Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T31406
(Former ID: TTDI03254)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Hematopoietic cell kinase (HCK)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
p61Hck; p59Hck; p59-HCK/p60-HCK; Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK; Hemopoietic cell kinase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
HCK
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Indeterminate colitis [ICD-11: DD72] | |||||
| Function |
Acts downstream of receptors that bind the Fc region of immunoglobulins, such as FCGR1A and FCGR2A, but also CSF3R, PLAUR, the receptors for IFNG, IL2, IL6 and IL8, and integrins, such as ITGB1 and ITGB2. During the phagocytic process, mediates mobilization of secretory lysosomes, degranulation, and activation of NADPH oxidase to bring about the respiratory burst. Plays a role in the release of inflammatory molecules. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and actin polymerization, formation of podosomes and cell protrusions. Inhibits TP73-mediated transcription activation and TP73-mediated apoptosis. Phosphorylates CBL in response to activation of immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptors. Phosphorylates ADAM15, BCR, ELMO1, FCGR2A, GAB1, GAB2, RAPGEF1, STAT5B, TP73, VAV1 and WAS. Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase found in hematopoietic cells that transmits signals from cell surface receptors and plays an important role in the regulation of innate immune responses, including neutrophil, monocyte, macrophage and mast cell functions, phagocytosis, cell survival and proliferation, cell adhesion and migration.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.10.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MGGRSSCEDPGCPRDEERAPRMGCMKSKFLQVGGNTFSKTETSASPHCPVYVPDPTSTIK
PGPNSHNSNTPGIREAGSEDIIVVALYDYEAIHHEDLSFQKGDQMVVLEESGEWWKARSL ATRKEGYIPSNYVARVDSLETEEWFFKGISRKDAERQLLAPGNMLGSFMIRDSETTKGSY SLSVRDYDPRQGDTVKHYKIRTLDNGGFYISPRSTFSTLQELVDHYKKGNDGLCQKLSVP CMSSKPQKPWEKDAWEIPRESLKLEKKLGAGQFGEVWMATYNKHTKVAVKTMKPGSMSVE AFLAEANVMKTLQHDKLVKLHAVVTKEPIYIITEFMAKGSLLDFLKSDEGSKQPLPKLID FSAQIAEGMAFIEQRNYIHRDLRAANILVSASLVCKIADFGLARVIEDNEYTAREGAKFP IKWTAPEAINFGSFTIKSDVWSFGILLMEIVTYGRIPYPGMSNPEVIRALERGYRMPRPE NCPEELYNIMMRCWKNRPEERPTFEYIQSVLDDFYTATESQYQQQP Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patented Agent(s) | [+] 1 Patented Agents | + | ||||
| 1 | Doramapimod | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Inflammatory bowel disease | [2], [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 11 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | 3-(6-allyloxy-2-naphthyl)-1-(4-piperidylmethyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | BK3 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | BK7 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | Doramapimod | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | SB19065 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 6 | Unii-I92MU0V408 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 7 | US8933228, 3 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 8 | US8933228, Ref 2 | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 9 | US9108950, 1 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 10 | PMID15546730C2 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 11 | PP121 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Quercetin | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | SRC FAMILY KINASE HCK-QUERCETIN COMPLEX | PDB:2HCK | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.00 Å | Mutation | Yes | [10] |
| PDB Sequence |
EDIIVVALYD
91 YEAIHHEDLS101 FQKGDQMVVL111 EESGEWWKAR122 SLATRKEGYI132 PSNYVARVDS 142 LETEEWFFKG152 ISRKDAERQL162 LAPGNMLGSF172 MIRDSETTKG182 SYSLSVRDYD 192 PRQGDTVKHY202 KIRTLDNGGF212 YISPRSTFST222 LQELVDHYKK232 GNDGLCQKLS 242 VPCMSSKPQK252 PWEKDAWEIP263 RESLKLEKKL273 GAGQFGEVWM283 ATYNKHTKVA 293 VKTMKPGSMS303 VEAFLAEANV313 MKTLQHDKLV323 KLHAVVTKEP333 IYIITEFMAK 343 GSLLDFLKSD353 EGSKQPLPKL363 IDFSAQIAEG373 MAFIEQRNYI383 HRDLRAANIL 393 VSASLVCKIA403 DFGLARVGAK423 FPIKWTAPEA433 INFGSFTIKS443 DVWSFGILLM 453 EIVTYGRIPY463 PGMSNPEVIR473 ALERGYRMPR483 PENCPEELYN493 IMMRCWKNRP 503 EERPTFEYIQ513 SVLDDFYTAT523 ESQQQQP
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: PTC299 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of HCK in complex with the fluorescent compound SKF86002 | PDB:4LUD | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.85 Å | Mutation | Yes | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
RIIVVALYDY
94 EAIHHEDLSF104 QKGDQMVVLE114 ESGEWWKARS124 LATRKEGYIP134 SNYVARLETE 147 EWFFKGISRK157 DAERQLLAPG167 NMLGSFMIRD177 SETTKGSYSL187 SVRDYDPRQG 197 DTVKHYKIRT207 LDGFYISPRS219 TFSTLQELVD229 HYKKGNDGLC239 QKLSVPCMSS 249 KPQKPWEKDA259 WEIPRESLKL269 EKKLGAGQFG279 EVWMATYNKH289 TKVAVKTMKP 299 SVEAFLAEAN312 VMKTLQHDKL322 VKLHAVVTKE332 PIYIITEFMA342 KGSLLDFLKS 352 DEGSKQPLPK362 LIDFSAQIAE372 GMAFIEQRNY382 IHRDLRAANI392 LVSASLVCKI 402 ADFGLARVIP425 IKWTAPEAIN435 FGSFTIKSDV445 WSFGILLMEI455 VTYGRIPYPG 465 MSNPELERGY479 RMPRPENCPE489 ELYNIMMRCW499 KNRPEERPTF509 EYIQSVLDDF 519 YTATESQEEI530 P
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
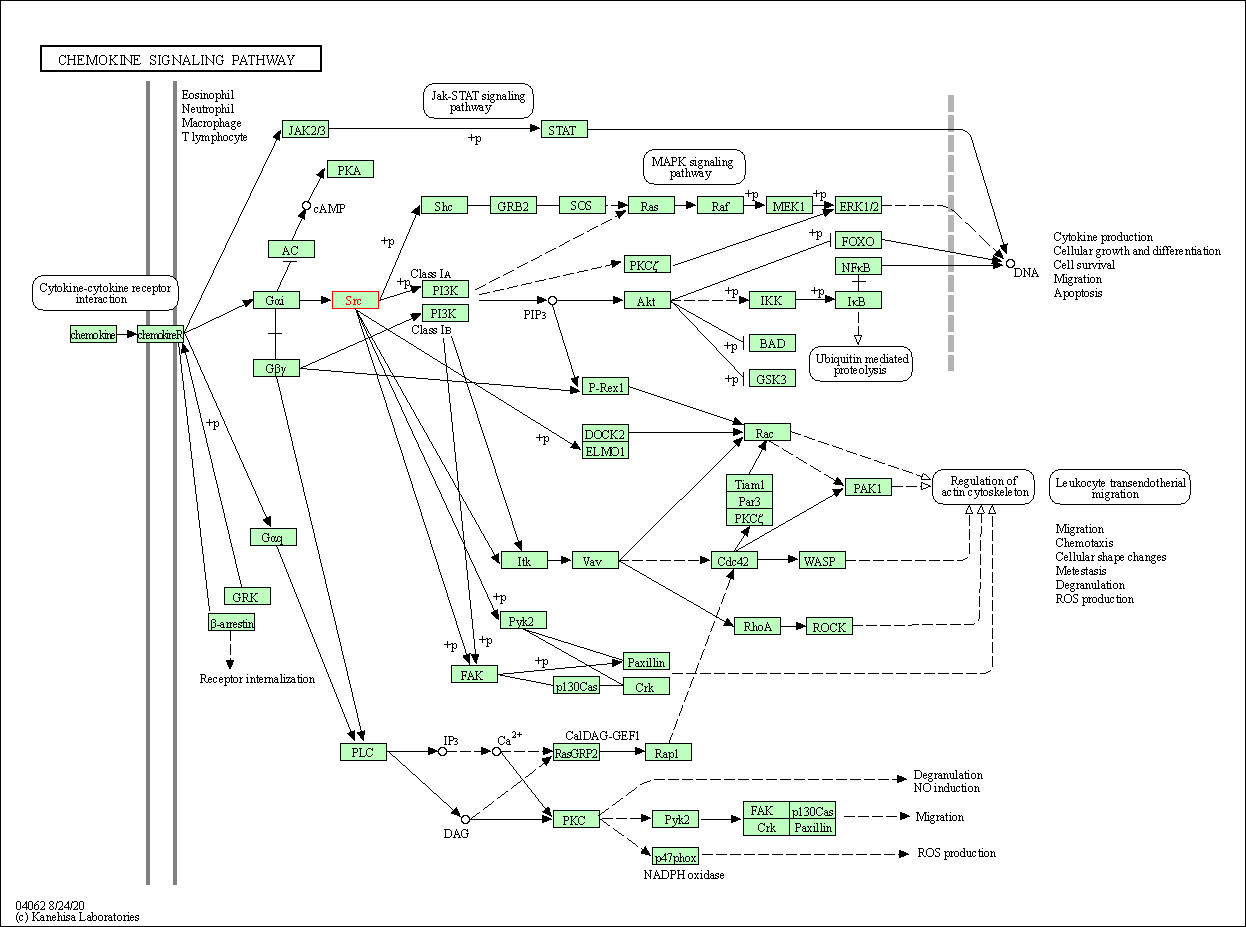
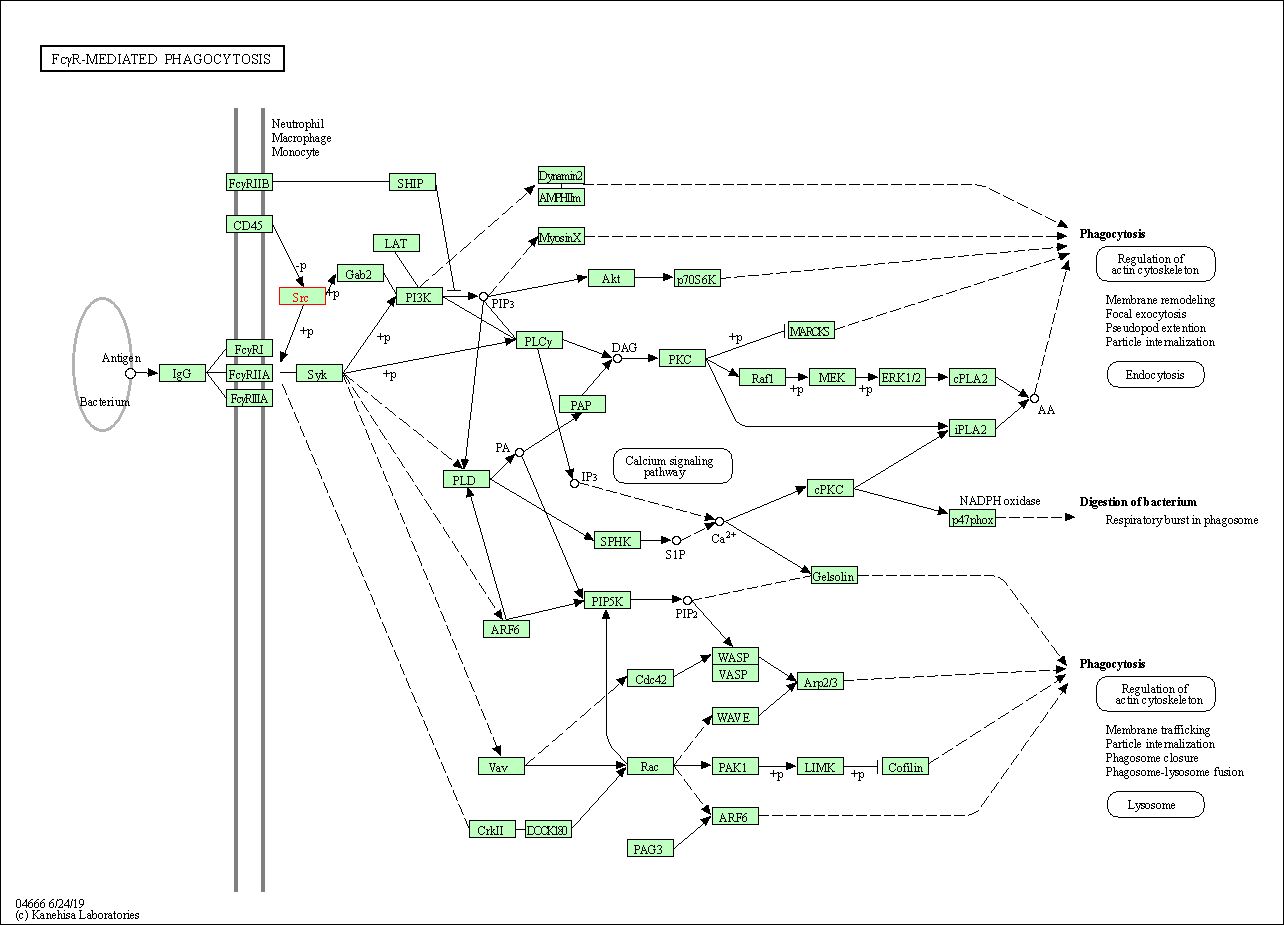
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | hsa04666 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 4.55E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.37E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.40E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.63E+01 | Topological coefficient | 8.70E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Targeted polypharmacology: discovery of dual inhibitors of tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinases. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Nov;4(11):691-9. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5668). | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800017152) | |||||
| REF 4 | Compositions and methods for treating toxoplasmosis, cryptosporidiosis, and other apicomplexan protozoan related diseases. US9765037. | |||||
| REF 5 | Respiratory formulations and compounds for use therein. US8933228. | |||||
| REF 6 | Anti-inflammatory compound having inhibitory activity against multiple tyrosine kinases and pharmaceutical composition containing same. US9062066. | |||||
| REF 7 | 1-pyrazolyl-3-(4-((2-anilinopyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)napththalen-1-yl) ureas as P38 MAP knase inhibitors. US9724347. | |||||
| REF 8 | 1-pyrazolyl-3-(4-((2-anilinopyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)napththalen-1-yl) ureas as p38 MAP kinase inhibitors. US9108950. | |||||
| REF 9 | Discovery of novel 2-(aminoheteroaryl)-thiazole-5-carboxamides as potent and orally active Src-family kinase p56(Lck) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Dec 20;14(24):6061-6. | |||||
| REF 10 | Crystal structure of the Src family tyrosine kinase Hck. Nature. 1997 Feb 13;385(6617):602-9. | |||||
| REF 11 | Kinase crystal identification and ATP-competitive inhibitor screening using the fluorescent ligand SKF86002. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Feb;70(Pt 2):392-404. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

