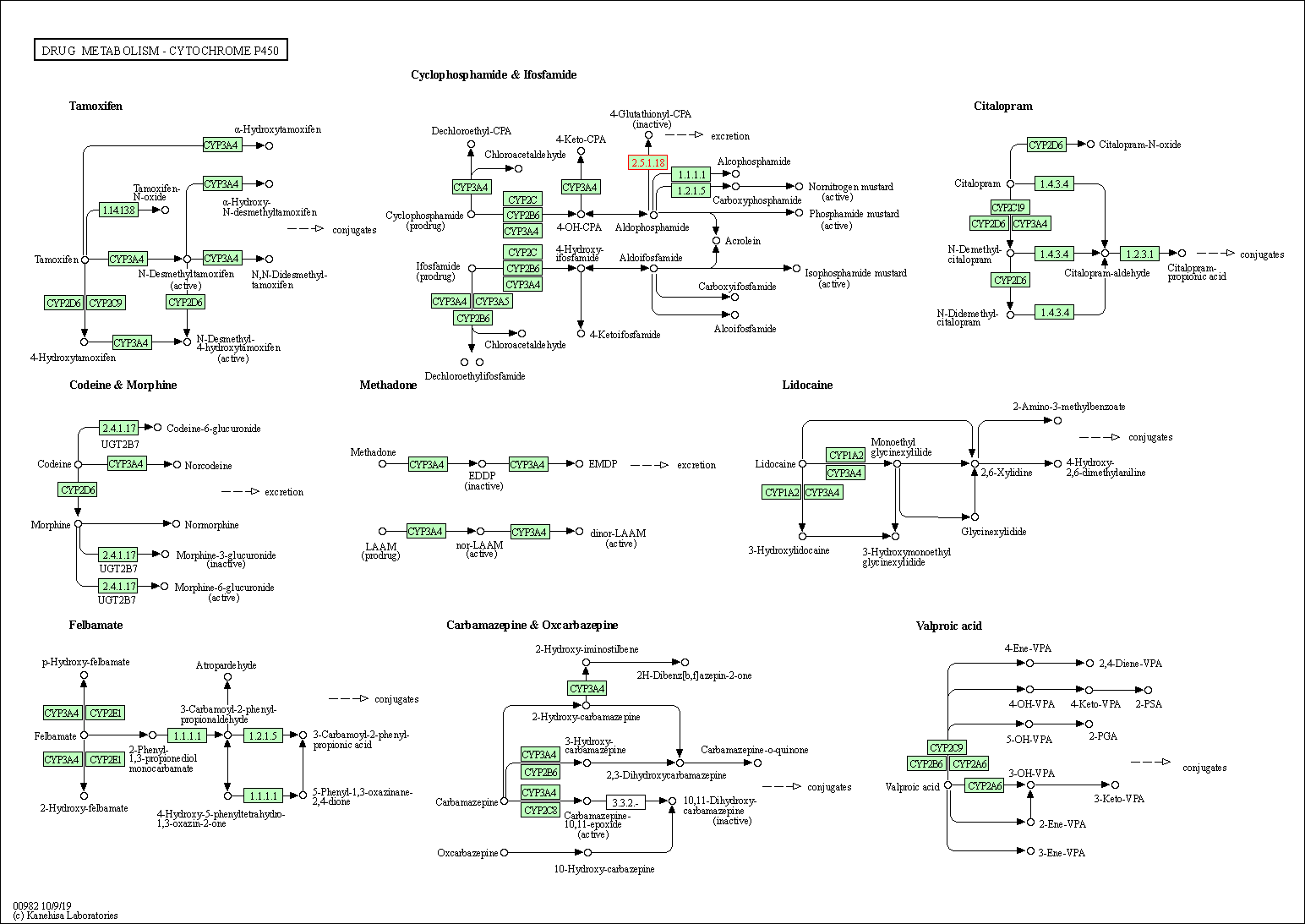
| Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | hsa00982 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
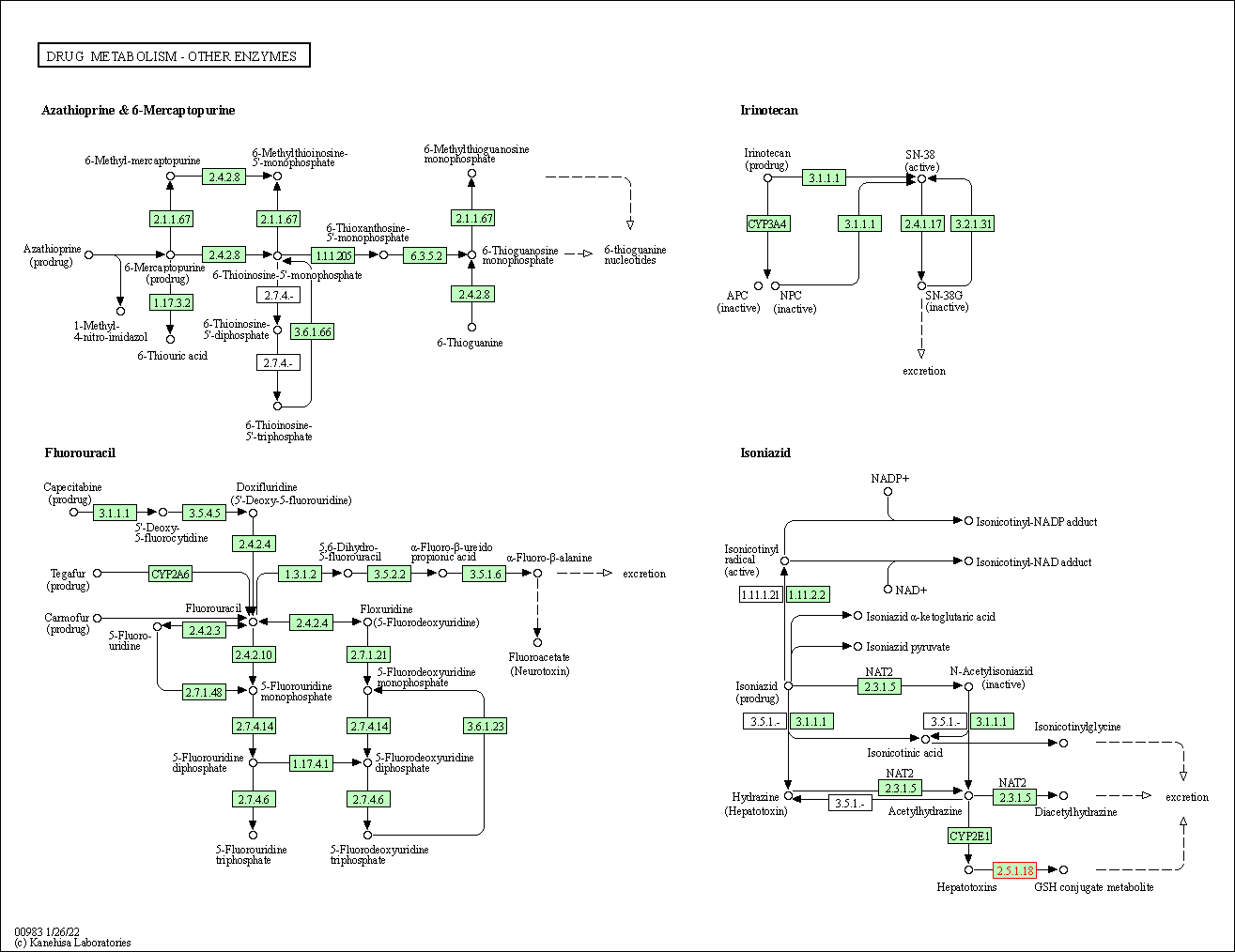
| Drug metabolism - other enzymes | hsa00983 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Glutathione-S-transferase A3 knockout mice are sensitive to acute cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Feb 1;242(3):241-6. | |||||
| REF 2 | Structural basis for featuring of steroid isomerase activity in alpha class glutathione transferases. J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 19;397(1):332-40. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

