Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T11487
(Former ID: TTDC00313)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (ACAT1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
T2; MAT; Acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, mitochondrial
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ACAT1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Adrenal cancer [ICD-11: 2D11] | |||||
| Function |
Plays a major role in ketone body metabolism.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Acyltransferase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.3.1.9
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MAVLAALLRSGARSRSPLLRRLVQEIRYVERSYVSKPTLKEVVIVSATRTPIGSFLGSLS
LLPATKLGSIAIQGAIEKAGIPKEEVKEAYMGNVLQGGEGQAPTRQAVLGAGLPISTPCT TINKVCASGMKAIMMASQSLMCGHQDVMVAGGMESMSNVPYVMNRGSTPYGGVKLEDLIV KDGLTDVYNKIHMGSCAENTAKKLNIARNEQDAYAINSYTRSKAAWEAGKFGNEVIPVTV TVKGQPDVVVKEDEEYKRVDFSKVPKLKTVFQKENGTVTAANASTLNDGAAALVLMTADA AKRLNVTPLARIVAFADAAVEPIDFPIAPVYAASMVLKDVGLKKEDIAMWEVNEAFSLVV LANIKMLEIDPQKVNINGGAVSLGHPIGMSGARIVGHLTHALKQGEYGLASICNGGGGAS AMLIQKL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T69CTT | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ATR-01 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Adrenocortical carcinoma | [1] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Benoxaprofen | Drug Info | Withdrawn from market | Inflammation | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 16 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ATR-01 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | PMID25470667-Compound-K-604 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 3 | Benoxaprofen | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | (Z)-2,6-diisopropyl-N-phenyloctadec-9-enamide | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | Nonanoic acid biphenyl-2-ylamide | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 6 | Octanoic acid biphenyl-2-ylamide | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 7 | PMID16242323C15a | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 8 | PMID16242323C15b | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 9 | PMID16242323C16 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 10 | PMID16242323C18a | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 11 | PMID16242323C18b | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 12 | PMID16242323C22c | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 13 | PMID16242323C22d | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 14 | PMID16242323C26a | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 15 | PMID16242323C26b | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 16 | PMID16242323C26c | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Coenzyme A | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystallographic and kinetic studies of human mitochondrial acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (T2): the importance of potassium and chloride for its structure and function | PDB:2IBY | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.85 Å | Mutation | Yes | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
PTLKEVVIVS
46 ATRTPIGSFL56 GSLSLLPATK66 LGSIAIQGAI76 EKAGIPKEEV86 KEAYMGNVLQ 96 GGEGQAPTRQ106 AVLGAGLPIS116 TPCTTINKVA127 SGMKAIMMAS137 QSLMCGHQDV 147 MVAGGMESMS157 NVPYVMNRGS167 TPYGGVKLED177 LIVKDGLTDV187 YNKIHMGSCA 197 ENTAKKLNIA207 RNEQDAYAIN217 SYTRSKAAWE227 AGKFGNEVIP237 VTVTVKGQPD 247 VVVKEDEEYK257 RVDFSKVPKL267 KTVFQKENGT277 VTAANASTLN287 DGAAALVLMT 297 ADAAKRLNVT307 PLARIVAFAD317 AAVEPIDFPI327 APVYAASMVL337 KDVGLKKEDI 347 AMWEVNEAFS357 LVVLANIKML367 EIDPQKVNIN377 GGAVSLGHPI387 GMSGARIVGH 397 LTHALKQGEY407 GLASICNGGG417 GASAMLIQKL427
|
|||||
|
|
LEU184
3.456
HIS192
3.588
MET193
3.778
GLY194
4.942
TYR219
2.935
ARG258
3.463
VAL259
3.370
ASP260
3.165
LYS263
2.741
VAL264
3.730
LEU267
3.368
VAL270
3.592
PHE271
3.838
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: Cysteine Sulfenic Acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystallographic and kinetic studies of human mitochondrial acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (T2): the importance of potassium and chloride for its structure and function | PDB:2IBY | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.85 Å | Mutation | Yes | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
PTLKEVVIVS
46 ATRTPIGSFL56 GSLSLLPATK66 LGSIAIQGAI76 EKAGIPKEEV86 KEAYMGNVLQ 96 GGEGQAPTRQ106 AVLGAGLPIS116 TPCTTINKVA127 SGMKAIMMAS137 QSLMCGHQDV 147 MVAGGMESMS157 NVPYVMNRGS167 TPYGGVKLED177 LIVKDGLTDV187 YNKIHMGSCA 197 ENTAKKLNIA207 RNEQDAYAIN217 SYTRSKAAWE227 AGKFGNEVIP237 VTVTVKGQPD 247 VVVKEDEEYK257 RVDFSKVPKL267 KTVFQKENGT277 VTAANASTLN287 DGAAALVLMT 297 ADAAKRLNVT307 PLARIVAFAD317 AAVEPIDFPI327 APVYAASMVL337 KDVGLKKEDI 347 AMWEVNEAFS357 LVVLANIKML367 EIDPQKVNIN377 GGAVSLGHPI387 GMSGARIVGH 397 LTHALKQGEY407 GLASICNGGG417 GASAMLIQKL427
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid degradation | hsa00071 | Affiliated Target |
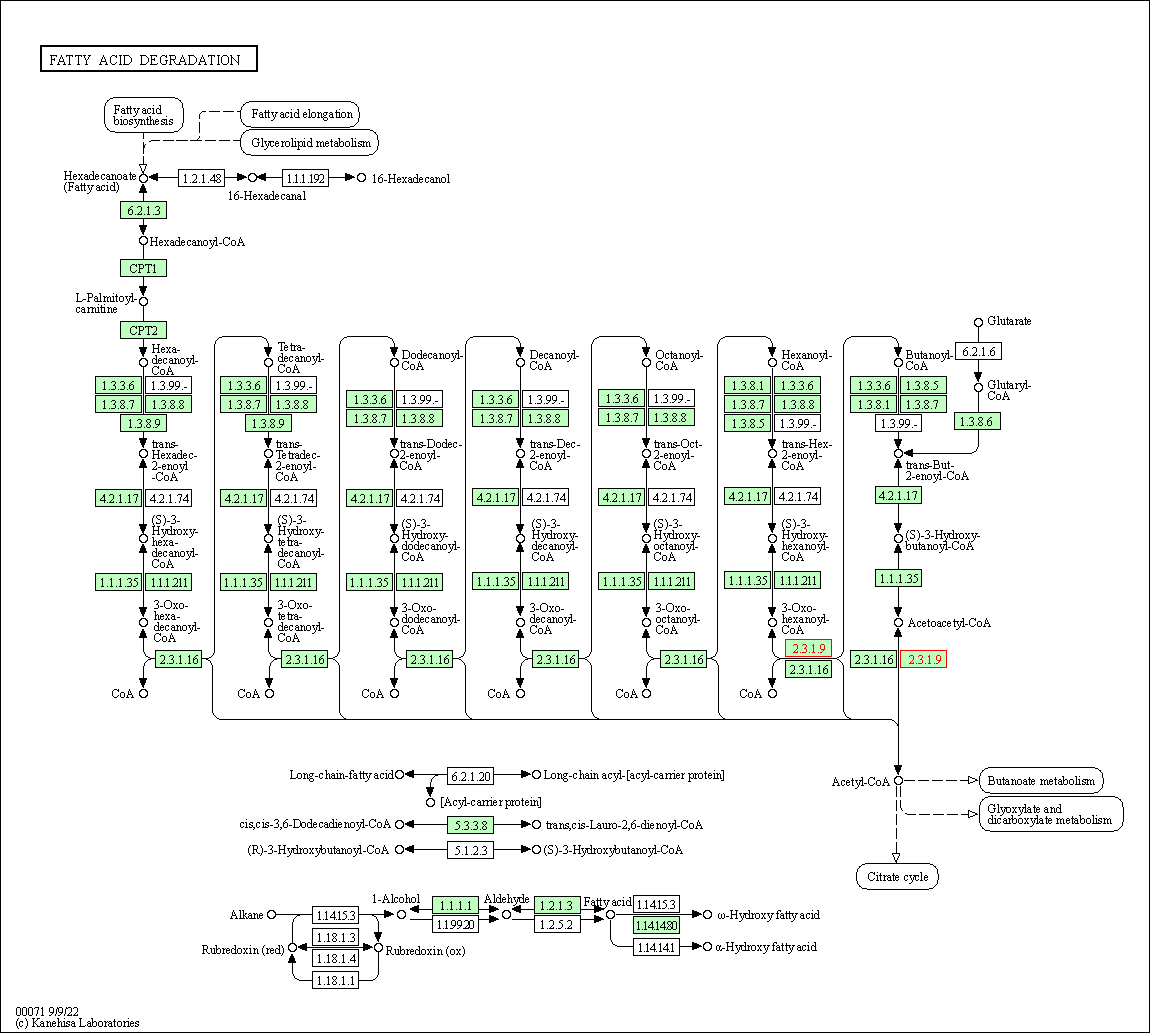
|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | hsa00280 | Affiliated Target |
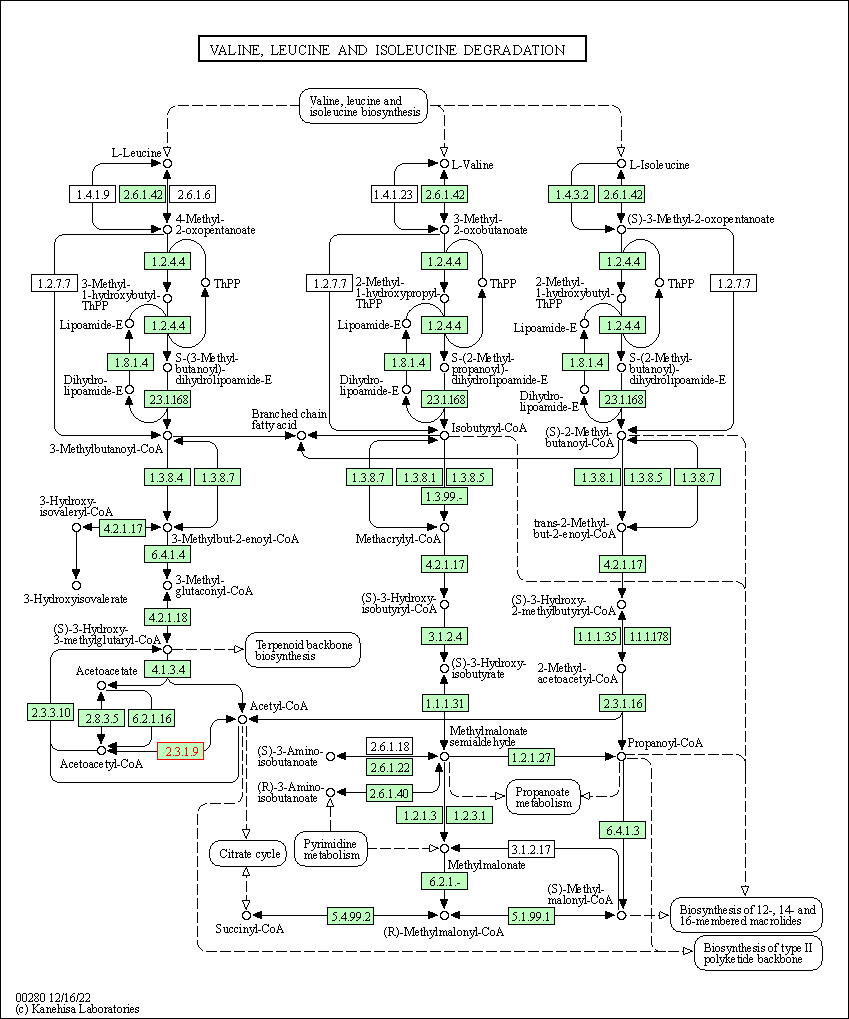
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Lysine degradation | hsa00310 | Affiliated Target |
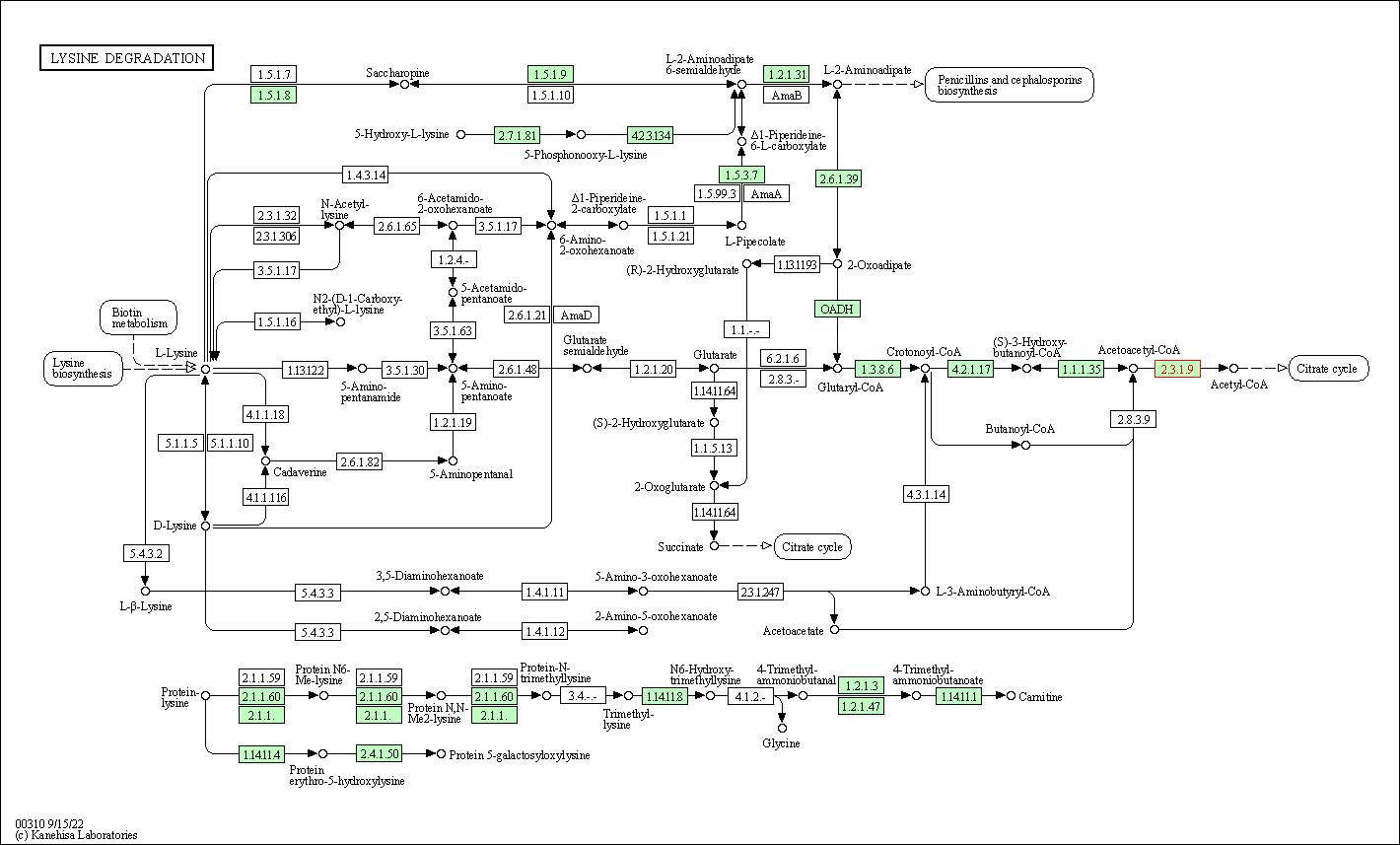
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Tryptophan metabolism | hsa00380 | Affiliated Target |
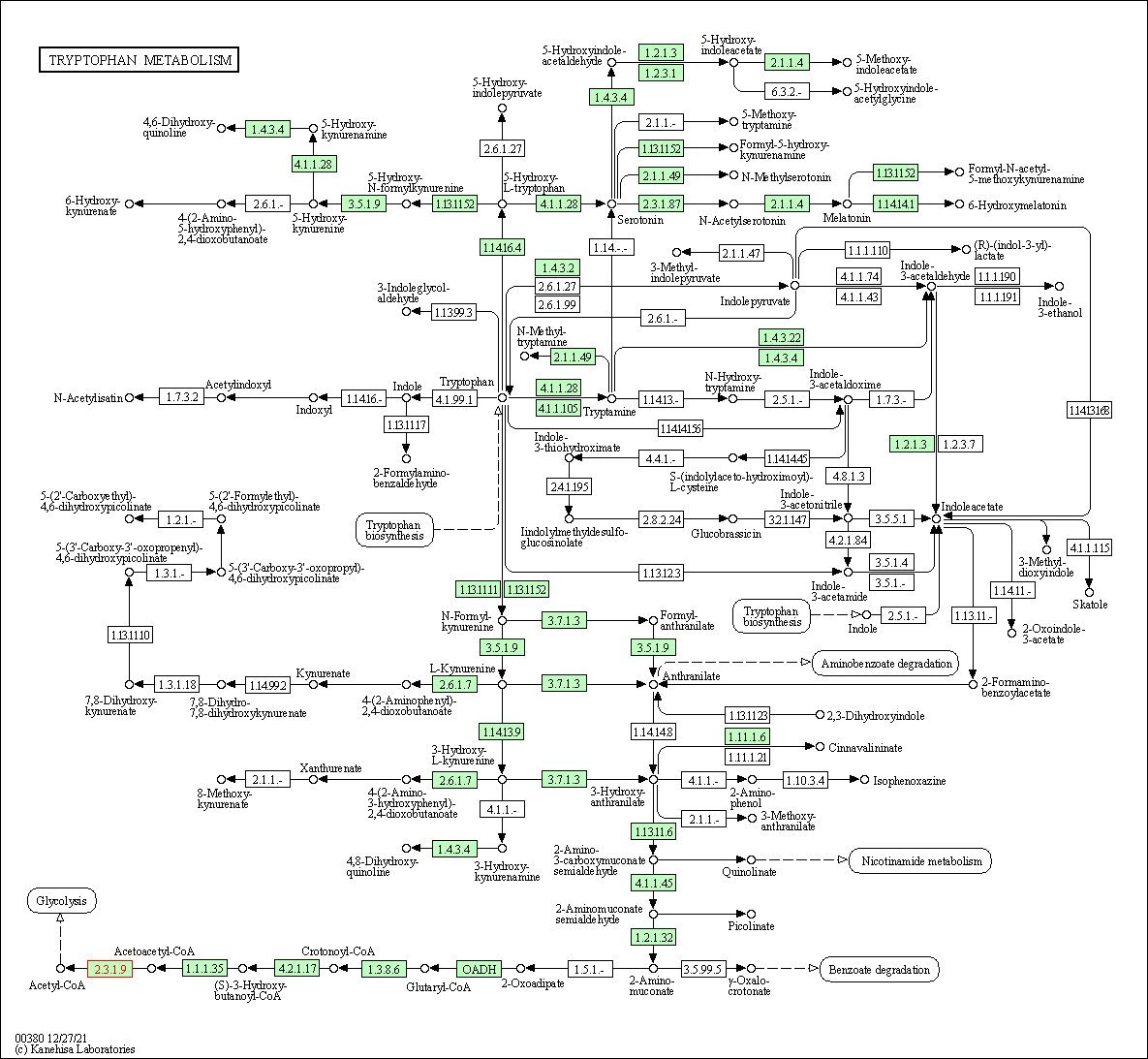
|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Pyruvate metabolism | hsa00620 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | hsa00630 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Butanoate metabolism | hsa00650 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | hsa00900 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fat digestion and absorption | hsa04975 | Affiliated Target |
|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 13 | Degree centrality | 1.40E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 5.40E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.80E-01 | Radiality | 1.30E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.69E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.56E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.48E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 2 | Benoxaprofen: side-effect profile in 300 patients. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1982 May 8;284(6326):1365-8. | |||||
| REF 3 | Acyltransferase inhibitors: a patent review (2010-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015 Feb;25(2):145-58. | |||||
| REF 4 | Inhibition of lyso-PAF: acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase by salicylates and other compounds. Prostaglandins. 1988 Jun;35(6):939-44. | |||||
| REF 5 | Biphenyl versus phenylpyridazine derivatives: the role of the heterocycle in a series of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyl transferase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2008 Mar 13;51(5):1474-7. | |||||
| REF 6 | Synthesis and biological activity of novel 4-phenyl-1,8-naphthyridin-2(1H)-on-3-yl ureas: potent acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor wit... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Jan 1;16(1):44-8. | |||||
| REF 7 | Crystallographic and kinetic studies of human mitochondrial acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase: the importance of potassium and chloride ions for its structure and function. Biochemistry. 2007 Apr 10;46(14):4305-21. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

