Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T14030
(Former ID: TTDNR00740)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Ras-related protein Rab-7a (RAB7A)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
RAB7
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
RAB7A
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Literature-reported target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Governs early-to-late endosomal maturation, microtubule minus-end as well as plus-end directed endosomal migration and positioning, and endosome-lysosome transport through different protein-protein interaction cascades. Plays a central role, not only in endosomal traffic, but also in many other cellular and physiological events, such as growth-factor-mediated cell signaling, nutrient-transportor mediated nutrient uptake, neurotrophin transport in the axons of neurons and lipid metabolism. Also involved in regulation of some specialized endosomal membrane trafficking, such as maturation of melanosomes, pathogen-induced phagosomes (or vacuoles) and autophagosomes. Plays a role in the maturation and acidification of phagosomes that engulf pathogens, such as S. aureus and M. tuberculosis. Plays a role in the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes. Plays important roles in microbial pathogen infection and survival, as well as in participating in the life cycle of viruses. Microbial pathogens possess survival strategies governed by RAB7A, sometimes by employing RAB7A function (e. g. Salmonella) and sometimes by excluding RAB7A function (e. g. Mycobacterium). In concert with RAC1, plays a role in regulating the formation of RBs (ruffled borders) in osteoclasts. Controls the endosomal trafficking and neurite outgrowth signaling of NTRK1/TRKA. Regulates the endocytic trafficking of the EGF-EGFR complex by regulating its lysosomal degradation. Involved in the ADRB2-stimulated lipolysis through lipophagy, a cytosolic lipase-independent autophagic pathway. Required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan. Key regulator in endo-lysosomal trafficking.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Small GTPase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MTSRKKVLLKVIILGDSGVGKTSLMNQYVNKKFSNQYKATIGADFLTKEVMVDDRLVTMQ
IWDTAGQERFQSLGVAFYRGADCCVLVFDVTAPNTFKTLDSWRDEFLIQASPRDPENFPF VVLGNKIDLENRQVATKRAQAWCYSKNNIPYFETSAKEAINVEQAFQTIARNALKQETEV ELYNEFPEPIKLDKNDRAKASAESCSC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Guanosine-5'-Triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | crystal structure of human small GTPase Rab7(GTP) | PDB:1T91 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | Yes | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
VLLKVIILGD
16 SGVGKTSLMN26 QYVNKKFSNQ36 YKATIGADFL46 TKEVMVDDRL56 VTMQIWDTAG 66 LERFQSLGVA76 FYRGADCCVL86 VFDVTAPNTF96 KTLDSWRDEF106 LIQASPRDPE 116 NFPFVVLGNK126 IDLENRQVAT136 KRAQAWCYSK146 NNIPYFETSA156 KEAINVEQAF 166 QTIARNALKQ176 ETEVEL
|
|||||
|
|
GLY15
4.708
ASP16
3.717
SER17
2.777
GLY18
2.883
VAL19
3.450
GLY20
3.103
LYS21
2.748
THR22
2.952
SER23
2.945
PHE33
3.543
SER34
3.737
ASN35
3.484
GLN36
4.936
TYR37
2.593
LYS38
4.214
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Phosphoaminophosphonic acid-guanylate ester | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of GTP-bound L129F mutant Rab7 | PDB:3LAW | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.80 Å | Mutation | Yes | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
KVLLKVIILG
15 DSGVGKTSLM25 NQYVNKKFSN35 QYKATIGADF45 LTKEVMVDDR55 LVTMQIWDTA 65 GQERFQSLGV75 AFYRGADCCV85 LVFDVTAPNT95 FKTLDSWRDE105 FLIQASPRDP 115 ENFPFVVLGN125 KIDFENRQVA135 TKRAQAWCYS145 KNNIPYFETS155 AKEAINVEQA 165 FQTIARNALK175 QETEVEL
|
|||||
|
|
ASP16
3.437
SER17
3.128
GLY18
3.268
VAL19
3.231
GLY20
2.907
LYS21
2.753
THR22
2.616
SER23
2.683
PHE33
3.695
SER34
2.917
ASN35
3.025
GLN36
4.773
TYR37
3.359
LYS38
4.584
ALA39
3.981
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitophagy - animal | hsa04137 | Affiliated Target |
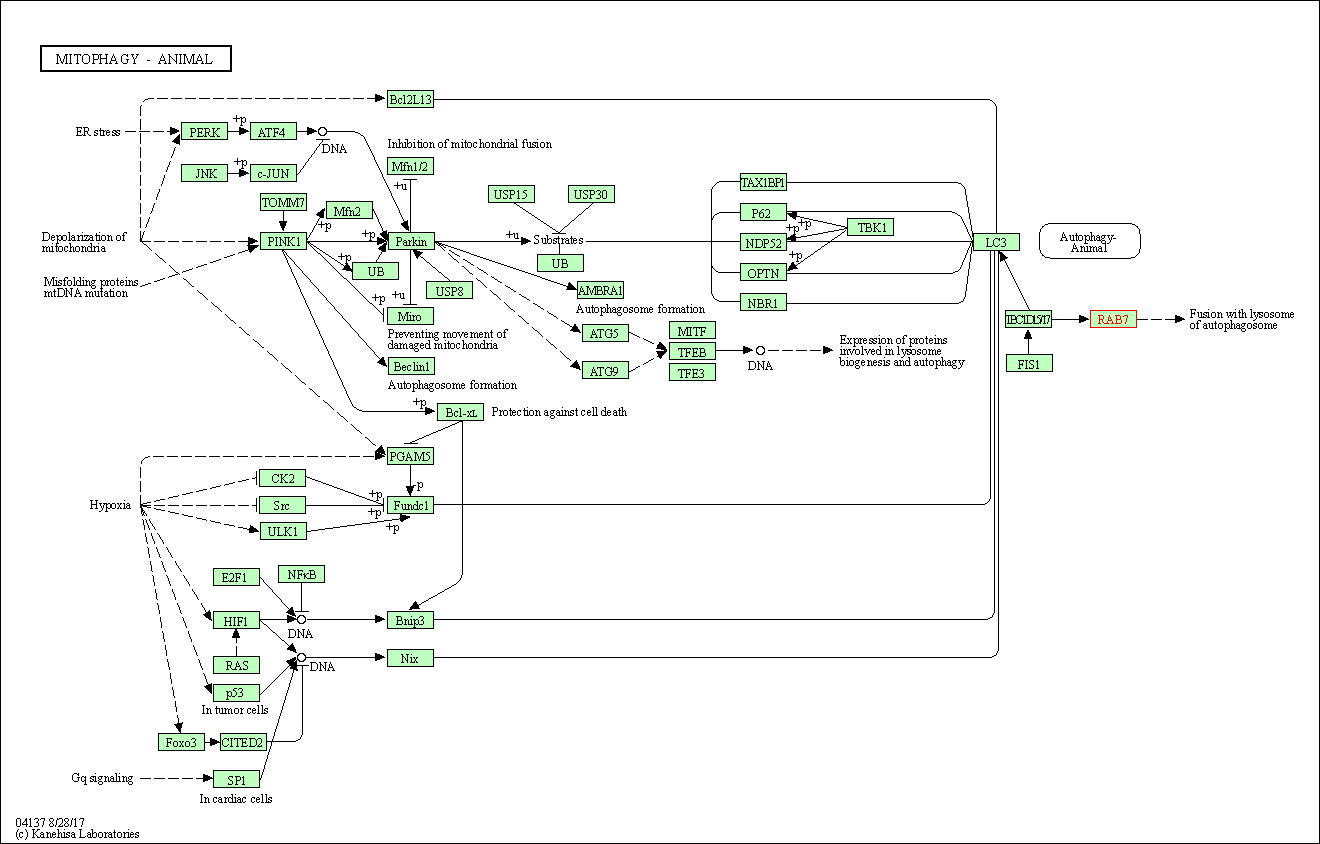
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |
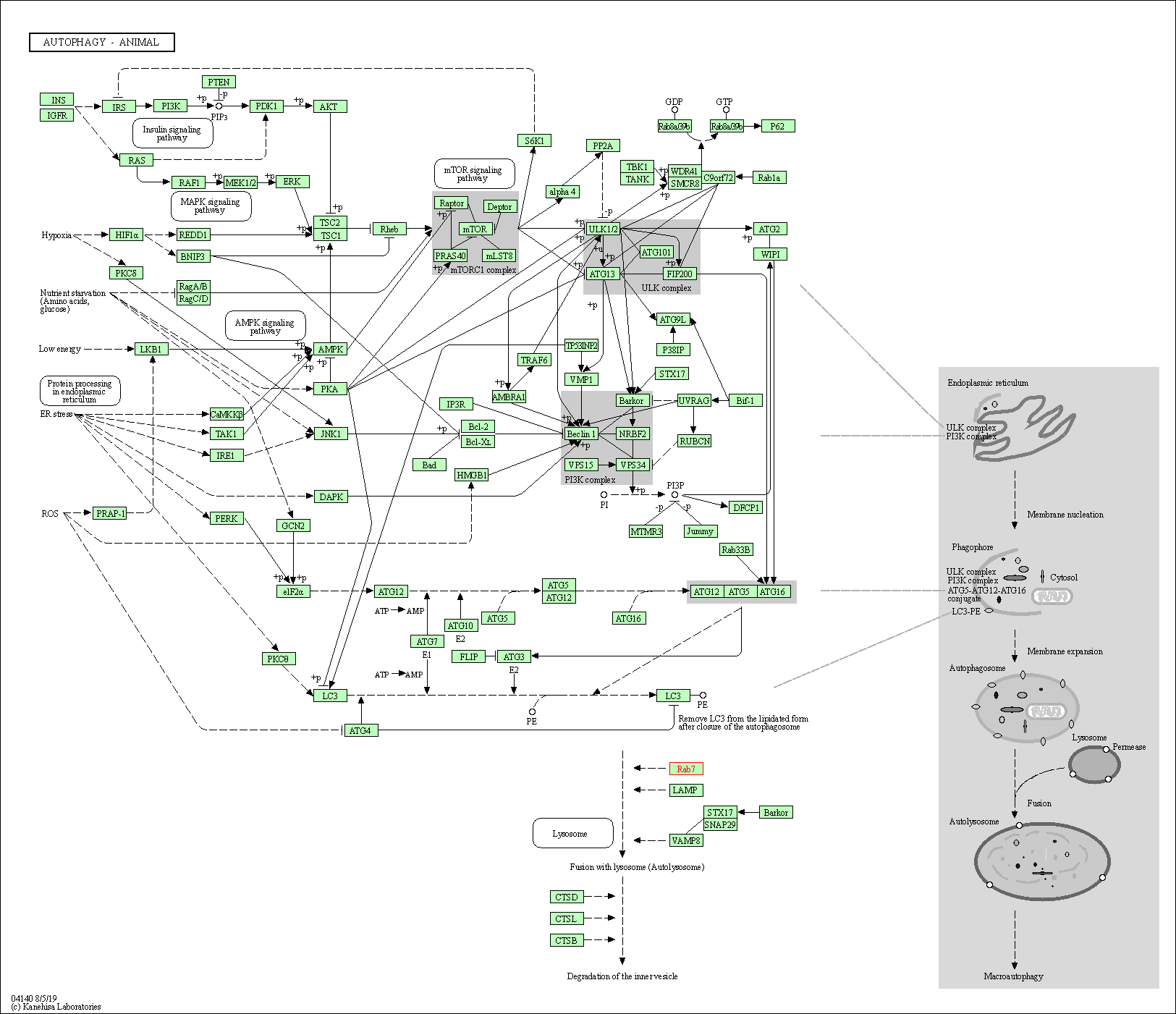
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Endocytosis | hsa04144 | Affiliated Target |
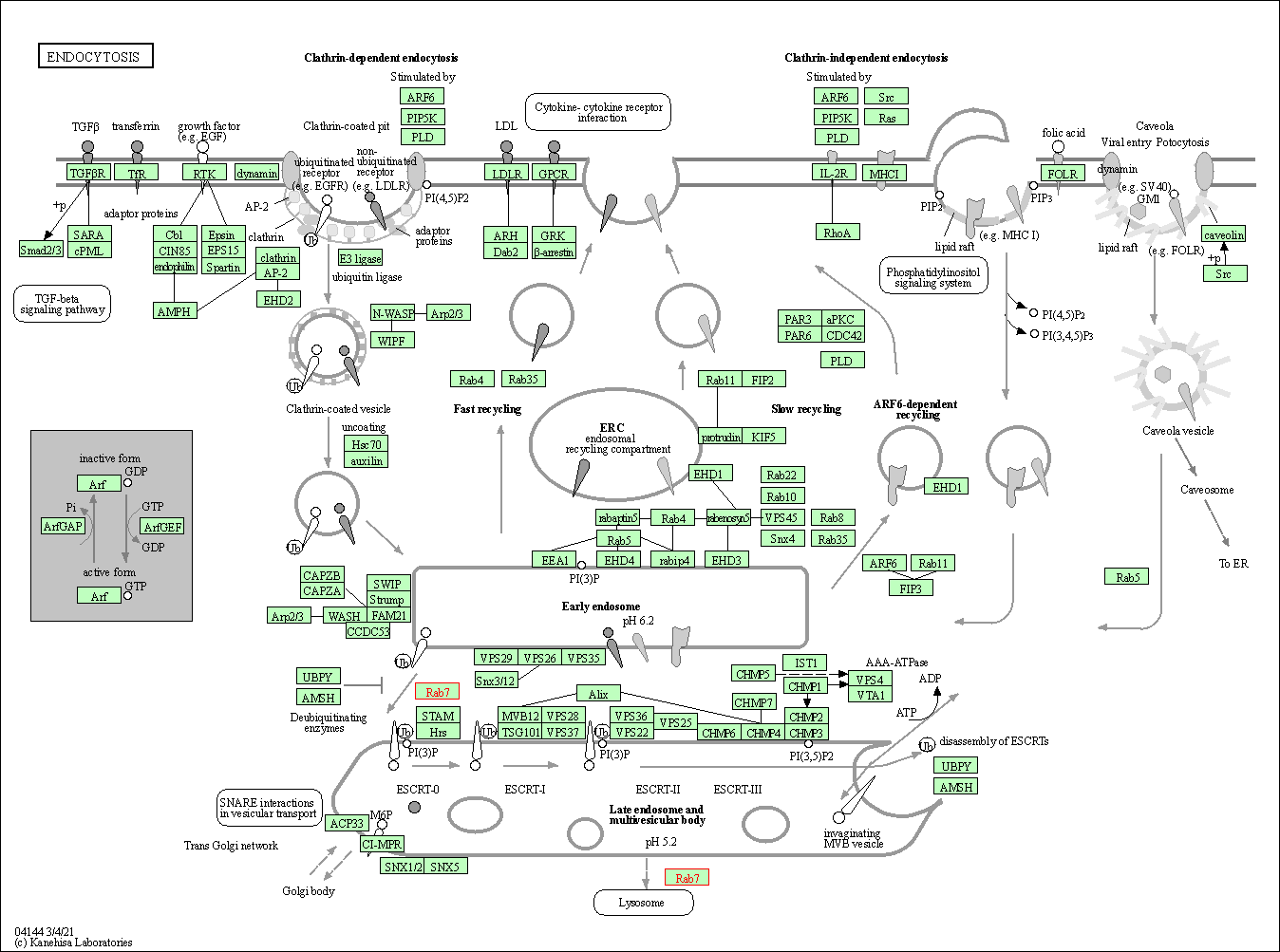
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phagosome | hsa04145 | Affiliated Target |
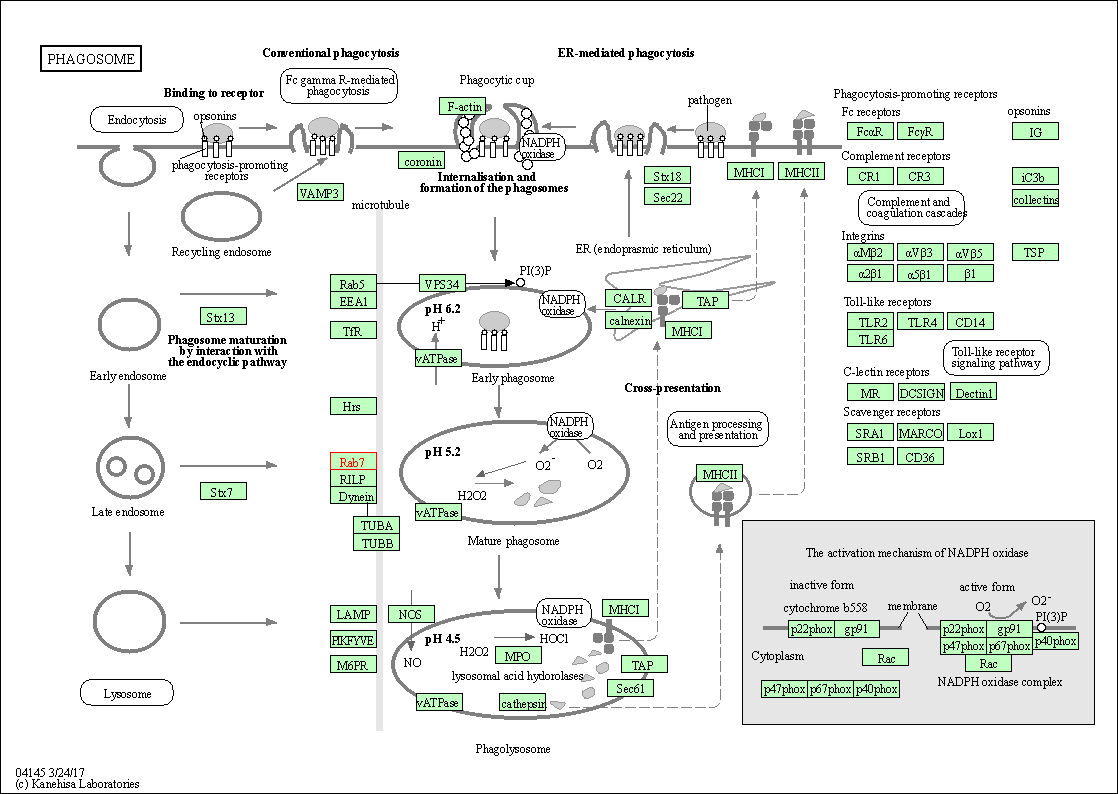
|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 27 | Degree centrality | 2.90E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.85E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.12E-01 | Radiality | 1.37E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 9.69E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 9.81E+00 | Topological coefficient | 6.92E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Modulation of RAB7A Protein Expression Determines Resistance to Cisplatin through Late Endocytic Pathway Impairment and Extracellular Vesicular Sec... Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 8;11(1). pii: E52. | |||||
| REF 2 | Structural basis for recruitment of RILP by small GTPase Rab7. EMBO J. 2005 Apr 20;24(8):1491-501. | |||||
| REF 3 | Disease mutations in Rab7 result in unregulated nucleotide exchange and inappropriate activation. Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Mar 15;19(6):1033-47. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

