Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T08922
(Former ID: TTDS00357)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 (ACACB)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase beta; Acetyl CoA carboxylase beta; ACCbeta; ACC2; ACC-beta; ACACB
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ACACB
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the ATP-dependent carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Carries out three functions: biotin carboxyl carrier protein, biotin carboxylase and carboxyltransferase. Involved in inhibition of fatty acid and glucose oxidation and enhancement of fat storage. May play a role in regulation of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation through malonyl- CoA-dependent inhibition of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Carbon-carbon ligase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 6.4.1.2
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MVLLLCLSCLIFSCLTFSWLKIWGKMTDSKPITKSKSEANLIPSQEPFPASDNSGETPQR
NGEGHTLPKTPSQAEPASHKGPKDAGRRRNSLPPSHQKPPRNPLSSSDAAPSPELQANGT GTQGLEATDTNGLSSSARPQGQQAGSPSKEDKKQANIKRQLMTNFILGSFDDYSSDEDSV AGSSRESTRKGSRASLGALSLEAYLTTGEAETRVPTMRPSMSGLHLVKRGREHKKLDLHR DFTVASPAEFVTRFGGDRVIEKVLIANNGIAAVKCMRSIRRWAYEMFRNERAIRFVVMVT PEDLKANAEYIKMADHYVPVPGGPNNNNYANVELIVDIAKRIPVQAVWAGWGHASENPKL PELLCKNGVAFLGPPSEAMWALGDKIASTVVAQTLQVPTLPWSGSGLTVEWTEDDLQQGK RISVPEDVYDKGCVKDVDEGLEAAERIGFPLMIKASEGGGGKGIRKAESAEDFPILFRQV QSEIPGSPIFLMKLAQHARHLEVQILADQYGNAVSLFGRDCSIQRRHQKIVEEAPATIAP LAIFEFMEQCAIRLAKTVGYVSAGTVEYLYSQDGSFHFLELNPRLQVEHPCTEMIADVNL PAAQLQIAMGVPLHRLKDIRLLYGESPWGVTPISFETPSNPPLARGHVIAARITSENPDE GFKPSSGTVQELNFRSSKNVWGYFSVAATGGLHEFADSQFGHCFSWGENREEAISNMVVA LKELSIRGDFRTTVEYLINLLETESFQNNDIDTGWLDYLIAEKVQAEKPDIMLGVVCGAL NVADAMFRTCMTDFLHSLERGQVLPADSLLNLVDVELIYGGVKYILKVARQSLTMFVLIM NGCHIEIDAHRLNDGGLLLSYNGNSYTTYMKEEVDSYRITIGNKTCVFEKENDPTVLRSP SAGKLTQYTVEDGGHVEAGSSYAEMEVMKMIMTLNVQERGRVKYIKRPGAVLEAGCVVAR LELDDPSKVHPAEPFTGELPAQQTLPILGEKLHQVFHSVLENLTNVMSGFCLPEPVFSIK LKEWVQKLMMTLRHPSLPLLELQEIMTSVAGRIPAPVEKSVRRVMAQYASNITSVLCQFP SQQIATILDCHAATLQRKADREVFFINTQSIVQLVQRYRSGIRGYMKTVVLDLLRRYLRV EHHFQQAHYDKCVINLREQFKPDMSQVLDCIFSHAQVAKKNQLVIMLIDELCGPDPSLSD ELISILNELTQLSKSEHCKVALRARQILIASHLPSYELRHNQVESIFLSAIDMYGHQFCP ENLKKLILSETTIFDVLPTFFYHANKVVCMASLEVYVRRGYIAYELNSLQHRQLPDGTCV VEFQFMLPSSHPNRMTVPISITNPDLLRHSTELFMDSGFSPLCQRMGAMVAFRRFEDFTR NFDEVISCFANVPKDTPLFSEARTSLYSEDDCKSLREEPIHILNVSIQCADHLEDEALVP ILRTFVQSKKNILVDYGLRRITFLIAQEKEFPKFFTFRARDEFAEDRIYRHLEPALAFQL ELNRMRNFDLTAVPCANHKMHLYLGAAKVKEGVEVTDHRFFIRAIIRHSDLITKEASFEY LQNEGERLLLEAMDELEVAFNNTSVRTDCNHIFLNFVPTVIMDPFKIEESVRYMVMRYGS RLWKLRVLQAEVKINIRQTTTGSAVPIRLFITNESGYYLDISLYKEVTDSRSGNIMFHSF GNKQGPQHGMLINTPYVTKDLLQAKRFQAQTLGTTYIYDFPEMFRQALFKLWGSPDKYPK DILTYTELVLDSQGQLVEMNRLPGGNEVGMVAFKMRFKTQEYPEGRDVIVIGNDITFRIG SFGPGEDLLYLRASEMARAEGIPKIYVAANSGARIGMAEEIKHMFHVAWVDPEDPHKGFK YLYLTPQDYTRISSLNSVHCKHIEEGGESRYMITDIIGKDDGLGVENLRGSGMIAGESSL AYEEIVTISLVTCRAIGIGAYLVRLGQRVIQVENSHIILTGASALNKVLGREVYTSNNQL GGVQIMHYNGVSHITVPDDFEGVYTILEWLSYMPKDNHSPVPIITPTDPIDREIEFLPSR APYDPRWMLAGRPHPTLKGTWQSGFFDHGSFKEIMAPWAQTVVTGRARLGGIPVGVIAVE TRTVEVAVPADPANLDSEAKIIQQAGQVWFPDSAYKTAQAVKDFNREKLPLMIFANWRGF SGGMKDMYDQVLKFGAYIVDGLRQYKQPILIYIPPYAELRGGSWVVIDATINPLCIEMYA DKESRGGVLEPEGTVEIKFRKKDLIKSMRRIDPAYKKLMEQLGEPDLSDKDRKDLEGRLK AREDLLLPIYHQVAVQFADFHDTPGRMLEKGVISDILEWKTARTFLYWRLRRLLLEDQVK QEILQASGELSHVHIQSMLRRWFVETEGAVKAYLWDNNQVVVQWLEQHWQAGDGPRSTIR ENITYLKHDSVLKTIRGLVEENPEVAVDCVIYLSQHISPAERAQVVHLLSTMDSPAST Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Metformin | Drug Info | Approved | Type-2 diabetes | [2] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PF-05175157 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Type-2 diabetes | [3] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Axokine | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 3 | Obesity | [4] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Activator | [+] 1 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Metformin | Drug Info | [1], [5] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 8 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | PF-05175157 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | Axokine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 3 | 2-[4-(2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)Phenoxy]Propanoic Acid | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 4 | A-80040 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 5 | AC-8632 | Drug Info | [6], [10] | |||
| 6 | CP-640186 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 7 | QLT-091382 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 8 | Soraphen A | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: CP-640186 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human ACC2 CT domain with CP-640186 | PDB:3FF6 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.19 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
PYVTKDLLQA
1704 KRFQAQTLGT1714 TYIYDFPEMF1724 RQALFKLWGS1734 PDKYPKDILT1744 YTELVLDSQG 1754 QLVEMNRLPG1764 GNEVGMVAFK1774 MRFKTQEYPE1784 GRDVIVIGND1794 ITFRIGSFGP 1804 GEDLLYLRAS1814 EMARAEGIPK1824 IYVAANSGAR1834 IGMAEEIKHM1844 FHVAWVDPED 1854 PHKGFKYLYL1864 TPQDYTRISS1874 LNSVHCKHIE1884 EGGESRYMIT1894 DIIGKDDGLG 1904 VENLRGSGMI1914 AGESSLAYEE1924 IVTISLVTCR1934 AIGIGAYLVR1944 LGQRVIQVEN 1954 SHIILTGASA1964 LNKVLGREVY1974 TSNNQLGGVQ1984 IMHYNGVSHI1994 TVPDDFEGVY 2004 TILEWLSYMP2014 KDNHSPVPII2024 TPTDPIDREI2034 EFLPSRAPYD2044 PRWMLAGRPH 2054 PTLKGTWQSG2064 FFDHGSFKEI2074 MAPWAQTVVT2084 GRARLGGIPV2094 GVIAVETRTV 2104 EVAVPADPAN2114 LDSEAKIIQQ2124 AGQVWFPDSA2134 YKTAQAIKDF2144 NREKLPLMIF 2154 ANWRGFSGGM2164 KDMYDQVLKF2174 GAYIVDGLRQ2184 YKQPILIYIP2194 PYAELRGGSW 2204 VVIDATINPL2214 CIEMYADKES2224 RGGVLEPEGT2234 VEIKFRKKDL2244 IKSMRRIDPA 2254 YKKLMEQLGE2264 PDLSDKDRKD2274 LEGRLKARED2284 LLLPIYHQVA2294 VQFADFHDTP 2304 GRMLEKGVIS2314 DILEWKTART2324 FLYWRLRRLL2334 LEDQVKQEIL2344 QASGELSHVH 2354 IQSMLRRWFV2364 ETEGAVKAYL2374 WDNNQVVVQW2384 LEQHWQRSTI2399 RENITYLKHD 2409 SVLKTIRGLV2419 EENPEVAVDC2429 VIYLSQHISP2439 AERAQVVHLL2449 |
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Soraphen A | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | The biotin carboxylase (BC) domain of human Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 2 (ACC2) in complex with Soraphen A | PDB:3GID | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | No | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
DFTVASPAEF
250 VTRFGGDRVI260 EKVLIANNGI270 AAVKCMRSIR280 RWAYEMFRNE290 RAIRFVVMVT 300 PEDLKANAEY310 IKMADHYVPV320 PGGPNNNNYA330 NVELIVDIAK340 RIPVQAVWAG 350 WGHASENPKL360 PELLCKNGVA370 FLGPPSEAMW380 ALGDKIASTV390 VAQTLQVPTL 400 PWSGSGLTVE410 KGCVKDVDEG440 LEAAERIGFP450 LMIKASEGKG463 IRKAESAEDF 473 PILFRQVQSE483 IPGSPIFLMK493 LAQHARHLEV503 QILADQYGNA513 VSLFGRDCSI 523 QHQKIVEEAP535 ATIAPLAIFE545 FMEQCAIRLA555 KTVGYVSAGT565 VEYLYSQDGS 575 FHFLELNPRL585 QVEHPCTEMI595 ADVNLPAAQL605 QIAMGVPLHR615 LKDIRLLYGE 625 SPWGVTPISF635 ETPSNPPLAR645 GHVIAARITS655 GTVQELNFRS676 SKNVWGYFSV 686 ASQFGHCFSW706 GENREEAISN716 MVVALKELSI726 RTTVEYLINL740 LETESFQNND 750
|
|||||
|
|
ILE270
4.291
VAL273
3.987
LYS274
3.101
ARG277
2.806
SER278
2.637
ARG281
3.652
PRO590
3.738
CYS591
4.698
GLU593
2.680
MET594
3.592
ASP597
3.950
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty acid biosynthesis | hsa00061 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Pyruvate metabolism | hsa00620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Propanoate metabolism | hsa00640 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| AMPK signaling pathway | hsa04152 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
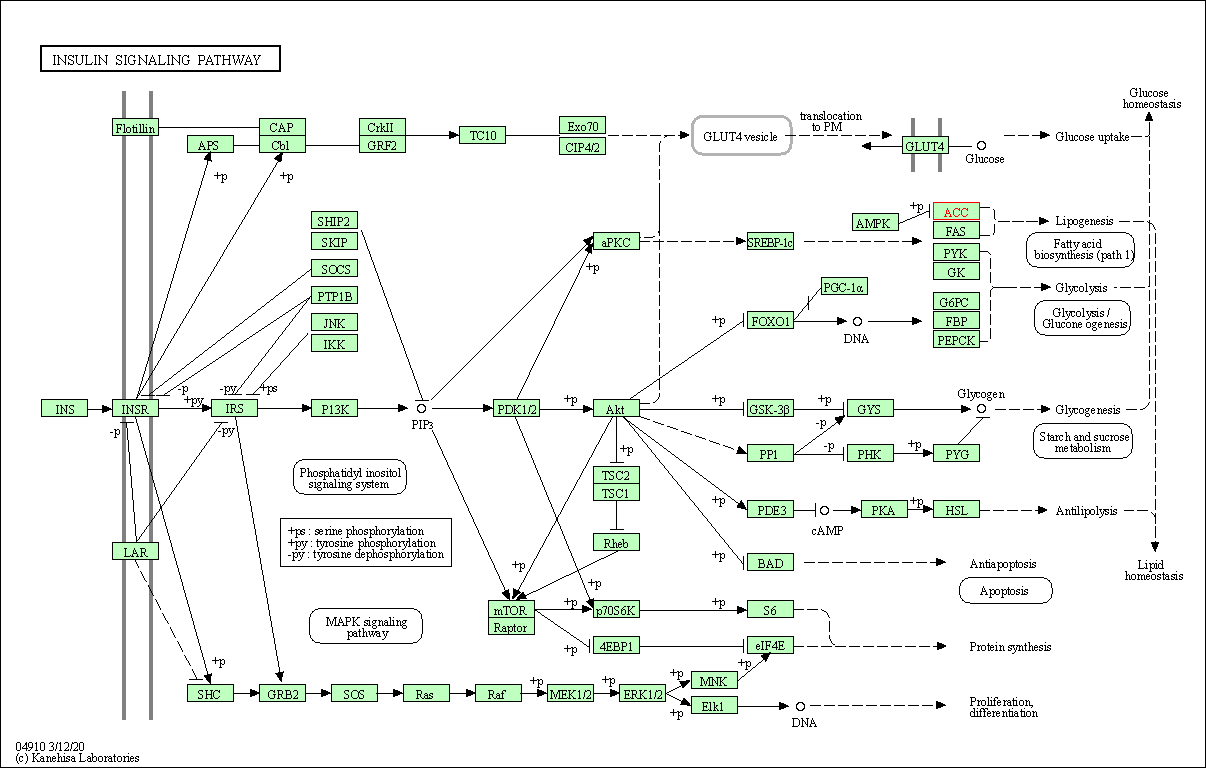
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
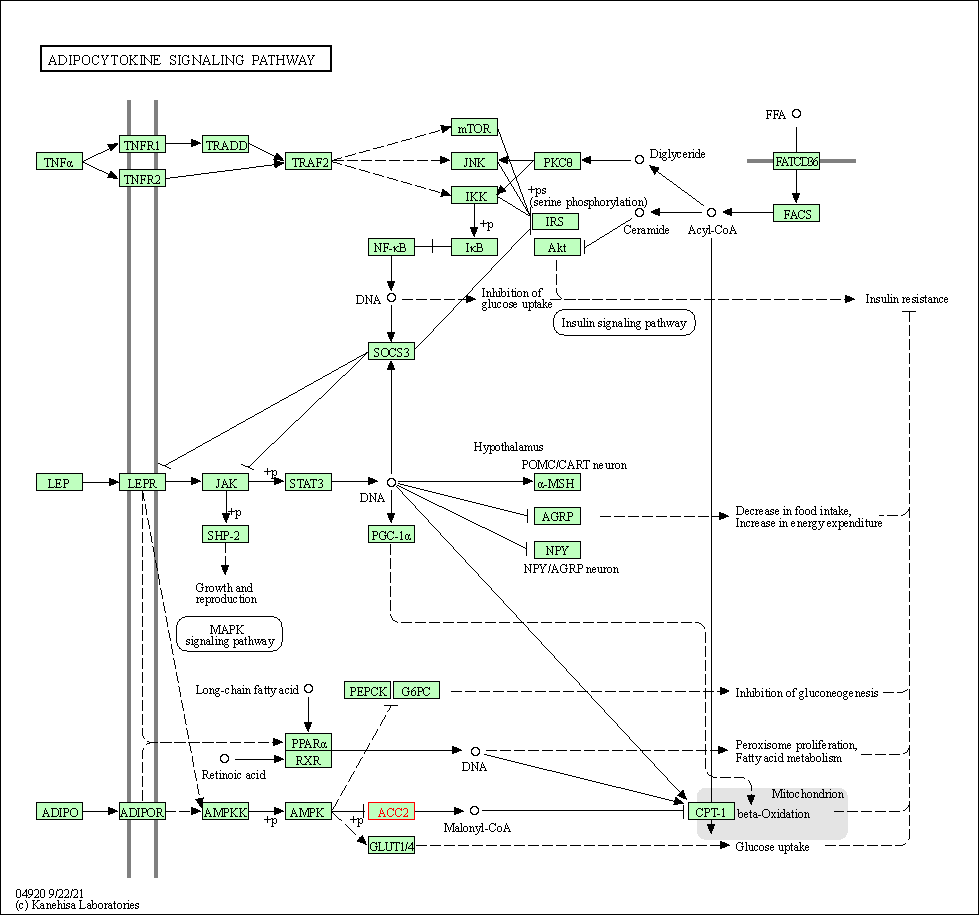
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
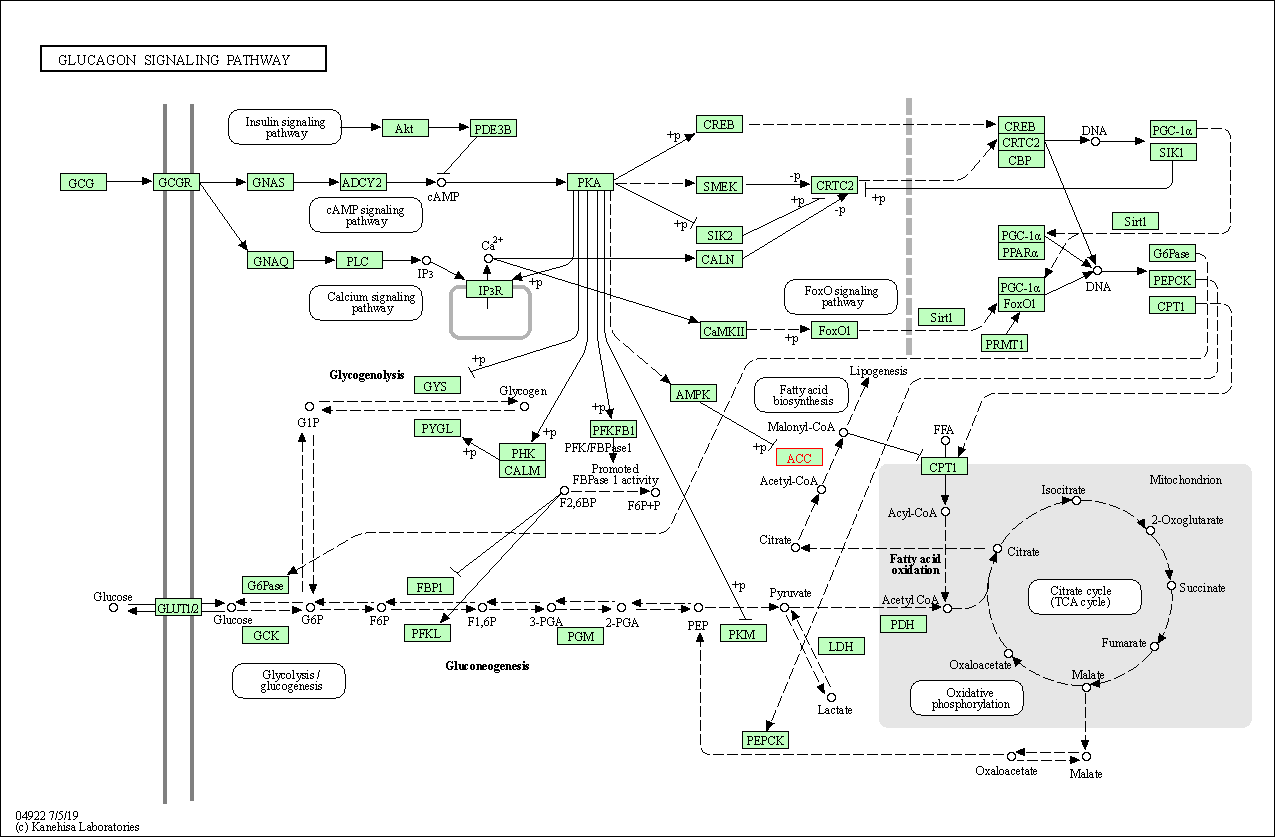
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 6 | Degree centrality | 6.45E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.10E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.94E-01 | Radiality | 1.33E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.17E+01 | Topological coefficient | 2.14E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 2 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Biotin-carboxyl carrier protein assembly | |||||
| 2 | Fatty acid biosynthesis initiation | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 9 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Fatty acid biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Pyruvate metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Propanoate metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 5 | Fatty acid metabolism | |||||
| 6 | AMPK signaling pathway | |||||
| 7 | Insulin signaling pathway | |||||
| 8 | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | |||||
| 9 | Glucagon signaling pathway | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TGF_beta_Receptor Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ChREBP activates metabolic gene expression | |||||
| 2 | Import of palmitoyl-CoA into the mitochondrial matrix | |||||
| 3 | Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 6 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Fatty Acid Biosynthesis | |||||
| 2 | Activation of Gene Expression by SREBP (SREBF) | |||||
| 3 | BDNF signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Leptin signaling pathway | |||||
| 5 | Fatty acid, triacylglycerol, and ketone body metabolism | |||||
| 6 | AMPK Signaling | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent and -independent mechanisms underlying in vitro antiglioma action of compound C. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 1;77(11):1684-93. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01792635) A 6-Week Study Of PF-05175157 In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800007390) | |||||
| REF 5 | Knockouts model the 100 best-selling drugs--will they model the next 100 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003 Jan;2(1):38-51. | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1264). | |||||
| REF 7 | Obesity: pathophysiology and clinical management. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(4):506-21. | |||||
| REF 8 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 9 | Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-{3-[2-(4-alkoxyphenoxy)thiazol-5-yl]-1- methylprop-2-ynyl}carboxy derivatives as selective acet... J Med Chem. 2006 Jun 29;49(13):3770-3. | |||||
| REF 10 | Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors. Science. 2000 Jun 30;288(5475):2379-81. | |||||
| REF 11 | (4-Piperidinyl)-piperazine: a new platform for acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Dec 1;19(23):6645-8. | |||||
| REF 12 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 13 | The human ACC2 CT-domain C-terminus is required for full functionality and has a novel twist. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009 May;65(Pt 5):449-61. | |||||
| REF 14 | Synthesis and characterization of a BODIPY-labeled derivative of Soraphen A that binds to acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 May 15;19(10):2804-7. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

