Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T23995
(Former ID: TTDC00178)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Protein kinase C theta (PRKCQ)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Protein kinase C theta type; PRKCT; NPKC-theta
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PRKCQ
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Transplant rejection [ICD-11: NE84] | |||||
| Function |
In TCR-CD3/CD28-co-stimulated T-cells, is required for the activation of NF-kappa-B and JUN, which in turn are essential for IL2 production, and participates in the calcium-dependent NFATC1 and NFATC2 transactivation. Mediates the activation of the canonical NF-kappa-B pathway (NFKB1) by direct phosphorylation of CARD11 on several serine residues, inducing CARD11 association with lipid rafts and recruitment of the BCL10-MALT1 complex, which then activates IKK complex, resulting in nuclear translocation and activation of NFKB1. May also play an indirect role in activation of the non-canonical NF-kappa-B (NFKB2) pathway. In the signaling pathway leading to JUN activation, acts by phosphorylating the mediator STK39/SPAK and may not act through MAP kinases signaling. Plays a critical role in TCR/CD28-induced NFATC1 and NFATC2 transactivation by participating in the regulation of reduced inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate generation and intracellular calcium mobilization. After costimulation of T-cells through CD28 can phosphorylate CBLB and is required for the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of CBLB, which is a prerequisite for the activation of TCR. During T-cells differentiation, plays an important role in the development of T-helper 2 (Th2) cells following immune and inflammatory responses, and, in the development of inflammatory autoimmune diseases, is necessary for the activation of IL17-producing Th17 cells. May play a minor role in Th1 response. Upon TCR stimulation, mediates T-cell protective survival signal by phosphorylating BAD, thus protecting T-cells from BAD-induced apoptosis, and by up-regulating BCL-X(L)/BCL2L1 levels through NF-kappa-B and JUN pathways. In platelets, regulates signal transduction downstream of the ITGA2B, CD36/GP4, F2R/PAR1 and F2RL3/PAR4 receptors, playing a positive role in 'outside-in' signaling and granule secretion signal transduction. May relay signals from the activated ITGA2B receptor by regulating the uncoupling of WASP and WIPF1, thereby permitting the regulation of actin filament nucleation and branching activity of the Arp2/3 complex. May mediate inhibitory effects of free fatty acids on insulin signaling by phosphorylating IRS1, which in turn blocks IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation and downstream activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Phosphorylates MSN (moesin) in the presence of phosphatidylglycerol or phosphatidylinositol. Phosphorylates PDPK1 at 'Ser-504' and 'Ser-532' and negatively regulates its ability to phosphorylate PKB/AKT1. Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that mediates non-redundant functions in T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling, including T-cells activation, proliferation, differentiation and survival, by mediating activation of multiple transcription factors such as NF-kappa-B, JUN, NFATC1 and NFATC2.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.13
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSPFLRIGLSNFDCGSCQSCQGEAVNPYCAVLVKEYVESENGQMYIQKKPTMYPPWDSTF
DAHINKGRVMQIIVKGKNVDLISETTVELYSLAERCRKNNGKTEIWLELKPQGRMLMNAR YFLEMSDTKDMNEFETEGFFALHQRRGAIKQAKVHHVKCHEFTATFFPQPTFCSVCHEFV WGLNKQGYQCRQCNAAIHKKCIDKVIAKCTGSAINSRETMFHKERFKIDMPHRFKVYNYK SPTFCEHCGTLLWGLARQGLKCDACGMNVHHRCQTKVANLCGINQKLMAEALAMIESTQQ ARCLRDTEQIFREGPVEIGLPCSIKNEARPPCLPTPGKREPQGISWESPLDEVDKMCHLP EPELNKERPSLQIKLKIEDFILHKMLGKGSFGKVFLAEFKKTNQFFAIKALKKDVVLMDD DVECTMVEKRVLSLAWEHPFLTHMFCTFQTKENLFFVMEYLNGGDLMYHIQSCHKFDLSR ATFYAAEIILGLQFLHSKGIVYRDLKLDNILLDKDGHIKIADFGMCKENMLGDAKTNTFC GTPDYIAPEILLGQKYNHSVDWWSFGVLLYEMLIGQSPFHGQDEEELFHSIRMDNPFYPR WLEKEAKDLLVKLFVREPEKRLGVRGDIRQHPLFREINWEELERKEIDPPFRPKVKSPFD CSNFDKEFLNEKPRLSFADRALINSMDQNMFRNFSFMNPGMERLIS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sotrastaurin acetate | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Renal transplantation | [1] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CDE-6960 | Drug Info | Terminated | Inflammation | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 20 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Sotrastaurin acetate | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | CDE-6960 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 3 | LY-317644 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | RO-320432 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | 2,3,3-Triphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 6 | 2-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-3,3-diphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 7 | 3,3-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 8 | 3,3-Bis-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-2-phenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 9 | 3-(4-Hydroxy-phenyl)-2,3-diphenyl-acrylonitrile | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 10 | 4-cycloheptyliden(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylphenol | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 11 | 4-cyclohexyliden(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylphenol | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 12 | 4-[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1-butenyl]phenol | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 13 | L-serine-O-phosphate | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 14 | LY-326449 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 15 | Phosphonothreonine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 16 | RO-316233 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 17 | Ro-32-0557 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 18 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophen-4-yl-methanol | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 19 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophene-4,5''-dicarbaldehyde | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 20 | [2,2':5',2'']Terthiophene-4-carbaldehyde | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: L-serine-O-phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of PKC-theta complexed with Staurosporine at 2A resolution | PDB:1XJD | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | Yes | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
IEDFILHKML
386 GKGSFGKVFL396 AEFKKTNQFF406 AIKALKKDVV416 LMDDDVECTM426 VEKRVLSLAW 436 EHPFLTHMFC446 TFQTKENLFF456 VMEYLNGGDL466 MYHIQSCHKF476 DLSRATFYAA 486 EIILGLQFLH496 SKGIVYRDLK506 LDNILLDKDG516 HIKIADFGMC526 KENMLGDAKT 536 NFCGTPDYIA547 PEILLGQKYN557 HSVDWWSFGV567 LLYEMLIGQS577 PFHGQDEEEL 587 FHSIRMDNPF597 YPRWLEKEAK607 DLLVKLFVRE617 PEKRLGVRGD627 IRQHPLFREI 637 NWEELERKEI647 DPQNMFRNFF696
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Phosphonothreonine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of PKC-theta complexed with Staurosporine at 2A resolution | PDB:1XJD | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.00 Å | Mutation | Yes | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
IEDFILHKML
386 GKGSFGKVFL396 AEFKKTNQFF406 AIKALKKDVV416 LMDDDVECTM426 VEKRVLSLAW 436 EHPFLTHMFC446 TFQTKENLFF456 VMEYLNGGDL466 MYHIQSCHKF476 DLSRATFYAA 486 EIILGLQFLH496 SKGIVYRDLK506 LDNILLDKDG516 HIKIADFGMC526 KENMLGDAKT 536 NFCGTPDYIA547 PEILLGQKYN557 HSVDWWSFGV567 LLYEMLIGQS577 PFHGQDEEEL 587 FHSIRMDNPF597 YPRWLEKEAK607 DLLVKLFVRE617 PEKRLGVRGD627 IRQHPLFREI 637 NWEELERKEI647 DPQNMFRNFF696
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
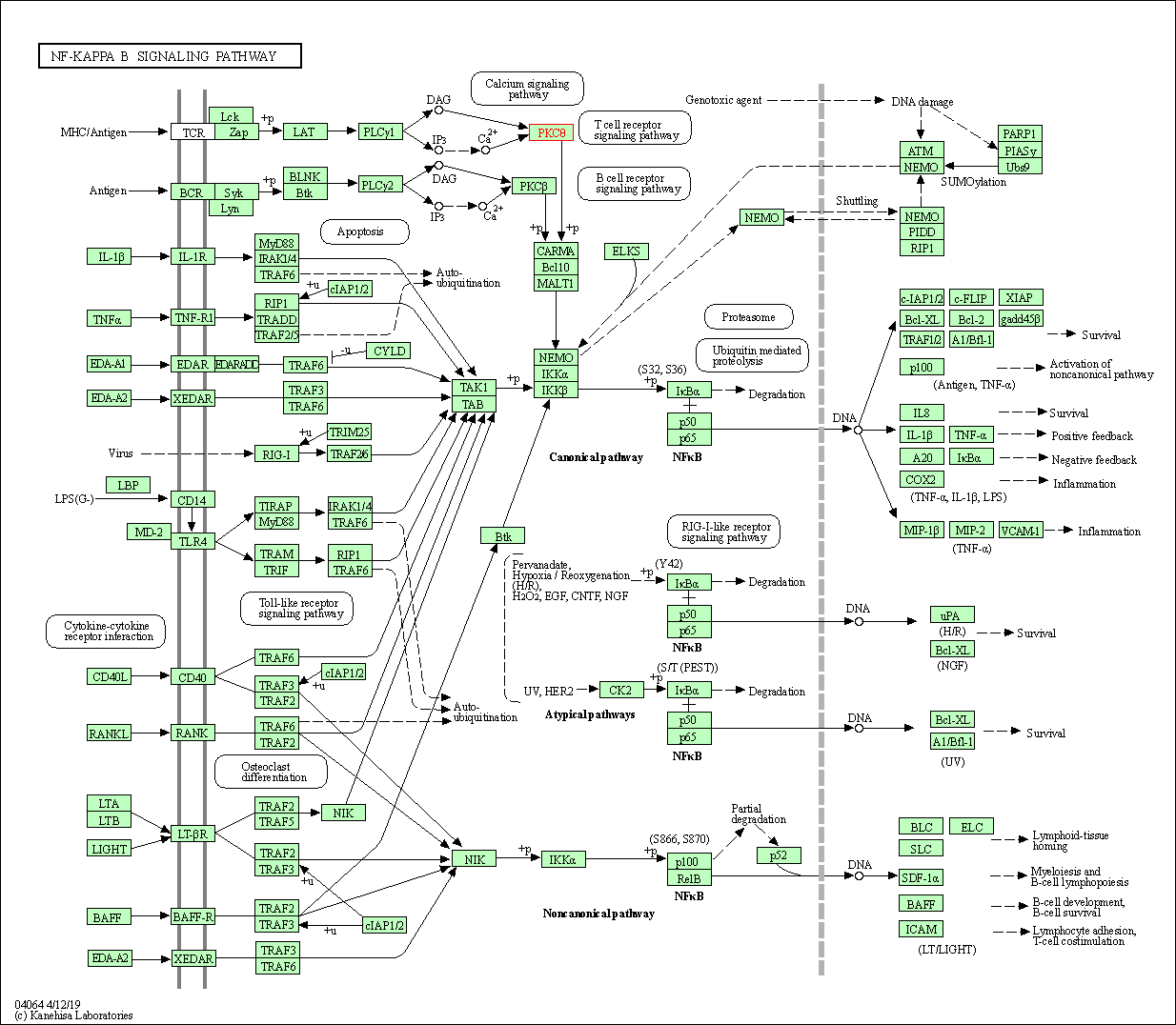
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
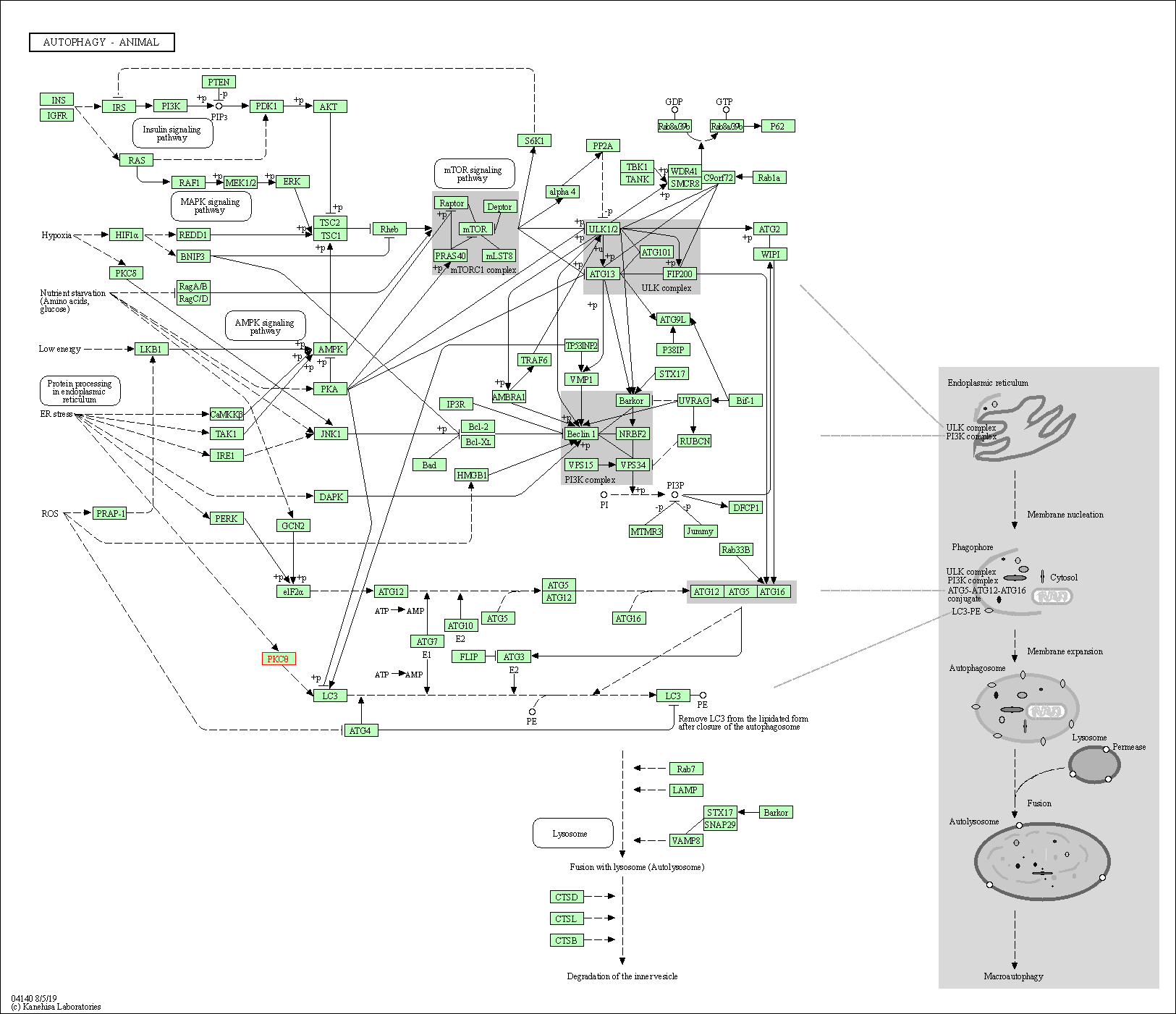
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
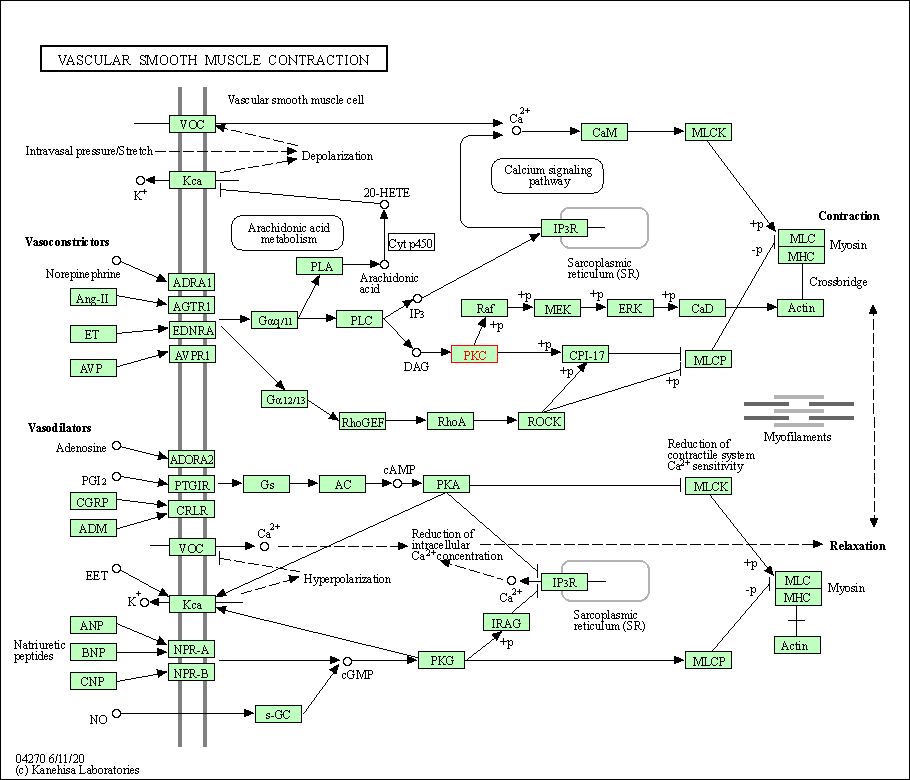
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
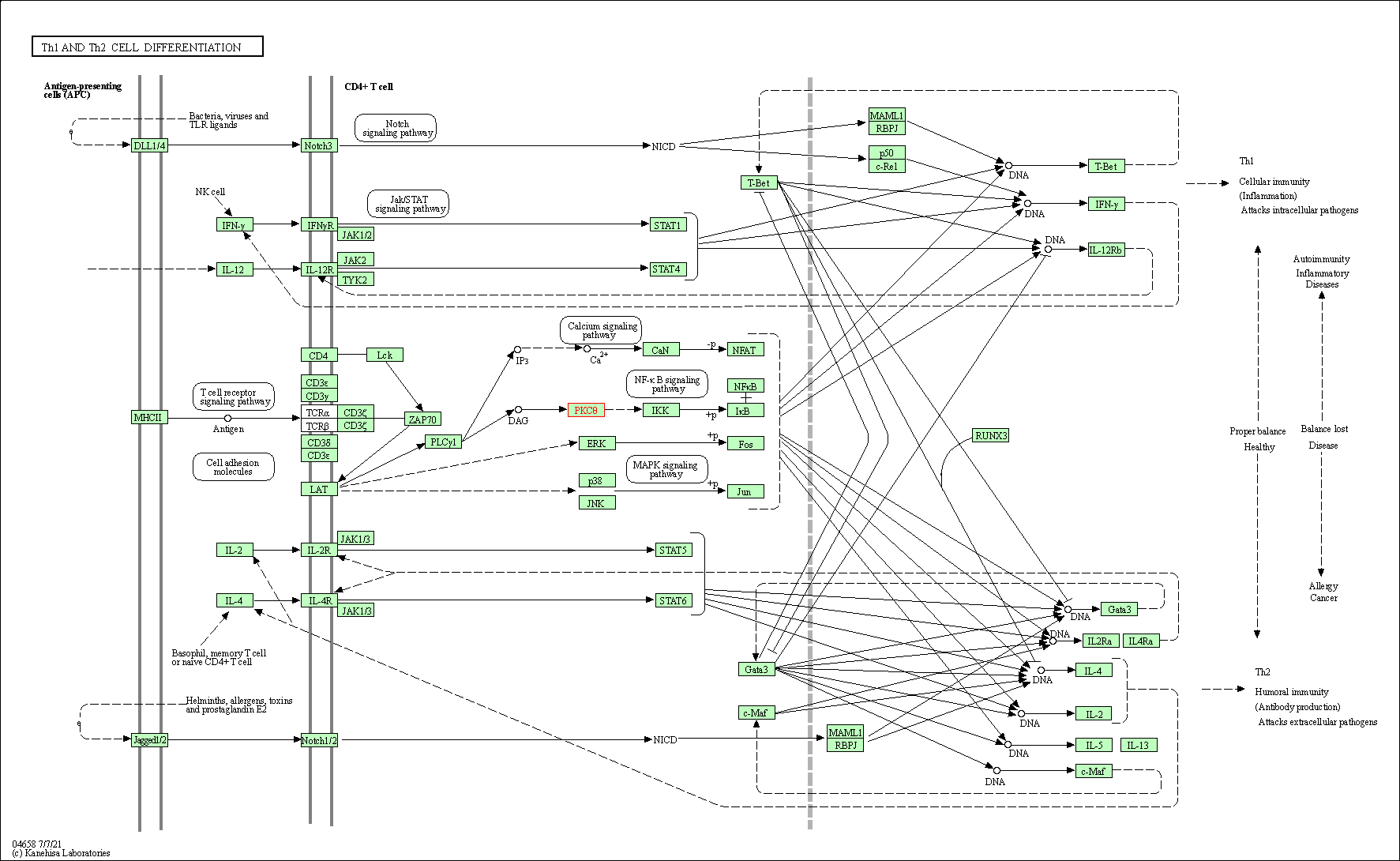
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
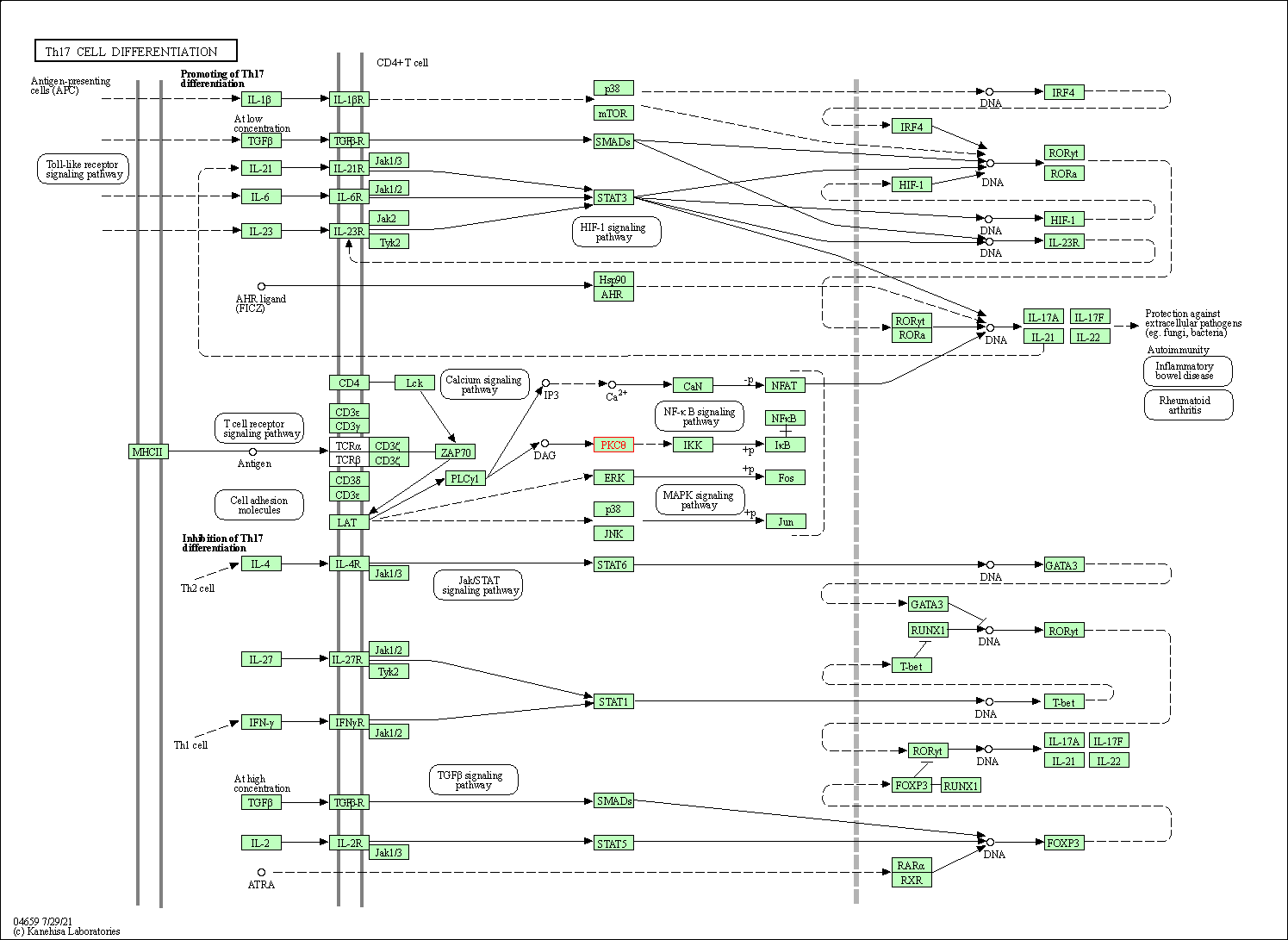
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
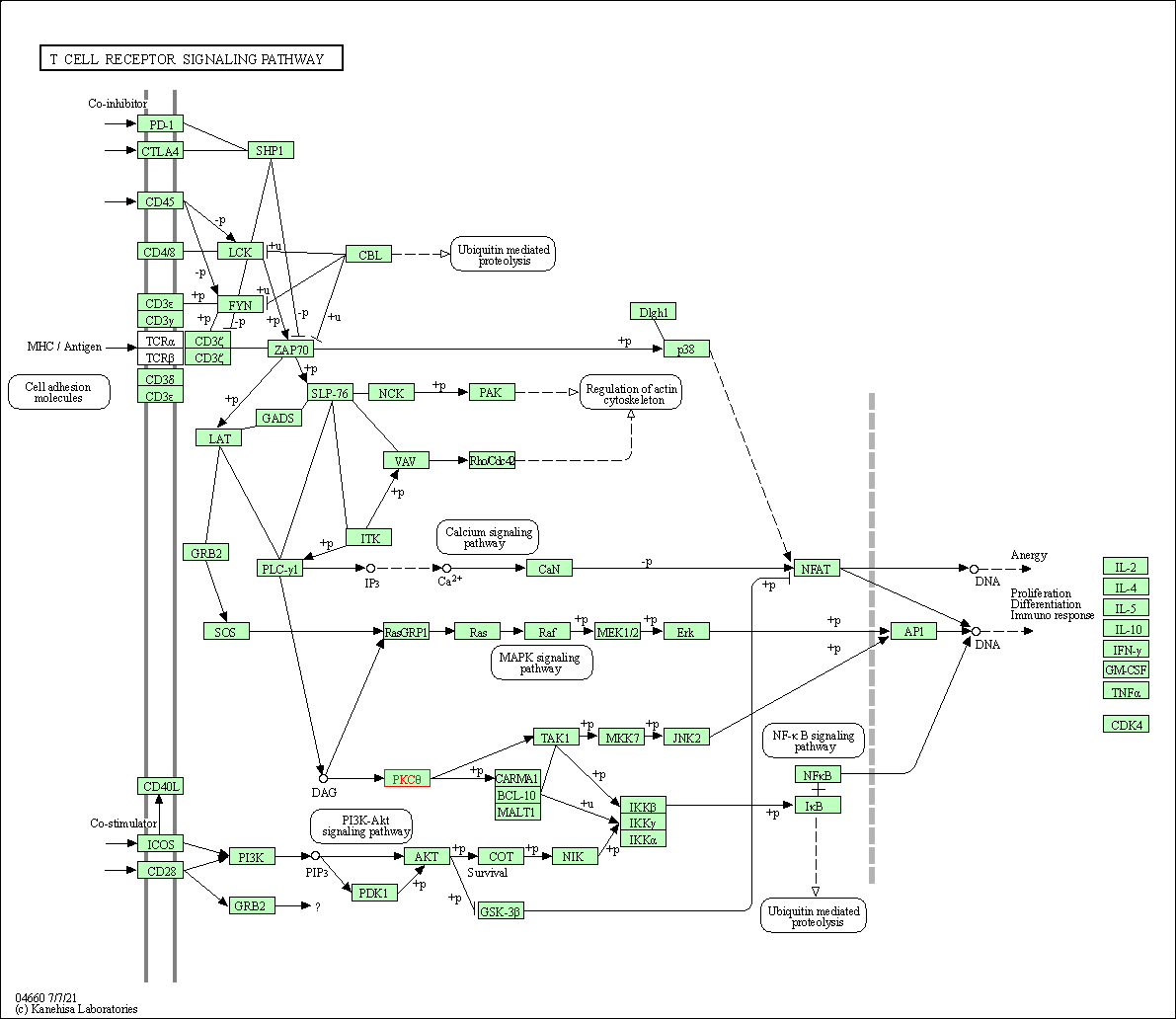
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
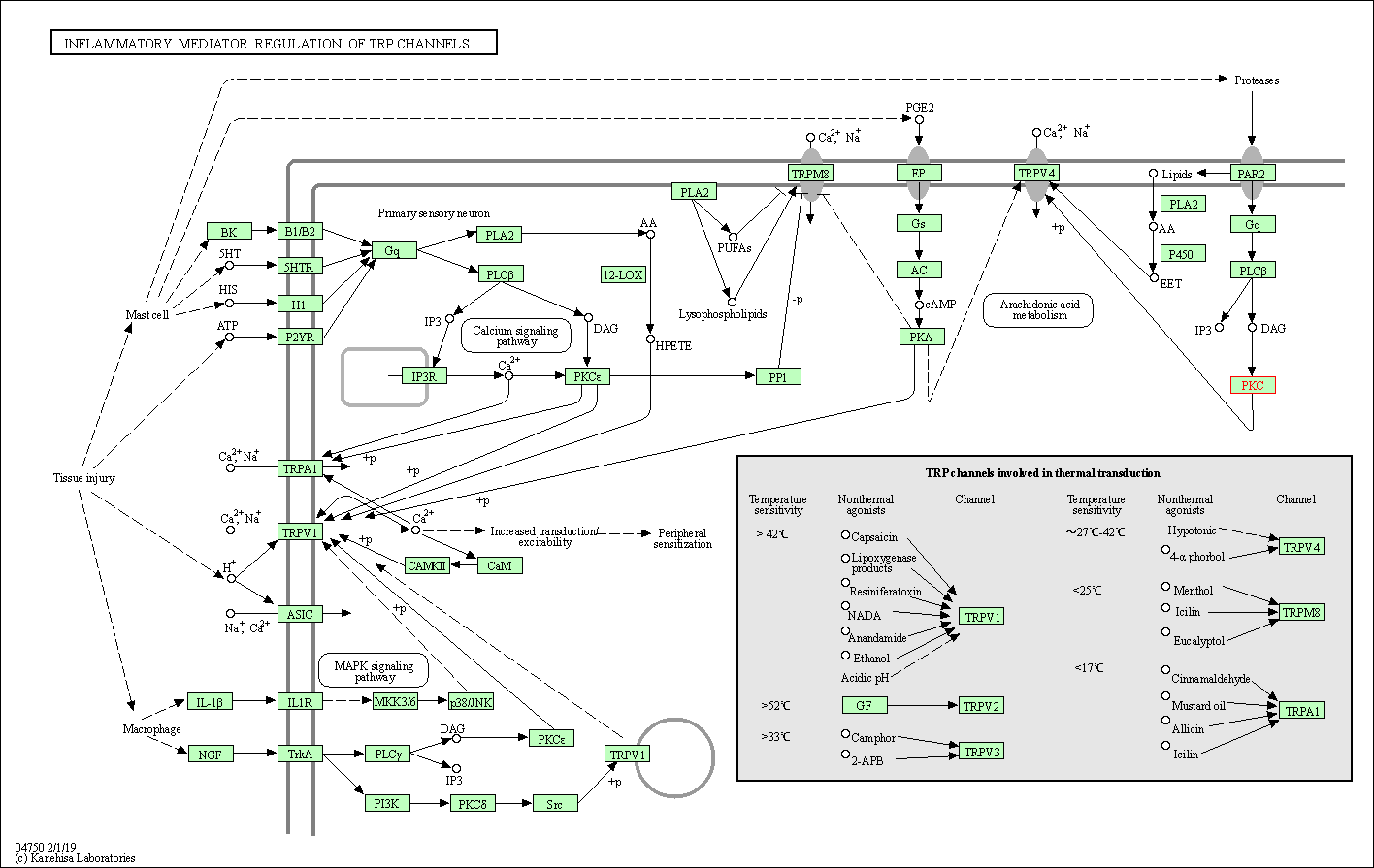
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
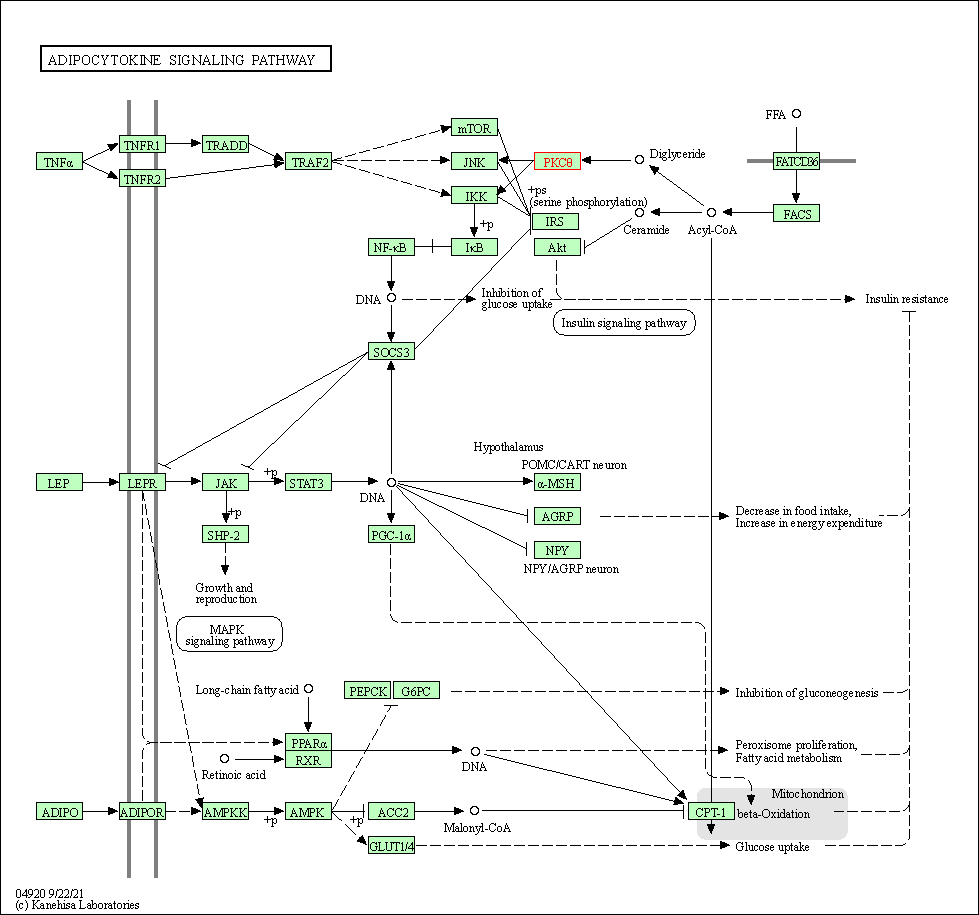
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 13 | Degree centrality | 1.40E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 1.04E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.22E-01 | Radiality | 1.39E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.08E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.44E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.52E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Emerging drugs for psoriasis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):145-63. | |||||
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025002) | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025002) | |||||
| REF 4 | Synthesis of bisindolylmaleimide macrocycles, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 5(18):2093-2096 (1995). | |||||
| REF 5 | Bisindolylmaleimide inhibitors of protein kinase C. Further conformational restriction of a tertiary amine side chain, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 4(11):1303-1308 (1994). | |||||
| REF 6 | Multivariate analysis by the minimum spanning tree method of the structural determinants of diphenylethylenes and triphenylacrylonitriles implicate... J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 7;35(3):573-83. | |||||
| REF 7 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 8 | (S)-13-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-10,11,14,15-tetrahydro-4,9:16, 21-dimetheno-1H, 13H-dibenzo[e,k]pyrrolo[3,4-h][1,4,13]oxadiazacyclohexadecene-1,3(2H... J Med Chem. 1996 Jul 5;39(14):2664-71. | |||||
| REF 9 | Inhibitors of protein kinase C. 1. 2,3-Bisarylmaleimides. J Med Chem. 1992 Jan;35(1):177-84. | |||||
| REF 10 | Novel protein kinase C inhibitors: synthesis and PKC inhibition of beta-substituted polythiophene derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999 Aug 2;9(15):2279-82. | |||||
| REF 11 | Catalytic domain crystal structure of protein kinase C-theta (PKCtheta). J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 26;279(48):50401-9. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

